Explore Any Narratives
Discover and contribute to detailed historical accounts and cultural stories. Share your knowledge and engage with enthusiasts worldwide.
In the realm of fluid dynamics and hydrodynamics, few names resonate as profoundly as Joseph Boussinesq. A French mathematician and physicist, Boussinesq's groundbreaking work in the late 19th century laid the foundation for modern understanding of fluid behavior, wave propagation, and buoyancy-driven flows. His Boussinesq approximation, developed between 1871 and 1872, remains a cornerstone in modeling natural convection, ocean waves, and atmospheric flows. This article delves into the life, contributions, and enduring legacy of this pioneering scientist, whose theories continue to shape contemporary research and engineering.
Born as Joseph Valentin Boussinesq in Saint-Hilaire, France, in 1821, Boussinesq exhibited an early aptitude for mathematics and physics. His academic journey was marked by a relentless pursuit of knowledge, leading him to become a professor at the University of Lille and later at the prestigious Sorbonne. Despite being largely self-taught, Boussinesq's interdisciplinary approach allowed him to make significant contributions not only to fluid dynamics but also to fields such as elasticity, heat conduction, and seismology.
Boussinesq's work was characterized by a unique blend of theoretical rigor and practical application. His ability to bridge complex mathematical theories with real-world phenomena set him apart as a fundamental scientist. This polymathic approach enabled him to tackle diverse challenges, from understanding wave propagation in water to extending Darcy's law for flow through porous media.
At the heart of Boussinesq's contributions lies the Boussinesq approximation, a seminal simplification in fluid mechanics. This approximation is pivotal in modeling scenarios where density variations are small yet significant, such as in natural convection, ocean waves, and atmospheric flows. By assuming that density differences are negligible except where they contribute to buoyancy forces, Boussinesq's model allows for more manageable and insightful analyses of complex fluid systems.
The Boussinesq approximation has found widespread applications in contemporary research. For instance, it is integral to computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations, enabling engineers and scientists to model and predict fluid behavior with greater accuracy. Recent studies, such as those conducted in 2023, have leveraged improved Boussinesq-type equations for tsunami modeling, enhancing our ability to understand and mitigate the impacts of these devastating natural phenomena.
Boussinesq's contributions to hydrodynamics extend beyond the Boussinesq approximation. His theories on wave propagation in water have been instrumental in advancing our understanding of solitary waves, now known as Boussinesq equations. These equations describe the behavior of waves in shallow water, providing critical insights for coastal engineering and hydraulics.
In addition to his work on wave propagation, Boussinesq made significant advancements in the study of flow through porous media. His extensions to Darcy's law have been foundational in understanding groundwater seepage and have laid the groundwork for modern techniques in aquifer management and carbon capture storage. These contributions underscore Boussinesq's role as a pioneer in both theoretical and applied hydrodynamics.
The enduring impact of Boussinesq's work is evident in the numerous concepts and theories named in his honor. The Boussinesq coefficient in hydraulics and the Boussinesq problem in soil mechanics are testaments to his lasting influence. His theories have bridged the gap between 19th-century mathematical rigor and 20th-century engineering advancements, making him a fundamental scientist whose contributions continue to inspire and guide researchers today.
In academic and cultural contexts, Boussinesq's name is often celebrated with descriptive titles that reflect his pioneering spirit. For example, the Greek phrase "Ζοζέφ-Μπουσίνεςκ-Ένας-Πρωτόπορος-της-Υδροδυναμικής-και-Θεμελιώδης-Επιστήμονας" translates to "Joseph-Boussinesq – A Pioneer of Hydrodynamics and Fundamental Scientist." This stylistic homage, reminiscent of ancient Greek compound names, underscores the high regard in which Boussinesq is held within the scientific community.
As we move further into the 21st century, Boussinesq's theories continue to find new applications and interpretations. Recent trends include the use of hybrid Boussinesq-Navier-Stokes solvers for modeling non-hydrostatic waves in offshore wind farms. Additionally, advancements in machine learning have led to enhanced approximations for climate flows, further extending the reach of Boussinesq's foundational work.
One of the most promising areas of application for Boussinesq's theories is in the field of renewable energy. His models are being used to optimize the design and efficiency of wave energy converters, which harness the power of ocean waves to generate electricity. Furthermore, his work on porous media flow is informing strategies for carbon capture and storage, a critical component in the fight against climate change.
Joseph Boussinesq's contributions to fluid dynamics and hydrodynamics have left an indelible mark on the scientific community. From the Boussinesq approximation to his pioneering work on wave propagation and porous media flow, his theories continue to shape our understanding of fluid behavior and inspire innovative solutions to modern challenges. As we look to the future, the legacy of this fundamental scientist will undoubtedly continue to guide and inspire generations of researchers and engineers.
