Explore Any Narratives
Discover and contribute to detailed historical accounts and cultural stories. Share your knowledge and engage with enthusiasts worldwide.
Stephen Hawking remains one of the most influential figures in modern science, renowned for his groundbreaking contributions to cosmology and theoretical physics. His work on black holes and the origins of the universe has reshaped our understanding of the cosmos. This article explores his legacy, focusing on his role as a visionary of cosmology and a symbolic figure of science.
Born in 1942, Stephen Hawking was diagnosed with ALS at the age of 21. Despite a grim prognosis, he defied expectations, living for over five decades while continuing his scientific pursuits. His resilience and intellect made him a symbol of human determination and brilliance.
Hawking's diagnosis of ALS, a neurodegenerative disease, initially gave him only a few years to live. However, he outlived this prognosis by 53 years, a testament to his extraordinary willpower and the support of advanced medical technology.
Despite his physical challenges, Hawking pursued his education with vigor. He earned his Ph.D. from the University of Cambridge, where he later became the Lucasian Professor of Mathematics, a position once held by Isaac Newton.
Hawking's most significant contributions lie in the field of cosmology, particularly his work on black holes and the Big Bang. His theories have had a profound impact on our understanding of the universe.
In 1974, Hawking proposed the theory of Hawking radiation, which suggests that black holes are not entirely black but emit radiation and can eventually evaporate. This discovery bridged the gap between quantum mechanics and general relativity.
Hawking's no-boundary proposal for the universe's origin suggests that the universe has no beginning or end in the traditional sense. This theory has been supported by recent data from the James Webb Space Telescope, which has provided insights into the early universe.
Hawking's ability to communicate complex scientific ideas to a broader audience is evident in his numerous publications. His books have sold millions of copies worldwide, making him a household name in the field of science.
Published in 1988, A Brief History of Time has sold over 25 million copies worldwide. The book explains the fundamental concepts of cosmology in an accessible manner, making it a bestseller and a classic in scientific literature.
In The Grand Design (2010), Hawking explores the origins of the universe and the role of a creator. He argues that the universe can arise spontaneously from nothing, challenging traditional notions of divine creation.
Even after his passing in 2018, Hawking's work continues to influence modern science. Recent developments in quantum gravity and AI simulations have validated many of his theories, ensuring his legacy endures.
In 2023–2025, AI simulations have validated analogs of Hawking radiation in laboratory settings using sound waves in Bose-Einstein condensates. These experiments provide empirical support for Hawking's theoretical predictions.
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has provided data that supports Hawking's no-boundary proposal. Observations of early galaxies are consistent with inflationary models, further validating his theories.
Stephen Hawking's contributions to cosmology and theoretical physics have left an indelible mark on the scientific community. His work on black holes, the Big Bang, and the origins of the universe continues to inspire and challenge scientists worldwide. As a visionary of cosmology and a symbolic figure of science, Hawking's legacy will endure for generations to come.
Stephen Hawking was not just a scientist; he became a cultural icon whose ideas transcended academia. His theories reshaped modern physics, while his public persona made science accessible and inspiring to millions. This section explores his dual role as a scientific pioneer and a pop culture figure.
Hawking had a unique ability to simplify complex scientific concepts, making them understandable to non-experts. His appearances on television shows, documentaries, and even animated series like The Simpsons and Futurama brought cosmology into mainstream conversations.
One of Hawking’s lifelong goals was to contribute to a Theory of Everything, a framework that unifies general relativity and quantum mechanics. While this remains an unfinished quest, his work laid critical groundwork for future physicists.
His collaboration with Roger Penrose on singularity theorems proved that the universe began as an infinitely dense point—a cornerstone of the Big Bang theory. This work earned them the Wolf Prize in Physics in 1988.
Beyond his scientific achievements, Hawking engaged deeply with philosophical questions about the universe, human existence, and the future of technology. His views on artificial intelligence (AI), alien life, and the multiverse sparked global debates.
Hawking was vocal about the potential dangers of uncontrolled AI development. In 2014, he warned:
"The development of full artificial intelligence could spell the end of the human race."
He advocated for ethical guidelines in AI research, emphasizing the need for safeguards to prevent catastrophic outcomes. His concerns remain relevant as AI technology advances rapidly.
Hawking’s exploration of the multiverse theory suggested that our universe is just one of many. In The Grand Design, he argued that the existence of multiple universes could explain the fine-tuned laws of physics that allow life to exist.
