Explore Any Narratives
Discover and contribute to detailed historical accounts and cultural stories. Share your knowledge and engage with enthusiasts worldwide.
Galileo Galilei, often hailed as the father of modern science, revolutionized our understanding of the universe through his groundbreaking observations and experiments. His contributions not only advanced scientific knowledge but also reshaped the way we perceive time and history. This article explores Galileo's life, his pivotal role in the Scientific Revolution, and his enduring influence on scientific chronology.
Born in Pisa, Italy, in 1564, Galileo Galilei showed an early aptitude for mathematics and the natural sciences. He studied at the University of Pisa, where he initially pursued medicine but later shifted his focus to mathematics and physics. His early experiments with pendulums and falling objects laid the foundation for his future scientific endeavors.
Galileo's academic career began at the University of Pisa, where he taught mathematics. However, his unconventional ideas and methods often clashed with the traditional Aristotelian views dominant at the time. In 1592, he moved to the University of Padua, where he spent nearly two decades teaching and conducting research. This period was marked by significant discoveries and the development of his scientific methodology.
Galileo's scientific contributions are vast and varied, encompassing astronomy, physics, and mathematics. His work not only challenged existing theories but also introduced new methods of inquiry that would become the cornerstone of modern science.
In 1609, Galileo heard about the invention of the telescope and quickly built his own improved version. His telescopic observations revealed unprecedented details about the cosmos, including the moons of Jupiter, the phases of Venus, and the rugged surface of the Moon. These discoveries provided compelling evidence for the Copernican heliocentric model, which placed the Sun at the center of the solar system.
Galileo's work in physics and mechanics was equally groundbreaking. He conducted experiments on the motion of objects, formulating the law of falling bodies and laying the groundwork for the concept of inertia. His book Two New Sciences, published in 1638, summarized his findings and established him as a pioneer in the field of mechanics.
"The book of nature is written in the language of mathematics."
Galileo's discoveries had a profound impact on scientific chronology, marking a pivotal shift from ancient to modern scientific thought. His work provided key chronological markers that historians use to delineate the Scientific Revolution, a period of rapid scientific advancement in the 16th and 17th centuries.
Before Galileo, the scientific community largely adhered to Aristotelian natural philosophy, which relied on logical reasoning rather than empirical evidence. Galileo's emphasis on observation and experimentation challenged this tradition, paving the way for a new era of scientific inquiry. His methods became the standard for future scientists, influencing the development of the scientific method.
Galileo's influence extended far beyond his lifetime. His work inspired subsequent generations of scientists, including Isaac Newton, who built upon Galileo's findings to develop the laws of motion and universal gravitation. The shift from Aristotelian to Galilean science marked a significant turning point in the history of science, reshaping our understanding of the natural world.
Galileo Galilei's contributions to science and chronology are unparalleled. His telescopic observations and experiments in physics challenged long-held beliefs and laid the foundation for modern scientific inquiry. As we continue to explore the universe and advance our understanding of the natural world, Galileo's legacy remains a testament to the power of observation, experimentation, and the relentless pursuit of knowledge.
In the next part of this article, we will delve deeper into Galileo's trial and condemnation by the Roman Inquisition, his later years under house arrest, and the enduring impact of his work on scientific institutions and historiography.
Galileo's advocacy for the heliocentric model brought him into direct conflict with the Catholic Church, which adhered to the geocentric view of the universe. In 1633, Galileo was tried by the Roman Inquisition and found "vehemently suspect of heresy." This trial marked a significant moment in the history of science, highlighting the tension between scientific discovery and religious doctrine.
The Catholic Church's opposition to heliocentrism was rooted in its interpretation of Scripture, which appeared to support a geocentric universe. Galileo's Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems, published in 1632, presented a compelling case for heliocentrism but was seen as a direct challenge to Church authority. The Inquisition's condemnation of Galileo was not just a personal attack but a broader attempt to suppress scientific ideas that conflicted with religious teachings.
Following his trial, Galileo was placed under house arrest for the remainder of his life. Despite this, he continued his scientific work, publishing Two New Sciences in 1638, a foundational text in the field of mechanics. His resilience and dedication to science, even in the face of persecution, have made him a symbol of the struggle for intellectual freedom.
