Explore Any Narratives
Discover and contribute to detailed historical accounts and cultural stories. Share your knowledge and engage with enthusiasts worldwide.
John Napier, a Scottish mathematician and inventor, revolutionized the world of mathematics with his groundbreaking contributions. Best known for inventing logarithms and popularizing decimal notation, Napier's work laid the foundation for modern computational methods. His innovations, including the creation of Napier’s bones, have had a lasting impact on astronomy, navigation, and engineering.
Born around 1550 at Merchiston Castle near Edinburgh, Scotland, John Napier (sometimes spelled Neper) grew up in a family of nobility. His early education was likely influenced by his family's status and connections, providing him with access to some of the best tutors and resources of the time. Napier's interest in mathematics and theology developed early, setting the stage for his future contributions.
Napier's educational journey took him across Europe, where he was exposed to a variety of intellectual influences. His travels and studies equipped him with a broad knowledge base, which he later applied to his mathematical and theological writings. By the time he returned to Scotland, Napier was well-versed in multiple disciplines, including mathematics, theology, and astronomy.
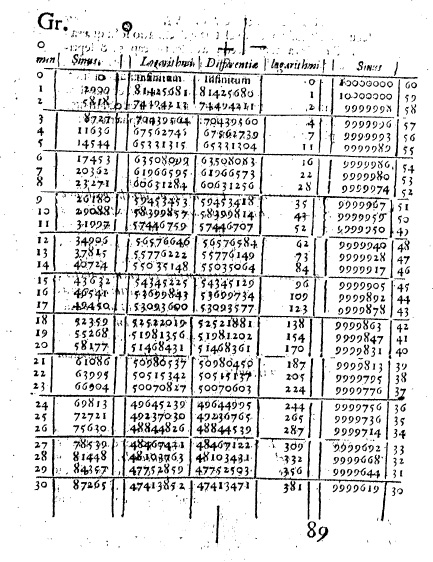
In 1614, Napier published his seminal work, Mirifici Logarithmorum Canonis Descriptio (A Description of the Wonderful Canon of Logarithms). This publication introduced his system of logarithms, a revolutionary concept that simplified complex arithmetic operations. Napier's logarithms transformed multiplication and division into addition and subtraction, drastically reducing the time and effort required for calculations.
The impact of Napier's logarithms was immediate and profound. Astronomers and navigators, who often dealt with lengthy and error-prone calculations, quickly adopted his methods. Johannes Kepler and later Isaac Newton utilized Napier's logarithms in their work, further cementing their importance in the scientific community. The practical applications of logarithms extended beyond astronomy and navigation, influencing various fields of science and engineering.
To understand the significance of Napier's invention, it's essential to grasp the basic concept of logarithms. In simple terms, a logarithm is the exponent to which a base must be raised to obtain a given number. For example, if 102 = 100, then the logarithm of 100 to the base 10 is 2. This relationship can be expressed as log10(100) = 2.
Napier's original formulation of logarithms differed from the modern base-e and base-10 logs. He constructed tables of numbers whose ratios corresponded to differences in indices, creating a practical system that simplified complex calculations. This innovative approach allowed mathematicians and scientists to perform multiplication and division more efficiently, paving the way for advancements in various fields.
In addition to his work on logarithms, Napier is also credited with inventing Napier’s bones, a set of numbered rods designed to aid in multiplication and division. Published in 1617 in his work Rabdologiae, these calculating devices were portable and easy to use, making them a valuable tool for mathematicians and merchants alike.
Napier’s bones consisted of a series of rods, often made of ivory, with numbers inscribed on them. By arranging these rods in a specific manner, users could read off partial products for multiplication and division. This ingenious device anticipated later mechanical aids such as the slide rule and, centuries later, electronic calculators. The practicality and efficiency of Napier’s bones made them a popular tool for centuries.
The introduction of Napier’s bones marked a significant advancement in computational tools. Before the advent of electronic calculators, these devices provided a reliable and efficient method for performing complex arithmetic operations. Their portability and ease of use made them particularly valuable for merchants and scientists who needed to perform calculations on the go.