This idea challenges traditional religious and philosophical views, positioning Hawking as a key figure in the science vs. religion debate. His atheistic stance, grounded in scientific evidence, continues to influence discussions about the nature of reality.
Hawking’s work was often collaborative, involving partnerships with other leading physicists. These relationships not only advanced his research but also fostered a spirit of scientific cooperation that defined his career.
Hawking’s collaboration with Roger Penrose in the 1960s and 1970s led to groundbreaking discoveries about black holes and singularities. Their joint work proved that:
This partnership earned them widespread acclaim, including the Albert Einstein Award and the Wolf Prize.
Hawking’s debates with Kip Thorne and other physicists led to significant advancements in understanding black hole thermodynamics. One of the most famous controversies was the black hole information paradox:
This ongoing debate highlights the dynamic nature of scientific inquiry and Hawking’s willingness to revise his theories in light of new evidence.
Hawking’s influence extended far beyond the scientific community. His books, lectures, and public appearances inspired generations of students, educators, and enthusiasts to engage with cosmology and theoretical physics.
Hawking’s story of perseverance in the face of adversity has motivated countless individuals to pursue careers in STEM fields. His life demonstrates that physical limitations do not define intellectual potential.
Hawking received numerous accolades throughout his career, reflecting his global impact. Some of the most notable include:
These honors underscore his role as a symbolic figure of science, celebrated not just for his discoveries but for his ability to inspire and educate.
Despite his immense contributions, Hawking’s career was not without challenges and controversies. His theories often sparked debates, and his personal life faced scrutiny. This section examines some of the key controversies and how they shaped his legacy.
The black hole information paradox remains one of the most contentious issues in modern physics. Hawking’s initial claim that information is lost in black holes clashed with the principles of quantum mechanics.
In 2004, after decades of debate, Hawking admitted that information might not be lost after all. This concession highlighted his intellectual honesty and commitment to scientific truth, even when it meant revising his own theories.
Hawking’s outspoken atheism and his assertion that the universe does not require a creator drew criticism from religious groups. In The Grand Design, he wrote:
"Because there is a law such as gravity, the universe can and will create itself from nothing."
This statement challenged traditional creation narratives, sparking debates between science and religion. While some viewed his stance as provocative, others praised his courage in addressing fundamental questions about existence.
In his final years, Hawking continued to contribute to science and public discourse, even as his health declined. His last published works and public statements reflected his enduring curiosity and concern for humanity’s future.
Hawking’s final paper, published posthumously in 2018, explored the theoretical existence of a multiverse and the implications for cosmology. He also issued warnings about:
These warnings underscored his role not just as a scientist but as a visionary deeply concerned with humanity’s future.
After his passing, efforts were made to preserve Hawking’s voice and ideas for future generations. In 2024, his archives were digitized, making his lectures, notes, and personal correspondence accessible to researchers and the public.
These efforts ensure that Hawking’s legacy as a visionary of cosmology and a symbolic figure of science will endure for decades to come.
Stephen Hawking’s theories continue to shape the future of cosmology and theoretical physics. As technology advances, scientists are finding new ways to test and expand upon his ideas, ensuring his legacy remains at the forefront of scientific discovery.
One of the most exciting developments in recent years is the attempt to observe Hawking radiation in controlled laboratory settings. While directly detecting this radiation from actual black holes remains beyond current technology, researchers have turned to analog systems to simulate the phenomenon.
These experiments not only validate Hawking’s theories but also open new avenues for understanding quantum gravity.
Hawking’s work on primordial black holes—hypothetical black holes formed in the early universe—has gained renewed interest. These objects, if they exist, could provide insights into the Big Bang and the nature of dark matter.
Confirming the existence of primordial black holes would be a monumental achievement, further cementing Hawking’s place in scientific history.
Beyond his scientific contributions, Hawking’s impact on education and public engagement with science is immeasurable. His ability to communicate complex ideas to a broad audience has inspired a new generation of scientists and educators.
Hawking’s books, particularly A Brief History of Time, set a new standard for science communication. His approach made abstract concepts like black holes and quantum mechanics accessible to millions.
His influence extends to modern science communicators, who strive to emulate his ability to make complex topics understandable and engaging.
Hawking’s life story has become a cornerstone of STEM education initiatives, particularly those aimed at encouraging students with disabilities to pursue careers in science.
By breaking barriers, Hawking has shown that intellectual curiosity and determination can overcome even the most daunting obstacles.
