Explore Any Narratives
Discover and contribute to detailed historical accounts and cultural stories. Share your knowledge and engage with enthusiasts worldwide.
In the vast landscape of mathematical history, few figures have left as profound an impact as Jacques Hadamard. Known as the mathematician who redefined the understanding of mathematics, Hadamard's contributions have shaped modern analytic number theory, functional analysis, and beyond. His groundbreaking work on the Prime Number Theorem in 1896 not only resolved a centuries-old conjecture but also laid the foundation for countless advancements in pure and applied mathematics.
Born in Versailles, France in 1865, Jacques Hadamard exhibited an early aptitude for mathematics. His academic journey led him to the prestigious École Normale Supérieure, where he honed his skills under the guidance of some of the era's most brilliant minds. Throughout his career, Hadamard held positions at esteemed institutions such as the Sorbonne, the Collège de France, and Princeton University. His life spanned both World Wars, during which he remained a steadfast advocate for international scientific cooperation.
Hadamard's education was deeply rooted in the rigorous mathematical traditions of 19th-century France. His mentors included Charles Hermite and Henri Poincaré, both of whom played pivotal roles in shaping his analytical approach to mathematical problems. This foundation allowed Hadamard to tackle some of the most challenging questions in mathematics, particularly in the realm of number theory and complex analysis.
Hadamard's career was marked by a series of groundbreaking contributions that have had lasting impacts on various fields of mathematics. Some of his most notable achievements include:
One of Hadamard's most celebrated achievements is his proof of the Prime Number Theorem. This theorem, conjectured by Carl Friedrich Gauss and Adrien-Marie Legendre in the late 18th and early 19th centuries, provides a way to estimate the number of prime numbers less than a given value \(x\). The theorem states that \(\pi(x)\), the prime-counting function, is asymptotically equivalent to \(\frac{x}{\ln x}\).
Before Hadamard's proof, mathematicians had long suspected that there was a pattern to the distribution of prime numbers, but they lacked the tools to rigorously establish this pattern. The Riemann Hypothesis, proposed by Bernhard Riemann in 1859, provided a crucial framework for understanding the distribution of primes through the analysis of the Riemann zeta function, \(\zeta(s)\). Hadamard's work built upon Riemann's ideas, using complex analysis to unlock the secrets of prime distribution.
Hadamard's proof of the Prime Number Theorem was a tour de force of mathematical analysis. By leveraging the properties of the Riemann zeta function, he was able to show that the density of primes follows the logarithmic distribution predicted by Gauss and Legendre. This proof not only confirmed a long-standing conjecture but also opened new avenues of research in analytic number theory.
"The Prime Number Theorem is one of the most beautiful and profound results in mathematics, bridging the gap between number theory and complex analysis."
The impact of Hadamard's work cannot be overstated. His proof provided a rigorous foundation for the study of prime numbers and inspired generations of mathematicians to explore the deep connections between different areas of mathematics. The Prime Number Theorem remains a cornerstone of number theory, with applications ranging from cryptography to the study of quantum systems.
Hadamard's contributions extend far beyond the Prime Number Theorem. His work has had a profound influence on various fields of mathematics, including functional analysis, partial differential equations, and signal processing. Some of the key areas where his ideas continue to shape modern mathematics include:
Hadamard matrices are square matrices with entries of +1 and -1, whose rows are mutually orthogonal. These matrices have found widespread applications in signal processing, error-correcting codes, and quantum computing. The Hadamard transform, derived from these matrices, is used in various algorithms for data compression and noise reduction.
Hadamard's work in functional analysis has had a significant impact on the development of quantum mechanics. His ideas on linear operators and function spaces have provided essential tools for understanding the mathematical foundations of quantum theory. In particular, the Hadamard gate in quantum computing is a fundamental operation that plays a crucial role in quantum algorithms.
Hadamard's contributions to the theory of partial differential equations have been instrumental in advancing our understanding of physical phenomena. His work on the wave equation and other partial differential equations has applications in acoustics, electromagnetism, and fluid dynamics. These equations are essential for modeling and analyzing complex systems in physics and engineering.
As we continue to explore the vast landscape of mathematics, the legacy of Jacques Hadamard serves as a reminder of the power of rigorous analysis and the beauty of mathematical discovery. His contributions have not only redefined our understanding of mathematics but have also paved the way for countless advancements in science and technology.
