Explore Any Narratives
Discover and contribute to detailed historical accounts and cultural stories. Share your knowledge and engage with enthusiasts worldwide.
Vera Rubin, a pioneering American astronomer, revolutionized our understanding of the universe by providing the first direct observational evidence for dark matter. Her groundbreaking measurements of galaxy rotation curves revealed that invisible mass holds galaxies together, fundamentally altering cosmology.
Born Vera Florence Cooper on July 23, 1928, in Philadelphia, Rubin developed an early fascination with the stars. Despite facing gender barriers, she pursued her passion for astronomy, earning her PhD from Georgetown University in 1954. Her thesis on galaxy motions, though initially overlooked, hinted at early insights into the supergalactic plane and deviations from the Hubble flow.
Rubin's journey was not without challenges. She was often discouraged from pursuing astronomy, a field dominated by men at the time. However, her determination and curiosity drove her forward. Her early work, though underappreciated, laid the groundwork for her future discoveries.
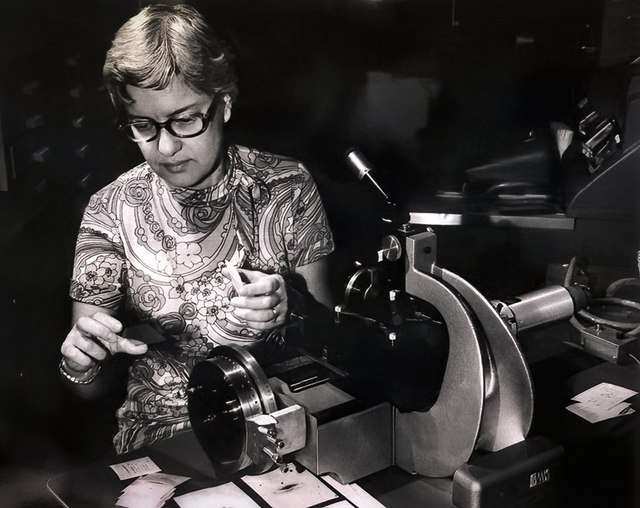
In collaboration with Kent Ford beginning in 1965, Rubin used advanced image-tube spectrographs to study the rotation curves of galaxies. Her observations at Kitt Peak, Lowell Observatory, and Palomar revealed something extraordinary: stars at the outer edges of galaxies orbited at unexpectedly high, flat speeds. This implied the presence of unseen mass, which we now call dark matter.
Rubin and Ford measured the rotation curves of over 60 spiral galaxies, including the Andromeda Galaxy (M31). Their findings, published in a key 1970 paper, showed that the outer stars of galaxies moved at speeds that defied predictions based on visible mass alone. This anomaly suggested the existence of dark matter, an invisible substance that exerts gravitational forces.
Their work was later confirmed by 21 cm hydrogen line radio observations, solidifying Rubin's place in astronomical history. Her discoveries shifted cosmology toward a new understanding of the universe, where dark matter plays a crucial role in holding galaxies together.
Vera Rubin's contributions to science are immense. She authored over 200 scientific papers and received numerous accolades, including the National Medal of Science (1993), the Bruce Medal, and the Gold Medal of the Royal Astronomical Society. She was also elected to the National Academy of Sciences in 1981.
Her legacy continues through the Vera C. Rubin Observatory in Chile, set to begin full operations soon. This state-of-the-art facility will focus on time-domain astronomy and further studies of dark matter, ensuring that Rubin's pioneering work inspires future generations of astronomers.
Beyond her scientific achievements, Rubin was a strong advocate for women in science. She mentored many young scientists and was the first woman staff astronomer at the Carnegie Institution's Department of Terrestrial Magnetism. Her dedication to breaking down gender barriers has left a lasting impact on the scientific community.
Vera Rubin's discoveries have fundamentally changed our understanding of the universe. Her work on dark matter has driven modern cosmology and inspired countless scientists. As we look to the future, the Vera C. Rubin Observatory will continue her legacy, uncovering more secrets of the cosmos.
Beyond her work on dark matter, Vera Rubin made another significant discovery in 1976: the Rubin-Ford effect. This phenomenon describes the peculiar velocities of galaxies, suggesting the existence of large-scale structure in the universe. These observations further solidified her reputation as a pioneer in astrophysics.
The Rubin-Ford effect refers to the unexpected motions of galaxies that cannot be explained by the gravitational pull of visible matter alone. Rubin and Ford noticed that galaxies exhibited peculiar velocities, indicating the presence of unseen mass influencing their movements. This discovery provided additional evidence for the existence of dark matter and its role in shaping the universe.
