SoftBank e OpenAI: L'affare da 22,5 miliardi del 2025
Il colosso giapponese SoftBank sta accelerando per perfezionare uno storico investimento in OpenAI. L'obiettivo è formalizzare un impegno di finanziamento da $22,5 miliardi entro la fine del 2025. Questo potenziale accordo, il più grande del settore tecnologico quest'anno, ribadisce la scommessa strategica di Masayoshi Son sull'intelligenza artificiale generativa.
La Corsa Contro il Tempo di SoftBank per Finalizzare l’Accordo
Secondo report esclusivi, SoftBank si sta muovendo con urgenza per rispettare una scadenza stringente. L'azienda deve trovare le ingenti risorse necessarie per onorare l'impegno preso con OpenAI nell'aprile dello scorso anno. Lo stato attuale della trattativa è in una fase critica di finalizzazione finanziaria.
OpenAI, da parte sua, non ha ancora ricevuto l'intera somma pattuita. L’azienda si aspetta però che il pagamento completo avvenga entro la fine del 2025, come da termini contrattuali. SoftBank ha declinato di commentare pubblicamente questi sviluppi operativi.
SoftBank sta lavorando senza sosta per assicurare $22,5 miliardi, utilizzando vendite di asset, prestiti e altre forme di finanziamento, per una delle più grandi scommesse sull'IA del CEO Masayoshi Son.
Il Meccanismo di Finanziamento: Un Puzzle Complesso
Per raccogliere una cifra così monumentale, SoftBank sta attingendo a molteplici fonti. La strategia è un mix articolato che sfrutta l'intera solidità del suo bilancio. Questo approccio evidenzia la portata senza precedenti dell'operazione.
- Vendite di Asset: Liquidazione di parti del portafoglio di investimenti e partecipazioni in società quotate.
- Margin Loan: Prestiti garantiti dalla sua cospicua partecipazione in Arm Holdings.
- Riserve di Cassa: Utilizzo delle liquidità aziendali disponibili.
- Emissione di Obbligazioni: Ricorso al mercato del debito corporate.
La Valutazione Esplosiva di OpenAI e lo Scenario Competitivo
L'accordo originale di aprile 2025 valorizzava OpenAI a $300 miliardi. Da allora, la valutazione dell'azienda di San Francisco è ulteriormente salita alle stelle. Sono in corso discussioni per finanziamenti aggiuntivi che potrebbero portare la valutazione complessiva fino a $900 miliardi.
Questa crescita stratosferica segnala la domanda surriscaldata per la tecnologia di OpenAI. La corsa al capitale per finanziare l'infrastruttura AI globale è diventata una priorità assoluta per tutti i giganti tecnologici. SoftBank, con questa mossa, si posiziona in prima linea in questa gara ad altissimi capitali.
La Strategia AI di Masayoshi Son: Riposizionare SoftBank
L’investimento in OpenAI non è un episodio isolato. Rientra in una strategia precisa e aggressiva del CEO Masayoshi Son. L'obiettivo dichiarato è riposizionare SoftBank all'avanguardia della rivoluzione dell'intelligenza artificiale.
Il conglomerato giapponese vuole essere un leader nella gara globale per le infrastrutture AI. Questa scommessa mira a competere direttamente con i principali player statunitensi e cinesi. Il settore richiede ormai centinaia di miliardi di dollari per progetti di data center dedicati all'IA.
Il Progetto Stargate: La Collaborazione Strategica USA
Un elemento cruciale del contesto è il progetto Stargate. Sia SoftBank che OpenAI sono investitori chiave in questo piano da $500 miliardi sostenuto dagli Stati Uniti. Lo scopo di Stargate è costruire data center di ultima generazione per addestrare i modelli AI del futuro.
L'iniziativa ha anche una chiara connotazione geopolitica. Mira a contrastare i significativi progressi della Cina nel campo dell'intelligenza artificiale. Questo rende l'investimento di SoftBank non solo una mossa finanziaria, ma anche strategica a livello globale.
Trend del Mercato: La Corsa ai Capitali per l'Infrastruttura AI
L’affare SoftBank-OpenAI è il sintomo più evidente di una tendenza macro. Le aziende tecnologiche e gli investitori stanno accorrendo per assicurarsi capitali. La posta in gioco è il finanziamento delle mastodontiche infrastrutture fisiche necessarie all'IA.
Questo sforzo finanziario multi-tool di SoftBank è un caso di studio. Dimostra come i grandi conglomerati stiano sfruttando al massimo i loro bilanci. L'obiettivo finale è ottenere un'esposizione diretta e significativa al settore dell'intelligenza artificiale generativa.
La Mosaicatura Finanziaria: Come SoftBank Raccoglie 22,5 Miliardi
La ricerca dei fondi da parte di SoftBank è un'operazione di ingegneria finanziaria su vasta scala. Ogni strumento disponibile viene valutato e utilizzato per avvicinarsi all'obiettivo totale. L'approccio ibrido riflette la complessità di mobilitare una tale liquidità in un lasso di tempo definito.
Liquidazione degli Asset: Il Primo Pilastro
La vendita di partecipazioni è la leva più diretta a disposizione del conglomerato. SoftBank sta mettendo sul mercato quote di suo portafoglio di investimenti, noto come Vision Fund. Questo processo include sia partecipazioni in società private che in aziende quotate in borsa.
La strategia non è priva di rischi, ma è dettata dalla necessità. La liquidazione fornisce un afflusso di cassa immediato per onorare l'impegno con OpenAI. La priorità assoluta è rispettare la scadenza contrattuale della fine del 2025.
Arm Holdings: La Joya de la Corona come Garanzia
Il titolo di Arm Holdings rappresenta un asset di straordinario valore per SoftBank. La partecipazione di controllo nel designer di chip è utilizzata come collaterale per ottenere margin loan sostanziosi. Questi prestiti consentono di accedere a liquidità senza dover vendere fisicamente le azioni.
È un modo intelligente per monetizzare il valore di Arm senza diluire la proprietà strategica. Questo strumento finanziario è cruciale per il raggiungimento dell'obiettivo dei 22,5 miliardi di dollari. Dimostra la profondità del bilancio di SoftBank.
La corsa alla raccolta fondi include piani per potenziali IPO di altre attività nel portafoglio di SoftBank, insieme a un più stretto controllo sugli asset per massimizzare il flusso di cassa.