Hawking’s work didn’t just advance science—it also sparked profound ethical and philosophical debates. His views on topics like artificial intelligence, alien life, and the future of humanity continue to shape global discussions.
Hawking’s warnings about artificial intelligence have become increasingly relevant as AI technology advances. He argued that while AI has the potential to solve many of humanity’s greatest challenges, it also poses existential risks.
"Success in creating AI would be the biggest event in human history. Unfortunately, it might also be the last, unless we learn how to avoid the risks."
His concerns have influenced policymakers and researchers alike, leading to:
Hawking’s legacy in this area ensures that the conversation about AI’s future remains grounded in both optimism and caution.
Hawking was a vocal advocate for the search for extraterrestrial life, but he also warned of the potential dangers of making contact. His views on this topic have shaped modern approaches to projects like SETI (Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence).
Hawking’s perspective on this issue reflects his broader concern for humanity’s long-term survival, a theme that defined much of his later work.
In the years since his passing, Hawking’s legacy has been preserved and expanded through digital technologies. From virtual reality to online archives, his ideas continue to reach new audiences in innovative ways.
In 2024, the University of Cambridge and the Hawking Estate launched a digital archive of Hawking’s personal and professional papers. This project makes his work accessible to researchers and the public alike.
This digital preservation ensures that future generations can explore Hawking’s contributions in unprecedented detail.
Emerging technologies like virtual reality (VR) are being used to bring Hawking’s lectures and ideas to life. These immersive experiences allow users to engage with his work in ways that were previously impossible.
These innovations ensure that Hawking’s legacy continues to inspire and educate in the digital age.
Stephen Hawking’s contributions to cosmology, theoretical physics, and science communication have left an indelible mark on the world. His work on black holes, the Big Bang, and the multiverse has reshaped our understanding of the universe, while his public engagement has inspired millions to explore the wonders of science.
Stephen Hawking was more than a scientist—he was a visionary who pushed the boundaries of human knowledge and a symbol of the limitless potential of the human mind. His legacy reminds us that curiosity, courage, and creativity can overcome even the greatest challenges. As we continue to explore the mysteries of the universe, Hawking’s ideas will undoubtedly guide and inspire us, ensuring that his impact endures for centuries to come.
Your personal space to curate, organize, and share knowledge with the world.
Discover and contribute to detailed historical accounts and cultural stories. Share your knowledge and engage with enthusiasts worldwide.
Connect with others who share your interests. Create and participate in themed boards about any topic you have in mind.
Contribute your knowledge and insights. Create engaging content and participate in meaningful discussions across multiple languages.
Already have an account? Sign in here

Discover the inspiring journey of Stephen Hawking in this comprehensive article. From his pioneering work on black holes...
View Board
Arthur Eddington: Pioneering Relativity and Stellar Science Arthur Stanley Eddington stands as one of the most influenti...
View Board
George Gamow: The Unbelievable Journey of a Theoretical Physicist and Cosmologist The Enigmatic Man Behind the Cosmic B...
View Board
Explore the remarkable legacy of Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar, the astrophysics luminary who revolutionized our understand...
View Board
Discover Neil deGrasse Tyson's life and work as a renowned astrophysicist, science communicator and director of the Hayd...