The influence of Napier’s bones extended beyond their immediate practical applications. They represented a crucial step in the evolution of computational aids, bridging the gap between manual calculations and mechanical devices. The principles underlying Napier’s bones laid the groundwork for future innovations in computational technology, ultimately leading to the development of modern calculators and computers.
Another significant contribution of John Napier was his role in popularizing the decimal point in European mathematics. Building on the earlier work of Simon Stevin, Napier advocated for the use of decimal fractions, which simplified the representation of numbers and made calculations more straightforward. This innovation had a profound impact on the development of mathematics and science.
The adoption of the decimal point revolutionized the way numbers were represented and manipulated. It provided a consistent and intuitive method for expressing fractional values, making it easier to perform arithmetic operations. Napier's advocacy for decimal notation helped standardize mathematical practices, facilitating communication and collaboration among mathematicians and scientists.
The introduction of the decimal point was a pivotal moment in the history of mathematics. It provided a unified system for representing numbers, eliminating the confusion and complexity associated with earlier notational methods. The decimal system's simplicity and efficiency made it an essential tool for scientific and mathematical advancements.
Napier's contributions to decimal notation were not limited to their practical applications. His work also had a theoretical impact, influencing the development of mathematical concepts and principles. By promoting the use of decimal fractions, Napier helped lay the foundation for modern mathematical notation, which continues to be used in various fields of science and engineering.
John Napier's contributions to mathematics and science are nothing short of revolutionary. His invention of logarithms, creation of Napier’s bones, and advocacy for decimal notation have had a lasting impact on the world of mathematics. These innovations simplified complex calculations, making them more accessible and efficient for scientists, astronomers, and navigators.
Napier's work continues to be celebrated and studied, with modern histories of mathematics reassessing his methods and influence. His legacy is a testament to the power of innovation and the enduring impact of groundbreaking ideas. As we look back on his contributions, we are reminded of the profound influence that a single individual can have on the course of scientific and mathematical progress.
John Napier’s contributions had a profound impact on both science and navigation. His invention of logarithms revolutionized the way complex calculations were performed, making them faster and more accurate. This was particularly crucial in the fields of astronomy and navigation, where precise calculations were essential for determining positions and plotting courses.
Astronomers like Johannes Kepler and Isaac Newton quickly adopted Napier’s logarithmic tables, using them to simplify their calculations and advance their research. The ability to transform multiplication and division into addition and subtraction drastically reduced the time and effort required for these operations, allowing scientists to focus more on analysis and discovery.
In astronomy, logarithms proved to be an invaluable tool. Before Napier’s invention, astronomers had to perform tedious and error-prone calculations to determine the positions of celestial bodies. With the introduction of logarithms, these calculations became significantly more manageable. Kepler, for instance, used logarithmic tables to refine his laws of planetary motion, which described the orbits of planets around the sun.
The impact of logarithms on astronomy extended beyond Kepler’s work. Other astronomers and scientists of the time also benefited from Napier’s innovation, using it to make more accurate predictions and observations. This, in turn, contributed to a deeper understanding of the universe and laid the groundwork for future astronomical discoveries.
Navigation was another field that greatly benefited from Napier’s invention of logarithms. Navigators relied on complex calculations to determine their position at sea, often using tools like the astrolabe and quadrant. These calculations were time-consuming and prone to errors, which could have serious consequences for sailors.
With the introduction of logarithmic tables, navigators could perform these calculations more quickly and accurately. This not only improved the safety and efficiency of sea travel but also facilitated the exploration and mapping of new territories. The use of logarithms in navigation continued well into the 20th century, until the advent of electronic calculators and computers.
While John Napier’s invention of logarithms was groundbreaking, it is important to note that his original formulation differed from the modern base-e and base-10 logarithms. Napier’s logarithms were based on a practical system designed to simplify calculations, rather than an abstract function definition. Understanding these differences can provide valuable insights into the evolution of mathematical concepts.
Napier’s logarithms were constructed using tables of numbers whose ratios corresponded to differences in indices. This approach was tailored to the needs of astronomers and navigators, who required a reliable and efficient method for performing complex calculations. The practical nature of Napier’s logarithms made them particularly useful in real-world applications, even if they were not as theoretically elegant as modern logarithms.