The advent of computational fluid dynamics (CFD) has revolutionized the way scientists and engineers approach fluid flow problems. At the core of many CFD models lies the Boussinesq approximation, which simplifies the complex Navier-Stokes equations by assuming constant density except in buoyancy terms. This approximation has become indispensable in simulating natural convection, ocean currents, and atmospheric circulation, making it a cornerstone of modern fluid dynamics research.
Recent studies have highlighted the critical role of Boussinesq-type equations in tsunami modeling. In 2023, researchers developed enhanced Boussinesq equations that account for nonlinear and dispersive effects, significantly improving the accuracy of tsunami propagation forecasts. These advancements have been instrumental in coastal hazard assessment and the design of early warning systems. Key improvements include:
The Boussinesq approximation is also pivotal in climate modeling, where it helps simulate large-scale atmospheric flows and ocean circulation patterns. A 2024 study demonstrated how machine learning-enhanced Boussinesq models could improve the prediction of El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) events. These models leverage historical climate data to refine the approximation, leading to more accurate forecasts of temperature anomalies and precipitation patterns.
As the world shifts toward sustainable energy solutions, Boussinesq's theories are finding new applications in renewable energy technologies. His work on wave propagation and fluid dynamics is particularly relevant to the development of wave energy converters (WECs), which harness the kinetic and potential energy of ocean waves to generate electricity. The efficiency and reliability of these systems depend heavily on accurate modeling of wave behavior, an area where Boussinesq's equations excel.
In the field of wave energy conversion, Boussinesq-type equations are used to optimize the design of WECs and assess their performance under varying wave conditions. Recent advancements include:
These innovations are not only improving the viability of wave energy as a renewable resource but also contributing to broader coastal engineering efforts, such as shoreline protection and erosion control.
Boussinesq's theories are also being applied to the design and optimization of offshore wind farms. The interaction between wind turbines and ocean waves presents complex fluid-structure interaction challenges that require sophisticated modeling techniques. Boussinesq-type equations, combined with finite element methods, are used to simulate the dynamic response of wind turbine foundations to wave loading. This research is critical for ensuring the structural integrity and longevity of offshore wind infrastructure.
Beyond his work in fluid dynamics, Boussinesq made significant contributions to the study of flow through porous media. His extensions to Darcy's law have been foundational in understanding groundwater seepage and have laid the groundwork for modern techniques in aquifer management and contaminant transport modeling. These contributions have had a lasting impact on the fields of hydrology and environmental engineering.
Boussinesq's theories on porous media flow have been instrumental in developing models for groundwater seepage and aquifer behavior. His work has enabled hydrologists to:
These applications are critical for ensuring the sustainable management of water resources, particularly in regions facing water scarcity and pollution challenges.
In recent years, Boussinesq's theories have found new relevance in the development of carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies. CCS involves the injection of carbon dioxide (CO₂) into deep geological formations, where it is stored to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions. Boussinesq's extensions to Darcy's law are used to model the flow of CO₂ through porous rock formations, helping engineers optimize injection strategies and assess the long-term stability of storage sites. Key advancements in this area include:
The Boussinesq problem, named in honor of Joseph Boussinesq, is a fundamental concept in soil mechanics and geotechnical engineering. This problem involves the calculation of stresses and displacements in an elastic half-space due to a point load applied at the surface. The solution to the Boussinesq problem has been widely used in the design of foundations, pavements, and other structures that transmit loads to the underlying soil.
The Boussinesq problem has numerous applications in geotechnical engineering, including:
By providing a theoretical framework for understanding the distribution of stresses in soil, the Boussinesq problem has enabled engineers to develop safer and more efficient foundation systems.
While the original Boussinesq problem assumes an elastic, homogeneous, and isotropic half-space, modern extensions have incorporated more complex soil behaviors, such as:
These advancements have expanded the applicability of the Boussinesq problem to a wider range of geotechnical challenges, from offshore foundation design to seismic soil-structure interaction.
Joseph Boussinesq's contributions to science and engineering have not gone unnoticed in the academic community. His theories are taught in universities worldwide as part of fluid mechanics, hydrodynamics, and geotechnical engineering curricula. The Boussinesq approximation, in particular, is a staple in courses on computational fluid dynamics and environmental fluid mechanics.
In recognition of his groundbreaking work, several key concepts and theories bear Boussinesq's name, including:
These named concepts serve as a testament to Boussinesq's enduring influence and the widespread adoption of his theories across multiple disciplines.
