Explore Any Narratives
Discover and contribute to detailed historical accounts and cultural stories. Share your knowledge and engage with enthusiasts worldwide.
The Feltz-Fontana Prize stands as a beacon of recognition in the scientific community, honoring groundbreaking contributions to neurophysiology and microbiome research. This prestigious award highlights the intricate relationship between the gut and the brain, a field that has gained significant traction in recent years. By focusing on the gut-brain axis, the prize underscores the importance of understanding how our microbiome influences neurological health and cognitive function.
The gut-brain axis is a bidirectional communication network that connects the central nervous system (CNS) with the enteric nervous system (ENS) of the gut. This axis plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis and influencing various physiological processes. Research has shown that the gut microbiome, composed of trillions of symbiotic bacteria, can significantly impact brain function and behavior.
The human microbiome begins to form at birth and is influenced by various environmental factors. Studies have revealed that even monozygotic twins, who share identical genetic material, exhibit minimal similarity in their microbiomes. This finding emphasizes the dominant role of environmental factors over genetic predisposition in shaping the microbiome.
To comprehend the gut-brain axis, it is essential to understand the basics of neurophysiology. Neurons, the fundamental units of the brain and nervous system, communicate through electrical signals known as action potentials. These signals are generated by the movement of ions, such as sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+), across the neuron membrane. The resting membrane potential of a neuron is typically around -70 mV, and during an action potential, it can reach up to 0 mV.
Recent advancements in microbiome research have shed light on the complex interactions between the gut microbiome and the brain. A 2023 thesis supervised by Chrysanthi Voyiatzaki detailed the formation of the microbiome at birth and the use of 16S rRNA gene analysis to reveal phylogenetic diversity. This research also explored interventions such as fecal transplantation, which has shown promise in restoring microbiome balance.
Another significant area of research is the link between the human microbiome and cognitive function. Studies have demonstrated that the microbiota can influence neurological health, with implications for various neuropsychiatric disorders. The gut microbiome's role in shaping psychology and the central nervous system is a growing field of interest, with potential applications in disease prevention and treatment.
The Feltz-Fontana Prize is likely tied to broader neuroscience education initiatives, such as the IBRO-translated booklets on brain science for youth. These resources, originally published in 2004 and translated into Greek post-2005, aim to foster a deeper understanding of neurophysiology and its intersections with microbiome research. The interdisciplinary nature of this research aligns with global trends in gut-brain axis studies.
To appreciate the scale and complexity of the gut microbiome, consider the following statistics:
The Feltz-Fontana Prize represents a pivotal recognition of the advancements in neurophysiology and microbiome research. By focusing on the gut-brain axis, this award highlights the critical role of the microbiome in influencing neurological health and cognitive function. As research continues to uncover the complexities of this bidirectional communication network, the potential for innovative interventions and treatments grows, promising a brighter future for neurological and psychological health.
One of the most pressing areas of research in the field of neurophysiology and microbiomes is the study of microbiota dysbiosis. This condition, characterized by an imbalance in the gut microbiome, has been linked to a range of neuropsychiatric disorders. Understanding the mechanisms behind dysbiosis and its impact on the brain is crucial for developing effective interventions and treatments.
Research has shown that microbiota dysbiosis can contribute to the development of various neuropsychiatric disorders, including depression, anxiety, and even neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's. The gut microbiome plays a significant role in regulating inflammation, immune responses, and the production of neurotransmitters, all of which can influence brain function and behavior.
One promising intervention for restoring microbiome balance is fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT). This procedure involves transferring fecal matter from a healthy donor to a recipient with dysbiosis. Studies have demonstrated the potential of FMT in treating conditions such as Clostridium difficile infection and inflammatory bowel disease. Moreover, emerging research suggests that FMT may also have applications in addressing neuropsychiatric disorders by restoring a healthy gut microbiome.
The field of neurophysiology has seen remarkable advancements in recent years, particularly in the area of brain imaging. Techniques such as positron emission tomography (PET) and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) have revolutionized our understanding of brain function and the gut-brain axis. These technologies allow researchers to visualize and study the intricate connections between the gut and the brain.
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) is a powerful imaging technique that uses radioactive tracers to visualize metabolic processes in the brain. PET scans can provide detailed information about brain activity, blood flow, and the distribution of neurotransmitters. This technology has been instrumental in studying the gut-brain axis, allowing researchers to observe how changes in the microbiome can influence brain function.
