Explore Any Narratives
Discover and contribute to detailed historical accounts and cultural stories. Share your knowledge and engage with enthusiasts worldwide.
Charles Hermite, a name synonymous with groundbreaking advancements in theoretical mathematics, stands as a titan in the realm of transcendental numbers and orthogonal polynomials. His work not only reshaped the landscape of 19th-century mathematics but also laid the foundation for modern quantum mechanics and analytic number theory. This article explores Hermite's life, his pivotal contributions, and the enduring impact of his discoveries on contemporary science.
Born in Dieuze, France in 1822, Charles Hermite overcame significant physical challenges to become one of the most influential mathematicians of his time. His journey began at the prestigious École Polytechnique in 1842, where he quickly distinguished himself despite his disabilities. By 1870, Hermite had succeeded Joseph Liouville at the Sorbonne, solidifying his reputation as a leader in mathematical innovation.
Hermite's early education was marked by a deep fascination with number theory and complex analysis. His mentors, including Joseph Liouville, played a crucial role in shaping his mathematical perspective. The rigorous academic environment of the École Polytechnique provided Hermite with the tools to tackle some of the most challenging problems in mathematics.
Throughout his career, Hermite collaborated with other mathematical luminaries, such as Karl Weierstrass, to advance the study of elliptic functions. These collaborations bridged the gap between complex analysis and algebra, contributing to the 19th-century rigor revolution in mathematics. His work echoed the axiomatic methods of ancient Greek mathematicians like Euclid and Archimedes, further cementing his legacy.
Hermite's contributions to mathematics are vast and varied, but his most notable achievements lie in the realms of transcendental numbers and Hermite polynomials. These discoveries have had a profound impact on both theoretical and applied mathematics.
In 1873, Hermite achieved a monumental feat by proving that e, the base of the natural logarithm, is a transcendental number. This means that e is not a root of any non-zero polynomial equation with rational coefficients. This breakthrough built upon the earlier work of Joseph Liouville and paved the way for future advancements in analytic number theory.
"Hermite's proof of the transcendence of e was a turning point in the study of numbers, opening new avenues for exploration in the field of mathematics."
Another significant contribution by Hermite is the development of Hermite polynomials, a class of orthogonal polynomials defined by the Rodrigues formula:
Hn(x) = (-1)n ex2 (dn/dxn) e-x2
These polynomials have found extensive applications in various fields, including:
The versatility and utility of Hermite polynomials have made them a cornerstone of modern mathematical research, with over 50,000 citations in academic literature as of 2025.
Hermite's work has had a lasting impact on various branches of science, particularly in the fields of quantum mechanics and analytic number theory. His discoveries continue to inspire new research and innovations, demonstrating the enduring relevance of his contributions.
The application of Hermite polynomials in quantum mechanics cannot be overstated. These polynomials are fundamental to the study of the quantum harmonic oscillator, a model that describes the behavior of particles in a harmonic potential. This model is crucial for understanding various physical phenomena, from molecular vibrations to the behavior of electrons in a crystal lattice.
Hermite's proof of the transcendence of e was a catalyst for further explorations in analytic number theory. His methods influenced subsequent mathematicians, including David Hilbert and Aleksandr Gelfond, who expanded upon his work to prove the transcendence of other important mathematical constants. These advancements have significantly enriched our understanding of the nature of numbers and their properties.
Charles Hermite's contributions to mathematics have left an indelible mark on the field, shaping the way we understand and approach theoretical sciences. From his groundbreaking proof of the transcendence of e to the development of Hermite polynomials, his work continues to inspire and drive innovation in various scientific disciplines. As we delve deeper into the complexities of modern mathematics, the legacy of Charles Hermite serves as a testament to the power of human ingenuity and the enduring quest for knowledge.
Charles Hermite's contributions extend far beyond his own era, influencing contemporary mathematical research and applications. His work in transcendental numbers and orthogonal polynomials continues to shape modern mathematical thought, with implications spanning from pure theory to practical applications in technology and science.
Hermite's proof that e is transcendental was not just a singular achievement but a catalyst for a broader exploration of transcendental numbers. This work laid the groundwork for subsequent mathematicians, including Ferdinand von Lindemann, who later proved the transcendence of π in 1882. Together, these discoveries resolved long-standing questions about the nature of these fundamental constants.