Boussinesq's work continues to inspire modern researchers, who build upon his theories to tackle contemporary challenges. For example, his theories on buoyancy-driven flows have been extended to study thermal convection in planetary interiors, while his work on porous media flow informs research on biological tissue mechanics and fuel cell technology. The interdisciplinary nature of Boussinesq's contributions ensures that his legacy will endure for generations to come.
The impact of Joseph Boussinesq on modern science and engineering cannot be overstated. His foundational theories continue to shape research across multiple disciplines, from fluid dynamics to geotechnical engineering. As we explore the final sections of this article, we will examine the broader implications of his work, its influence on contemporary research, and the future directions inspired by his pioneering contributions.
Boussinesq's theories have transcended their original domains, finding applications in fields as diverse as biomedical engineering, environmental science, and renewable energy. For instance, his work on porous media flow has been adapted to model fluid transport in biological tissues, aiding in the development of drug delivery systems and tissue engineering techniques. Similarly, his theories on wave propagation are being used to optimize offshore renewable energy systems, including both wave and wind energy technologies.
In environmental science, Boussinesq's contributions are instrumental in modeling pollutant transport in groundwater and surface water systems. His extensions to Darcy's law enable researchers to simulate the movement of contaminants through soil and aquifers, which is critical for environmental remediation and water resource management. Recent studies have leveraged these models to:
As technology advances, so too does the application of Boussinesq's theories. Emerging trends in computational modeling, machine learning, and experimental techniques are opening new avenues for exploring and extending his work. This section highlights some of the most promising developments on the horizon.
The integration of machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) with traditional fluid dynamics models is revolutionizing the field. Researchers are now using ML algorithms to enhance the Boussinesq approximation, improving its accuracy and computational efficiency. Key innovations include:
These advancements are not only accelerating research but also enabling the development of more sustainable and efficient engineering solutions.
The advent of quantum computing presents another exciting frontier for Boussinesq's theories. Quantum algorithms have the potential to solve complex fluid dynamics problems that are currently intractable with classical computers. For example, quantum simulations could provide deeper insights into turbulent flows and multi-phase fluid interactions, areas where Boussinesq's theories play a crucial role. While still in its infancy, this field holds immense promise for future breakthroughs.
Despite their widespread use and adaptability, Boussinesq's theories are not without challenges. Understanding these limitations is essential for researchers and engineers seeking to apply his work effectively. This section explores some of the key challenges and ongoing efforts to address them.
The Boussinesq approximation, while powerful, relies on several simplifying assumptions that may not hold in all scenarios. For instance, the assumption of small density variations can break down in highly stratified fluids or extreme thermal gradients. Researchers are actively working to:
Another challenge lies in the computational complexity of applying Boussinesq's theories to large-scale or highly detailed models. Simulating complex fluid-structure interactions, for example, can require substantial computational resources. To mitigate these challenges, researchers are exploring:
For students and professionals alike, a wealth of educational resources is available to deepen their understanding of Boussinesq's theories and their applications. This section highlights some of the most valuable learning opportunities, from academic courses to online platforms.
Many leading universities offer courses and programs that cover Boussinesq's contributions as part of their fluid mechanics, hydrodynamics, and geotechnical engineering curricula. Notable examples include:
These programs provide students with both theoretical knowledge and practical skills, preparing them to apply Boussinesq's theories in real-world scenarios.
In addition to traditional academic programs, numerous online platforms offer courses and tutorials on Boussinesq's theories and their applications. Platforms such as:
These resources make it easier than ever for professionals to stay updated on the latest advancements and refine their expertise.
To illustrate the practical impact of Boussinesq's work, this section presents a series of case studies highlighting real-world applications of his theories. These examples demonstrate the versatility and relevance of his contributions in addressing contemporary challenges.
One of the most critical applications of Boussinesq's theories is in tsunami modeling. Following the devastating 2011 Tōhoku tsunami, researchers developed advanced Boussinesq-type models to improve the accuracy of tsunami forecasts. These models were instrumental in:
This case study underscores the life-saving potential of Boussinesq's theories in disaster preparedness and response.
In the realm of renewable energy, Boussinesq's theories have been applied to optimize the design and operation of offshore wind farms. A notable example is the Hornsea Project in the UK, one of the world's largest offshore wind farms. Engineers used Boussinesq-type models to:
This application demonstrates how Boussinesq's work is driving innovation in sustainable energy solutions.
