Pioneers in Neuroscience and Linguistic Research: A Deep Dive
Introduction to Neuroscience and Linguistic Research
The term pioneer in neuroscience and linguistic research refers to groundbreaking leaders in the study of the brain and language. These fields have evolved significantly, merging to form neurolinguistics, a discipline that explores how the brain processes language. This article delves into the key aspects, historical context, and recent advancements in these interconnected domains.
Key Elements and Recent Developments
Definition and Etymology
The term pioneer originates from ancient Greek, signifying an innovative leader in scientific fields. In the context of neuroscience, it refers to the study of the brain and nervous systems, while linguistic research focuses on the structure and function of language. The fusion of these fields, known as neurolinguistics, has seen remarkable progress with technologies like fMRI and AI.
Recent Advancements
Recent years have witnessed significant strides in neurolinguistics. Advanced imaging techniques such as functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) have allowed researchers to map language centers in the brain, including the Broca's area and Wernicke's area. Additionally, the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has revolutionized the analysis of linguistic networks within the brain.
Historical Context and Background
Historical Framework
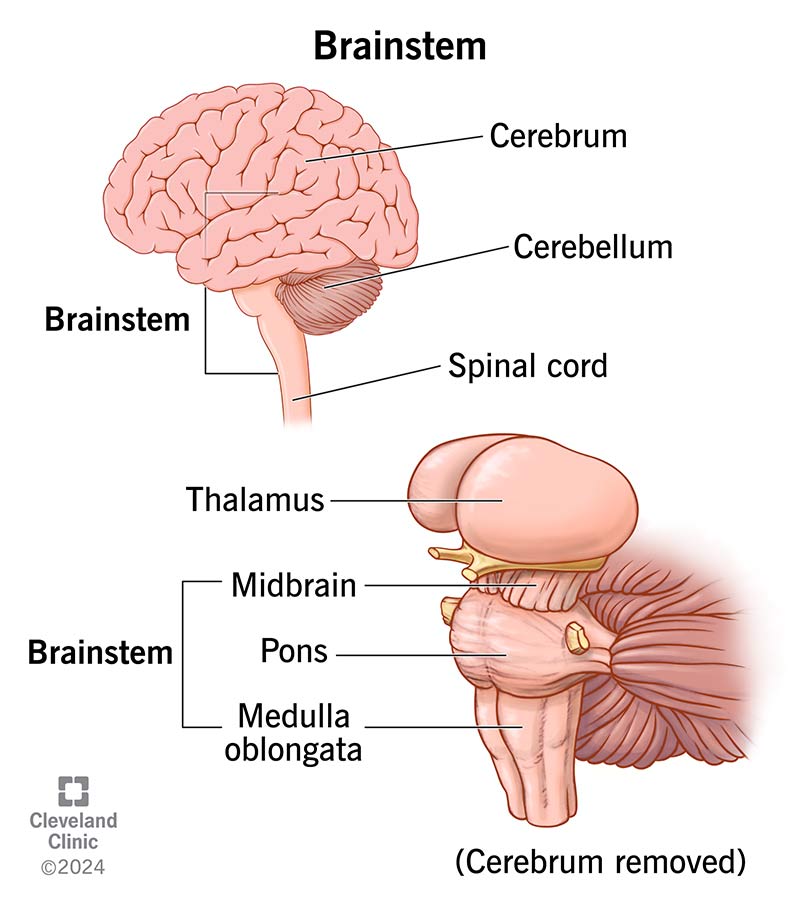
The intersection of neuroscience and linguistic research dates back to the 19th century. In 1861, Paul Broca discovered the language center in the brain, marking a pivotal moment in the field. Modern pioneers like Noam Chomsky and Steven Pinker have further bridged the gap between linguistics and the biology of the brain, contributing to our understanding of genetic language acquisition and cognitive processes.
Related Terms and Concepts
Several Greek terms provide insight into the historical and philosophical context of pioneering research. For instance, porosis refers to hardening or blindness, which can be metaphorically linked to intellectual or spiritual blindness in research. Similarly, ptochos and talaiporos denote poverty and misery, respectively, offering a metaphorical framework for understanding the challenges and triumphs in scientific exploration.
Current Trends and Significant Information
Emerging Trends
The field of neurolinguistics is currently experiencing a surge in the use of AI for analyzing brain language networks. Researchers are increasingly focusing on multilingualism and neuroplasticity, exploring how the brain adapts to learning multiple languages and the underlying neural mechanisms.
Notable Figures and Contributions
While specific individuals with the exact title of pioneer in neuroscience and linguistic research are not readily identifiable, several prominent researchers have made significant contributions. Figures like Angela Friederici and Edden Papaleontiou-Louca have advanced our understanding of language processing and brain function through their groundbreaking work.
