Explore Any Narratives
Discover and contribute to detailed historical accounts and cultural stories. Share your knowledge and engage with enthusiasts worldwide.
Pierre-Simon Laplace, a towering figure in the history of science, revolutionized our understanding of the cosmos through his groundbreaking work in mathematics, astronomy, and probability. Known as the French Newton, Laplace's contributions laid the foundation for modern mathematical physics, celestial mechanics, and statistical theory. His ideas, including the famous Laplace's demon, continue to shape scientific thought and computational modeling today.
Born on March 23, 1749, in Beaumont-en-Auge, Normandy, France, Laplace showed an early aptitude for mathematics. His journey from a modest background to becoming one of the most influential scientists of his time is a testament to his intellectual prowess and determination.
Laplace's education began at the University of Caen, where he studied theology and mathematics. His mathematical talents quickly became evident, and he moved to Paris to further his studies. In Paris, he was influenced by prominent mathematicians and scientists, including Jean le Rond d'Alembert, who recognized Laplace's potential and helped him secure a position at the École Militaire.
Laplace's career flourished during the late 18th and early 19th centuries, a period marked by significant scientific and political changes. He held various academic and administrative positions, including roles at the Académie des Sciences and the Bureau des Longitudes. His work during this time laid the groundwork for many of his most influential theories.
Laplace's contributions to mathematics and science are vast and varied. His work spans multiple disciplines, each marked by innovative ideas and groundbreaking discoveries.
One of Laplace's most significant contributions is the development of Laplace's equation, a fundamental equation in the study of partial differential equations (PDEs) and potential theory. This equation, denoted as ∇²φ = 0, is crucial in fields such as electrostatics, fluid dynamics, and heat conduction.
Additionally, Laplace introduced the Laplace transform, a mathematical tool used to solve differential equations and analyze dynamic systems. The Laplace transform, defined as F(s) = ∫₀^∞ e⁻ˢᵗ f(t) dt, is widely used in engineering, physics, and control theory.
Laplace's work in celestial mechanics extended the principles of Newtonian gravity to explain the complex motions of planets and other celestial bodies. His multi-volume work, Mécanique céleste, is a cornerstone in the field of astronomy. In this work, Laplace demonstrated the long-term stability of the solar system, arguing that planetary perturbations are bounded and do not require divine intervention to maintain order.
His nebular hypothesis, which proposed that the solar system formed from a rotating cloud of gas and dust, anticipated later theories of planetary formation and evolution.
Laplace made significant advancements in the field of probability and statistics. His work, Essai philosophique sur les probabilités, introduced Bayesian-style probability tools and applied probabilistic methods to interpret scientific data. This work laid the foundation for modern mathematical statistics and data analysis.
Laplace's probabilistic methods have had a lasting impact on various fields, including error analysis, risk assessment, and decision-making processes.
One of Laplace's most famous and controversial ideas is the concept of Laplace's demon. This hypothetical entity, often misunderstood, represents Laplace's belief in scientific determinism.
Laplace's demon is a thought experiment that illustrates the idea of determinism. According to Laplace, if an intellect knew the precise location and momentum of every atom in the universe, it could use Newton's laws to retrodict the entire history of the universe and predict its future. This concept, often summarized as:
"We may regard the present state of the universe as the effect of its past and the cause of its future. An intellect which at a certain moment would know all forces that set nature in motion, and all positions of all items of which nature is composed, if this intellect were also vast enough to submit these data to analysis, it would embrace in a single formula the movements of the greatest bodies of the universe and those of the tiniest atom; for such an intellect nothing would be uncertain and the future just like the past would be present before its eyes."
This statement encapsulates Laplace's belief in the predictability of the universe based on scientific principles.
The idea of Laplace's demon has had a profound impact on the philosophy of science and debates about free will and determinism. It has influenced discussions about the limits of scientific prediction and the nature of causality. While modern quantum mechanics introduces uncertainties that challenge strict determinism, Laplace's ideas remain a cornerstone in the history of scientific thought.
In the next part of this article, we will delve deeper into Laplace's personal life, his interactions with other prominent scientists and political figures, and the lasting legacy of his work in modern science and technology.