OpenAI: Una Valutazione in Orbita e Nuovi Investitori
Il panorama finanziario di OpenAI evolve parallelamente agli sforzi di SoftBank. La discussione su una valutazione fino a $900 miliardi trasforma completamente le dimensioni del mercato dell'IA. Un simile traguardo renderebbe OpenAI una delle aziende più preziose al mondo.
Il Ruolo di Amazon e Altri Giganti Tech
I colloqui per il finanziamento aggiuntivo di OpenAI coinvolgono altri colossi. Amazon è citato come potenziale investitore in questo nuovo round di finanziamento. La partecipazione di più big player tecnologici ridistribuisce l'equilibrio di potere nel settore.
Questo interesse convergente valida la tecnologia di OpenAI come infrastruttura critica del futuro. La competizione per accaparrarsi una fazione di OpenAI è feroce. SoftBank, con il suo ingente impegno in essere, rischia di vedere diluita la sua posizione relativa se entreranno nuovi soci con capitali freschi.
Implicazioni per il Mercato Secondario e le Aspettative
La rapida rivalutazione ha effetti a catena sul mercato secondario delle quote. Gli investitori preesistenti vedono il valore dei loro stake aumentare in modo esponenziale. Questo crea un circolo virtuoso di attrazione di ulteriore capitale.
- Surriscaldamento valutario: Le aspettative sul futuro dell'IA spingono i multipli a livelli storici.
- Pressione competitiva: Altri fondi e conglomerati sono costretti a valutare investimenti analoghi.
- Rischio di correzione: Una valutazione così alta solleva interrogativi sulla sostenibilità nel lungo termine.
Stargate: La Spina Dorsale Fisica dell'IA del Futuro
Il progetto Stargate non è un semplice data center. È un'iniziativa infrastrutturale senza precedenti, paragonabile a grandi opere pubbliche del passato. Con un costo stimato di 500 miliardi di dollari, rappresenta l'impegno concreto per l'addestramento della prossima generazione di modelli.
Obiettivi Tecnologici e Geopolitici di Stargate
L'obiettivo principale è costruire la potenza di calcolo necessaria per modelli di intelligenza artificiale di livello superiore. Questi modelli richiederanno quantità di energia e capacità di elaborazione oggi inimmaginabili. Stargate intende fornire questa piattaforma su suolo americano.
Parallelamente, il progetto ha una chiara lettura geopolitica. È una risposta diretta agli ingenti investimenti cinesi nell'IA. Garantire la sovranità tecnologica in questo campo è considerato una priorità strategica nazionale per gli USA.
La Sinergia tra SoftBank, OpenAI e Stargate
L'investimento di SoftBank in OpenAI e la partecipazione in Stargate sono due facce della stessa medaglia. OpenAI svilupperà i software e gli algoritmi più avanzati. Stargate fornirà l'hardware e l'energia necessari per farli funzionare.
SoftBank, facendo da ponte finanziario e strategico, si assicura un posto al tavolo in entrambe le iniziative. Questa posizione le consente di influenzare lo sviluppo dell'intero ecosistema. È una mossa per controllare una parte significativa della catena del valore dell'IA.
L'Impatto sul Settore e la Nuova Corsa all'Oro Tech
La notizia dell'accordo SoftBank-OpenAI agisce da catalizzatore per l'intero settore tecnologico globale. Segnala che la fase di ricerca e sviluppo è conclusa e inizia l'era dello scale-up industriale. La posta in gioco non è mai stata così alta.
La Reazione a Catena negli Investimenti in Infrastrutture
Altri fondi di private equity e sovereign wealth fund saranno costretti a ricalibrare le loro strategie. L'entità degli investimenti necessari richiede portafogli di dimensioni simili a quelli di SoftBank. Potremmo assistere alla formazione di nuovi consorzi e joint venture su larga scala.
L'attenzione si sposta inevitabilmente verso le aziende che forniscono componenti critici. Si parla di semiconduttori avanzati (GPU), sistemi di raffreddamento e fornitori di energia verde. La corsa all'oro moderna è una corsa a chilowatt, teraflop e dataset.
Pressioni Finanziarie e Scenari di Rischio
L'aggressiva leva finanziaria utilizzata da SoftBank non è priva di pericoli. Un cambiamento nel sentiment di mercato o un ritardo nei ritorni dell'IA potrebbe creare tensioni. La società sta effettivamente scommettendo una parte significativa del suo futuro su un unico settore.
- Rischio di Concentrazione: Troppe risorse sono allocate in un'unica area tecnologica.
- Rischio di Liquidità: La vendita di asset in fretta potrebbe realizzare prezzi non ottimali.
- Rischio Geopolitico: Progetti come Stargate sono sensibili a tensioni internazionali.
Nonostante i rischi, la visione di Masayoshi Son sembra chiara. Il costo del non partecipare alla rivoluzione dell'IA è percepito come superiore al costo di un investimento titanico. Questa filosofia guida ogni mossa del conglomerato giapponese in questo 2025 decisivo.
La Strategia Visionaria di Masayoshi Son: Scommettere sul Futuro
Masayoshi Son, fondatore e CEO di SoftBank, è storicamente noto per le sue scommesse ad alto rischio e ad alta ricompensa. L'investimento da $22.5 miliardi in OpenAI ne è l'ultima, più eclatante dimostrazione. La sua filosofia si basa sulla convinzione di essere all'alba della Singolarità, un punto di svolta storico in cui l'intelligenza artificiale supererà quella umana.
Questo accordo non è un semplice investimento finanziario. È un posizionamento strategico per controllare una parte fondamentale dell'infrastruttura tecnologica del futuro. Per Son, il rischio maggiore non è perdere dei soldi, ma essere esclusi dalla prossima rivoluzione industriale.
Dal Vision Fund all'AI-First Strategy: Un'Evoluzione Logica
Il Vision Fund ha già investito miliardi in centinaia di startup tecnologiche. Tuttavia, l'approccio si è ora radicalmente focalizzato. La strategia è passata dal "internet of things" e dalla mobilità ad un'unica parola d'ordine: intelligenza artificiale.
OpenAI rappresenta l'asset principe di questa nuova fase. Concentrare risorse così ingenti su un'unica azienda segna un cambiamento tattico. L'obiettivo è avere un'influenza decisiva sullo sviluppo dell'AGI (Artificial General Intelligence), piuttosto che piccole partecipazioni in molteplici settori.
