Explore Any Narratives
Discover and contribute to detailed historical accounts and cultural stories. Share your knowledge and engage with enthusiasts worldwide.
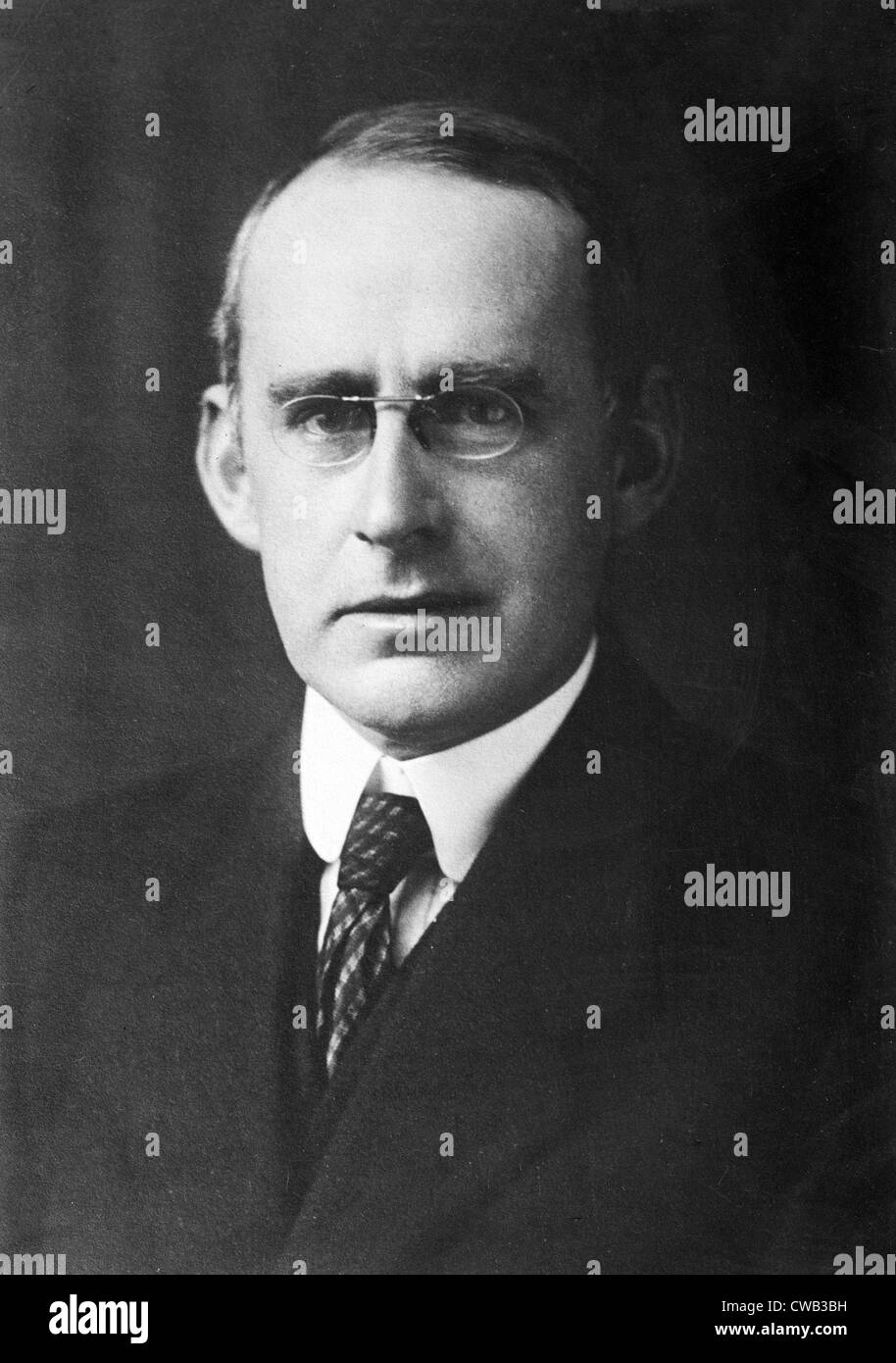
Arthur Stanley Eddington stands as one of the most influential astrophysicists of the early 20th century. His work bridged observation and theory, shaping modern understanding of stars and cosmology. Eddington's leadership in confirming Einstein’s general relativity and his groundbreaking models of stellar interiors placed him at the forefront of scientific revolution.
