Explore Any Narratives
Discover and contribute to detailed historical accounts and cultural stories. Share your knowledge and engage with enthusiasts worldwide.
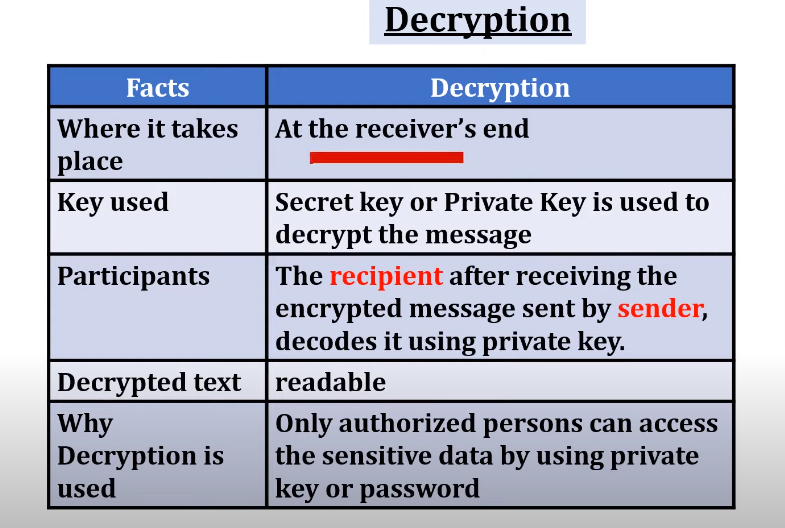
Encryption is the cornerstone of modern data security, transforming readable data into an unreadable format to prevent unauthorized access. As cyber threats evolve, so do encryption technologies, ensuring confidentiality, integrity, and authentication across digital ecosystems. In 2025, encryption is not just a best practice—it’s a regulatory necessity and a strategic imperative for enterprises worldwide.
At its core, encryption is a cryptographic process that converts plaintext (readable data) into ciphertext (unreadable data) using algorithms and keys. This process ensures that only authorized parties with the correct key can decrypt and access the original information. Encryption serves three primary security goals:
Encryption methods are broadly categorized into two types: symmetric and asymmetric.
Encryption protects data in three states:
The encryption landscape in 2025 is shaped by quantum computing threats, regulatory mandates, and innovative cryptographic techniques. Organizations are increasingly adopting advanced encryption strategies to stay ahead of cyber threats and compliance requirements.
Quantum computing poses a significant threat to traditional encryption algorithms like RSA and ECC. Quantum computers can potentially break these algorithms using Shor’s algorithm, which efficiently factors large numbers and solves discrete logarithms. To counter this, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has been leading the charge in developing post-quantum cryptography (PQC) standards.
In 2024, NIST finalized several PQC algorithms, including:
NIST’s roadmap aims to phase out RSA and ECC by 2030, with full deprecation by 2035. According to a 2025 Global Encryption Trends Study, 57-60% of organizations are already prototyping PQC solutions to future-proof their security infrastructure.
"By 2030, quantum computers could render current encryption standards obsolete, making the transition to post-quantum cryptography a critical priority for enterprises." — NIST, 2024
Regulatory bodies worldwide are tightening data protection laws, mandating stronger encryption standards. Key regulations shaping encryption practices in 2025 include:
Compliance with these regulations is not optional. Organizations failing to adopt strong encryption face severe penalties, reputational damage, and increased vulnerability to data breaches.
Effective encryption relies on secure key management. Poor key management practices, such as co-locating keys with data or using weak keys, can undermine even the strongest encryption algorithms. In 2025, 58% of large enterprises are leveraging AI and automation to enhance key management.
AI-driven solutions offer several advantages:
By automating key lifecycle management, organizations can significantly reduce human error and improve overall security posture.
Beyond traditional encryption methods, several cutting-edge technologies are gaining traction in 2025. These innovations address specific challenges, such as processing encrypted data without decryption and securing data in multi-party environments.
Homomorphic encryption is a groundbreaking technology that allows computations to be performed on encrypted data without decrypting it. This capability is particularly valuable for:
While still in the early stages of enterprise adoption, homomorphic encryption is gaining momentum as organizations seek to balance data utility with security.