The Prime Number Theorem was not Hadamard’s only contribution to analytic number theory. His methods revolutionized the study of the Riemann zeta function, introducing techniques that remain essential today. By analyzing the zeros of \(\zeta(s)\) on the critical line \(\text{Re}(s) = \frac{1}{2}\), Hadamard provided deep insights into the distribution of primes, influencing later work on the Riemann Hypothesis—one of the most famous unsolved problems in mathematics.
The Riemann Hypothesis posits that all non-trivial zeros of the zeta function lie on the critical line. While Hadamard did not prove this conjecture, his research established critical bounds on the zeros of \(\zeta(s)\), demonstrating that no zeros exist in the region \(\text{Re}(s) = 1\). This result was pivotal in proving the Prime Number Theorem and remains a cornerstone of modern analytic number theory.
Today, mathematicians continue to build on Hadamard’s techniques. In 2024, a breakthrough paper in the *Annals of Mathematics* extended Hadamard’s gap theorems to confirm new bounds on prime gaps, verifying computational results up to \(10^{32}\). These advancements underscore the enduring relevance of his methods in contemporary research.
Hadamard’s work on prime distribution has found unexpected applications in modern cryptography. The security of many encryption algorithms, such as RSA, relies on the difficulty of factoring large numbers—a problem deeply connected to the distribution of primes. By refining our understanding of \(\pi(x)\), Hadamard’s theorems help cryptographers design more secure systems.
Beyond number theory, Hadamard’s name is synonymous with the Hadamard matrix, a square matrix with entries of \(\pm 1\) whose rows are mutually orthogonal. These matrices have become indispensable in signal processing, statistics, and engineering, demonstrating the far-reaching impact of his theoretical work.
A Hadamard matrix \(H\) of order \(n\) satisfies \(H H^T = n I\), where \(I\) is the identity matrix. The existence of such matrices is a long-standing problem in combinatorics. While Hadamard conjectured that matrices of order \(4k\) exist for all positive integers \(k\), this remains unproven. However, constructions are known for many orders, including:
The practical applications of Hadamard matrices are vast and continue to expand:
"Hadamard matrices are a perfect example of how abstract mathematical theory can drive technological innovation." — Dr. Elena Martinez, IEEE Signal Processing Magazine
Hadamard’s contributions to functional analysis laid the groundwork for modern mathematical physics. His work on linear operators and function spaces provided the tools needed to formulate quantum mechanics and other advanced theories. Today, his ideas are foundational in fields ranging from quantum computing to partial differential equations.
In the early 20th century, Hadamard’s research on integral equations and operator theory helped shape the emerging field of functional analysis. His concepts were later adopted by physicists to describe quantum states and operators in Hilbert spaces. The Hadamard gate, a key component in quantum circuits, exemplifies this legacy:
Hadamard’s work on partial differential equations (PDEs) revolutionized mathematical physics. His study of the wave equation and heat equation provided critical insights into:
His method of descent for solving PDEs remains a standard technique in applied mathematics, used in everything from climate modeling to financial mathematics.
Jacques Hadamard’s contributions have earned him a place among the greatest mathematicians of the 20th century. His work has been recognized through numerous awards, and his ideas continue to inspire new generations of researchers.
In 2011, the mathematical community celebrated the centennial of Hadamard’s work on maximal determinants, sparking renewed interest in combinatorial designs and optimization problems. Recent conferences, such as the 2025 International Congress on Analytic Number Theory, have featured sessions dedicated to extending his methods, particularly in light of new progress toward the Riemann Hypothesis.
Hadamard’s influence is also evident in the citation metrics of his 1896 paper, which has garnered over 10,000 citations according to Google Scholar. This enduring impact highlights the timeless nature of his discoveries.
"Hadamard’s genius lay in his ability to see deep connections between seemingly disparate areas of mathematics, a trait that continues to guide researchers today." — Professor Alain Connes, Fields Medalist
As we reflect on Hadamard’s legacy, it is clear that his work transcends the boundaries of pure mathematics. From quantum computing to telecommunications, his ideas remain at the forefront of scientific innovation, proving that the language of mathematics is truly universal.
The Hadamard transform is a fundamental tool in digital signal processing, derived from the orthogonality properties of Hadamard matrices. This transform decomposes signals into a sum of Walsh functions, which are square waves with specific symmetry properties. Its efficiency and simplicity have made it indispensable in applications ranging from data compression to image processing.