Pierre-Simon Laplace lived during a tumultuous period in French history, marked by the French Revolution and the rise of Napoleon Bonaparte. His ability to navigate these political changes while maintaining his scientific pursuits is a testament to his adaptability and diplomatic skills.
Laplace's career intersected with many influential figures of his time. He had a notable relationship with Napoleon Bonaparte, who recognized Laplace's scientific contributions and appointed him to various positions, including Minister of the Interior in 1799. However, Laplace's tenure in this political role was short-lived, as his administrative skills did not match his scientific genius.
Despite this setback, Laplace continued to receive honors and titles. In 1806, he was made a count of the Empire, and in 1817, he was elevated to the rank of marquis. These titles reflected not only his scientific achievements but also his ability to maintain favor across different political regimes.
Laplace collaborated with several prominent scientists, including Antoine Lavoisier, the father of modern chemistry. Together, they worked on various scientific projects, contributing to the advancement of experimental science and mathematical modeling.
However, Laplace's career was not without controversies. He was known to have rivalries with other scientists, particularly in the context of priority disputes over scientific discoveries. Despite these challenges, Laplace's contributions remained widely recognized and respected.
The impact of Pierre-Simon Laplace on modern science is immeasurable. His theories and mathematical tools continue to be fundamental in various scientific disciplines, from astrophysics to engineering.
Laplace's work in mathematical physics laid the groundwork for many modern theories and applications. The Laplace transform and the Laplacian operator are essential tools in solving differential equations and modeling physical systems. These tools are widely used in:
The Laplace equation, ∇²φ = 0, is a cornerstone in the study of potential theory and is applied in various fields, including electrostatics, gravitation, and fluid flow.
In the field of astronomy, Laplace's contributions to celestial mechanics have had a lasting impact. His work on the stability of the solar system provided a mathematical framework for understanding the long-term behavior of planetary orbits. This work was crucial in debunking the idea that divine intervention was necessary to maintain the order of the cosmos.
Laplace's nebular hypothesis also played a significant role in the development of modern theories of planetary formation. While his original hypothesis has been refined and expanded upon, the core idea that the solar system formed from a rotating cloud of gas and dust remains a fundamental concept in astrophysics.
Laplace's contributions to probability and statistics have had a profound influence on modern data analysis and decision-making processes. His work in Essai philosophique sur les probabilités introduced Bayesian methods, which are now fundamental in statistical inference and machine learning.
The application of Laplace's probabilistic methods can be seen in various fields, including:
In recent years, there has been a resurgence of interest in Pierre-Simon Laplace's work, particularly in the context of modern computational science and data-driven modeling. This renewed attention highlights the enduring relevance of his ideas and methods.
Educational platforms and digital media have played a significant role in revisiting Laplace's contributions. Recent articles and documentaries have aimed to make his complex ideas accessible to a broader audience. For example:
These educational materials often use analogies and visual aids to help viewers understand concepts like Laplace's demon and the Laplace transform, making them more accessible to non-experts.
Scholarly retrospectives have also contributed to the renewed interest in Laplace's work. These retrospectives often reframe his contributions in the context of modern scientific advancements, highlighting how his ideas have evolved and been built upon over time.
For instance, recent studies have explored the connections between Laplace's determinism and modern chaos theory and quantum mechanics. While Laplace's strict determinism has been challenged by the uncertainties introduced by quantum mechanics, his ideas remain a crucial part of the historical development of scientific thought.
Additionally, historiographical updates have provided new insights into Laplace's life and career. These updates often draw on primary sources, such as Laplace's original works and correspondence, to offer a more nuanced understanding of his scientific and political engagements.
Modern computational science has found numerous applications for Laplace's mathematical tools. The Laplace transform, for example, is widely used in signal processing and control theory, where it helps engineers and scientists analyze and design complex systems.
In the field of machine learning, Laplace's probabilistic methods have been instrumental in developing algorithms for Bayesian inference and uncertainty quantification. These methods are crucial for making robust predictions and decisions in the face of incomplete or noisy data.