Statistics and Data
Although comprehensive data on the term pioneer in neuroscience and linguistic research is limited, some statistical insights can be gleaned from related terms and concepts:
- Porosis: Referenced in contexts of hardening or blindness, offering metaphorical insights into research challenges.
- Ptochos: Appears 29 times in the New Testament, often translated as "poor," providing a metaphorical framework for scientific exploration.
- Talaiporos: Used twice in the New Testament, translated as "wretched," offering insights into the struggles and triumphs in research.
The integration of AI and fMRI technologies has revolutionized our understanding of how the brain processes language, marking a new era in neurolinguistics.
For a more comprehensive understanding, further research in academic databases such as PubMed and Google Scholar is recommended, focusing on terms like pioneer in neuroscience linguistic research.
The Role of Technology in Advancing Neuroscience and Linguistic Research
The advent of cutting-edge technologies has significantly propelled the fields of neuroscience and linguistic research. Innovations such as functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI), Electroencephalography (EEG), and Magnetoencephalography (MEG) have provided unprecedented insights into the workings of the human brain. These technologies allow researchers to observe brain activity in real-time, offering a deeper understanding of how language is processed and acquired.
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI)
fMRI is one of the most widely used tools in neurolinguistics. It measures brain activity by detecting changes in blood flow, which are closely linked to neural activity. This technology has been instrumental in identifying key language areas in the brain, such as Broca's area and Wernicke's area. Studies using fMRI have shown that these regions are not only involved in language production and comprehension but also play a role in more complex linguistic tasks.
Electroencephalography (EEG) and Magnetoencephalography (MEG)
EEG and MEG are non-invasive techniques that measure electrical activity and magnetic fields generated by neural activity, respectively. These methods offer high temporal resolution, making them ideal for studying the rapid dynamics of language processing. Researchers have used EEG and MEG to investigate various aspects of language, including syntax, semantics, and phonology, providing valuable insights into the temporal aspects of linguistic processing.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Neurolinguistics
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) has opened new avenues in neurolinguistic research. These technologies enable the analysis of large datasets, uncovering patterns and relationships that would be difficult to identify through traditional methods. AI and ML algorithms can process vast amounts of neuroimaging data, helping researchers to better understand the complex interactions between brain regions involved in language processing.
AI-Driven Language Models
AI-driven language models, such as transformer-based models, have revolutionized the field of natural language processing. These models can simulate human-like language understanding and generation, providing a powerful tool for studying linguistic structures and their neural correlates. Researchers are increasingly using these models to explore how the brain processes and generates language, bridging the gap between computational linguistics and neuroscience.
Machine Learning for Brain Data Analysis
Machine Learning techniques are particularly useful for analyzing complex neuroimaging data. Algorithms such as Support Vector Machines (SVM), Random Forests, and Deep Neural Networks (DNN) can classify and predict brain activity patterns associated with different linguistic tasks. These methods have been employed to study various aspects of language, including speech perception, reading, and bilingual language processing.
Multilingualism and Neuroplasticity: Insights from Neurolinguistic Research
The study of multilingualism and neuroplasticity has gained significant attention in recent years. Research in these areas has revealed how the brain adapts to learning and using multiple languages, offering insights into the cognitive and neural mechanisms underlying language acquisition and processing.
The Cognitive Benefits of Multilingualism
Studies have shown that multilingual individuals often exhibit enhanced cognitive abilities, such as improved executive function, attention, and problem-solving skills. These benefits are thought to arise from the constant need to switch between languages, which strengthens the brain's cognitive control mechanisms. Additionally, multilingualism has been linked to delayed onset of cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases, highlighting the protective effects of language learning on brain health.
Neuroplasticity and Language Learning
Neuroplasticity refers to the brain's ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections throughout life. This process is particularly evident in language learning, where the brain adapts to new linguistic structures and sounds. Research has shown that learning a new language can lead to structural changes in the brain, including increased grey matter density in regions associated with language processing. These findings underscore the dynamic nature of the brain and its capacity for lifelong learning.
Challenges and Future Directions in Neuroscience and Linguistic Research
Despite the significant advancements in neuroscience and linguistic research, several challenges remain. Addressing these challenges will be crucial for furthering our understanding of the brain and language, and for developing innovative applications in education, healthcare, and technology.
Methodological Challenges
One of the primary challenges in neurolinguistic research is the integration of data from multiple sources and methodologies. Combining insights from neuroimaging, behavioral studies, and computational modeling requires sophisticated analytical techniques and interdisciplinary collaboration. Additionally, the high cost and complexity of neuroimaging technologies can limit their accessibility, posing a barrier to research in certain settings.
Ethical Considerations
The use of advanced technologies in neuroscience and linguistic research raises important ethical considerations. Issues such as data privacy, informed consent, and the potential misuse of neuroimaging data must be carefully addressed. Researchers must adhere to strict ethical guidelines to ensure the responsible conduct of research and the protection of participants' rights and well-being.