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) is another advanced imaging technique that measures brain activity by detecting changes in blood flow. fMRI has been widely used to study the gut-brain axis, providing insights into how the microbiome can affect cognitive function, emotional regulation, and even pain perception. This non-invasive method has become a cornerstone of neurophysiology research.
The vagus nerve is a critical component of the gut-brain axis, serving as a major communication highway between the gut and the brain. This nerve, which is the longest cranial nerve in the body, plays a crucial role in transmitting signals that regulate various physiological processes, including digestion, heart rate, and even mood.
The vagus nerve is intimately involved in the communication between the gut microbiome and the brain. Research has shown that the microbiome can influence the activity of the vagus nerve, which in turn can affect brain function and behavior. For example, certain bacteria in the gut can produce neurotransmitters that are then transmitted to the brain via the vagus nerve, influencing mood and cognitive function.
Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) is a therapeutic technique that has shown promise in treating various neurological and psychiatric conditions. By stimulating the vagus nerve, researchers aim to modulate the gut-brain axis and restore balance to the microbiome. VNS has been used to treat conditions such as epilepsy, depression, and even inflammatory diseases, highlighting its potential as a versatile therapeutic tool.
The Feltz-Fontana Prize is not only a recognition of scientific achievement but also a catalyst for educational initiatives and public awareness. By highlighting the importance of neurophysiology and microbiome research, the prize aims to foster a deeper understanding of the gut-brain axis and its implications for health and disease.
One notable educational initiative is the translation of IBRO (International Brain Research Organization) booklets on brain science. These resources, originally published in 2004 and translated into Greek post-2005, provide accessible and engaging information about the brain and its functions. The booklets cover a range of topics, from the basics of neurophysiology to the latest advancements in brain research, making them valuable tools for educating youth and the general public.
Public awareness campaigns play a crucial role in disseminating information about the gut-brain axis and the importance of microbiome health. These campaigns aim to educate the public about the latest research findings, the potential applications of microbiome-based interventions, and the importance of maintaining a healthy gut microbiome. By raising awareness, these initiatives can empower individuals to take proactive steps towards improving their neurological and psychological health.
The Feltz-Fontana Prize continues to be a driving force in the advancement of neurophysiology and microbiome research. By recognizing groundbreaking contributions and fostering educational initiatives, the prize highlights the critical role of the gut-brain axis in health and disease. As research continues to uncover the complexities of this bidirectional communication network, the potential for innovative interventions and treatments grows, promising a brighter future for neurological and psychological health.
The field of gut-brain axis research is rapidly evolving, with new discoveries and technological advancements paving the way for innovative treatments and interventions. As we look to the future, several key areas of research are poised to make significant contributions to our understanding of the complex relationship between the gut microbiome and neurological health.
One of the most promising avenues of research is the development of personalized medicine approaches that target the gut microbiome. By leveraging advances in genomic sequencing and data analytics, researchers aim to tailor microbiome-based therapies to individual patients. This personalized approach could revolutionize the treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders, allowing for more precise and effective interventions.
The future of neurophysiology research will also be shaped by advancements in brain imaging techniques. Emerging technologies, such as diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and magnetoencephalography (MEG), promise to provide even more detailed insights into the structural and functional connections within the brain. These tools will enhance our understanding of the gut-brain axis and its role in health and disease.
While the potential of gut-brain axis research is vast, it is not without its challenges and ethical considerations. As we continue to explore the complexities of the microbiome and its impact on neurological health, it is crucial to address these issues to ensure the responsible and equitable advancement of the field.
The use of advanced genomic sequencing and data analytics in microbiome research raises important questions about data privacy and security. As researchers collect and analyze vast amounts of personal health data, it is essential to implement robust measures to protect patient confidentiality and prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information.
The ability to manipulate the gut microbiome through interventions such as fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) and probiotics also presents ethical considerations. Researchers and healthcare providers must carefully weigh the potential benefits and risks of these treatments, ensuring that they are used responsibly and with the best interests of patients in mind.
The research surrounding the Feltz-Fontana Prize and the gut-brain axis offers several key takeaways and practical applications. These insights can empower individuals to take proactive steps towards improving their neurological and psychological health.
One of the most accessible ways to support a healthy gut microbiome is through diet and lifestyle interventions. Consuming a balanced diet rich in fiber, fermented foods, and probiotics can promote the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut. Additionally, regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management techniques can further enhance microbiome health and overall well-being.