The implications of the Rubin-Ford effect are profound. It suggests that the universe is not uniform but instead has a complex, large-scale structure influenced by dark matter. This discovery has driven further research into the distribution and nature of dark matter, as well as its impact on the formation and evolution of galaxies.
Throughout her career, Vera Rubin faced numerous challenges as a woman in a male-dominated field. Despite these obstacles, she became a strong advocate for women in science, mentoring many young scientists and breaking down gender barriers. Her efforts have had a lasting impact on the scientific community.
Rubin's journey was marked by perseverance and determination. She was often discouraged from pursuing astronomy, but her passion for the stars drove her forward. Her achievements paved the way for future generations of women in science, proving that gender should not be a barrier to success.
As the first woman staff astronomer at the Carnegie Institution's Department of Terrestrial Magnetism, Rubin mentored many young scientists. She believed in the importance of supporting and encouraging women in science, and her efforts have inspired countless individuals to pursue careers in astronomy and other STEM fields.
Despite her groundbreaking discoveries and numerous accolades, Vera Rubin never received the Nobel Prize. This oversight has sparked debates within the scientific community, with many arguing that her contributions to astronomy were deserving of the highest honor.
Many prominent scientists, including physicist Lisa Randall, have argued that Rubin's work on dark matter was deserving of the Nobel Prize. Her discoveries fundamentally changed our understanding of the universe and have driven significant advancements in cosmology. The Nobel Prize committee's decision to overlook her achievements has been a subject of controversy and discussion.
While Rubin may not have received the Nobel Prize, her legacy is undeniable. Her work on dark matter has inspired countless scientists and has led to the development of new fields in astrophysics and particle physics. The Vera C. Rubin Observatory, named in her honor, stands as a testament to her enduring impact on the scientific community.
The Vera C. Rubin Observatory, located in Chile, is a state-of-the-art facility dedicated to advancing our understanding of the universe. Named in honor of Vera Rubin, the observatory is set to begin full operations soon and will focus on time-domain astronomy and further studies of dark matter.
The observatory will generate 20 terabytes of data nightly, providing unprecedented insights into the nature of dark matter and its role in the universe. By imaging the southern sky every few nights, the observatory will help scientists probe the mysteries of dark matter, dark energy, and transient astronomical events.
The Vera C. Rubin Observatory is not only a tribute to Rubin's pioneering work but also a symbol of inspiration for future generations of scientists. It serves as a reminder of the importance of curiosity, determination, and the pursuit of knowledge. As the observatory begins its operations, it will continue Rubin's legacy, uncovering more secrets of the cosmos and inspiring countless individuals to explore the wonders of the universe.
Vera Rubin's work on dark matter has sparked ongoing debates and research into the nature of this mysterious substance. While her observations provided conclusive evidence for the existence of dark matter, the exact nature of dark matter remains a subject of intense study and discussion.
Several theories have been proposed to explain the nature of dark matter. Some of the leading candidates include:
Scientists around the world are actively searching for dark matter using a variety of methods. From underground detectors to particle accelerators, the quest to understand dark matter is one of the most exciting and challenging endeavors in modern physics. Vera Rubin's pioneering work continues to inspire and guide these efforts, driving the scientific community toward a deeper understanding of the universe.
Vera Rubin's contributions to astronomy and cosmology are immeasurable. Her discoveries have fundamentally changed our understanding of the universe and have inspired countless scientists to explore the mysteries of the cosmos. As we look to the future, the Vera C. Rubin Observatory will continue her legacy, uncovering more secrets of the universe and inspiring future generations of scientists.
Vera Rubin's work has left an indelible mark on modern cosmology. Her discoveries have not only reshaped our understanding of the universe but have also opened new avenues of research that continue to drive scientific inquiry today. The impact of her findings extends far beyond her lifetime, influencing numerous fields within astrophysics and particle physics.
The Standard Model of Cosmology, also known as the Lambda-CDM model, incorporates dark matter as a fundamental component. Rubin's observations provided the empirical foundation for this model, which describes the composition and evolution of the universe. According to this model, dark matter constitutes approximately 27% of the universe's total mass and energy, while ordinary matter makes up only about 5%.
Rubin's work has inspired the emergence of new fields dedicated to understanding dark matter. These include:
Vera Rubin's contributions to science have been recognized through numerous awards and honors. These accolades reflect the profound impact of her work and her role as a trailblazer for women in science. Her legacy continues to be celebrated, inspiring future generations of scientists.
Throughout her career, Rubin received several prestigious awards, including:
In addition to awards, Rubin's legacy is honored through various tributes, including:
The concept of dark matter, popularized by Vera Rubin's work, has permeated popular culture and education. From documentaries to science fiction, dark matter has captured the public's imagination, highlighting the importance of scientific discovery in shaping our understanding of the universe.