"And yet it moves."
One of Galileo's most enduring contributions was his development of the scientific method. His emphasis on observation, experimentation, and mathematical analysis revolutionized the way scientific inquiry was conducted. This method became the gold standard for future generations of scientists, ensuring that his influence would extend far beyond his own discoveries.
Galileo's approach to science was rooted in direct observation and hands-on experimentation. Unlike his predecessors, who relied heavily on philosophical reasoning, Galileo believed that the natural world could only be understood through systematic observation. His experiments with falling objects and pendulums demonstrated the importance of empirical evidence in scientific inquiry.
Galileo was a firm believer in the power of mathematics to describe the natural world. He famously stated that "the book of nature is written in the language of mathematics." His work in kinematics and the study of motion used mathematical principles to explain physical phenomena, setting a precedent for future scientific research.
Galileo's contributions had a lasting impact on both modern science and the way we understand the timeline of scientific progress. His work marked the beginning of the Scientific Revolution, a period that saw the rapid advancement of scientific knowledge and the establishment of new methods of inquiry.
The Scientific Revolution, spanning the 16th to 17th centuries, was characterized by a shift from Aristotelian natural philosophy to empirical science. Galileo's discoveries and methods played a crucial role in this transition. His emphasis on observation and experimentation influenced scientists like Isaac Newton and Johannes Kepler, who built upon his work to develop their own theories.
Galileo's life and work provide key chronological markers that historians use to delineate the progression of scientific thought. Some of the most significant dates include:
These dates serve as critical reference points in the history of science, illustrating the rapid pace of discovery and the challenges faced by early modern scientists.
In recent decades, scholars have re-examined Galileo's life and work, providing new insights into his methods, his relationship with the Church, and his broader impact on science and society. This ongoing research has led to a more nuanced understanding of Galileo's legacy.
Modern scholarship has moved beyond the simplistic narrative of "science vs. religion" to explore the complex political, social, and intellectual context of Galileo's trial. Historians now emphasize the role of personal rivalries, institutional politics, and the broader cultural climate of the time. This more nuanced view helps to explain why Galileo's ideas were met with such resistance and how his trial became a defining moment in the history of science.
The digitization of Galileo's manuscripts, instruments, and correspondence has opened new avenues for research. Museums and libraries around the world have made his works accessible online, allowing scholars and the public to explore his contributions in unprecedented detail. These digital resources have facilitated new studies of Galileo's methods, his network of correspondents, and the dissemination of his ideas across Europe.
"The history of science is not just about discoveries; it's about the people who made them and the world they lived in."
In the final part of this article, we will explore Galileo's enduring cultural impact, his representation in modern media, and the lessons his life offers for contemporary science and society.
Galileo's influence extends far beyond the realms of science and chronology, permeating culture, art, and public imagination for centuries. His story has become a symbol of the struggle between intellectual progress and societal resistance, ensuring his place in global cultural narratives.
Worldwide, numerous memorials, statues, and institutions honor Galileo's contributions. The Galileo Museum in Florence, Italy, houses many of his original instruments, offering visitors a tangible connection to his groundbreaking work. Cities such as Galileo, California, and Galileo, Georgia, bear his name, reflecting his lasting impact.
Galileo's life and legacy are frequently explored in modern media, ensuring his ideas remain relevant to new generations. From films to educational curricula, his story continues to inspire and educate.
Multiple films and TV productions have dramatized Galileo's life, often focusing on his clash with the Church. Notable examples include Galileo (1968), directed by Liliana Cavani, and the BBC series The Last Man in Europe. His name also appears in literature, symbolizing scientific inquiry and defiance.
"Galileo taught us to look up at the stars and not just accept what we are told."
Galileo remains a cornerstone of science education worldwide. His methods and discoveries are taught in schools as foundational to the scientific method. Many educational institutions incorporate hands-on experiments inspired by his work, such as building simple telescopes or replicating his pendulum studies.
Galileo's life offers timeless lessons for today's scientific community and society. His dedication to evidence-based research, courage in the face of opposition, and interdisciplinary approach remain vital guides for modern scientists.