Il modello di finanziamento multi-tool di SoftBank, che spazia dalle vendite di asset ai prestiti garantiti da Arm, è un caso di studio su come i conglomerati possiano rimodellare i loro bilanci per inseguire una visione lungimirante del futuro tecnologico.
Le Reazioni del Mercato e le Prospettive per il Settore Tech
L'annuncio dell'accordo ha inviato onde d'urto attraverso i mercati finanziari e tecnologici globali. Gli analisti stanno rivalutando i modelli di valutazione per tutte le aziende operanti nel campo dell'IA. La soglia per essere considerati un player rilevante si è alzata improvvisamente di diversi ordini di grandezza.
Vincitori e Vinti nella Nuova Era dell'IA
Gli evidenti vincitori immediati sono OpenAI e i suoi azionisti esistenti. Anche aziende come NVIDIA, fornitrice cruciale di GPU, vedono confermata la domanda esponenziale per i loro prodotti. I potenziali "vinti" sono quelle aziende e fondi di investimento che non dispongono della scala finanziaria per competere in questa nuova arena.
- Vincitori: Società di semiconduttori, infrastrutture cloud, fornitori di energia e possessori di dataset proprietari.
- Sotto pressione: Startup AI con modelli di business non scalabili, fondi venture capital di medie dimensioni, aziende tech non allineate con l'IA.
- Incoraggiati: Governi che stanno sviluppando politiche industriali sull'IA, centri di ricerca e università con talento specializzato.
La Risposta dei Competitori Diretti: Microsoft, Google, Amazon
SoftBank non è l'unico soggetto che punta su OpenAI. Microsoft rimane il partner tecnologico e cloud primario con un investimento di lungo corso. La mossa di SoftBank potrebbe spingere altri giganti, come Google (DeepMind) e Amazon, a consolidare o aumentare i loro impegni.
Il rischio è una frammentazione dell'ecosistema AI in campi chiusi controllati da diversi consorzi. La competizione si sposterà dalla singola applicazione alla supremazia sull'intero stack tecnologico, dal chip al modello finale.
Considerazioni Etiche, Regolatorie e Sociali
Investimenti di questa portata sollevano inevitabilmente interrogativi che vanno oltre la finanza e la tecnologia. Il controllo di un'infrastruttura così critica da parte di pochi soggetti privati attira l'attenzione dei regolatori. L'equilibrio tra innovazione e supervisione è più delicato che mai.
Governance dell'IA e il Ruolo dei Capitali Privati
La struttura di governance di OpenAI, con il suo insolito board a controllo non-profit, potrebbe subire pressioni. Iniettare 22.5 miliardi di dollari da un singolo investitore pone questioni di influenza e controllo. La missione originale di sviluppare un'IA "sicura e benefica" per l'umanità potrebbe entrare in tensione con gli obiettivi finanziari.
Le autorità di concorrenza, specialmente nell'Unione Europea e negli Stati Uniti, esamineranno attentamente l'accordo. Potrebbero emergere preoccupazioni sull'accentramento del potere di mercato e sulla creazione di barriere all'ingresso insormontabili.
Impatto sul Lavoro e sulla Società: La Grande Domanda
La promessa di capitali così ingenti accelera lo sviluppo di tecnologie che potrebbero automatizzare intere categorie professionali. Da un lato, si generano nuovi posti di lavoro altamente specializzati. Dall'altro, si acuisce il timore di una dislocazione di massa del mercato del lavoro.
La società civile chiederà con sempre maggiore insistenza un dialogo sulle finalità di queste tecnologie. Investimenti faraonici come quello di SoftBank rendono imperativo un dibattito pubblico sulla direzione del progresso tecnologico.
Conclusione: La Partita del Secolo nel Campo Tecnologico
Il tentativo di SoftBank di finalizzare l'investimento da $22.5 miliardi in OpenAI è molto più di una notizia finanziaria. È un evento di definizione epocale per l'intero settore tecnologico globale. Segna il momento in cui il capitale necessario per competere nell'IA ha raggiunto un ordine di grandezza paragonabile ai bilanci degli stati nazionali.
Punti Chiave della Trattativa SoftBank-OpenAI
- Entità Senza Precedenti: Un investimento singolo da 22,5 miliardi di dollari nell'IA generativa è il più grande mai tentato.
- Scadenza Stringente: La corsa contro il tempo per raccogliere fondi entro la fine del 2025 aggiunge drammaticità all'operazione.
- Strategia Multi-Fonte: SoftBank sta utilizzando un mix complesso di vendite di asset, prestiti ed emissioni di bond.
- Valutazione Esplosiva: La crescita potenziale di OpenAI da 300 a 900 miliardi di dollari ridefinisce i parametri del settore.
- Contesto Geopolitico: L'accordo si intreccia con il progetto Stargate da 500 miliardi, parte della competizione USA-Cina.
Uno Sguardo al Futuro: Cosa Ci Attende
Se SoftBank riuscirà nell'impresa, l'ecosistema AI ne uscirà radicalmente trasformato. La barriera all'ingresso diventerà quasi invalicabile per nuovi arrivati senza capitali illimitati. Potremmo assistere alla formazione di pochi, grandi consorzi che controlleranno lo sviluppo dell'intelligenza artificiale generale.
Il 2025 sarà ricordato come l'anno in cui la fase speculativa dell'IA è culminata nella fase industriale. La scommessa di Masayoshi Son è un punto di non ritorno. Il suo esito determinerà non solo il futuro di SoftBank, ma influenzerà profondamente la traiettoria tecnologica, economica e sociale dei prossimi decenni.
La partita è aperta. La corsa per i 22,5 miliardi di SoftBank verso OpenAI è la cartina al tornasole di un'epoca in cui la tecnologia richiede capitali da fantascienza per costruire il futuro. Il mondo guarda e aspetta di vedere se questo sarà veramente l'affare tecnologico definitivo del 2025, e quale nuovo ordine nascerà dalle sue conseguenze.



DeFi: A Revolution in the Financial Sector
Decentralized Finance, or DeFi, is fundamentally reshaping the global financial landscape. By leveraging blockchain technology, DeFi creates an open, permissionless alternative to traditional banking. This innovative system allows users to access financial services directly from each other, bypassing centralized intermediaries like banks and brokers.
What is Decentralized Finance (DeFi)?