Multi-Party Computation (MPC) enables multiple parties to jointly compute a function over their private inputs without revealing those inputs to each other. MPC is ideal for scenarios requiring:
MPC is becoming a viable solution for large-scale privacy needs, offering a balance between data collaboration and security.
Confidential computing focuses on protecting data in use through hardware-based Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs). TEEs create secure enclaves within processors where data can be processed without exposure to the rest of the system, including the operating system or hypervisor.
Key benefits of confidential computing include:
Enterprises are increasingly adopting TEEs to address the challenges of securing data during processing, a critical gap in traditional encryption strategies.
To maximize the effectiveness of encryption, organizations should adhere to best practices that align with current threats and regulatory requirements. Here are key recommendations for 2025:
Cryptographic agility refers to the ability to swiftly transition between encryption algorithms and protocols in response to evolving threats or advancements. A robust framework includes:
Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) is a security model that eliminates the concept of trust within a network. Instead, it enforces strict identity verification and least-privilege access for every user and device. Encryption plays a pivotal role in ZTA by:
ZTA is rapidly replacing traditional perimeter-based security models, offering a more resilient approach to cybersecurity.
Effective key management is critical to the success of any encryption strategy. Best practices include:
By prioritizing key management, organizations can mitigate risks associated with key compromise and ensure the long-term integrity of their encryption strategies.
While encryption is essential, complementary techniques like data masking and tokenization provide additional layers of security, particularly in non-production environments.
These techniques are particularly valuable in hybrid cloud environments, where data may be processed across multiple platforms.
The encryption landscape in 2025 is defined by rapid technological advancements, evolving threats, and stringent regulatory requirements. Organizations must adopt a proactive approach to encryption, leveraging post-quantum cryptography, AI-driven key management, and emerging technologies like homomorphic encryption and confidential computing.
By integrating encryption into a broader Zero Trust Architecture and prioritizing cryptographic agility, enterprises can future-proof their data security strategies. The statistics speak for themselves: 72% of organizations with robust encryption strategies experience reduced breach impacts, highlighting the tangible benefits of a well-implemented encryption framework.
As we move further into 2025, encryption will continue to be a cornerstone of cybersecurity, enabling organizations to protect their most valuable asset—data—in an increasingly complex and threat-filled digital world.
The adoption of cloud computing and hybrid IT environments has transformed how organizations store, process, and transmit data. However, these environments introduce unique encryption challenges, particularly around data sovereignty, key management, and performance. In 2025, addressing these challenges is critical for maintaining security and compliance.
One of the most significant challenges in cloud encryption is data sovereignty—the requirement that data be subject to the laws of the country in which it is stored. With 144 countries enforcing data protection laws, organizations must ensure their encryption strategies comply with regional regulations such as:
To navigate these complexities, enterprises are adopting multi-region encryption strategies, where data is encrypted differently based on its storage location. This approach ensures compliance while maintaining global data accessibility.
Cloud environments often rely on shared responsibility models, where the cloud provider secures the infrastructure, but the organization is responsible for data security. This model complicates key management, as organizations must:
A 2025 study by Encryption Consulting found that 65% of enterprises now use third-party key management solutions to retain control over their encryption keys, reducing reliance on cloud providers.
Encryption can introduce latency in cloud environments, particularly for high-volume transactions or real-time data processing. To mitigate this, organizations are leveraging:
By optimizing encryption performance, businesses can maintain operational efficiency without compromising security.
Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) is a security framework that operates on the principle of "never trust, always verify." Encryption is a foundational component of ZTA, ensuring that data remains protected regardless of its location or the network’s trustworthiness.
ZTA relies on several key principles where encryption plays a vital role:
According to a 2025 report by Randtronics, organizations implementing ZTA with robust encryption saw a 40% reduction in breach incidents compared to those relying on traditional perimeter-based security.
To integrate encryption effectively within a ZTA framework, organizations should:
By embedding encryption into every layer of the ZTA framework, organizations can achieve a defense-in-depth strategy that significantly enhances security posture.