Future Directions
The future of neuroscience and linguistic research holds great promise. Emerging technologies, such as optogenetics and brain-computer interfaces, are expected to provide even deeper insights into the workings of the brain. Additionally, the continued integration of AI and machine learning will enhance our ability to analyze complex brain data and develop more accurate models of language processing. Interdisciplinary collaboration will be key to advancing these fields and translating research findings into practical applications.
The integration of AI and advanced neuroimaging technologies has the potential to revolutionize our understanding of the brain and language, paving the way for innovative applications in education, healthcare, and beyond.
As we continue to explore the complexities of the human brain and language, the role of pioneers in neuroscience and linguistic research will remain crucial. Their groundbreaking work and innovative approaches will shape the future of these fields, offering new insights and transforming our understanding of the intricate relationship between the brain and language.
Interdisciplinary Collaborations Driving Neurolinguistic Breakthroughs
The future of neuroscience and linguistic research lies in the power of interdisciplinary collaboration. By bridging gaps between neuroscientists, linguists, computer scientists, and cognitive psychologists, researchers can develop more comprehensive models of language processing. These collaborations are essential for tackling complex questions about how the brain acquires, processes, and produces language across different contexts and populations.
Neuroscience and Cognitive Psychology
The intersection of neuroscience and cognitive psychology has led to significant advancements in understanding language acquisition and processing. Cognitive psychologists bring expertise in behavioral experiments and theoretical models, while neuroscientists provide insights into the neural mechanisms underlying these processes. Together, they can create more accurate and detailed models of how language is represented and processed in the brain.
Linguistics and Computer Science
The collaboration between linguistics and computer science has given rise to the field of computational linguistics. This interdisciplinary approach involves developing algorithms and models that can process and analyze human language. By leveraging machine learning and natural language processing techniques, researchers can gain deeper insights into linguistic structures and their neural correlates.
Educational and Clinical Applications of Neurolinguistic Research
The findings from neurolinguistic research have far-reaching implications for education and clinical practice. By understanding the neural mechanisms underlying language processing, educators and clinicians can develop more effective strategies for language teaching, speech therapy, and the treatment of language disorders.
Enhancing Language Education
Insights from neurolinguistics can inform the development of more effective language teaching methods. For example, understanding how the brain processes second languages can help educators design curricula that optimize language acquisition. Additionally, the use of neurofeedback and brain-based learning techniques can enhance the learning experience by tailoring instruction to individual neural profiles.
Advancing Speech and Language Therapy
Neurolinguistic research has significant implications for the diagnosis and treatment of speech and language disorders. By identifying the neural bases of conditions such as aphasia, dyslexia, and specific language impairment, clinicians can develop more targeted and effective interventions. Advanced neuroimaging techniques can also aid in the early detection of these disorders, allowing for timely and appropriate treatment.
Ethical and Societal Implications of Neurolinguistic Advancements
As neuroscience and linguistic research continue to advance, it is crucial to consider the ethical and societal implications of these developments. The potential applications of neurolinguistic research raise important questions about privacy, consent, and the responsible use of neurotechnologies.
Privacy and Data Security
The use of advanced neuroimaging technologies and AI-driven analysis raises concerns about data privacy and security. Neuroimaging data can reveal sensitive information about an individual's cognitive abilities, health status, and even personal thoughts. It is essential to establish robust data protection measures and ethical guidelines to safeguard this information and ensure its responsible use.
Informed Consent and Participant Rights
Obtaining informed consent is a critical aspect of ethical research in neuroscience and linguistics. Participants must be fully aware of the purposes, methods, and potential risks of the research. Additionally, researchers must ensure that participants' rights and well-being are protected throughout the study. This includes providing clear information about data usage, storage, and sharing, as well as offering the option to withdraw from the study at any time.
Future Prospects and Emerging Technologies
The future of neuroscience and linguistic research is bright, with emerging technologies poised to revolutionize our understanding of the brain and language. Innovations such as optogenetics, brain-computer interfaces, and advanced AI models hold great promise for uncovering new insights and developing practical applications.
Optogenetics and Brain Stimulation
Optogenetics is a cutting-edge technique that uses light to control neural activity. This technology allows researchers to precisely manipulate specific neurons, providing unprecedented insights into the neural circuits underlying language processing. By combining optogenetics with neuroimaging techniques, scientists can gain a more detailed understanding of how different brain regions contribute to language acquisition and production.
Brain-Computer Interfaces
Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) are devices that enable direct communication between the brain and external technologies. These interfaces have the potential to revolutionize the field of neurolinguistics by allowing researchers to study language processing in real-time and develop new methods for communication and rehabilitation. BCIs can also provide valuable insights into the neural mechanisms of language, offering new avenues for treating language disorders and enhancing cognitive abilities.