DeFi represents a paradigm shift in how financial services are built and delivered. At its core, DeFi is the application of distributed ledger technology to financial services, providing instruments through smart contracts on programmable blockchains. The term itself was formally coined in 2018 by Ethereum developers, marking the beginning of a new financial era built on transparency and accessibility.
Unlike traditional finance (TradFi), which relies on centralized institutions to facilitate transactions, DeFi enables peer-to-peer interactions. This system is mediated by self-executing software programs instead of institutional gatekeepers, creating a more open and inclusive financial ecosystem for users worldwide.
The Fundamental Shift from Centralized Systems
The traditional financial system operates on a centralized model where institutions act as trusted third parties. Banks, credit card companies, and stock exchanges control the flow of money and information. DeFi challenges this model by creating a trustless environment where the code itself enforces the rules.
This shift eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing costs and increasing efficiency. Users maintain direct control over their assets through private keys, fundamentally changing the relationship individuals have with their money and financial services.
How DeFi Works: The Core Mechanics
The entire DeFi ecosystem is powered by a combination of blockchain infrastructure and smart contract technology. These components work together to create a seamless, automated financial system that operates without central control.
The Power of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts form the backbone of all DeFi applications. These are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They automatically facilitate, verify, and enforce the negotiation or performance of a transaction when predetermined conditions are met.
Smart contracts run on open-source software maintained by developer communities, ensuring transparency and collective oversight. This eliminates the need for manual approval processes and human intermediaries, making financial operations faster and more efficient.
Key Operational Principles of DeFi
DeFi operates on several defining principles that distinguish it from traditional finance:
- Automation: Transactions execute automatically through smart contracts without human intervention
- Transparency: All transaction history is publicly visible on the blockchain
- Accessibility: Participation requires only an internet connection and digital wallet
- Speed: Transactions settle in minutes rather than days
- Non-custodial: Users maintain full control of their assets through private keys
Major Financial Services in DeFi
DeFi platforms have democratized access to a comprehensive range of financial services that were previously available only through traditional institutions. The ecosystem now offers sophisticated alternatives to conventional banking products.
Lending and Borrowing Platforms
DeFi lending protocols allow users to lend their digital assets and earn interest, or borrow against their cryptocurrency holdings. These platforms use algorithmic matching rather than credit scores, making lending more accessible. Interest rates are typically determined by supply and demand dynamics rather than set by central authorities.
The process is completely automated through smart contracts, eliminating the need for loan officers or approval committees. Borrowers can access funds almost instantly by providing collateral in cryptocurrency, which is held in smart contracts until the loan is repaid.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs)
Decentralized exchanges enable peer-to-peer trading of digital assets without intermediaries. Unlike traditional exchanges that hold users' funds, DEXs allow traders to maintain control of their private keys throughout the transaction process. This significantly reduces counterparty risk and eliminates the need for custodial services.
DEXs use automated market maker (AMM) models rather than order books, allowing for permissionless trading of any token pair. Liquidity is provided by users who deposit assets into liquidity pools, earning fees from trades executed against their deposited assets.
Yield Farming and Staking
Yield farming involves providing liquidity to DeFi protocols in exchange for rewards, typically in the form of additional tokens. This has become a popular way for investors to generate returns on their cryptocurrency holdings. The returns can be significantly higher than traditional savings accounts, though they come with increased risk.
Staking involves locking up cryptocurrencies to support network operations, such as validating transactions on proof-of-stake blockchains. In return, stakers receive rewards, creating a way to earn passive income while contributing to network security and functionality.
DeFi represents a competitive, contestable ecosystem where multiple protocols compete to offer superior services and user experiences, driving innovation forward.
The Transformative Benefits of DeFi
The adoption of decentralized finance brings numerous advantages that address limitations inherent in traditional financial systems. These benefits extend beyond technical improvements to encompass broader social and economic impacts.
Financial Inclusion and Global Accessibility
DeFi fundamentally democratizes finance by allowing anyone with an internet connection to access sophisticated financial services. This is particularly transformative for the approximately 1.7 billion adults globally who remain unbanked. These individuals can now participate in financial markets without needing approval from traditional institutions.
The pseudonymous nature of DeFi transactions provides privacy while maintaining transparency of the underlying transactions. Users can engage with financial services without submitting extensive personal documentation or meeting minimum balance requirements that often exclude lower-income populations.
Enhanced Transparency and Security
Every transaction on DeFi protocols is recorded on a public blockchain, creating an immutable and transparent audit trail. This level of transparency is unprecedented in traditional finance, where transaction details are typically private. The open-source nature of most DeFi projects allows for community auditing of code, potentially identifying vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
While DeFi has experienced security incidents, the transparent nature of blockchain means that exploits are publicly visible and can be addressed by the community. This contrasts with traditional finance, where security breaches may go undisclosed for extended periods.
Cost Reduction and Efficiency Gains
By eliminating intermediaries, DeFi significantly reduces transaction costs associated with financial services. Traditional cross-border payments that involve multiple banks and currency conversions can incur substantial fees, while DeFi transactions typically cost a fraction of these amounts. The automation of processes through smart contracts also reduces operational costs.
Transaction settlement occurs much faster in DeFi ecosystems compared to traditional banking systems. While international bank transfers can take several days to clear, DeFi transactions typically confirm within minutes, regardless of the geographical location of the participants.
The Technical Architecture Powering DeFi
The sophisticated functionality of Decentralized Finance rests on a robust technical foundation. This architecture enables the complex financial operations that define the DeFi ecosystem while maintaining security and decentralization.
The DeFi Stack: Settlement, Application, and Interface Layers
DeFi systems operate through a layered model often conceptualized as the DeFi Stack Reference (DSR) model. This framework consists of three primary components that work together to deliver financial services. Each layer has distinct responsibilities while interacting seamlessly with the others.
- Settlement Layer: The underlying blockchain infrastructure that records and validates all transactions
- Applications Layer: DeFi protocols that implement specific financial functions like lending or trading
- Interfaces Layer: User-facing applications and wallets that enable interaction with DeFi services
The settlement layer provides the foundational security and consensus mechanism. The applications layer contains the business logic encoded in smart contracts. The interfaces layer translates this functionality into user-friendly experiences accessible to non-technical participants.
Ethereum and the Multi-Chain Ecosystem
Ethereum has emerged as the primary blockchain for DeFi applications, particularly because of its pioneering smart contract functionality. The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) provides a standardized environment for executing decentralized applications. This standardization has fostered tremendous innovation and compatibility across different protocols.