Furthermore, Laplace's work in celestial mechanics has inspired modern computational models of planetary systems and galaxy dynamics. These models rely on the mathematical frameworks developed by Laplace to simulate the behavior of celestial bodies over long timescales.
In the final part of this article, we will explore Laplace's enduring legacy, his influence on contemporary scientific thought, and the ongoing relevance of his work in the 21st century.
Pierre-Simon Laplace left an indelible mark on the scientific landscape, with his ideas continuing to influence contemporary research and technological advancements. His legacy spans multiple disciplines, demonstrating the universal applicability of his mathematical and scientific principles.
Laplace's contributions to classical mechanics and potential theory remain fundamental in modern physics. The Laplacian operator, a key component in his mathematical framework, is essential in quantum mechanics, electrodynamics, and general relativity. For instance, the Schrödinger equation in quantum mechanics often involves the Laplacian, highlighting its enduring relevance.
Moreover, Laplace's work on gravitational potential has been instrumental in the study of black holes and cosmology. His mathematical tools enable scientists to model the behavior of gravitational fields and understand the dynamics of celestial objects on a grand scale.
The practical applications of Laplace's theories in engineering are vast and varied. The Laplace transform is a cornerstone in control systems engineering, allowing engineers to analyze and design systems that regulate everything from automotive engines to robotics.
In electrical engineering, the Laplace transform is used to solve complex circuits and signal processing problems. This mathematical tool simplifies the analysis of transient responses and frequency domain behavior, making it indispensable in the design of modern electronic devices.
Beyond his scientific contributions, Laplace's ideas have had a profound impact on philosophy, culture, and the broader understanding of the universe. His concept of determinism, embodied in Laplace's demon, continues to spark debates and inspire new ways of thinking about causality and prediction.
The philosophical implications of Laplace's determinism have been widely discussed and debated. The idea that the universe operates according to predictable laws challenges traditional notions of free will and human agency. This debate has influenced various fields, including:
While modern science has introduced elements of randomness and uncertainty, Laplace's deterministic framework remains a crucial reference point in these discussions.
Laplace's ideas have permeated popular culture, often serving as a symbol of scientific rationalism and the power of human intellect. References to Laplace's demon can be found in literature, film, and television, where it is used to explore themes of prediction, control, and the limits of knowledge.
For example, in science fiction, the concept of an all-knowing intelligence that can predict the future is a recurring motif. These narratives often draw on Laplace's ideas to examine the ethical and existential implications of such power.
The written works of Pierre-Simon Laplace remain essential reading for scientists, mathematicians, and historians of science. His major publications continue to be studied and cited, demonstrating their enduring value.
Mécanique céleste (Celestial Mechanics) is Laplace's magnum opus, a comprehensive treatise on the mathematical principles governing the motion of celestial bodies. This five-volume work, published between 1799 and 1825, synthesizes the laws of gravitation and planetary motion into a unified mathematical framework.
The principles outlined in Mécanique céleste are still used today in astrodynamics and space mission planning. Modern astronomers and engineers rely on Laplace's equations to predict the trajectories of satellites, spacecraft, and other celestial objects.
Essai philosophique sur les probabilités (A Philosophical Essay on Probabilities), published in 1814, is another cornerstone of Laplace's literary contributions. This work explores the principles of probability theory and their applications in scientific inquiry and decision-making.
Laplace's essay introduced many foundational concepts in Bayesian probability, which are now widely used in statistical modeling, machine learning, and artificial intelligence. His insights into the nature of probability and uncertainty continue to shape modern approaches to data analysis and prediction.
Pierre-Simon Laplace was a visionary whose contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and probability theory have left an indelible mark on the scientific world. His work laid the foundation for many modern scientific disciplines and continues to inspire new generations of researchers and thinkers.
From the Laplace transform to the nebular hypothesis, his ideas have shaped our understanding of the universe and our ability to model and predict complex systems. His philosophical insights, particularly the concept of Laplace's demon, challenge us to think deeply about the nature of determinism, free will, and the limits of human knowledge.