Conclusion: The Path Forward for Neuroscience and Linguistic Research
The field of neuroscience and linguistic research has made remarkable strides in recent years, driven by advancements in technology, interdisciplinary collaborations, and innovative methodologies. From the discovery of key language areas in the brain to the development of AI-driven language models, these breakthroughs have deepened our understanding of how the brain processes and produces language.
Key Takeaways
- Interdisciplinary collaboration is essential for advancing neurolinguistic research and developing comprehensive models of language processing.
- Emerging technologies, such as optogenetics and brain-computer interfaces, hold great promise for uncovering new insights into the neural mechanisms of language.
- Educational and clinical applications of neurolinguistic research can enhance language teaching methods and improve the diagnosis and treatment of language disorders.
- Ethical considerations must be prioritized to ensure the responsible use of neurotechnologies and the protection of participants' rights and privacy.
The journey of exploring the intricate relationship between the brain and language is far from over. As we continue to push the boundaries of neuroscience and linguistic research, the role of pioneers in these fields will remain crucial. Their innovative approaches and groundbreaking discoveries will shape the future of our understanding of the human mind and its remarkable capacity for language.
In conclusion, the field of neurolinguistics stands at the precipice of exciting new discoveries and applications. By fostering interdisciplinary collaborations, leveraging emerging technologies, and addressing ethical considerations, researchers can continue to unravel the mysteries of the brain and language. The insights gained from these endeavors will not only advance our scientific knowledge but also have profound implications for education, healthcare, and society as a whole.
Feltz-Fontana Prize: Neurophysiology and Microbiome Research
Introduction to the Feltz-Fontana Prize
The Feltz-Fontana Prize stands as a beacon of recognition in the scientific community, honoring groundbreaking contributions to neurophysiology and microbiome research. This prestigious award highlights the intricate relationship between the gut and the brain, a field that has gained significant traction in recent years. By focusing on the gut-brain axis, the prize underscores the importance of understanding how our microbiome influences neurological health and cognitive function.
Understanding the Gut-Brain Axis
The gut-brain axis is a bidirectional communication network that connects the central nervous system (CNS) with the enteric nervous system (ENS) of the gut. This axis plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis and influencing various physiological processes. Research has shown that the gut microbiome, composed of trillions of symbiotic bacteria, can significantly impact brain function and behavior.
The Role of the Microbiome
The human microbiome begins to form at birth and is influenced by various environmental factors. Studies have revealed that even monozygotic twins, who share identical genetic material, exhibit minimal similarity in their microbiomes. This finding emphasizes the dominant role of environmental factors over genetic predisposition in shaping the microbiome.
Neurophysiology Basics
To comprehend the gut-brain axis, it is essential to understand the basics of neurophysiology. Neurons, the fundamental units of the brain and nervous system, communicate through electrical signals known as action potentials. These signals are generated by the movement of ions, such as sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+), across the neuron membrane. The resting membrane potential of a neuron is typically around -70 mV, and during an action potential, it can reach up to 0 mV.
Recent Developments in Microbiome Research
Recent advancements in microbiome research have shed light on the complex interactions between the gut microbiome and the brain. A 2023 thesis supervised by Chrysanthi Voyiatzaki detailed the formation of the microbiome at birth and the use of 16S rRNA gene analysis to reveal phylogenetic diversity. This research also explored interventions such as fecal transplantation, which has shown promise in restoring microbiome balance.
Microbiome and Cognitive Function
Another significant area of research is the link between the human microbiome and cognitive function. Studies have demonstrated that the microbiota can influence neurological health, with implications for various neuropsychiatric disorders. The gut microbiome's role in shaping psychology and the central nervous system is a growing field of interest, with potential applications in disease prevention and treatment.
Interdisciplinary Research
The Feltz-Fontana Prize is likely tied to broader neuroscience education initiatives, such as the IBRO-translated booklets on brain science for youth. These resources, originally published in 2004 and translated into Greek post-2005, aim to foster a deeper understanding of neurophysiology and its intersections with microbiome research. The interdisciplinary nature of this research aligns with global trends in gut-brain axis studies.
Key Statistics and Data
To appreciate the scale and complexity of the gut microbiome, consider the following statistics:
- The human gut hosts trillions of bacteria, with analysis of over 300,000 16S rRNA genes revealing high phylogenetic diversity in the early microbiome.
- Monozygotic twins exhibit only slightly higher microbiome similarity than dizygotic twins, underscoring the minimal impact of genetic factors on microbiome composition.
- Neuron firing can reach frequencies of 100-1000 Hz, with long-term potentiation (LTP) strengthening synapses via AMPA receptor insertion post-NMDA activation.