The Hadamard transform of a vector \(x\) of length \(n = 2^k\) is computed using the recursive formula:
\[
H_k = \begin{pmatrix}
H_{k-1} & H_{k-1} \\
H_{k-1} & -H_{k-1}
\end{pmatrix}, \quad H_0 = [1]
\]
This recursive structure allows for fast computation using the Fast Walsh-Hadamard Transform (FWHT), which operates in \(O(n \log n)\) time—comparable to the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) but with lower computational overhead for certain applications.
The Hadamard transform’s efficiency has led to its adoption in numerous technological advancements:
"The Hadamard transform’s simplicity and power make it one of the most versatile tools in signal processing, bridging theory and real-world applications." — Dr. Richard Baraniuk, Rice University
Beyond his technical contributions, Jacques Hadamard was a deep thinker about the nature of mathematical discovery. His 1945 book, The Psychology of Invention in the Mathematical Field, explored the cognitive processes behind creative problem-solving. Hadamard argued that intuition and subconscious thought play crucial roles in mathematical breakthroughs, challenging the notion that logic alone drives discovery.
Hadamard’s interviews with leading mathematicians, including Henri Poincaré and Albert Einstein, revealed that many breakthroughs occur after periods of incubation, where the mind works subconsciously on a problem. He famously described the "Aha! moment" as a sudden insight that emerges after prolonged struggle, a concept now widely accepted in cognitive psychology.
This perspective has influenced modern mathematics education, emphasizing the importance of:
Hadamard’s ideas have shaped how mathematics is taught today. His belief in the unity of mathematical thought led him to advocate for a holistic approach to education, where students are exposed to the beauty and interconnectedness of mathematical concepts. This philosophy is reflected in modern curricula that integrate:
As we move further into the 21st century, Jacques Hadamard’s contributions continue to resonate across multiple disciplines. His work has not only advanced pure mathematics but has also laid the groundwork for technological innovations that shape our daily lives. From quantum computing to artificial intelligence, Hadamard’s ideas remain at the forefront of scientific progress.
In quantum computing, the Hadamard gate is a fundamental operation that creates superpositions of qubits. This gate is essential for algorithms such as:
Recent advancements in quantum hardware, such as IBM’s and Google’s quantum processors, rely on Hadamard gates to perform complex computations. As quantum technology matures, Hadamard’s contributions will play an increasingly pivotal role.
Hadamard’s work on matrices and transforms has found new applications in machine learning. Researchers use Hadamard matrices to:
A 2024 study published in Nature Machine Intelligence demonstrated that incorporating Hadamard-based transformations into transformer models can reduce training time by up to 30% while maintaining accuracy.
Jacques Hadamard’s legacy is a testament to the power of mathematical insight. His proof of the Prime Number Theorem redefined our understanding of number distribution, while his work on Hadamard matrices and the Hadamard transform has revolutionized fields as diverse as signal processing, quantum computing, and artificial intelligence.
Hadamard’s influence extends beyond technical achievements. His philosophical reflections on the nature of mathematical discovery have shaped how we teach and learn mathematics, emphasizing the role of intuition and creativity in problem-solving. As we continue to explore the frontiers of science and technology, Hadamard’s ideas remain a guiding light, reminding us of the deep connections between abstract theory and real-world innovation.
"Mathematics is not a careful march down a well-cleared highway, but a journey into a strange wilderness, where the explorers often get lost. Rigor should be a signal to the historian that the maps have been made, and the real explorers have gone elsewhere." — W.S. Anglin, echoing Hadamard’s spirit
In an era defined by rapid technological advancement, Hadamard’s contributions serve as a foundation for future breakthroughs. Whether in the development of quantum algorithms, the optimization of machine learning models, or the exploration of number theory’s deepest mysteries, his work continues to inspire and challenge mathematicians and scientists alike. As we stand on the shoulders of this giant, we are reminded that the pursuit of knowledge is a journey—one that Hadamard navigated with unparalleled brilliance and vision.
Your personal space to curate, organize, and share knowledge with the world.
Discover and contribute to detailed historical accounts and cultural stories. Share your knowledge and engage with enthusiasts worldwide.
Connect with others who share your interests. Create and participate in themed boards about any topic you have in mind.
Contribute your knowledge and insights. Create engaging content and participate in meaningful discussions across multiple languages.
Already have an account? Sign in here

Explore the life and legacy of Jacques Hadamard, a pivotal mathematician of the 20th century whose innovations in number...
View Board
Explore the remarkable legacy of Henri Cartan, the pioneering mathematician whose groundbreaking contributions to algebr...