However, the DeFi ecosystem is expanding beyond Ethereum to include multiple blockchain networks. This multi-chain approach addresses scalability challenges and offers users more options. Cross-chain bridges and interoperability protocols are becoming increasingly sophisticated, allowing assets and data to move seamlessly between different blockchain environments.
Key DeFi Protocols and Applications
The DeFi landscape features a diverse array of protocols, each specializing in different financial functions. These applications work together to create a comprehensive alternative to traditional finance.
Leading Lending Protocols
Aave and Compound represent two of the most prominent DeFi lending protocols. These platforms allow users to supply assets to liquidity pools and earn interest, or borrow assets by providing collateral. The interest rates are algorithmically determined based on supply and demand dynamics within each market.
These protocols introduced innovative features like flash loans—uncollateralized loans that must be borrowed and repaid within a single transaction block. Such innovations demonstrate the unique capabilities enabled by blockchain technology that have no direct equivalent in traditional finance.
Automated Market Makers and DEXs
Uniswap pioneered the automated market maker model that revolutionized decentralized trading. Instead of using traditional order books, Uniswap employs constant product market maker algorithms to determine prices. This allows for permissionless trading of any ERC-20 token pair without requiring counterparties.
Other major DEXs like SushiSwap and Curve Finance have built upon this foundation with additional features. These platforms have collectively processed trillions of dollars in trading volume, demonstrating substantial adoption and proving the viability of decentralized exchange models.
DeFi protocols are designed to be modular and interchangeable, allowing different applications to interact seamlessly—a characteristic known as composability that enables unprecedented innovation.
Derivatives and Synthetic Assets
Synthetix allows users to mint synthetic assets that track the value of real-world assets like commodities, stocks, and fiat currencies. These synthetic assets, or "synths," enable exposure to traditional markets without requiring direct ownership of the underlying assets. This expands investment opportunities for cryptocurrency holders.
Derivative protocols like dYdX offer margin trading, futures, and perpetual contracts in a decentralized format. These platforms provide sophisticated financial instruments previously available only through traditional brokerages, now accessible through non-custodial DeFi interfaces.
The Risks and Challenges in DeFi
Despite its transformative potential, DeFi faces significant challenges that users must carefully consider. Understanding these risks is essential for anyone participating in the decentralized finance ecosystem.
Smart Contract Vulnerabilities and Security Risks
Smart contracts can contain bugs or security flaws that expose user funds to significant risk. Unlike traditional software, deployed smart contracts are typically immutable, meaning flaws cannot be easily patched. This permanence amplifies the consequences of coding errors or vulnerabilities.
The DeFi sector has experienced several high-profile exploits resulting in substantial financial losses. These incidents highlight the importance of thorough security auditing and the limitations of current smart contract development practices. Users must exercise caution and understand that they bear responsibility for their own security.
Market Volatility and Economic Risks
The cryptocurrency assets underlying DeFi protocols experience substantial price volatility. This volatility can create cascading effects throughout the ecosystem. Sharp price declines can trigger automated liquidations in lending protocols, potentially creating market instability.
Additionally, some DeFi protocols employ complex tokenomics that may not be sustainable long-term. Yield farming incentives, liquidity mining rewards, and governance token distributions can create economic models vulnerable to sudden changes in market conditions or user behavior.
Regulatory Uncertainty and Compliance Challenges
The regulatory landscape for DeFi remains ambiguous and varies significantly across jurisdictions. This creates compliance challenges and legal uncertainty for both developers and users. Regulatory agencies worldwide are grappling with how to apply existing financial regulations to decentralized systems.
Key areas of regulatory focus include anti-money laundering (AML) requirements, know-your-customer (KYC) procedures, securities regulations, and tax compliance. The decentralized nature of these protocols creates fundamental challenges for applying traditional regulatory frameworks designed for centralized intermediaries.
- Technical Vulnerabilities: Code exploits and smart contract bugs
- Price Volatility: Rapid cryptocurrency value fluctuations
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Evolving and inconsistent legal frameworks
- User Error: Irreversible mistakes in transaction execution
- Scaling Limitations: Network congestion and high transaction fees
DeFi vs. Traditional Finance: A Comparative Analysis
Understanding the fundamental differences between DeFi and traditional finance clarifies why this technology represents such a disruptive force in the financial sector.
Custody and Control of Assets
In traditional finance, institutions maintain custody of client assets. Banks hold deposits, brokerages hold securities, and payment processors control transaction flows. This creates counterparty risk—the risk that these intermediaries might fail, become insolvent, or restrict access to funds.
DeFi operates on a non-custodial model where users maintain control of their assets through private keys. Funds are held in smart contracts rather than with third parties. This fundamental shift in custody arrangements redistributes responsibility and risk from institutions to individual users.
Accessibility and Inclusion
Traditional financial systems often exclude individuals based on geography, wealth, documentation, or credit history. Banking services require physical infrastructure, minimum balances, and extensive paperwork. These barriers leave billions of people without access to basic financial tools.
DeFi requires only an internet connection and a digital wallet for participation. There are no minimum balance requirements, no geographical restrictions, and no need for credit checks or identification documents. This dramatically lowers barriers to financial participation.
Transparency and Auditability
Traditional financial systems operate with limited transparency. Transaction details are typically private, known only to the parties directly involved and their financial institutions. This opacity can hide inefficiencies, conflicts of interest, or even fraudulent activities.
DeFi transactions are recorded on public blockchains, creating complete transparency. Anyone can audit transaction histories, verify protocol operations, or examine smart contract code. This transparency builds trust through verifiability rather than through institutional reputation.
Operational Hours and Settlement Speed
Traditional financial markets operate within specific hours and close on weekends and holidays. Settlement of transactions, particularly across borders, can take several business days to complete. This delay creates friction and opportunity costs in global finance.
DeFi markets operate 24/7/365 without interruption. Settlement occurs within minutes or even seconds, regardless of the time or day. This continuous operation and rapid settlement significantly improve capital efficiency and market responsiveness.
The Future Evolution of Decentralized Finance
The trajectory of DeFi points toward continued innovation and increasing integration with traditional financial systems. Several emerging trends will likely shape the next phase of development in the decentralized finance sector.
Institutional Adoption and Hybrid Models
Major financial institutions are gradually exploring DeFi integration. This institutional interest could bring significant capital, regulatory clarity, and professional standards to the ecosystem. We are likely to see the emergence of hybrid models that combine elements of both centralized and decentralized finance.