Conclusion of Part 1
The Feltz-Fontana Prize represents a pivotal recognition of the advancements in neurophysiology and microbiome research. By focusing on the gut-brain axis, this award highlights the critical role of the microbiome in influencing neurological health and cognitive function. As research continues to uncover the complexities of this bidirectional communication network, the potential for innovative interventions and treatments grows, promising a brighter future for neurological and psychological health.
The Impact of Microbiota Dysbiosis on Neurological Health
One of the most pressing areas of research in the field of neurophysiology and microbiomes is the study of microbiota dysbiosis. This condition, characterized by an imbalance in the gut microbiome, has been linked to a range of neuropsychiatric disorders. Understanding the mechanisms behind dysbiosis and its impact on the brain is crucial for developing effective interventions and treatments.
Link Between Dysbiosis and Neuropsychiatric Disorders
Research has shown that microbiota dysbiosis can contribute to the development of various neuropsychiatric disorders, including depression, anxiety, and even neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's. The gut microbiome plays a significant role in regulating inflammation, immune responses, and the production of neurotransmitters, all of which can influence brain function and behavior.
Fecal Microbiota Transplantation (FMT)
One promising intervention for restoring microbiome balance is fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT). This procedure involves transferring fecal matter from a healthy donor to a recipient with dysbiosis. Studies have demonstrated the potential of FMT in treating conditions such as Clostridium difficile infection and inflammatory bowel disease. Moreover, emerging research suggests that FMT may also have applications in addressing neuropsychiatric disorders by restoring a healthy gut microbiome.
Advancements in Neurophysiology and Brain Imaging
The field of neurophysiology has seen remarkable advancements in recent years, particularly in the area of brain imaging. Techniques such as positron emission tomography (PET) and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) have revolutionized our understanding of brain function and the gut-brain axis. These technologies allow researchers to visualize and study the intricate connections between the gut and the brain.
Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) is a powerful imaging technique that uses radioactive tracers to visualize metabolic processes in the brain. PET scans can provide detailed information about brain activity, blood flow, and the distribution of neurotransmitters. This technology has been instrumental in studying the gut-brain axis, allowing researchers to observe how changes in the microbiome can influence brain function.
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI)
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) is another advanced imaging technique that measures brain activity by detecting changes in blood flow. fMRI has been widely used to study the gut-brain axis, providing insights into how the microbiome can affect cognitive function, emotional regulation, and even pain perception. This non-invasive method has become a cornerstone of neurophysiology research.
The Role of the Vagus Nerve in the Gut-Brain Axis
The vagus nerve is a critical component of the gut-brain axis, serving as a major communication highway between the gut and the brain. This nerve, which is the longest cranial nerve in the body, plays a crucial role in transmitting signals that regulate various physiological processes, including digestion, heart rate, and even mood.
Vagus Nerve and Microbiome Communication
The vagus nerve is intimately involved in the communication between the gut microbiome and the brain. Research has shown that the microbiome can influence the activity of the vagus nerve, which in turn can affect brain function and behavior. For example, certain bacteria in the gut can produce neurotransmitters that are then transmitted to the brain via the vagus nerve, influencing mood and cognitive function.
Vagus Nerve Stimulation
Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) is a therapeutic technique that has shown promise in treating various neurological and psychiatric conditions. By stimulating the vagus nerve, researchers aim to modulate the gut-brain axis and restore balance to the microbiome. VNS has been used to treat conditions such as epilepsy, depression, and even inflammatory diseases, highlighting its potential as a versatile therapeutic tool.
Educational Initiatives and Public Awareness
The Feltz-Fontana Prize is not only a recognition of scientific achievement but also a catalyst for educational initiatives and public awareness. By highlighting the importance of neurophysiology and microbiome research, the prize aims to foster a deeper understanding of the gut-brain axis and its implications for health and disease.
IBRO-Translated Booklets on Brain Science
One notable educational initiative is the translation of IBRO (International Brain Research Organization) booklets on brain science. These resources, originally published in 2004 and translated into Greek post-2005, provide accessible and engaging information about the brain and its functions. The booklets cover a range of topics, from the basics of neurophysiology to the latest advancements in brain research, making them valuable tools for educating youth and the general public.
Public Awareness Campaigns
Public awareness campaigns play a crucial role in disseminating information about the gut-brain axis and the importance of microbiome health. These campaigns aim to educate the public about the latest research findings, the potential applications of microbiome-based interventions, and the importance of maintaining a healthy gut microbiome. By raising awareness, these initiatives can empower individuals to take proactive steps towards improving their neurological and psychological health.
Conclusion of Part 2
The Feltz-Fontana Prize continues to be a driving force in the advancement of neurophysiology and microbiome research. By recognizing groundbreaking contributions and fostering educational initiatives, the prize highlights the critical role of the gut-brain axis in health and disease. As research continues to uncover the complexities of this bidirectional communication network, the potential for innovative interventions and treatments grows, promising a brighter future for neurological and psychological health.