The use of probiotics and prebiotics is another practical application of microbiome research. Probiotics are live bacteria that can confer health benefits when consumed, while prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that promote the growth of beneficial bacteria. Incorporating these supplements into one's diet can help maintain a healthy gut microbiome and support optimal brain function.
The Feltz-Fontana Prize stands as a testament to the remarkable advancements in neurophysiology and microbiome research. By recognizing the intricate relationship between the gut and the brain, this prestigious award highlights the potential of the gut-brain axis to revolutionize our understanding of neurological health and disease.
As research continues to uncover the complexities of this bidirectional communication network, the potential for innovative interventions and treatments grows. From personalized medicine and advanced brain imaging techniques to diet and lifestyle interventions, the future of gut-brain axis research is bright and full of promise.
In conclusion, the Feltz-Fontana Prize not only celebrates the achievements of researchers in the field but also serves as a catalyst for further exploration and discovery. By fostering a deeper understanding of the gut-brain axis and its implications for health and disease, this award paves the way for a brighter future in neurological and psychological health. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of the microbiome and its impact on the brain, we can look forward to a new era of personalized, effective, and ethical treatments that improve the lives of individuals worldwide.
Embracing the insights and practical applications of this research, we can all take proactive steps towards supporting a healthy gut microbiome and, in turn, a healthier brain. The journey of discovery is far from over, and the Feltz-Fontana Prize will undoubtedly continue to inspire and guide the way.
Your personal space to curate, organize, and share knowledge with the world.
Discover and contribute to detailed historical accounts and cultural stories. Share your knowledge and engage with enthusiasts worldwide.
Connect with others who share your interests. Create and participate in themed boards about any topic you have in mind.
Contribute your knowledge and insights. Create engaging content and participate in meaningful discussions across multiple languages.
Already have an account? Sign in here

Explore the transformative legacy of Paul Broca, a pioneering figure in neuroanatomy whose groundbreaking discovery of “...
View Board