The impact of Hermite's research is evident in the formulation of Hilbert's seventh problem, which asked whether ab is transcendental for algebraic a and irrational algebraic b. This problem was later solved by the Gelfond-Schneider theorem in 1934, further illustrating the enduring influence of Hermite's initial insights.
The relevance of Hermite polynomials in quantum mechanics is profound. These polynomials are essential in describing the wave functions of the quantum harmonic oscillator, a fundamental model in quantum physics. The harmonic oscillator model is used to approximate the behavior of atoms in molecules, the vibrations of crystal lattices, and even the quantum states of light in optical cavities.
In addition to quantum mechanics, Hermite polynomials play a crucial role in statistical mechanics and thermodynamics. They are used in the Edgeworth expansion, which refines the central limit theorem by providing higher-order corrections to the normal distribution. This application is particularly valuable in fields requiring precise statistical modeling, such as financial mathematics and climate science.
Hermite's mathematical rigor and innovative approaches draw parallels with the foundational work of ancient Greek mathematicians. The axiomatic methods pioneered by Euclid and the exhaustive techniques of Archimedes find echoes in Hermite's systematic and precise mathematical proofs. This connection highlights the timeless nature of mathematical inquiry and the continuous build-up of knowledge across centuries.
The axiomatic method, a hallmark of Greek mathematics, involves deriving theorems from a small set of initial axioms or postulates. Hermite's work exemplifies this method, particularly in his proofs regarding transcendental numbers. By establishing clear, logical steps and building upon previously proven results, Hermite's approach mirrors the structured reasoning of ancient Greek mathematicians.
This methodological alignment is not merely historical but also practical. The axiomatic approach ensures that mathematical proofs are robust and universally applicable, a principle that remains central to modern mathematical research. Hermite's adherence to this method has contributed to the longevity and relevance of his discoveries.
Archimedes' method of exhaustion, used to calculate the area of a circle and the volume of a sphere, involved approximating these shapes with polygons and polyhedra, respectively. This proto-calculus technique foreshadowed the development of integral calculus and the study of limits. Hermite's work on approximation theory and his use of polynomial approximations can be seen as a sophisticated extension of Archimedes' foundational ideas.
In modern mathematics, Hermite's methods are employed in numerical analysis and computational mathematics, where polynomial approximations are used to solve complex differential equations and model physical phenomena. This connection underscores the continuous evolution of mathematical techniques from ancient times to the present day.
The influence of Charles Hermite is not confined to historical mathematical achievements but extends into current research and educational curricula. His theories and methods are integral to advanced mathematical courses and continue to inspire new generations of mathematicians and scientists.
In recent years, Hermite polynomials have found new applications in the field of machine learning and artificial intelligence. These polynomials are used in Gaussian processes, a type of probabilistic model that is fundamental in Bayesian machine learning. Gaussian processes rely on kernel functions, and Hermite polynomials provide a basis for constructing these kernels, enabling more accurate and efficient modeling of complex data.
Furthermore, Hermite polynomials are utilized in the study of neural tangent kernels, which are essential for understanding the training dynamics of deep neural networks. This application highlights the versatility of Hermite's work and its relevance to cutting-edge technological advancements.
Hermite's contributions are a staple in advanced mathematics education, particularly in courses on analytic number theory, orthogonal polynomials, and quantum mechanics. His proofs and methodologies are taught to illustrate the power of rigorous mathematical reasoning and the beauty of abstract mathematical structures.
In Greece, Hermite's work is often studied in the context of the broader historical development of mathematics, linking ancient Greek contributions with modern European advancements. This educational approach not only honors the legacy of ancient Greek mathematicians but also demonstrates the continuous progression of mathematical thought.
The ongoing relevance of Hermite's work is evident in several contemporary trends and future research directions. As mathematical research continues to evolve, Hermite's foundational contributions provide a solid basis for exploring new frontiers in science and technology.
Recent advancements in transcendental number theory have built upon Hermite's initial discoveries. Modern mathematicians are exploring the transcendence of new classes of numbers and developing more sophisticated techniques for proving transcendence. These efforts are driven by the desire to understand the fundamental nature of numbers and their relationships.
One notable trend is the use of modular forms and algorithmic proofs to establish the transcendence of complex expressions involving e and π. For example, recent research has focused on proving the transcendence of values such as π + e and eπ, building on the foundational work of Hermite and his successors.