These hybrid approaches might feature permissioned DeFi applications designed for institutional use while maintaining interoperability with public DeFi protocols. Such developments could bridge the gap between traditional finance's regulatory compliance and DeFi's efficiency and transparency.
Enhanced Scalability Solutions
Layer 2 scaling solutions and alternative blockchain architectures are addressing the throughput limitations of earlier DeFi platforms. Technologies like rollups, sidechains, and sharding promise to significantly reduce transaction costs while increasing speed. These improvements are essential for DeFi to support mass adoption.
As these scaling solutions mature, users will experience faster transaction confirmation times and lower fees. This will make DeFi applications more practical for everyday financial activities and micro-transactions, expanding their potential use cases beyond speculative trading and yield farming.
Improved User Experience and Accessibility
The current complexity of DeFi interfaces presents a significant barrier to mainstream adoption. Future developments will focus on simplifying user interactions, abstracting away technical complexity, and creating more intuitive experiences. Better education, onboarding tools, and customer support structures will also emerge.
Wallet technology will evolve to provide both security and simplicity. Social recovery mechanisms, biometric authentication, and insurance products will make self-custody more accessible to non-technical users. These improvements will be crucial for bringing DeFi to the next hundred million users.
The long-term success of DeFi depends on establishing global standards to ensure interoperability among different blockchains and integration with traditional financial systems.
Regulatory Developments and Compliance Frameworks
The evolving regulatory landscape will significantly influence DeFi's development and mainstream adoption. Governments worldwide are developing approaches to balance innovation with consumer protection and financial stability.
Current Regulatory Approaches
Regulatory bodies are taking varied approaches to DeFi oversight. Some jurisdictions are creating innovation-friendly frameworks with regulatory sandboxes, while others are applying existing securities and financial regulations more strictly. The decentralized nature of these protocols challenges traditional regulatory models built around identifiable intermediaries.
Key regulatory focus areas include anti-money laundering compliance, investor protection, taxation, and systemic risk management. Regulators are particularly concerned about potential consumer harm from poorly understood products, fraud, and market manipulation in relatively unregulated environments.
The Path Toward Regulatory Clarity
Industry collaboration with regulators will likely produce more nuanced frameworks that distinguish between different types of DeFi activities. Some protocols may qualify for lighter regulation if they are genuinely decentralized, while others with centralized elements may face stricter oversight similar to traditional financial services.
Compliance tools built directly into DeFi protocols may emerge, enabling automated regulatory adherence without compromising decentralization. These could include transaction monitoring, identity verification layers, and reporting mechanisms that operate transparently on-chain.
DeFi's Impact on Global Financial Systems
Decentralized Finance represents more than just technological innovation—it embodies a philosophical shift toward more open, accessible, and transparent financial systems. Its impact extends beyond cryptocurrency enthusiasts to potentially reshape global economic structures.
Democratization of Financial Services
DeFi lowers barriers to financial participation on an unprecedented scale. Individuals in underserved regions can access sophisticated financial tools without relying on traditional banking infrastructure. This democratization could stimulate economic activity in developing economies and provide new opportunities for wealth creation.
The programmability of money through smart contracts enables entirely new financial products and services. These innovations can address specific needs of communities that traditional finance has historically overlooked or underserved.
Redefining Trust in Financial Systems
DeFi shifts trust from centralized institutions to transparent, auditable code and decentralized networks. This represents a fundamental change in how financial trust is established and maintained. The "trustless" nature of blockchain-based systems doesn't eliminate trust but redistributes it to mathematical verification and economic incentives.
This redefinition of trust could reduce systemic risks associated with "too big to fail" financial institutions. By distributing risk across decentralized networks rather than concentrating it in central entities, DeFi could potentially create more resilient financial infrastructure.
Financial Innovation and Composability
The composability of DeFi protocols—their ability to interact and build upon one another—creates unprecedented opportunities for financial innovation. Developers can combine existing building blocks to create new applications quickly, much like assembling Lego pieces. This accelerates innovation cycles far beyond traditional financial product development.
This composability enables complex financial instruments that would be difficult or impossible to create in traditional systems. It also fosters collaboration across projects and reduces duplication of effort, as protocols can specialize in specific functions while interoperating with complementary services.
Practical Considerations for DeFi Participants
For individuals considering participation in DeFi, understanding practical considerations is essential for navigating this emerging landscape safely and effectively.
Security Best Practices
Users must prioritize security when interacting with DeFi protocols. This involves using hardware wallets for significant holdings, implementing multi-signature arrangements where appropriate, and thoroughly researching protocols before investing. Understanding private key management is non-negotiable for DeFi participation.
Additional security measures include using separate wallets for different activities, regularly updating software, and being cautious of phishing attempts. Since transactions are irreversible, preventing unauthorized access is paramount.
- Use hardware wallets for significant asset storage
- Research protocols extensively before committing funds
- Start with small amounts to test understanding
- Verify website URLs and contract addresses carefully
- Keep software updated and use antivirus protection
Risk Management Strategies
Given the volatility and emerging nature of DeFi, appropriate risk management is crucial. This includes diversifying across different protocols and asset types, avoiding over-leverage, and understanding the specific risks of each DeFi activity. Users should only invest amounts they can afford to lose completely.
Staying informed about protocol developments, security audits, and community governance decisions helps participants make educated decisions. Participating in decentralized governance, when available, provides insight into protocol direction and potential risks.
Tax and Record-Keeping Obligations
DeFi transactions often have tax implications that vary by jurisdiction. The programmable nature of DeFi can create complex tax scenarios that may not fit neatly into existing frameworks. Users should maintain detailed records of all transactions, including swaps, yield farming rewards, and gas fees.
Consulting with tax professionals familiar with cryptocurrency regulations is advisable for significant DeFi activity. As regulatory clarity improves, more specialized tools for DeFi tax reporting and compliance will likely become available.
Conclusion: The Transformative Potential of DeFi
Decentralized Finance represents one of the most significant innovations in the financial sector in decades. By leveraging blockchain technology and smart contracts, DeFi creates an alternative financial system that is more open, accessible, and transparent than traditional models. While still in its early stages, its impact is already being felt across global markets.
The journey toward mainstream DeFi adoption will involve addressing current challenges around security, user experience, and regulation. As these challenges are met, DeFi has the potential to complement and eventually transform aspects of traditional finance. The technology enables financial services that are borderless, programmable, and available to anyone with internet access.