Dark matter has become a staple in science fiction and non-fiction media. Some notable examples include:
Vera Rubin was a strong advocate for public engagement in science. She believed in the importance of communicating scientific discoveries to the broader public, fostering a greater appreciation for astronomy and cosmology. Today, initiatives like the Vera Rubin Observatory's outreach programs continue this tradition, bringing the wonders of the universe to people of all ages.
While Vera Rubin's work provided compelling evidence for the existence of dark matter, many questions remain unanswered. The search for dark matter is an ongoing challenge, with scientists employing a variety of methods to detect and understand this elusive substance.
Despite decades of research, dark matter has yet to be directly detected. Some of the key challenges include:
Scientists are continually developing new experiments and technologies to uncover the mysteries of dark matter. Some promising approaches include:
Vera Rubin's life and work exemplify the power of curiosity, perseverance, and scientific inquiry. Her discoveries have fundamentally altered our understanding of the universe, revealing the existence of dark matter and its crucial role in cosmic structure. Beyond her scientific achievements, Rubin's advocacy for women in science has paved the way for future generations of researchers.
As we reflect on Rubin's contributions, several key takeaways emerge:
In the words of Vera Rubin herself,
"We have peered into a new world, and have seen that it is more mysterious and more complex than we had imagined."Her pioneering spirit and unwavering dedication to science continue to inspire us to explore the unknown, pushing the boundaries of human knowledge and understanding. As the Vera C. Rubin Observatory begins its mission, we stand on the shoulders of a giant, ready to uncover even more secrets of the cosmos.



Your personal space to curate, organize, and share knowledge with the world.
Discover and contribute to detailed historical accounts and cultural stories. Share your knowledge and engage with enthusiasts worldwide.
Connect with others who share your interests. Create and participate in themed boards about any topic you have in mind.
Contribute your knowledge and insights. Create engaging content and participate in meaningful discussions across multiple languages.
Already have an account? Sign in here

**Meta Description:** Discover Vera Rubin's groundbreaking work on dark matter, which revolutionized cosmology. Learn ...
View Board
Jocelyn Bell Burnell pioneering astronomer who discovered pulsars leaving a lasting legacy in astrophysics through groun...
View Board
Explore the extraordinary legacy of Riccardo Giacconi, the Nobel laureate who revolutionized X-ray astronomy. Discover h...
View Board
Discover the bizarre exoplanet with a diamond atmosphere found by JWST. Explore its helium-carbon sky, soot clouds, and ...
View Board
Explore the vast cosmos—its galaxies, black holes, exoplanets, dark matter, and humanity's quest to understand the unive...
View Board
George Gamow: The Unbelievable Journey of a Theoretical Physicist and Cosmologist The Enigmatic Man Behind the Cosmic B...
View Board
George Ellery Hale revolutionized astrophysics through solar discoveries, groundbreaking telescopes like Mount Wilson an...
View BoardGiovanni Schiaparelli: Pioneering Italian Astronomer and His Impact on Planetary Exploration Introduction Giovanni Vir...
View Board
Explore the remarkable legacy of Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar, the astrophysics luminary who revolutionized our understand...
View Board
Explore the life of Galileo Galilei, the pioneering scientist who revolutionized our understanding of the universe. Delv...
View Board
Arthur Eddington: Pioneering Relativity and Stellar Science Arthur Stanley Eddington stands as one of the most influenti...
View Board
Discover Neil deGrasse Tyson's life and work as a renowned astrophysicist, science communicator and director of the Hayd...
View Board
Explore Leon-Foykw's groundbreaking astronomy theories & innovations that still shape space exploration. Learn how his w...
View Board
Explore the incredible legacy of Arthur Eddington, a pioneering figure in astrophysics and cosmology, who brilliantly br...
View Board
**Meta Description:** Explore the life of William Herschel, the astronomer who discovered Uranus and revolutionized our ...
View Board
Giovanni Schiaparelli, a renowned Italian astronomer, made groundbreaking observations of Mars, sparking controversy wit...
View Board
Discover the inspiring journey of Stephen Hawking in this comprehensive article. From his pioneering work on black holes...
View Board
Discover Maria Mitchell, America's first female astronomer. Explore her 1847 comet discovery, impact on women in STEM, a...
View Board
Discover how Alan Guth, a renowned physicist, revolutionized cosmology with his groundbreaking theory of cosmic inflatio...
View Board
Discover Stephen Hawking's groundbreaking contributions to cosmology, his resilience against ALS, and his enduring legac...
View Board
Comments