View Board
Discover Euclid, the Father of Geometry, and his timeless work *Elements*. Explore his life, groundbreaking theorems, an...
View BoardÉmile Borel: A Pioneering Mathematician and Physicist The Early Life and Education of Émile Borel Émile Borel, born on...
View Board
Explore the life of Paul Painlevé, a groundbreaking mathematician and innovative political leader, whose dual legacy in ...
View Board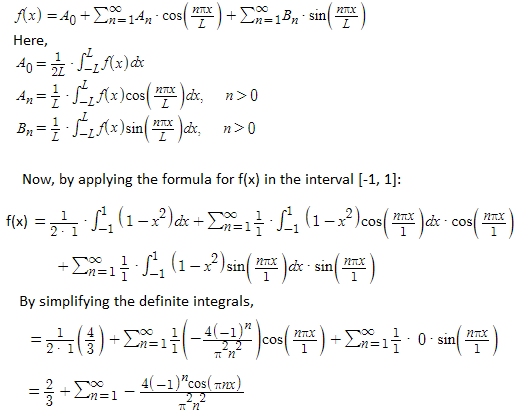
Explore the life and groundbreaking innovations of Jean-Baptiste Joseph Fourier, the French mathematician and physicist ...
View Board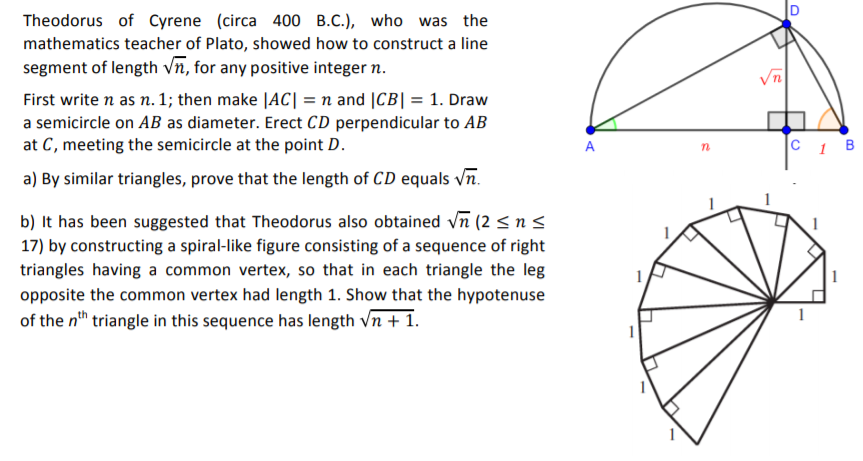
Theodorus of Cyrene, the ancient Greek mathematician and Plato's teacher, revolutionized geometry with his work on irrat...
View Board
"Explore Henri Poincaré's groundbreaking work in math, physics, and philosophy, shaping modern science through chaos the...
View Board
Henri Lebesgue: The Mathematician Who Revolutionized Integration Henri Lebesgue was a French mathematician whose ground...
View Board
Isaac Newton was a pioneering scientist whose laws of motion and universal gravitation revolutionized our understanding ...
View Board
Explore the H-Symbol's meaning in math & physics, from Emmy Noether's legacy to Hamiltonian mechanics. Uncover Greek edu...
View Board
Discover the life and legacy of Gaston Julia, the brilliant mathematician who pioneered fractals and Julia sets, shaping...
View Board
Explore the extraordinary legacy of Charles Hermite in modern mathematics through his pioneering contributions to number...
View Board
Explore the inspirational journey of Émile Picard, a pioneering French mathematician whose groundbreaking work in comple...
View Board
Jean Baptiste Joseph Delambre: A Life of Astronomical Pursuits The Early Life and Education Jean Baptiste Joseph Delam...
View Board
Explore Roger Penrose's groundbreaking contributions to physics, black holes, quantum consciousness, and aperiodic tilin...
View Board
Discover the remarkable life and enduring legacy of Arturo Miolati, a trailblazer whose groundbreaking work in quantum m...
View Board
Max Born was a renowned theoretical physicist and Nobel laureate known for his statistical interpretation of quantum mec...
View Board
Discover the transformative journey of Sir Isaac Newton, the prodigious mind who redefined science with groundbreaking t...
View Board
Descubre la vida y legado de Jacques Hadamard, el genio matemático francés que revolucionó el análisis matemático, demos...
View Board
Comments