The field of quantum computing holds immense promise for revolutionizing computation and solving problems that are currently intractable for classical computers. Hermite polynomials are poised to play a significant role in this emerging field, particularly in the development of quantum algorithms and the simulation of quantum systems.
Quantum computers rely on the principles of quantum mechanics, and the quantum harmonic oscillator, described using Hermite polynomials, is a fundamental model in this context. As quantum computing technology advances, the applications of Hermite's work are expected to expand, contributing to breakthroughs in areas such as cryptography, materials science, and drug discovery.
The interdisciplinary nature of modern scientific research has led to collaborations between mathematicians, physicists, computer scientists, and engineers. Hermite's work serves as a bridge between these disciplines, providing a common mathematical framework that facilitates cross-disciplinary innovation.
For instance, the study of Hermite polynomials in the context of signal processing and data analysis has led to advancements in fields such as telecommunications and medical imaging. These collaborations highlight the versatility and applicability of Hermite's mathematical contributions in solving real-world problems.
Charles Hermite's legacy is a testament to the enduring power of mathematical innovation. His groundbreaking work in transcendental numbers and Hermite polynomials has not only advanced the field of mathematics but also found applications in diverse scientific and technological domains. From quantum mechanics to machine learning, Hermite's contributions continue to inspire and drive progress.
The connection between Hermite's work and the foundational principles of ancient Greek mathematics underscores the timeless nature of mathematical inquiry. By building upon the axiomatic methods of Euclid and the exhaustive techniques of Archimedes, Hermite's achievements exemplify the continuous evolution of mathematical thought.
As we look to the future, the relevance of Hermite's work is set to grow, with new applications emerging in fields such as quantum computing and artificial intelligence. The enduring legacy of Charles Hermite serves as a reminder of the profound impact that mathematical discovery can have on our understanding of the universe and our ability to innovate and solve complex problems.
Charles Hermite's influence extends far beyond the borders of France, shaping mathematical research and education worldwide. His theories have been adopted and expanded upon by mathematicians across the globe, demonstrating the universal applicability of his work. From Europe to Asia, Hermite's contributions continue to inspire new generations of scholars and researchers.
In Europe, Hermite's work has been particularly influential in shaping the development of analytic number theory and complex analysis. His collaborations with German mathematician Karl Weierstrass helped bridge the gap between French and German mathematical traditions, fostering a more unified approach to mathematical research on the continent.
The École Polytechnique and the Sorbonne, where Hermite studied and taught, remain centers of mathematical excellence, continuing to produce groundbreaking research inspired by his methods. European mathematicians have built upon Hermite's foundations to explore new frontiers in algebraic geometry and differential equations.
Across the Atlantic, Hermite's theories have been integrated into the curricula of prestigious North American institutions. Universities such as Harvard, MIT, and Stanford include Hermite polynomials in their advanced mathematics and physics courses. These institutions have also contributed significantly to expanding the applications of Hermite's work in quantum field theory and statistical mechanics.
American mathematicians like Norbert Wiener and John von Neumann drew inspiration from Hermite's rigorous approach to mathematical problems. This influence is evident in the development of functional analysis and ergodic theory, fields that have profound implications for modern physics and engineering.
The connection between Hermite's mathematical contributions and ancient Greek mathematical philosophy offers a fascinating perspective on the evolution of mathematical thought. This relationship highlights how fundamental principles discovered thousands of years ago continue to inform and inspire modern mathematical research.
The axiomatic method, perfected by Euclid in his seminal work Elements, forms the backbone of Hermite's mathematical proofs. This method involves deriving complex theorems from a small set of self-evident axioms, ensuring logical consistency and universal applicability. Hermite's proof of the transcendence of e exemplifies this approach, building upon established mathematical principles to arrive at groundbreaking conclusions.
This methodological continuity underscores the timeless nature of mathematical truth. Just as Euclid's geometric proofs remain valid today, Hermite's algebraic and analytic proofs continue to stand as pillars of mathematical knowledge, demonstrating the enduring power of rigorous logical reasoning.
Archimedes' method of exhaustion, used to calculate areas and volumes with remarkable precision, can be seen as an early form of approximation theory. Hermite's work on polynomial approximations and interpolation extends this ancient technique, providing more sophisticated tools for modern mathematical analysis.