Future Directions in Gut-Brain Axis Research
The field of gut-brain axis research is rapidly evolving, with new discoveries and technological advancements paving the way for innovative treatments and interventions. As we look to the future, several key areas of research are poised to make significant contributions to our understanding of the complex relationship between the gut microbiome and neurological health.
Personalized Medicine and Microbiome Therapy
One of the most promising avenues of research is the development of personalized medicine approaches that target the gut microbiome. By leveraging advances in genomic sequencing and data analytics, researchers aim to tailor microbiome-based therapies to individual patients. This personalized approach could revolutionize the treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders, allowing for more precise and effective interventions.
Advanced Brain Imaging Techniques
The future of neurophysiology research will also be shaped by advancements in brain imaging techniques. Emerging technologies, such as diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and magnetoencephalography (MEG), promise to provide even more detailed insights into the structural and functional connections within the brain. These tools will enhance our understanding of the gut-brain axis and its role in health and disease.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While the potential of gut-brain axis research is vast, it is not without its challenges and ethical considerations. As we continue to explore the complexities of the microbiome and its impact on neurological health, it is crucial to address these issues to ensure the responsible and equitable advancement of the field.
Data Privacy and Security
The use of advanced genomic sequencing and data analytics in microbiome research raises important questions about data privacy and security. As researchers collect and analyze vast amounts of personal health data, it is essential to implement robust measures to protect patient confidentiality and prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Ethical Implications of Microbiome Manipulation
The ability to manipulate the gut microbiome through interventions such as fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) and probiotics also presents ethical considerations. Researchers and healthcare providers must carefully weigh the potential benefits and risks of these treatments, ensuring that they are used responsibly and with the best interests of patients in mind.
Key Takeaways and Practical Applications
The research surrounding the Feltz-Fontana Prize and the gut-brain axis offers several key takeaways and practical applications. These insights can empower individuals to take proactive steps towards improving their neurological and psychological health.
Diet and Lifestyle Interventions
One of the most accessible ways to support a healthy gut microbiome is through diet and lifestyle interventions. Consuming a balanced diet rich in fiber, fermented foods, and probiotics can promote the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut. Additionally, regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management techniques can further enhance microbiome health and overall well-being.
Probiotics and Prebiotics
The use of probiotics and prebiotics is another practical application of microbiome research. Probiotics are live bacteria that can confer health benefits when consumed, while prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that promote the growth of beneficial bacteria. Incorporating these supplements into one's diet can help maintain a healthy gut microbiome and support optimal brain function.
Conclusion: The Future of Neurophysiology and Microbiome Research
The Feltz-Fontana Prize stands as a testament to the remarkable advancements in neurophysiology and microbiome research. By recognizing the intricate relationship between the gut and the brain, this prestigious award highlights the potential of the gut-brain axis to revolutionize our understanding of neurological health and disease.
As research continues to uncover the complexities of this bidirectional communication network, the potential for innovative interventions and treatments grows. From personalized medicine and advanced brain imaging techniques to diet and lifestyle interventions, the future of gut-brain axis research is bright and full of promise.
In conclusion, the Feltz-Fontana Prize not only celebrates the achievements of researchers in the field but also serves as a catalyst for further exploration and discovery. By fostering a deeper understanding of the gut-brain axis and its implications for health and disease, this award paves the way for a brighter future in neurological and psychological health. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of the microbiome and its impact on the brain, we can look forward to a new era of personalized, effective, and ethical treatments that improve the lives of individuals worldwide.
Embracing the insights and practical applications of this research, we can all take proactive steps towards supporting a healthy gut microbiome and, in turn, a healthier brain. The journey of discovery is far from over, and the Feltz-Fontana Prize will undoubtedly continue to inspire and guide the way.
Top Web Content Trends for 2025: AI, Short-Form, and Personalization
Introduction: The Evolution of Web Content in 2025
The digital content landscape is undergoing a seismic shift in 2025. AI-driven content creation, short-form video dominance, and real-time personalization are reshaping how editors and marketers approach web content. As attention spans shrink and competition intensifies, staying ahead requires adopting these trends while maintaining authenticity and performance.
According to recent studies, 69% of marketers now use AI to assist in content creation, with 72% reporting better results from AI-enhanced workflows. This shift isn’t just about efficiency—it’s about meeting audience expectations for dynamic, engaging, and personalized experiences. Editors must balance automation with human oversight to ensure quality and compliance.
The Rise of AI in Content Creation
How AI is Transforming Editorial Workflows
AI is no longer a futuristic concept—it’s a mainstream tool for content creators. From drafting and editing to SEO optimization and repurposing, AI is streamlining repetitive tasks. This allows editors to focus on strategy, creativity, and quality control.