Born on 28 December 1882, Eddington demonstrated exceptional mathematical talent from a young age. He studied at Owens College, Manchester, and later at Trinity College, Cambridge, where he excelled in physics and astronomy.
Eddington’s academic journey led him to the Royal Observatory, Greenwich, where he served as Chief Assistant from 1906 to 1913. His precision in observational work and theoretical insights quickly earned recognition.
Eddington’s most famous achievement came during the 1919 solar eclipse. He led expeditions to the island of Príncipe and Sobral, Brazil, to measure starlight deflection near the Sun.
The team’s measurements matched Einstein’s prediction of 1.75 arcseconds deflection for light grazing the solar limb. This confirmation made front-page news and catapulted relativity to global attention.
“Light deflected by gravity: a triumph of thought over observation.” — Arthur Eddington, 1919
The expedition faced immense logistical and environmental hurdles, including war-time restrictions and unpredictable weather. Eddington’s determination ensured the success of this historic experiment.
Eddington transformed our understanding of stars through innovative theories and mathematical models. His work laid the foundation for modern stellar physics.
He formulated the mass–luminosity relation, showing that a star’s brightness scales roughly with the third to fourth power of its mass. This became a cornerstone of stellar evolution studies.
Eddington emphasized the role of radiation pressure in supporting massive stars against gravitational collapse. His equations described energy transport through radiative processes in stellar interiors.
He introduced the Eddington limit, the maximum luminosity a star can achieve before radiation pressure blows away its outer layers. For a one-solar-mass object, this limit is approximately 3.3×10⁴ times the Sun’s luminosity.
Eddington didn’t limit himself to academic papers; he became a pioneering science communicator through accessible books. His ability to translate complex ideas for the public earned him a wide audience.
Eddington authored books that shaped both specialists and the general public. Two of his most cited works are:
His writings demystified Einstein’s theories for English readers. Eddington’s clear prose helped general relativity gain traction in academic and public discourse. He avoided jargon while preserving scientific rigor.
“The theory of relativity is a masterpiece of abstract thought… but its consequences are woven into the fabric of the universe.” — Arthur Eddington
World War I severed scientific ties between Britain and Germany. Eddington took it upon himself to rebuild these connections through translation and advocacy.
He translated key German papers on relativity into English, ensuring Anglo-American scientists weren’t isolated. This effort was crucial in spreading Einstein’s ideas during a time of political tension.
Eddington used lectures, articles, and public debates to champion relativity. His 1919 eclipse results provided empirical evidence that resonated globally, helping to heal scientific diplomacy.
By 1920, Eddington’s efforts had made relativity a mainstream topic in British universities. He helped create a framework for English-speaking scientists to engage with Einstein’s revolution.
Beyond mathematics and observation, Eddington explored the philosophy of physics. His imaginative approach inspired generations of thinkers and scientists.
Eddington questioned the limits of human perception in science. He argued that physical laws reflect our means of measurement rather than absolute truth. His essays often blended logic with poetic insight.
Many of Eddington’s ideas persist in modern astrophysics. The Eddington limit, for instance, remains vital for understanding:
Modern scholars re-examine the 1919 results for statistical robustness and context. While measurement limits existed, the core conclusion—that gravity bends light—stands uncontested. Eddington’s role as scientist and advocate continues to spark debate.
Eddington’s blend of rigorous theory, observational leadership, and public engagement made him a model scientist-intellectual. His legacy endures in both cosmic-scale physics and the broader dialogue about science’s place in society.
Today, Arthur Eddington’s theoretical framework remains deeply embedded in cutting-edge astrophysical research. His concepts continue to guide investigations of extreme celestial phenomena and energy processes.
The Eddington limit serves as a critical benchmark for understanding high-energy astrophysical systems. Modern applications include:
For a solar-mass object, the Eddington luminosity approximates 3.3×10⁴ times the Sun’s luminosity, adjusted for composition and opacity.
Eddington’s mass–luminosity relation—showing stellar brightness scaling as roughly M^3–M^4—remains a foundational empirical pattern in stellar evolution. This relationship underpins:
Eddington’s dual role as researcher and public educator established a template for modern scientist-communicators. His approach resonates in today’s discussions about trust in scientific expertise.