In contemporary mathematics, these approximation methods are essential for numerical analysis and computational mathematics. They enable scientists and engineers to model complex systems, from weather patterns to quantum interactions, with unprecedented accuracy. This evolution from ancient Greek methods to modern mathematical techniques illustrates the continuous progression of mathematical thought.
Beyond the realm of pure mathematics, Hermite's theories have found numerous practical applications in modern technology. These applications demonstrate the real-world impact of abstract mathematical concepts and highlight the importance of fundamental research in driving technological innovation.
One of the most promising areas of application for Hermite polynomials is in the field of quantum computing. Quantum computers leverage the principles of quantum mechanics to perform calculations at speeds unimaginable with classical computers. The quantum harmonic oscillator, described using Hermite polynomials, is a fundamental model in quantum computing.
Researchers are exploring how Hermite polynomials can be used to develop more efficient quantum algorithms and error-correction methods. These advancements could revolutionize fields such as cryptography, materials science, and pharmaceutical research, offering solutions to problems that are currently beyond the reach of classical computation.
In the field of signal processing, Hermite polynomials are used to analyze and manipulate signals in various applications, from telecommunications to medical imaging. These polynomials provide a robust framework for Fourier analysis and wavelet transforms, enabling more accurate and efficient signal processing techniques.
For example, in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), Hermite polynomials help in reconstructing high-resolution images from raw data, improving diagnostic accuracy. Similarly, in wireless communications, these polynomials are used to optimize signal transmission and reduce interference, enhancing the reliability and speed of data transfer.
Preserving and promoting the legacy of Charles Hermite is crucial for inspiring future generations of mathematicians and scientists. Educational initiatives around the world are dedicated to teaching Hermite's theories and methodologies, ensuring that his contributions continue to influence mathematical research and education.
Mathematical competitions, such as the International Mathematical Olympiad (IMO) and the Putnam Competition, often feature problems inspired by Hermite's work. These competitions challenge students to apply Hermite's theories in creative and innovative ways, fostering a deeper understanding of advanced mathematical concepts.
By engaging with Hermite's proofs and methodologies, students develop critical thinking skills and a greater appreciation for the beauty and elegance of mathematical reasoning. These competitions play a vital role in identifying and nurturing young mathematical talent, ensuring the continued advancement of the field.
The digital age has made it easier than ever to access and study Hermite's original works and related research. Online platforms such as arXiv, JSTOR, and Project Euclid provide open access to a vast array of mathematical literature, including papers and books that build upon Hermite's contributions.
Educational institutions and mathematical societies have also created digital archives dedicated to preserving Hermite's legacy. These resources include digitized versions of his original manuscripts, lecture notes, and correspondence, offering invaluable insights into his mathematical thought process and collaborative efforts.
Charles Hermite's contributions to mathematics have left an indelible mark on the field, influencing generations of mathematicians and shaping the course of scientific progress. His groundbreaking work on transcendental numbers and Hermite polynomials has not only advanced theoretical mathematics but also found practical applications in diverse technological domains.
The connection between Hermite's methodologies and the foundational principles of ancient Greek mathematics highlights the timeless nature of mathematical inquiry. By building upon the axiomatic methods of Euclid and the exhaustive techniques of Archimedes, Hermite's achievements exemplify the continuous evolution of mathematical thought and its enduring relevance.
As we look to the future, the applications of Hermite's work are set to expand even further, particularly in emerging fields such as quantum computing and artificial intelligence. These advancements underscore the profound impact that fundamental mathematical research can have on our understanding of the universe and our ability to innovate and solve complex problems.
In conclusion, Charles Hermite's legacy serves as a testament to the power of human ingenuity and the boundless potential of mathematical discovery. His work continues to inspire and challenge mathematicians, scientists, and engineers, driving progress and shaping the future of theoretical and applied sciences. As we celebrate his contributions, we are reminded of the enduring importance of rigorous mathematical reasoning and the timeless pursuit of knowledge.
"Mathematics is the music of reason, and Charles Hermite composed some of its most beautiful symphonies."
Your personal space to curate, organize, and share knowledge with the world.
Discover and contribute to detailed historical accounts and cultural stories. Share your knowledge and engage with enthusiasts worldwide.
Connect with others who share your interests. Create and participate in themed boards about any topic you have in mind.