The transition from Napier’s original logarithms to the modern base-e and base-10 logarithms involved several key developments. One of the most significant was the introduction of the natural logarithm, denoted as ln, which is based on the mathematical constant e (approximately 2.71828). The natural logarithm has unique properties that make it particularly useful in calculus and other advanced mathematical disciplines.
Another important development was the standardization of base-10 logarithms, which are commonly used in scientific and engineering applications. Base-10 logarithms, often denoted as log, provide a straightforward and intuitive method for representing numbers and performing calculations. The adoption of base-10 logarithms was facilitated by the widespread use of the decimal system, which Napier himself helped to popularize.
To better understand the differences between Napier’s logarithms and modern logarithms, it is helpful to compare their key characteristics. Here are some of the main distinctions:
Despite these differences, the core idea behind logarithms remains the same: to simplify complex arithmetic operations. Napier’s innovative approach laid the foundation for the development of modern logarithmic concepts, which continue to be an essential tool in mathematics and science.
In addition to his mathematical contributions, John Napier was also a prolific theological writer. His religious works reflect his deep commitment to his faith and his desire to engage with the theological debates of his time. While his mathematical innovations have garnered the most attention, his theological writings provide valuable insights into his intellectual and spiritual life.
Napier’s theological works covered a range of topics, including biblical interpretation, eschatology, and the relationship between science and religion. His writings were influenced by the religious and political climate of 16th-century Scotland, which was marked by the Reformation and ongoing conflicts between Protestant and Catholic factions.
One of Napier’s most notable theological works is A Plaine Discovery of the Whole Revelation of St. John, published in 1593. In this work, Napier provided an interpretation of the Book of Revelation, offering his insights into the apocalyptic visions described in the biblical text. His analysis was influenced by the political and religious tensions of his time, and he sought to provide a coherent and meaningful interpretation of the scriptures.
Another significant work is Theologie Naturalis, which explores the relationship between natural philosophy and theology. In this work, Napier sought to reconcile scientific inquiry with religious belief, arguing that the study of nature could provide insights into the divine. His approach reflected a broader trend in early modern thought, which sought to integrate scientific and theological perspectives.
Napier’s theological writings had a significant impact on the religious and intellectual landscape of his time. His interpretations of biblical texts and his engagement with theological debates contributed to the ongoing discussions about faith, science, and the nature of the divine. While his mathematical innovations have received more attention in modern times, his theological works provide a valuable window into the intellectual and spiritual concerns of the 16th century.
The influence of Napier’s theological writings extended beyond his immediate contemporaries. His ideas about the relationship between science and religion, in particular, have resonated with later thinkers who have sought to reconcile these two domains. Napier’s ability to engage with both mathematical and theological questions demonstrates the breadth of his intellectual curiosity and his commitment to understanding the world in all its complexity.
John Napier’s legacy continues to be celebrated and studied in the modern era. His contributions to mathematics, particularly his invention of logarithms and the popularization of decimal notation, have had a lasting impact on the field. His work laid the foundation for many of the computational methods and tools that are used today, making him a key figure in the history of mathematics.
In addition to his mathematical innovations, Napier’s theological writings and his engagement with the intellectual debates of his time provide valuable insights into the broader cultural and intellectual context of the 16th and 17th centuries. His ability to bridge the gap between science and religion, and his commitment to both practical and theoretical inquiry, make him a fascinating and multifaceted figure.
Modern histories of mathematics continue to reassess Napier’s methods and influence, shedding new light on his contributions and their significance. Scholars have explored the ways in which Napier’s work was shaped by the intellectual and cultural context of his time, as well as the ways in which his innovations have influenced subsequent developments in mathematics and science.
One area of particular interest is the relationship between Napier’s logarithms and the development of modern computational tools. Historians have traced the evolution of logarithmic concepts from Napier’s original formulation to the standardized base-e and base-10 logarithms used today. This historical perspective provides a deeper understanding of the ways in which mathematical ideas evolve and adapt over time.