In an era of misinformation, Galileo's commitment to empirical evidence serves as a reminder of the importance of data-driven conclusions. His approach underscores the necessity of rigorous testing and peer review, principles that underpin contemporary scientific integrity.
Galileo's trial highlights the tension between scientific discovery and ethical or societal considerations. Modern scientists continue to grapple with similar challenges, such as the ethical implications of genetic engineering or artificial intelligence. Galileo's story encourages open dialogue between science and broader society.
Galileo Galilei stands as a towering figure in the annals of science, his contributions reshaping our understanding of the universe and the very nature of inquiry. From his telescopic discoveries to his unwavering defense of empirical evidence, Galileo's legacy endures in every scientific endeavor. His trial and subsequent house arrest remind us of the challenges faced by pioneers who challenge established norms.
Yet beyond the history books, Galileo's spirit lives on in museums, media, and classrooms. His emphasis on observation, experimentation, and mathematical analysis continues to guide scientists worldwide. As we confront new frontiers—from exploring exoplanets to unraveling genetic codes—Galileo's example remains a beacon of curiosity and courage.
In celebrating Galileo, we honor not just a brilliant mind, but a relentless advocate for the pursuit of truth. His story compels us to ask difficult questions, test assumptions, and embrace the unknown. In an ever-evolving world, Galileo's legacy is more relevant than ever, urging each generation to look up, question, and discover.
Your personal space to curate, organize, and share knowledge with the world.
Discover and contribute to detailed historical accounts and cultural stories. Share your knowledge and engage with enthusiasts worldwide.
Connect with others who share your interests. Create and participate in themed boards about any topic you have in mind.
Contribute your knowledge and insights. Create engaging content and participate in meaningful discussions across multiple languages.
Already have an account? Sign in here

Explore the life of Galileo Galilei, the pioneering scientist who revolutionized our understanding of the universe. Delv...
View Board
Jean Baptiste Joseph Delambre: A Life of Astronomical Pursuits The Early Life and Education Jean Baptiste Joseph Delam...