DeFi embodies a shift toward financial systems that prioritize transparency, accessibility, and user sovereignty over centralized control. It represents not just technological advancement but a philosophical reimagining of how financial systems should operate in a digital age. As the ecosystem matures, it may help address longstanding issues of financial exclusion and opacity that have characterized traditional finance.
The future of finance will likely feature a blend of centralized and decentralized elements, with each serving different needs and preferences. DeFi's greatest contribution may ultimately be in pushing the entire financial sector toward greater innovation, efficiency, and inclusion. Its continued evolution will be one of the most important financial narratives to watch in the coming decade.
Popular Cryptocurrency Scams and How to Avoid Them
The world of cryptocurrencies is rapidly evolving, with the potential for both astronomical returns and significant losses. While many enthusiasts celebrate these digital assets for their innovation and decentralized nature, it's equally important to acknowledge the risks associated with this space. Scammers and hackers have found new avenues in cryptocurrencies to exploit unsuspecting investors, leading to the rise of various scams. In this article, we will delve into some of the most common cryptocurrency scams and provide practical tips to help you avoid them.
Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks are one of the most prevalent forms of scamming in the crypto world. Attackers often pose as trusted entities such as exchanges, wallets, or reputable projects, attempting to steal personal information or funds. They may use phishing emails, websites, or even fake social media accounts to deceive users into sharing sensitive data such as private keys or login credentials.
These attackers frequently deploy sophisticated techniques to make their attempts appear legitimate. For instance, they might create phishing websites that mimic those of well-known exchanges. These sites often have similar URLs and design elements to the real ones but are designed to capture user information and transfer funds to the attacker's controlled addresses.
To avoid falling prey to phishing attacks:
- Never reveal sensitive information over email or any unsecured communication channels.
- Carefully check the URL of the website you're visiting, especially if you've received a link via email or social media.
- Safeguard your private keys and keep them secure. Use hardware wallets when possible.
- Be wary of requests for urgent action or unexpected security updates. Legitimate companies rarely pressure clients into action.
Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) and Token Sales
Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) have been a popular method for raising capital since 2017. However, the lack of regulation in this space has led to numerous scams where fraudulent projects raise money under false pretenses. Investors are often misled by exaggerated promises, misleading marketing materials, and outright theft.
A common tactic in ICO scams involves creating projects with flashy websites and social media presence, often using celebrity endorsements to build credibility. Once the project gains traction, they initiate a token sale, during which investors are encouraged to send their cryptocurrencies. After collecting substantial funds, the creators may either run away with the money or simply disappear without providing any actual value or product.
To avoid falling victim to ICO scams:
- Conduct thorough due diligence before investing. Verify the team behind the project, check their track record, and understand the technology or product they're offering.
- Stay cautious of projects with vague or unrealistic business models. A clear roadmap and well-defined goals should be evident.
- Invest only what you can afford to lose, and never lend funds to others for investments.
- Always read the whitepaper and smart contract code thoroughly before making an investment decision.
Dollar-Crypto Tethering Schemes
Tether, a blockchain-based stablecoin, was once thought to be anchored to the US dollar and thus serve as a reliable form of exchange in times of market volatility. Unfortunately, questions about its reserves and transparency have raised serious concerns. Similar schemes involving other stablecoins have also emerged, often with dubious backing mechanisms. These tethers can lead to significant financial losses if investors believe they are stable but turn out to be unsupported.
Fraudulent tethering schemes usually involve creating a platform or project that claims to back its tokens with actual dollars but does not do so transparently. Investors are often lured by promised high returns or innovative features, only to find themselves exposed to a fraudulent scheme.
Here are ways to avoid such schemes:
- Verify the reserve ratio and audited reports for any stablecoin you plan to use. Only invest in assets that have transparent and verifiable backing mechanisms.
- Use reputable exchanges and custodians that follow industry best practices for auditing and transparency.
- Be wary of any stablecoin issued by a lesser-known entity or a platform that lacks a proven track record.
- Stay informed about regulatory developments related to stablecoins and their issuers.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Scams
Decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms have transformed traditional financial services through smart contracts and blockchain technology. However, the lack of intermediaries comes with significant risks, including smart contract vulnerabilities and liquidity manipulation attacks.
Smart contract hacks occur when attackers exploit flaws in the code to drain funds from wallets or smart contracts. One high-profile example includes the Sushiswap hack, where attackers exploited a bug to drain millions of dollars worth of funds from DeFi protocols. Similarly, liquidity manipulation attacks involve creating large volumes of trades to manipulate the price of coins or tokens, leading to financial losses for unsuspecting users.
To protect yourself in the DeFi space:
- Educate yourself on smart contract security principles and red flags that may indicate vulnerabilities.
- Always perform a comprehensive review of any DeFi application you intend to use, including audits and reviews by reputable security firms.
- Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) and strong passwords to secure your accounts and private keys.
- Monitor your transactions and balances closely, and consider using DeFi monitoring tools.
Market Manipulation Schemes
Cryptocurrencies are susceptible to market manipulation, where scammers intentionally cause price fluctuations to their advantage. This can be achieved through coordinated buying/selling activities, spreading rumors, or running pump-and-dump schemes.
Pump-and-dump schemes involve a group of actors colluding to artificially inflate the price of a coin by spreading positive news or creating fake buy orders. Once the price reaches certain levels, they quickly sell off their holdings, causing the price to drop sharply and leaving other investors holding worthless assets.
To avoid falling into these traps:
- Stay informed about legitimate developments in the crypto space. Reliable news sources can help separate fact from fiction.
- Be skeptical of sudden price movements that lack corresponding news or fundamental reasons.
- Use reputable exchanges with robust risk management systems and transparent trading activities.
- Consider trading strategies that involve longer-term analysis rather than short-term speculation.
The Role of Education and Awareness
One of the most effective defenses against cryptocurrency scams is education. Understanding how these scams work and knowing the signs to watch out for can significantly reduce your risk. Regularly staying updated on the latest scams and security measures is crucial in this constantly evolving landscape.
Additionally, community engagement plays a vital role. Platforms like Reddit, Telegram, and other forums dedicated to discussing cryptocurrencies can provide valuable insights and warnings from other experienced users. Building a network of trustworthy peers can help ensure that you receive credible information and advice.