Discover how Louis Pasteur revolutionized medicine with germ theory, vaccines, and pasteurization. Explore his enduring ...
View Board
Louis Pasteur, the father of modern microbiology, revolutionized science with germ theory, pasteurization, and vaccines....
View Board
Explore the inspiring journey of Gerty Cori, the first woman Nobel laureate in Physiology or Medicine, who defied societ...
View Board
Discover the groundbreaking journey of Barry Marshall, a trailblazer in gastroenterology whose bold hypotheses and revol...
View Board
Explore the life and legacy of Karl Landsteiner, the visionary who revolutionized medical science with the discovery of ...
View Board
**Meta Description:** Discover how Francisco Mojica, the Spanish microbiologist behind CRISPR’s groundbreaking discove...
View Board
Discover how AI is revolutionizing the fight against antibiotic resistance by accelerating drug discovery, predicting ou...
View Board
"Explore how Santiago Ramón y Cajal, father of modern neuroscience, revolutionized brain science with the neuron doctrin...
View Board
"Manuel Elkin Patarroyo, a pioneering immunologist, developed a malaria vaccine and advocates for global health, inspiri...
View Board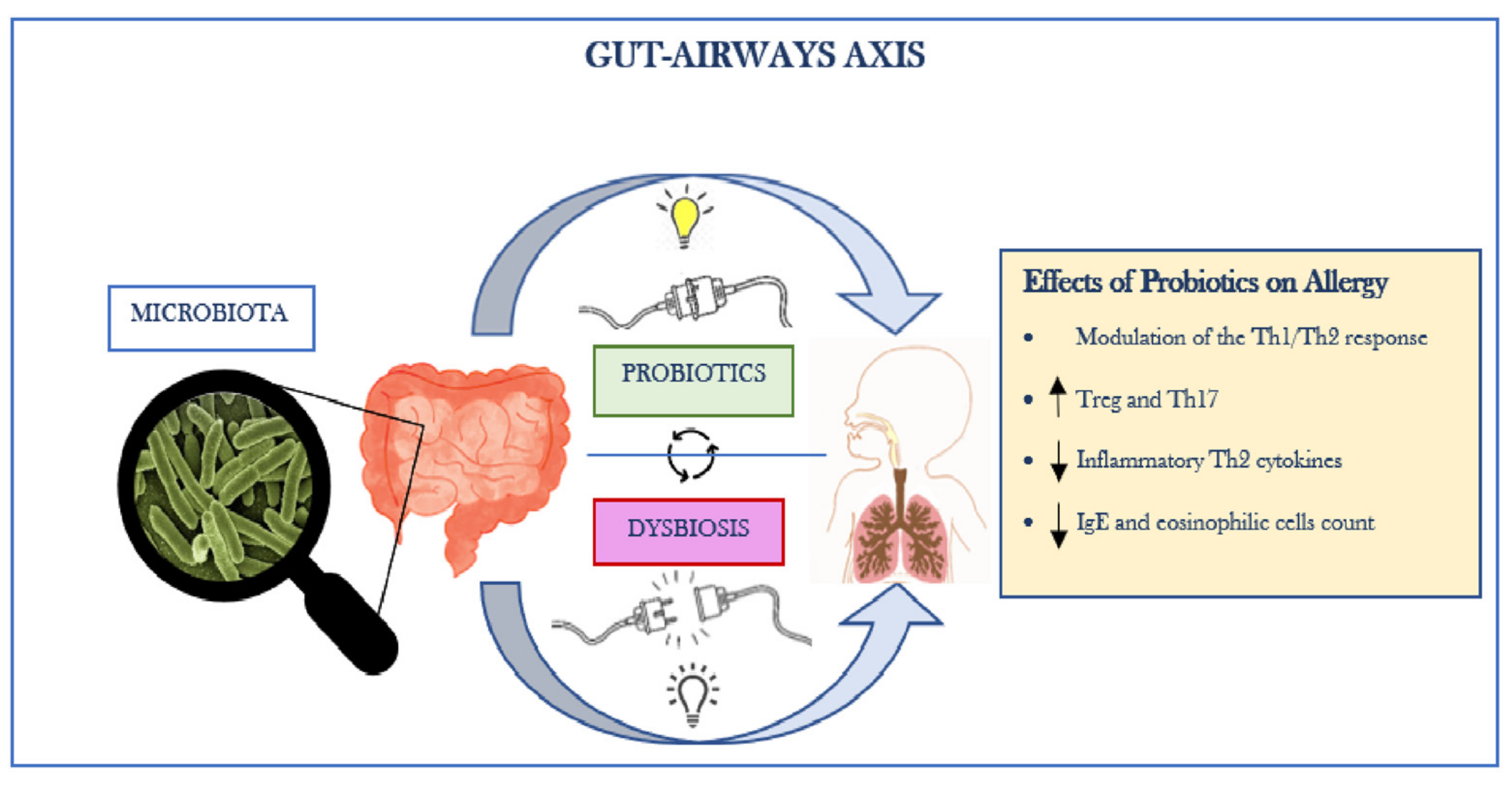
Explore the far-reaching health benefits of probiotics beyond digestive wellness in our in-depth article. Discover how "...
View Board
Discover the health benefits and enticing flavors of fermented foods in "The Renaissance of Fermented Foods: A Journey t...
View Board
"Discover Luigi Galvani's frog leg experiments that sparked modern neurophysiology. Learn how his work shaped neuroscien...
View Board
Discover the fascinating legacy of Félix d'Herelle, the self-taught pioneer behind bacteriophage therapy. This captivati...
View Board
"Explore Manuel García's vocal science legacy & laryngoscope invention. Discover how his innovations shaped modern voice...
View Board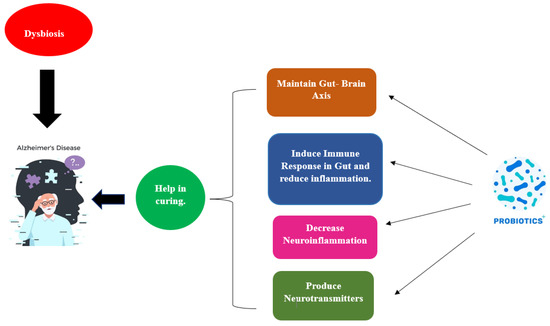
Explore the spirited revival of fermented foods as both a health movement and a nod to culinary heritage in our in-depth...
View Board
"Discover how Fleming's 1928 penicillin discovery revolutionized medicine, saving millions. Learn about the antibiotic e...
View Board
"Explore microbiology's impact on health, industry, and the environment. Discover groundbreaking findings like penicilli...
View Board
Explore the remarkable life and enduring legacy of Max von Laue, the pioneering physicist behind the groundbreaking tech...
View Board
Discover the inspiring journey of Dorothy Hodgkin, a trailblazer in X-ray crystallography whose groundbreaking discoveri...
View Board
Comments