View Board
Discover the intriguing life of Léon Foucault, the pioneering French physicist who elegantly demonstrated the Earth's ro...
View Board
Uncover the overlooked legacy of Robert Hooke, a true genius of the Scientific Revolution. From pioneering microscopy an...
View Board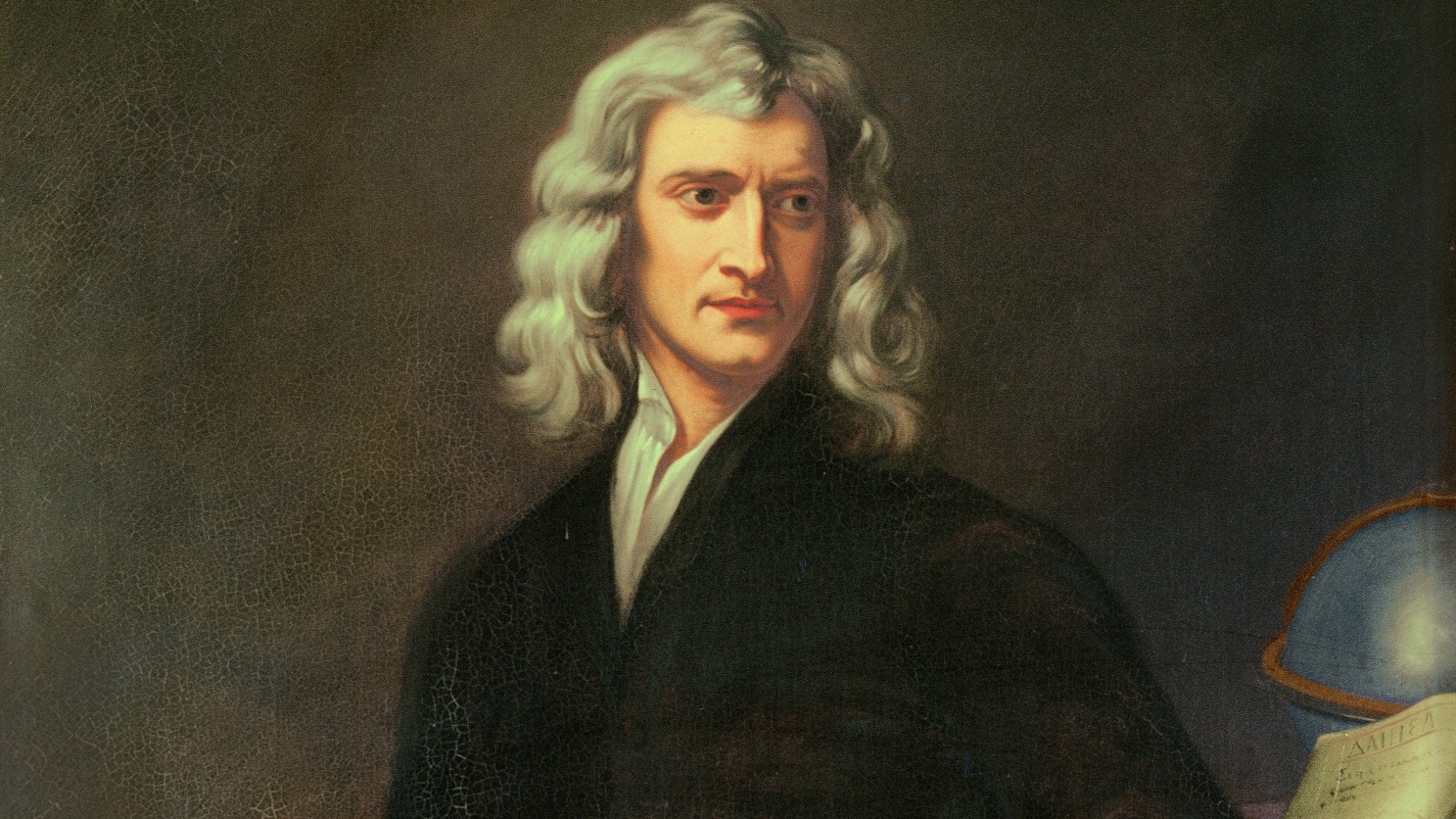
Isaac Newton was a pioneering scientist whose laws of motion and universal gravitation revolutionized our understanding ...
View Board
Max Born was a renowned theoretical physicist and Nobel laureate known for his statistical interpretation of quantum mec...
View Board
George Gamow: The Unbelievable Journey of a Theoretical Physicist and Cosmologist The Enigmatic Man Behind the Cosmic B...
View Board
Explore the fascinating life of Michael Faraday, the pioneering scientist whose groundbreaking work in electromagnetism ...
View Board
Archimedes, the genius of ancient Greece, revolutionized mathematics, physics, and engineering with discoveries like pi,...
View Board
Discover how Isaac Newton revolutionized science with his laws of motion, universal gravitation, and optics. Explore his...
View Board
Discover the enduring legacy of Jean-Baptiste Biot, a remarkable polymath at the crossroads of Enlightenment and 19th-ce...
View Board
768 **Meta Description:** Explore the life of Enrico Fermi, the architect of the nuclear age. From quantum theory to th...
View Board
George Washington Carver: The Pioneering Scientist and Educator George Washington Carver (1864-1943) was a scientist, i...
View BoardÉmile Borel: A Pioneering Mathematician and Physicist The Early Life and Education of Émile Borel Émile Borel, born on...
View Board
Fritz Haber: A Chemist Whose Work Changed the World The Rise of a Scientist Fritz Haber was born on December 9, 1868, i...
View Board
Discover the inspiring journey of Stephen Hawking in this comprehensive article. From his pioneering work on black holes...
View Board
Walter Brattain: The Transistor Pioneer Who Changed Electronics Early Life and Education of Walter Brattain Walter Hous...
View Board
Explore the life and legacy of Jules Henri Poincaré, a prodigy whose innovative work bridged mathematics and physics. Di...
View BoardDiscover the transformative legacy of Louis Paul Cailletet, the French physicist whose groundbreaking work with gases re...
View Board
Alessandro Volta, a pioneering Italian physicist, revolutionized electricity with the invention of the voltaic pile, sha...
View Board
Comments