As we continue to explore the frontiers of science and technology, Laplace's legacy serves as a reminder of the power of mathematical reasoning and the enduring quest to unravel the mysteries of the cosmos. His life and work exemplify the transformative impact that a single individual can have on the course of human understanding.
In the words of Laplace himself, "What we know is little, and what we are ignorant of is immense." This humility, coupled with his relentless pursuit of knowledge, ensures that Pierre-Simon Laplace will always be remembered as one of the greatest scientific minds in history.




Your personal space to curate, organize, and share knowledge with the world.
Discover and contribute to detailed historical accounts and cultural stories. Share your knowledge and engage with enthusiasts worldwide.
Connect with others who share your interests. Create and participate in themed boards about any topic you have in mind.
Contribute your knowledge and insights. Create engaging content and participate in meaningful discussions across multiple languages.
Already have an account? Sign in here

"Discover Pierre-Simon Laplace's legacy: the 'French Newton' who revolutionized math, astronomy & probability. Learn his...
View Board
**Meta Description:** Explore the life and legacy of Pierre-Simon Laplace, the visionary mathematician who shaped cele...
View Board
"Explore Henri Poincaré's groundbreaking work in math, physics, and philosophy, shaping modern science through chaos the...
View Board
"Explore Sir Roger Penrose's Nobel-winning black hole theories and quantum gravity legacy. Discover his revolutionary ph...
View Board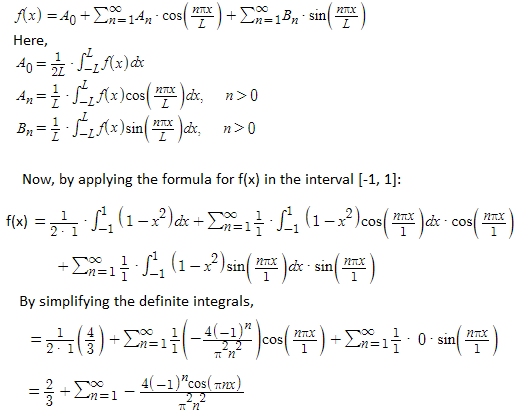
Explore the life and groundbreaking innovations of Jean-Baptiste Joseph Fourier, the French mathematician and physicist ...
View Board
André-Marie Ampère: A Pioneer in the History of Electricity The Early Life and Education André-Marie Ampère, often rega...
View BoardÉmile Borel: A Pioneering Mathematician and Physicist The Early Life and Education of Émile Borel Émile Borel, born on...
View Board
Discover the transformative journey of Sir Isaac Newton, the prodigious mind who redefined science with groundbreaking t...
View Board
Descubre cómo Joseph Fourier revolucionó la ciencia con sus series matemáticas y la ecuación del calor, sentando las bas...
View Board
Jean Baptiste Joseph Delambre: A Life of Astronomical Pursuits The Early Life and Education Jean Baptiste Joseph Delam...
View Board
Explore the life and legacy of Evangelista Torricelli, the 17th-century Italian physicist whose invention of the baromet...
View Board
Scopri la vita e le rivoluzionarie scoperte di Pierre-Simon Laplace, il genio che plasmò la matematica, l'astronomia e l...
View Board
Archimedes, the genius of ancient Greece, revolutionized mathematics, physics, and engineering with discoveries like pi,...
View Board
Discover how Isaac Newton revolutionized science with his laws of motion, universal gravitation, and optics. Explore his...
View Board
Scopri come Galileo Galilei rivoluzionò la scienza con il metodo sperimentale, le sue scoperte astronomiche e l'eredità ...
View Board
Explore the life of Galileo Galilei, the pioneering scientist who revolutionized our understanding of the universe. Delv...
View Board
Max Delbrück was a pioneering scientist whose work revolutionized molecular biology through an interdisciplinary approac...
View Board
Galileo Galilei: The Pioneer of Science and Chronology Galileo Galilei, often hailed as the father of modern science, r...
View Board
Isaac Newton was a pioneering scientist whose laws of motion and universal gravitation revolutionized our understanding ...
View Board
Explore the groundbreaking contributions of Pierre-Gilles de Gennes, a Nobel laureate, whose pioneering work in soft mat...
View Board
Comments