The financial services sector has been at the forefront of adopting Zero Trust with encryption. A leading global bank implemented a ZTA model in 2024, integrating:
The result was a 50% reduction in fraud-related incidents and full compliance with PCI DSS 4.0 and GDPR requirements. This case study underscores the effectiveness of combining ZTA with advanced encryption techniques.
The Internet of Things (IoT) has exploded in recent years, with an estimated 30 billion connected devices worldwide in 2025. However, IoT devices often lack robust security measures, making them prime targets for cyberattacks. Encryption is essential for securing IoT ecosystems, but it must be adapted to the unique constraints of these devices.
IoT devices present several encryption challenges:
To address these challenges, organizations are turning to lightweight cryptographic algorithms designed specifically for IoT.
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has been developing lightweight cryptography standards to secure IoT devices. These standards include:
In 2025, NIST finalized several lightweight cryptography algorithms, enabling broader adoption across IoT deployments. These algorithms are particularly critical for industrial IoT (IIoT) and medical IoT (MIoT), where data security is paramount.
Encryption for IoT must address both data in transit and data at rest:
A 2025 study by GoldComet found that 68% of IoT deployments now incorporate lightweight encryption, significantly reducing vulnerability to attacks like man-in-the-middle (MITM) and data tampering.
Blockchain technology is emerging as a complementary solution for IoT security. By leveraging blockchain’s decentralized and immutable ledger, IoT networks can achieve:
In 2025, 22% of enterprise IoT projects are integrating blockchain with encryption to enhance security and trust in decentralized IoT ecosystems.
The healthcare industry handles some of the most sensitive data, including electronic Protected Health Information (ePHI). With the rise of telemedicine, wearable health devices, and electronic health records (EHRs), encryption is critical for compliance and patient trust.
Healthcare organizations must comply with stringent regulations that mandate encryption:
Non-compliance with these regulations can result in fines up to $1.5 million per violation under HIPAA, making encryption a non-negotiable priority.
Healthcare encryption faces several unique challenges:
To overcome these challenges, healthcare providers are adopting:
The rapid growth of telemedicine has heightened the need for end-to-end encryption (E2EE). A leading telehealth provider implemented:
As a result, the provider achieved HIPAA compliance and a 35% reduction in data breach risks, demonstrating the critical role of encryption in modern healthcare.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and encryption are increasingly intertwined, with AI enhancing encryption strategies and encryption securing AI models and datasets. In 2025, this synergy is driving innovations in automated key management, threat detection, and privacy-preserving AI.
Managing encryption keys manually is prone to human error and inefficiency. AI is transforming key management by:
A 2025 report by Encryption Consulting highlights that 58% of large enterprises now use AI-driven key management, reducing key-related incidents by 45%.
AI models require vast amounts of data, often including sensitive information. Encryption techniques like homomorphic encryption and secure multi-party computation (MPC) enable:
These techniques are particularly valuable in sectors like healthcare and finance, where data privacy is paramount.
AI is also being used to enhance threat detection and optimize encryption strategies:
By integrating AI with encryption, organizations can achieve a more proactive and adaptive security posture, capable of responding to emerging threats in real-time.
As we look beyond 2025, the encryption landscape will continue to evolve in response to quantum computing, regulatory changes, and emerging technologies. Organizations must adopt forward-looking strategies to ensure long-term data security.
The advent of quantum computing poses an existential threat to current encryption standards. Quantum computers could potentially break widely used algorithms like RSA and ECC using Shor’s algorithm. To
As encryption becomes a global regulatory mandate, organizations must navigate a complex landscape of data protection laws. In 2025, 144 countries enforce data protection regulations covering 79-82% of the world’s population, making encryption a legal requirement rather than an optional security measure.
Key regulations shaping encryption strategies include:
Failure to comply with these mandates can result in fines up to $1.5 million per violation under HIPAA and up to 4% of global revenue under GDPR, emphasizing the business risk of inadequate encryption.
With 72% of organizations operating in multi-jurisdictional environments, encryption must align with varying legal requirements. Challenges include:
To address these issues, organizations are adopting dynamic encryption frameworks that automatically adjust encryption protocols based on data location and applicable laws.