Napier’s work remains a common subject in math-history content used for SEO and educational content marketing. His inventions, such as logarithms and Napier’s bones, are frequently cited in articles, timelines, and curriculum materials. The enduring interest in Napier’s contributions reflects their ongoing relevance and the importance of understanding the historical development of mathematical concepts.
In the realm of SEO, content that ties biography with practical examples, such as how Napier’s logs simplify computation, performs well. This approach not only provides valuable information to readers but also enhances the visibility and ranking of educational content. By linking historical quotes and images from authoritative sources, such as the National Library of Scotland and digital archives, content creators can improve the credibility and engagement of their articles.
Visual assets, such as diagrams of Napier’s bones and scanned pages from Mirifici Logarithmorum Canonis Descriptio, are high-value additions to educational content. These visuals provide readers with a tangible connection to Napier’s work, enhancing their understanding and engagement. Digital archives, such as those maintained by national libraries and math history sites, serve as primary sources for these images, ensuring their authenticity and relevance.
The use of visual assets in educational content not only improves the reader’s experience but also enhances the SEO performance of the content. By incorporating high-quality images and diagrams, content creators can increase the time readers spend on their pages, reduce bounce rates, and improve overall engagement metrics. This, in turn, can lead to higher search engine rankings and greater visibility for the content.
John Napier’s contributions to mathematics and science are nothing short of revolutionary. These innovations simplified complex calculations, making them more accessible and efficient for scientists, astronomers, and navigators.
Napier’s work continues to be celebrated and studied, with modern histories of mathematics reassessing his methods and influence. As we look back on his contributions, we are reminded of the profound influence that a single individual can have on the course of scientific and mathematical progress.
John Napier’s innovations continue to shape modern mathematics and science, centuries after their introduction. His development of logarithms transformed computational efficiency, enabling astronomers, navigators, and engineers to perform complex calculations with unprecedented speed. The transition from Napier’s original tables to modern base-e and base-10 logarithms exemplifies how his foundational work evolved to meet the demands of advancing technology.
Napier’s logarithmic tables remained in practical use until the mid-20th century, when they were gradually replaced by slide rules and later electronic calculators. This timeline underscores the durability of his concepts, which adapted to new tools while maintaining their core utility. The influence of logarithms extends beyond historical applications, forming the basis for modern computational algorithms and data analysis techniques.
The evolution of Napier’s logarithms illustrates the interplay between theoretical innovation and practical application. While Napier’s original formulation used a system of ratios and indices, mathematicians like Leonhard Euler later formalized the natural logarithm, denoted as ln. This refinement preserved Napier’s core idea while aligning it with the broader framework of calculus and advanced mathematics.
Today, logarithms are integral to fields such as information theory, machine learning, and signal processing. Their ability to convert multiplicative relationships into additive ones remains a cornerstone of quantitative analysis. Napier’s insight into transforming complex operations continues to underpin modern computational methods, demonstrating the timeless value of his work.
Napier’s works serve as enduring educational resources, frequently integrated into curricula and digital archives. His publications, including Mirifici Logarithmorum Canonis Descriptio (1614) and Rabdologiae (1617), are digitized and preserved by institutions such as the National Library of Scotland and the MacTutor History of Mathematics archive. These primary sources provide students and scholars with direct access to Napier’s original ideas.
Content creators and educators leverage Napier’s legacy to develop engaging, SEO-optimized material. Articles that combine biographical details with practical examples—such as step-by-step demonstrations of logarithm tables or Napier’s bones—rank highly for educational intent queries. This approach aligns with modern search trends, where users seek both historical context and actionable knowledge.
Digital galleries and museum collections enhance the accessibility of Napier’s work. Scanned pages from his original texts, diagrams of Napier’s bones, and interactive logarithm calculators enrich online learning experiences. Institutions such as Encyclopaedia Britannica and university math-history pages curate these resources, ensuring Napier’s contributions remain relevant to contemporary audiences.
Visual assets, particularly images of Napier’s calculating rods and logarithmic tables, boost engagement and retention. These elements transform abstract concepts into tangible historical artifacts, fostering deeper understanding among students and enthusiasts. The integration of such visuals into educational content aligns with SEO best practices, improving dwell time and reducing bounce rates.