Contribute your knowledge and insights. Create engaging content and participate in meaningful discussions across multiple languages.
Already have an account? Sign in here

Explore the extraordinary legacy of Charles Hermite in modern mathematics through his pioneering contributions to number...
View Board
Explore the life and legacy of Jacques Hadamard, a pivotal mathematician of the 20th century whose innovations in number...
View Board
Descubre el legado matemático de Émile Picard, visionario del siglo XIX. Explora sus teoremas, métodos y contribuciones ...
View Board
Discover the power of mathematical symbols and the visionaries behind them. Explore history, innovation, and the future ...
View Board
Entdecken Sie das Leben und Werk von Évariste Galois, dem mathematischen Genie, das die moderne Algebra revolutionierte....
View Board
Descubre la vida y legado de Jacques Hadamard, el genio matemático francés que revolucionó el análisis matemático, demos...
View Board
Descubre cómo Henri Lebesgue revolucionó el análisis matemático con su integral, superando límites clásicos y sentando b...
View Board
Discover the life and legacy of Gaston Julia, the brilliant mathematician who pioneered fractals and Julia sets, shaping...
View Board
Discover Euclid, the Father of Geometry, and his timeless work *Elements*. Explore his life, groundbreaking theorems, an...
View Board
"Explore Jacques Hadamard's legacy: Prime Number Theorem proof, functional analysis, and impact on modern tech. Discover...
View Board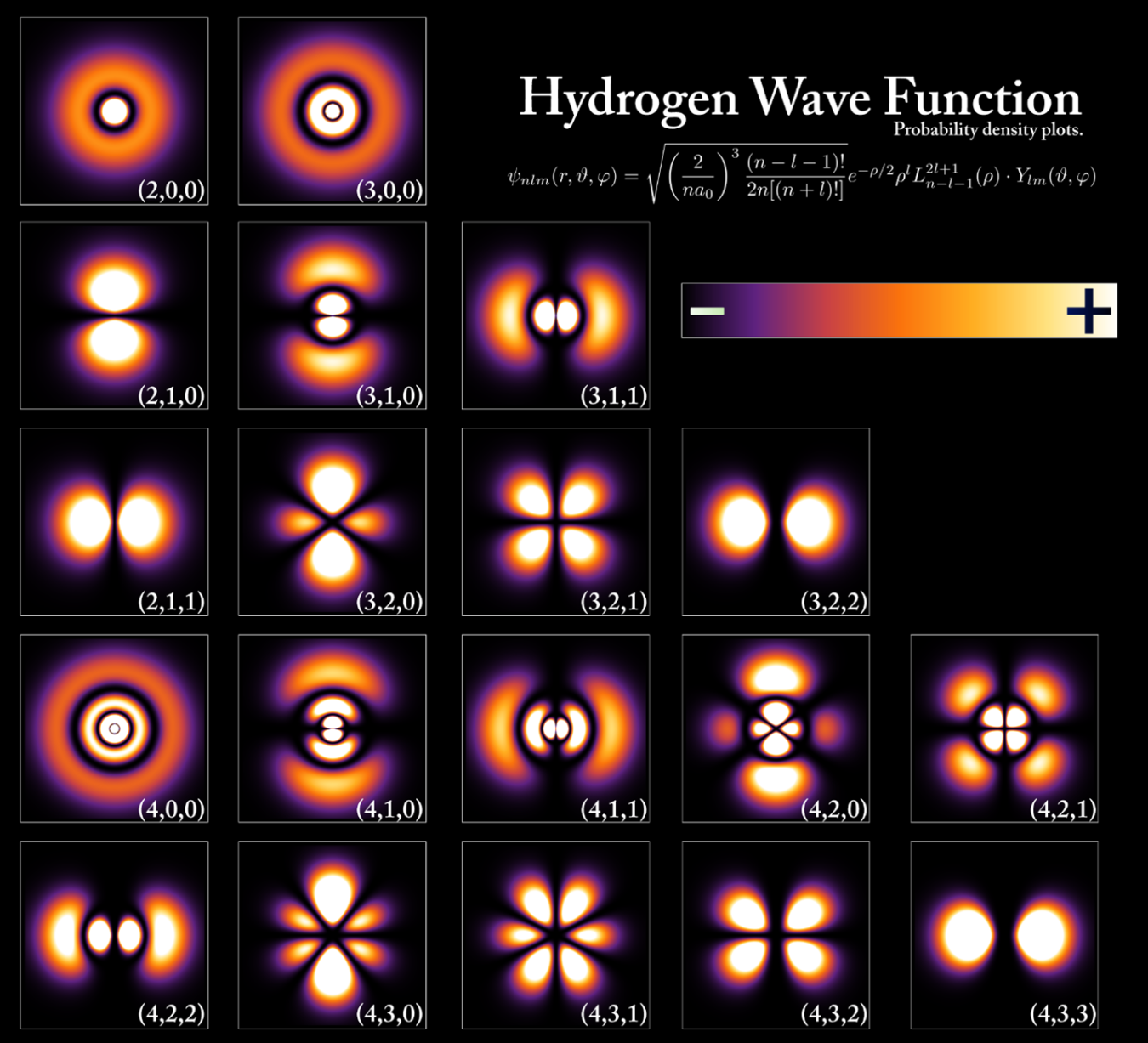
Erwin Schrödinger's groundbreaking work in quantum mechanics, his famous thought experiment Schrödinger's cat, and his c...