The advent of quantum computing poses an existential threat to current encryption standards. Quantum computers could break widely used algorithms like RSA and ECC using Shor’s algorithm, rendering today’s encryption obsolete.
In 2024, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) finalized post-quantum cryptography (PQC) algorithms, including:
NIST’s roadmap mandates phasing out RSA and ECC by 2030, with full deprecation by 2035. According to the 2025 Global Encryption Trends Study, 57-60% of organizations are already prototyping PQC solutions to avoid costly last-minute transitions.
“Organizations that delay PQC adoption risk catastrophic security failures as quantum computing capabilities advance.” — NIST, 2024
Enterprises should take the following steps to prepare for PQC:
By adopting a phased approach, organizations can mitigate risks while maintaining operational continuity.
Encryption in 2025 is increasingly intertwined with AI, edge computing, and decentralized architectures. These technologies demand innovative encryption strategies to address new security challenges.
Artificial intelligence is transforming encryption management through:
A 2025 study by Encryption Consulting reveals that 58% of large enterprises now use AI for key management, reducing key-related incidents by 45%.
In 2025, 68% of IoT deployments incorporate lightweight encryption, reducing vulnerabilities in smart factories, healthcare devices, and connected homes.
Blockchain technology enables decentralized encryption by creating immutable, distributed ledger systems. Key applications include:
By 2025, 22% of enterprise blockchain projects integrate encryption to secure decentralized applications (dApps) and data exchanges.
Encryption in 2025 is no longer a standalone security measure—it’s a strategic imperative embedded in every layer of digital infrastructure. From post-quantum cryptography to AI-driven key management, organizations must adopt a holistic, adaptive approach to encryption.
As cyber threats grow more sophisticated, encryption remains the last line of defense. Organizations that prioritize robust encryption strategies, align with global regulations, and embrace emerging technologies will not only protect data but also build trust with customers, partners, and regulators. In 2025 and beyond, encryption is the foundation of digital trust—securing today’s transactions and safeguarding tomorrow’s innovation.



Your personal space to curate, organize, and share knowledge with the world.
Discover and contribute to detailed historical accounts and cultural stories. Share your knowledge and engage with enthusiasts worldwide.
Connect with others who share your interests. Create and participate in themed boards about any topic you have in mind.
Contribute your knowledge and insights. Create engaging content and participate in meaningful discussions across multiple languages.
Already have an account? Sign in here

Unlock the intricacies of the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) in our comprehensive guide. Explore its key mechanisms,...
View Board
Discover the pivotal role of the Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange in secure communications. Learn how this foundational crypt...
View Board
Explore the fascinating evolution of cryptography, from ancient methods to modern breakthroughs, in our insightful artic...
View Board
Discover the power of Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) in "Understanding Elliptic Curve Cryptography: A Modern Approach...
View Board
Discover the essentials of encryption and decryption, the backbone of data security, in this comprehensive guide. Learn ...
View Board
Explore the essentials of Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) as the foundation of secure digital communication. Discover ho...
View Board
Explore how digital signatures are revolutionizing data security by verifying identity and ensuring data integrity in th...
View Board
Discover how the SHA-256 hashing algorithm secures digital data, powers blockchain, and ensures integrity. Learn its key...
View Board
Explore the fascinating journey of the monoalphabetic cipher, from its historical roots in ancient civilizations to its ...
View Board
Explore the captivating history of polyalphabetic ciphers, a cornerstone of cryptography that revolutionized secure comm...