Key AI applications in 2025 include:
- Automated drafting for blog posts, social media, and newsletters
- SEO optimization with real-time keyword suggestions
- Content repurposing across multiple formats (e.g., turning a blog into a video script)
- Personalization engines that adapt content to user behavior
However, human oversight remains critical. AI can generate content quickly, but editors must ensure accuracy, brand voice, and compliance with platform policies. The best workflows combine AI efficiency with human expertise.
Statistics: AI Adoption in Content Marketing
69% of marketers now use AI for content creation, with 72% reporting improved results in engagement and efficiency.
These numbers highlight the growing reliance on AI, but they also underscore the need for editors to adapt and upskill. AI tools are only as effective as the strategies behind them.
Short-Form Video: The Dominant Content Format
Why Short-Form Video Rules Social Media
Short-form video continues to dominate social platforms like TikTok, Instagram Reels, and YouTube Shorts. Its snackable, vertical format is perfect for mobile users and algorithms favor it for higher reach and engagement.
Brands are leveraging short-form video for:
- Acquisition (attracting new audiences)
- Engagement (keeping users interacting)
- Conversion (driving sales through shoppable content)
Despite its popularity, short-form video isn’t replacing long-form content. Instead, it complements it. Editors should repurpose long-form content into micro-assets (clips, quotes, highlights) to feed social channels.
The Role of Editors in Short-Form Content
Editors play a crucial role in optimizing short-form video:
- Script refinement for clarity and impact
- Captioning and accessibility (captions improve SEO and inclusivity)
- Repurposing strategies (extracting key moments from long-form)
As platforms prioritize video, editors must adapt their workflows to include visual storytelling alongside traditional text-based content.
Real-Time Personalization: The Future of User Experience
How Dynamic Content Enhances Engagement
Real-time personalization is transforming how users interact with websites and apps. Content, layouts, and CTAs now adapt in-session based on user behavior, preferences, and past interactions.
Key benefits of personalization include:
- Higher engagement (users see content tailored to their interests)
- Improved conversions (personalized CTAs perform better)
- First-party data collection (valuable for post-cookie marketing)
Editors must work closely with data teams to ensure personalization is ethical, compliant, and effective. Consent and transparency are critical in this era of data privacy.
Implementing Personalization in Editorial Workflows
To succeed with personalization, editors should:
- Use AI-driven tools to segment audiences
- Test dynamic content variations (A/B testing)
- Monitor engagement metrics (time on page, click-through rates)
Personalization isn’t just about technology—it’s about understanding audience needs and delivering value at every touchpoint.
Conclusion: Adapting to the Future of Web Content
The trends shaping web content in 2025—AI integration, short-form video, and real-time personalization—are here to stay. Editors who embrace these changes while maintaining authenticity and quality will thrive in this competitive landscape.
In Part 2, we’ll dive deeper into interactive content, sustainable design, and the role of E-E-A-T in modern SEO. Stay tuned for actionable insights to elevate your editorial strategy.
Interactive and Immersive Content: Engaging Audiences in 2025
The Rise of AR, VR, and Shoppable Experiences
Interactive content is no longer optional—it’s a necessity for brands looking to boost engagement and capture first-party data. Augmented reality (AR) filters, virtual reality (VR) experiences, and shoppable videos are transforming passive viewers into active participants.
Key interactive formats gaining traction include:
- Shoppable videos (clickable products within video content)
- Live Q&A sessions (real-time audience interaction)
- Polls and quizzes (gamified engagement tools)
- AR try-on filters (virtual product previews)
These formats not only increase dwell time but also provide valuable insights into user preferences. Editors should collaborate with designers and developers to integrate interactive elements seamlessly into their content strategies.
Why Interactive Content Works
Interactive content succeeds because it:
- Encourages active participation rather than passive consumption
- Provides personalized experiences tailored to user inputs
- Generates first-party data for targeted marketing
According to industry reports, interactive content can increase engagement rates by up to 50% compared to static content. This makes it a powerful tool for editors aiming to stand out in crowded digital spaces.
Sustainable and Performant Web Design: Balancing Creativity and Efficiency
The Shift Toward Eco-Friendly Digital Experiences
Sustainability is no longer just a buzzword—it’s a core consideration in web design trends for 2025. As digital consumption grows, so does the environmental impact of data-heavy websites. Editors and designers are now prioritizing:
- Reduced bloat (optimized images, minimal scripts)
- Efficient motion design (intentional animations)
- Variable fonts (reducing load times)
These practices not only lower carbon footprints but also improve page load speeds, which directly impacts SEO and user experience.
Performance Metrics That Matter
Google’s Core Web Vitals remain a critical benchmark for web performance. Editors should focus on:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) (loading speed)
- First Input Delay (FID) (interactivity)
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) (visual stability)
Websites that excel in these areas see higher rankings and lower bounce rates. Editors must work with developers to ensure content is both visually compelling and technically optimized.