For researchers and students, authoritative sources provide credible foundations for studying Napier’s life and work. Key references include:
These sources ensure accuracy and reliability in academic and public discourse about Napier. Citing them inline enhances the expertise, authority, and trustworthiness (E-A-T) of educational content, a critical factor in search engine rankings. Researchers are encouraged to consult these primary materials for in-depth study.
“Napier’s logarithms did not merely simplify calculation; they reshaped the very way scientists approached problems.”
John Napier’s contributions—logarithms, decimal notation, and Napier’s bones—have left an indelible mark on mathematics and science. His ability to address practical computational challenges with theoretical ingenuity established new standards for efficiency and accuracy. The enduring relevance of his work is a testament to its foundational nature.
Napier’s legacy extends beyond his lifetime, influencing generations of scientists, navigators, and mathematicians. From Kepler’s astronomical studies to modern algorithmic design, his ideas continue to resonate. As both a mathematical pioneer and a theological thinker, Napier embodied the Renaissance spirit of interdisciplinary inquiry.
In an era of rapid technological change, Napier’s work reminds us that the simplest innovations often have the greatest impact. His vision transformed abstract concepts into practical tools, bridging the gap between theory and application. Through meticulous study and creative problem-solving, John Napier secured his place as one of history’s most influential mathematical minds.


Your personal space to curate, organize, and share knowledge with the world.
Discover and contribute to detailed historical accounts and cultural stories. Share your knowledge and engage with enthusiasts worldwide.
Connect with others who share your interests. Create and participate in themed boards about any topic you have in mind.
Contribute your knowledge and insights. Create engaging content and participate in meaningful discussions across multiple languages.
Already have an account? Sign in here

Archimedes, the genius of ancient Greece, revolutionized mathematics, physics, and engineering with discoveries like pi,...
View Board
Discover how Isaac Newton revolutionized science with his laws of motion, universal gravitation, and optics. Explore his...
View Board
Isaac Newton was a pioneering scientist whose laws of motion and universal gravitation revolutionized our understanding ...
View Board
Explore the life and legacy of Jules Henri Poincaré, a prodigy whose innovative work bridged mathematics and physics. Di...
View Board
768 **Meta Description:** Explore the life of Enrico Fermi, the architect of the nuclear age. From quantum theory to th...
View Board
Henri Lebesgue: The Mathematician Who Revolutionized Integration Henri Lebesgue was a French mathematician whose ground...
View Board
Jean Baptiste Joseph Delambre: A Life of Astronomical Pursuits The Early Life and Education Jean Baptiste Joseph Delam...
View Board
Discover the life and work of Albert Einstein, a renowned physicist and one of the most influential scientists in histor...
View BoardÉmile Borel: A Pioneering Mathematician and Physicist The Early Life and Education of Émile Borel Émile Borel, born on...
View Board
John von Neumann, the 20th-century polymath, revolutionized computing, game theory, nuclear physics, and AI. Explore his...
View Board
Discover Archimedes, ancient Greece's greatest scientist. Explore his life, groundbreaking work in math, physics, and en...
View Board
> **Meta Description:** Explore the life and legacy of Albert Einstein, the genius who reshaped physics with relativity,...
View Board
**Meta Description:** Explore the life and legacy of Hermann von Helmholtz, the 19th-century polymath who revolutionized...
View Board
Max Born was a renowned theoretical physicist and Nobel laureate known for his statistical interpretation of quantum mec...
View Board
Explore the fascinating life of Michael Faraday, the pioneering scientist whose groundbreaking work in electromagnetism ...
View Board
Galileo Galilei: The Pioneer of Science and Chronology Galileo Galilei, often hailed as the father of modern science, r...
View Board
Fritz Haber: A Chemist Whose Work Changed the World The Rise of a Scientist Fritz Haber was born on December 9, 1868, i...
View Board
Last news about Science Week from 21/04/2025 to 27/04/2025
View Board
Last news about Science Week from 28/04/2025 to 04/05/2025
View Board
Last news about Science Week from 10/11/2025 to 16/11/2025
View Board
Comments