Eddington’s books—like The Expanding Universe—demonstrated how complex ideas could be made accessible without sacrificing accuracy. This model now inspires initiatives such as:
The 1919 eclipse story remains a powerful narrative framework. Its elements—scientific curiosity, logistical challenges, wartime context—continue to captivate audiences in documentaries, museum exhibits, and educational materials.
“Science is a chase, and the greatest fascination lies in the chase itself.” — Arthur Eddington
Arthur Stanley Eddington transformed astrophysics through empirical verification, theoretical innovation, and exceptional communication. His confirmation of general relativity, revolutionary stellar models, and philosophical insights collectively reshaped 20th-century science.
Eddington challenged contemporaries to consider the limits of human perception in scientific inquiry. He argued that physical laws reflect observational frameworks rather than absolute truths—a perspective that anticipates modern debates about theory-dependent knowledge.
As astronomy advances into new domains—from gravitational wave astronomy to exoplanet characterization—Eddington’s legacy endures. His integration of rigorous theory, precise observation, and public engagement remains a guiding ideal for scientists and communicators alike. The man who bent starlight to prove relativity continues to inspire both the equations and the narratives that shape our cosmic understanding.





Your personal space to curate, organize, and share knowledge with the world.
Discover and contribute to detailed historical accounts and cultural stories. Share your knowledge and engage with enthusiasts worldwide.
Connect with others who share your interests. Create and participate in themed boards about any topic you have in mind.
Contribute your knowledge and insights. Create engaging content and participate in meaningful discussions across multiple languages.
Already have an account? Sign in here

George Gamow: The Unbelievable Journey of a Theoretical Physicist and Cosmologist The Enigmatic Man Behind the Cosmic B...
View Board
Explore the remarkable legacy of Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar, the astrophysics luminary who revolutionized our understand...
View Board
Explore the incredible legacy of Arthur Eddington, a pioneering figure in astrophysics and cosmology, who brilliantly br...
View Board
Discover Stephen Hawking's groundbreaking contributions to cosmology, his resilience against ALS, and his enduring legac...
View Board
Discover Neil deGrasse Tyson's life and work as a renowned astrophysicist, science communicator and director of the Hayd...
View Board
Discover the inspiring journey of Stephen Hawking in this comprehensive article. From his pioneering work on black holes...
View Board
Discover the life and work of Albert Einstein, a renowned physicist and one of the most influential scientists in histor...
View Board
George Ellery Hale revolutionized astrophysics through solar discoveries, groundbreaking telescopes like Mount Wilson an...
View Board
**Meta Description:** Explore the life of William Herschel, the astronomer who discovered Uranus and revolutionized our ...
View Board
Discover how Alan Guth, a renowned physicist, revolutionized cosmology with his groundbreaking theory of cosmic inflatio...
View Board
> **Meta Description:** Explore the life and legacy of Albert Einstein, the genius who reshaped physics with relativity,...
View Board
**Meta Description:** Discover Vera Rubin's groundbreaking work on dark matter, which revolutionized cosmology. Learn ...
View Board
"Explore Sir Roger Penrose's Nobel-winning black hole theories and quantum gravity legacy. Discover his revolutionary ph...
View Board
Discover how Georges Lemaître, a Catholic priest and physicist, pioneered the Big Bang theory and revolutionized our und...
View Board
Jean Baptiste Joseph Delambre: A Life of Astronomical Pursuits The Early Life and Education Jean Baptiste Joseph Delam...
View Board
Max Born was a renowned theoretical physicist and Nobel laureate known for his statistical interpretation of quantum mec...
View Board
Explore the extraordinary legacy of Riccardo Giacconi, the Nobel laureate who revolutionized X-ray astronomy. Discover h...
View Board
Jocelyn Bell Burnell pioneering astronomer who discovered pulsars leaving a lasting legacy in astrophysics through groun...
View Board
Louis Néel Nobel laureate revolutionized magnetism research with discovery of antiferromagnetism advancing condensed mat...
View Board
768 **Meta Description:** Explore the life of Enrico Fermi, the architect of the nuclear age. From quantum theory to th...
View Board
Comments