View Board
Discover the groundbreaking achievements of Alain Aspect, the quantum physicist who transformed our understanding of rea...
View Board
Max Born was a renowned theoretical physicist and Nobel laureate known for his statistical interpretation of quantum mec...
View Board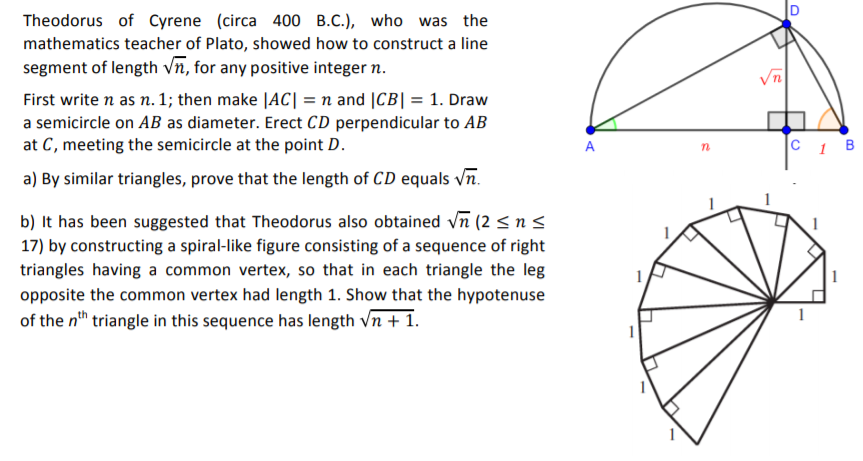
Theodorus of Cyrene, the ancient Greek mathematician and Plato's teacher, revolutionized geometry with his work on irrat...
View Board
Explore the remarkable legacy of Henri Cartan, the pioneering mathematician whose groundbreaking contributions to algebr...
View BoardExplore the transformative potential of quantum computing in our in-depth article, revealing how its advanced processing...
View Board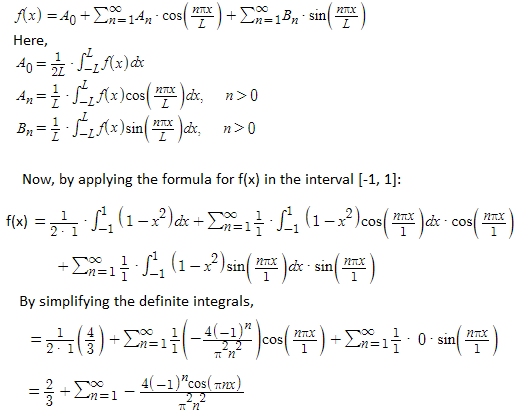
Explore the life and groundbreaking innovations of Jean-Baptiste Joseph Fourier, the French mathematician and physicist ...
View Board
Explore Roger Penrose's groundbreaking contributions to physics, black holes, quantum consciousness, and aperiodic tilin...
View Board
Discover Alan Turing's groundbreaking contributions to computing, AI, and WWII codebreaking. Explore his legacy and endu...
View Board
Discover the rich history, cultural significance, and modern appeal of the name Nils. Explore its origins, meaning, and ...
View Board
Comments