View Board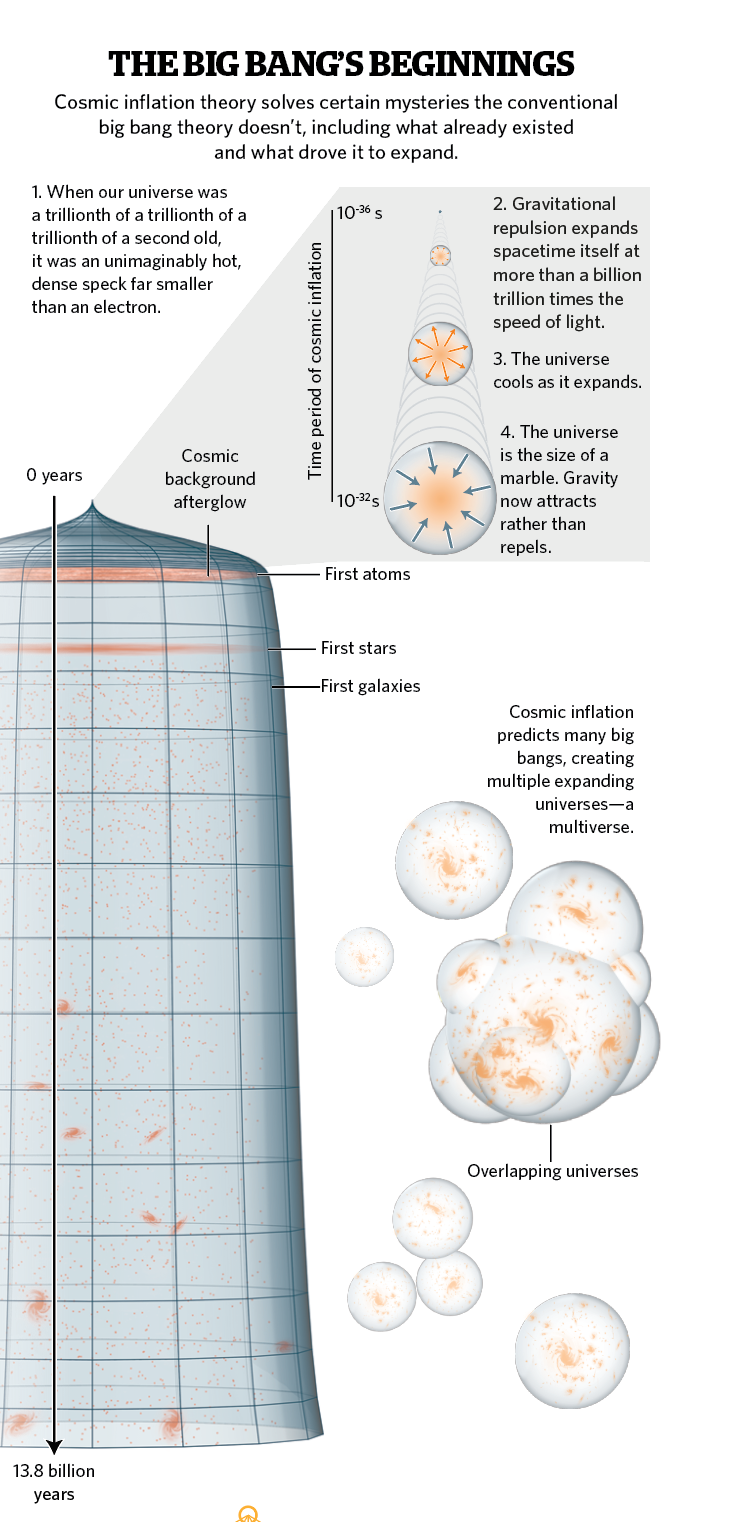
Discover how Alan Guth, a renowned physicist, revolutionized cosmology with his groundbreaking theory of cosmic inflatio...
View Board
"Explore Sir Roger Penrose's Nobel-winning black hole theories and quantum gravity legacy. Discover his revolutionary ph...
View Board
Discover the life and work of Albert Einstein, a renowned physicist and one of the most influential scientists in histor...
View Board
Explore Roger Penrose's groundbreaking contributions to physics, black holes, quantum consciousness, and aperiodic tilin...
View Board
Explore the incredible legacy of Arthur Eddington, a pioneering figure in astrophysics and cosmology, who brilliantly br...
View Board
Explore the life and legacy of Jules Henri Poincaré, a prodigy whose innovative work bridged mathematics and physics. Di...
View Board
Discover how Georges Lemaître, a Catholic priest and physicist, pioneered the Big Bang theory and revolutionized our und...
View Board
George Ellery Hale revolutionized astrophysics through solar discoveries, groundbreaking telescopes like Mount Wilson an...
View Board
Louis Néel Nobel laureate revolutionized magnetism research with discovery of antiferromagnetism advancing condensed mat...
View Board
Jean Baptiste Joseph Delambre: A Life of Astronomical Pursuits The Early Life and Education Jean Baptiste Joseph Delam...
View Board
**Meta Description:** Explore the life of William Herschel, the astronomer who discovered Uranus and revolutionized our ...
View Board
768 **Meta Description:** Explore the life of Enrico Fermi, the architect of the nuclear age. From quantum theory to th...
View Board
**Meta Description:** Discover Vera Rubin's groundbreaking work on dark matter, which revolutionized cosmology. Learn ...
View Board
Explore the life and enduring legacy of Julio Palacios, a pioneering physicist from the 20th century whose groundbreakin...
View Board
Explore the vast cosmos—its galaxies, black holes, exoplanets, dark matter, and humanity's quest to understand the unive...
View Board
Comments