Joseph Boussinesq's contributions to fluid dynamics, hydrodynamics, and geotechnical engineering have left an indelible mark on the scientific community. His theories, from the Boussinesq approximation to his extensions of Darcy's law, continue to underpin cutting-edge research and engineering solutions. As we have explored throughout this article, his work has found applications in diverse fields, from tsunami modeling to renewable energy optimization, demonstrating its enduring relevance and adaptability.
To summarize the key points discussed:
As we look to the future, the legacy of Joseph Boussinesq serves as a reminder of the power of interdisciplinary research and theoretical innovation. His ability to bridge complex mathematical concepts with practical engineering solutions has inspired generations of scientists and engineers. By continuing to build upon his foundational work, we can address some of the most pressing challenges of our time, from climate change to sustainable energy. In the words of Boussinesq himself, "The pursuit of knowledge is a journey without end, and each discovery opens new horizons for exploration."
In conclusion, Joseph Boussinesq's pioneering spirit and groundbreaking contributions have cemented his place as one of the most influential scientists in the history of fluid dynamics. His theories will undoubtedly continue to shape the future of science and engineering, driving innovation and inspiring new generations of researchers to push the boundaries of what is possible.
Your personal space to curate, organize, and share knowledge with the world.
Discover and contribute to detailed historical accounts and cultural stories. Share your knowledge and engage with enthusiasts worldwide.
Connect with others who share your interests. Create and participate in themed boards about any topic you have in mind.
Contribute your knowledge and insights. Create engaging content and participate in meaningful discussions across multiple languages.
Already have an account? Sign in here

James Clerk Maxwell unified electricity and magnetism into a single mathematical framework, his work laying the foundati...
View Board
Max Born was a renowned theoretical physicist and Nobel laureate known for his statistical interpretation of quantum mec...
View Board
Isaac Newton was a pioneering scientist whose laws of motion and universal gravitation revolutionized our understanding ...
View Board
Discover the enduring legacy of Léon Brillouin, a 20th-century visionary physicist who bridged theoretical and applied s...
View Board
Discover the groundbreaking legacy of Louis de Broglie, the pioneering scientist behind wave-particle duality. This insi...
View Board
Explore the incredible legacy of Arthur Eddington, a pioneering figure in astrophysics and cosmology, who brilliantly br...
View Board
Louis Néel Nobel laureate revolutionized magnetism research with discovery of antiferromagnetism advancing condensed mat...
View Board
MIT researchers transform ordinary concrete into structural supercapacitors, storing 10x more energy in foundations, tur...
View Board
George Gamow: The Unbelievable Journey of a Theoretical Physicist and Cosmologist The Enigmatic Man Behind the Cosmic B...
View Board
Otto Hahn's groundbreaking contributions to radiochemistry and nuclear physics left a lasting legacy in science, from hi...
View BoardÉmile Borel: A Pioneering Mathematician and Physicist The Early Life and Education of Émile Borel Émile Borel, born on...
View Board
Jean Baptiste Joseph Delambre: A Life of Astronomical Pursuits The Early Life and Education Jean Baptiste Joseph Delam...
View Board
Explore the life and enduring legacy of Julio Palacios, a pioneering physicist from the 20th century whose groundbreakin...
View Board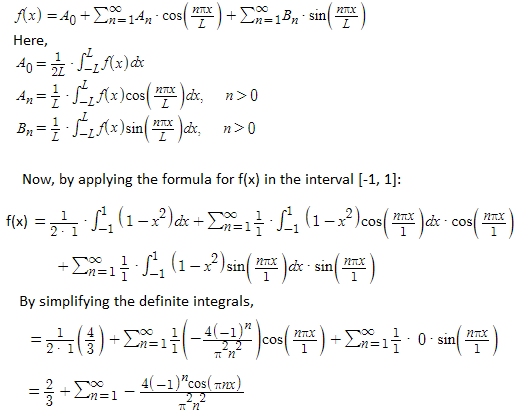
Explore the life and groundbreaking innovations of Jean-Baptiste Joseph Fourier, the French mathematician and physicist ...
View Board
Pioneering innovator Charles Hard Townes revolutionised science with his groundbreaking work on the maser and laser, ear...
View Board
Explore the remarkable legacy of Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar, the astrophysics luminary who revolutionized our understand...
View Board
Discover the groundbreaking achievements of Alain Aspect, the quantum physicist who transformed our understanding of rea...
View Board
Archimedes, the genius of ancient Greece, revolutionized mathematics, physics, and engineering with discoveries like pi,...
View Board
Explore the life and legacy of Jules Henri Poincaré, a prodigy whose innovative work bridged mathematics and physics. Di...
View Board
Discover how André-Marie Ampère, the father of electromagnetism, revolutionized science with Ampère's Law and shaped mod...
View Board
Comments