View Board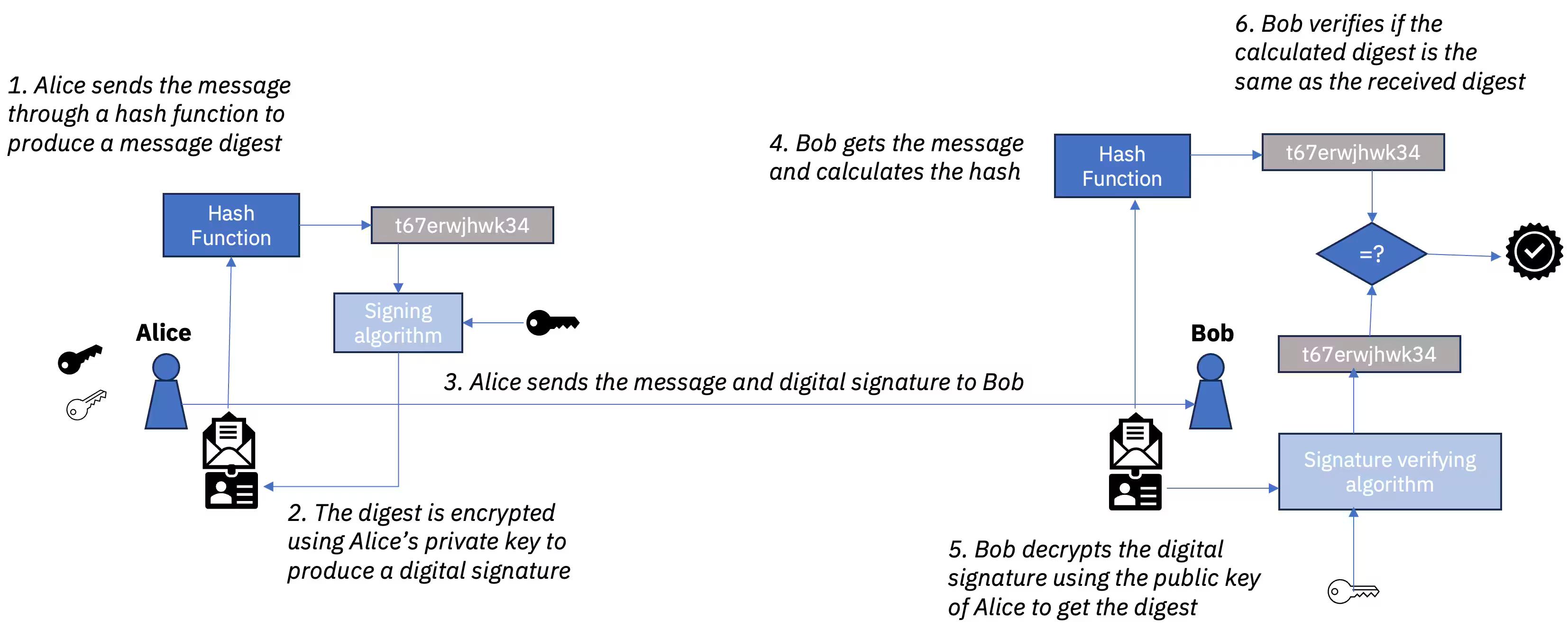
Understanding hash functions is crucial for data security. Learn about their mechanics, types, applications, and securit...
View Board
Explore the fascinating world of Roman cryptography and uncover the ancient techniques that safeguarded military and per...
View Board
Explore the fascinating journey of cryptography from ancient times to modern day in "The Evolution of Early Cryptographi...
View Board
**Meta Description:** "Discover how quantum cryptography revolutionizes secure communication with unbreakable encrypti...
View Board
Descubra como a criptografia de chave assimétrica protege dados sem compartilhar segredos, revolucionando a segurança di...
View Board
Descubra a cifra monoalfabética, um clássico da criptografia que ensina fundamentos essenciais de segurança da informaçã...
View Board
Descubra como a Troca de Chaves Diffie-Hellman protege HTTPS, VPNs e mensagens. Domine este pilar essencial da segurança...
View Board
Descubra como o algoritmo SHA-256 garante segurança digital, desde blockchain até proteção de senhas. Entenda seu funcio...
View Board
AES एन्क्रिप्शन: डिजिटल सुरक्षा का सबसे विश्वसनीय मानक। जानें कैसे AES-256 आपके डेटा को हैकर्स से सुरक्षित रखता है।
View Board
आधुनिक क्रिप्टोग्राफी को समझें हिंदी वर्णमाला के माध्यम से। जानें कैसे स्वर-व्यंजन पब्लिक-प्राइवेट कीज़ की तरह क
View Board
Comments