E-E-A-T and Authenticity: The Pillars of Trustworthy Content
Why Expertise and Authority Matter More Than Ever
Google’s E-E-A-T guidelines (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) are shaping content strategies in 2025. Audiences and algorithms alike reward substantive, expertise-driven content over shallow, SEO-first pieces.
To align with E-E-A-T, editors should:
- Feature subject-matter experts as authors or contributors
- Cite credible sources and data-backed insights
- Maintain transparency in sourcing and disclosures
Content that demonstrates authenticity and depth performs better in search rankings and builds long-term audience trust.
The Role of Editors in Upholding E-E-A-T
Editors are the gatekeepers of content quality. Their responsibilities include:
- Fact-checking claims and statistics
- Ensuring consistent brand voice and tone
- Optimizing for accessibility (captions, alt text, semantic HTML)
By prioritizing E-E-A-T, editors future-proof their content against algorithm updates and audience skepticism.
Repurposing Content: Maximizing Value Across Platforms
Turning Long-Form Content into Micro-Assets
Repurposing is no longer a bonus—it’s a workflow standard. Editors must extract maximum value from every piece of content by adapting it for multiple formats:
- Blog posts → Social media snippets, infographics
- Videos → Short clips, GIFs, quotes
- Podcasts → Transcripts, audiograms, tweet threads
AI tools can automate parts of this process, but human editors ensure context and quality are preserved across formats.
Tools for Efficient Repurposing
Editors can leverage tools like:
- Creative automation platforms (e.g., Canva, Adobe Express)
- AI-powered summarization (e.g., Jasper, Copy.ai)
- Video editing software (e.g., CapCut, Descript)
These tools streamline repurposing while allowing editors to focus on strategy and storytelling.
Conclusion: Staying Ahead in 2025’s Content Landscape
The trends shaping web content in 2025—interactive experiences, sustainable design, E-E-A-T compliance, and repurposing—demand a proactive approach from editors. By embracing these shifts, content teams can create engaging, high-performing, and future-proof digital experiences.
In Part 3, we’ll explore emerging metrics, AI ethics, and actionable steps to implement these trends in your workflow. Stay tuned for the final insights to elevate your content strategy.
Emerging Metrics: Measuring Success Beyond Clicks
Moving Beyond Traditional KPIs
In 2025, engagement quality is surpassing raw traffic as the primary measure of content success. Editors must track metrics that reflect meaningful interactions, including:
- Time in view (how long users actively engage)
- Completion rates (for videos and long-form content)
- Interaction depth (scroll depth, clicks, shares)
These metrics provide deeper insights into audience behavior and content effectiveness than traditional vanity metrics like page views.
Aligning Metrics with Business Goals
Editors should collaborate with analytics teams to:
- Define custom KPIs tied to brand objectives
- Use A/B testing for dynamic content variations
- Monitor conversion funnels from content to action
Brands using advanced engagement metrics see up to 30% higher conversion rates compared to those relying solely on traffic data.
AI Ethics and Editorial Responsibility
Navigating the Challenges of AI-Generated Content
While AI accelerates content production, it introduces ethical dilemmas. Editors must address:
- Bias in algorithms (ensuring diverse perspectives)
- Transparency (disclosing AI assistance)
- Copyright concerns (avoiding plagiarism)
Human oversight remains critical to maintain brand integrity and audience trust.
Best Practices for Ethical AI Use
To leverage AI responsibly, editors should:
- Audit AI tools for bias and accuracy
- Combine AI outputs with human expertise
- Implement clear attribution policies
This approach ensures AI enhances—rather than replaces—authentic storytelling.
Actionable Steps for Editors in 2025
Immediate Workflow Adjustments
Editors can start optimizing their processes by:
- Adopting AI-assisted drafting tools for efficiency
- Integrating interactive elements into 30% of content
- Prioritizing mobile-first, short-form video formats
Small, strategic changes can yield significant ROI improvements.
Long-Term Strategic Shifts
For sustained success, focus on:
- Building a cross-functional content team (editors + designers + data analysts)
- Investing in sustainable web design training
- Developing a first-party data strategy for personalization
These investments future-proof content operations against evolving digital trends.
Conclusion: The Future of Web Content is Here
The 2025 content landscape demands a balance between innovation and authenticity. Editors who master AI integration, interactive formats, and data-driven personalization—while upholding E-E-A-T principles—will lead the industry.
Key takeaways for success:
- Embrace AI as a tool, not a replacement
- Prioritize engagement over vanity metrics
- Design for sustainability and performance
- Repurpose strategically across platforms
The future belongs to editors who adapt quickly, measure wisely, and create content that resonates. Start implementing these trends today to stay ahead in 2025 and beyond.