In conclusion, while cryptocurrencies offer exciting possibilities for innovation and investment, they also come with unique risks. By learning about common scams, maintaining a vigilant mindset, and educating yourself and others, you can better protect yourself against these threats. As a responsible crypto investor, always prioritize caution and due diligence to ensure a safer and more sustainable journey in the world of digital assets.
Stay safe out there!
The Role of Regulatory Bodies
Regulatory bodies play a crucial role in mitigating some of the risks associated with cryptocurrencies. Countries around the world are increasingly introducing regulations to protect investors and consumers. For instance, the SEC (Securities and Exchange Commission) in the United States has taken several actions to crack down on fraudulent ICOs and crypto offerings. Similar efforts are being made by regulators in other countries to ensure that market participants adhere to established guidelines.
However, the patchwork of regulatory frameworks globally can create confusion and make it challenging for investors to navigate. Clear and consistent regulatory standards can help investors make informed decisions and avoid falling into traps set by scammers. Engaging with regulatory bodies and staying informed about local regulations can offer additional layers of protection.
For individuals looking to navigate regulatory landscapes, consider the following:
- Research the regulatory status of exchanges, wallets, and token offerings in your region.
- Understand the legal implications of holding and trading certain digital assets.
- Stay updated on regulatory developments and compliance measures.
- Engage with community groups and forums focusing on crypto compliance issues.
The Importance of Secure Wallets
A secure wallet is essential in protecting your investments from hacking and theft. Hardware wallets and paper wallets are popular choices among experts due to their strong security features. Hardware wallets store your private keys offline, which makes them highly resistant to online attacks. Paper wallets involve printing out your private keys and storing them securely, though they require greater care to prevent physical damage.
Software wallets are generally more convenient but come with higher risks due to their reliance on internet-connected devices. It’s crucial to ensure that you use reliable software wallets and follow best practices such as two-factor authentication, regular backups, and avoiding phishing attacks.
To enhance security with wallets:
- Choose reputable hardware wallets like Ledger Nano X or Trezor from well-known manufacturers.
- Consider using software wallets like Exodus, MyEtherWallet, or MetaMask but prioritize security settings and enable two-factor authentication.
- Always keep your software wallets’ passwords and private keys secure. Avoid sharing them and use alphanumeric combinations instead of easily guessable names or dates.
- Regularly update the versions of your wallet software to protect against known vulnerabilities.
Using Reputable Exchanges
Selecting a reputable crypto exchange is another crucial step in protecting your investments. Exchanges handle billions of dollars daily and act as central hubs for trading and liquidity provision. While exchanges offer convenience and access to a wide range of assets, they also introduce centralized risk, including potential hacks, internal mismanagement, and regulatory issues.
When choosing an exchange:
- Review the exchange’s regulatory compliance status. Look for licenses and certifications issued by relevant financial authorities.
- Evaluate the exchange’s security measures. Check if they offer two-factor authentication, cold storage for funds, and robust security protocols.
- Assess the exchange’s trading volume and fees. Higher trading volumes and lower fees typically indicate a more trustworthy platform.
- Read reviews and feedback from other users. Sites like CoinMarketCap, Trustpilot, and others can provide valuable insights.
Protecting Your Identity and Privacy
Identity and privacy are critical considerations in the crypto space. Revealing too much personal information can put you at risk of identity theft, while lack of privacy can expose you to targeted scams. Many exchanges and wallet providers offer privacy features, but it's important to understand how these work and whether they meet your needs.
To protect your identity and privacy:
- Limit the amount of personal information shared with crypto platforms.
- Use pseudonyms or aliases when registering for accounts wherever possible.
- Consider using mixers or tumblers for additional privacy when sending funds.
- Regularly monitor your account activity and report any suspicious transactions immediately.
Conclusion
While the world of cryptocurrencies offers vast opportunities for innovation and financial freedom, it also presents unique challenges and pitfalls. By understanding common scams, adhering to best security practices, and staying informed about regulatory landscapes, you can better protect yourself from falling victim to frauds. Utilizing secure wallets, choosing reputable exchanges, and maintaining strong privacy measures are all essential steps in safeguarding your investments.
Armed with knowledge and vigilance, you can navigate the complexities of the crypto ecosystem with confidence. Remember, the key to successful investments lies not only in finding profitable opportunities but in ensuring that these opportunities come with minimal risk.
Stay informed, stay cautious, and stay secure!
Community Engagement and Reporting Scams
Building a strong community around your cryptocurrency investments can be invaluable. Crypto communities are active forums where individuals share experiences, warn each other about scams, and provide support. Platforms like Reddit, Telegram, Discord, and specialized crypto communities can offer a wealth of information and resources. Joining these groups allows you to stay informed about the latest trends, scams, and security measures.
Here are some ways to engage and utilize crypto communities effectively:
- Participate Actively: Engage in discussions, ask questions, and contribute valuable insights. Active participation can help build a strong reputation within the community.
- Follow Trusted Users: Identify and follow trusted users or influencers who consistently share verified information and useful tips.
- Report Suspected Scams: If you come across something suspicious, report it to the community or the appropriate authority. Collective vigilance can help prevent larger-scale scams.
- Share Verified Information: Share verified information about legitimate projects, exchanges, and wallets. This helps protect fellow members from false information.
Beyond community engagement, reporting scams to the relevant authorities or platforms is crucial. Most exchanges and regulatory bodies have mechanisms in place to receive tips about scams. Providing detailed information can lead to quicker resolutions and prevent further losses for victims.
Utilizing Security Software and Tools
There are several security tools and software solutions that can significantly enhance your protection against scams. Here are some tools that can help:
- Antivirus Software: Make sure your computer has up-to-date antivirus software to mitigate the risk of malware and viruses that could compromise your crypto-related activities.
- Firewalls: Use firewalls to control incoming and outgoing network traffic and protect against unauthorized access.
- Security Suites: Comprehensive security suites can provide additional layers of protection against various cyber threats.
- Security Monitors: Tools like Blockscout, Etherscan, and other blockchain explorers can help monitor transfers and detect unusual activities.
In addition to using security software, it’s crucial to maintain good cybersecurity hygiene:
- Keep your operating system and application software up to date.
- Avoid opening attachments or clicking on links from unknown or suspicious sources.
- Use strong and unique passwords for different accounts.
- Enable and regularly update two-factor authentication whenever possible.
Stay Informed About Emerging Threats
The crypto space is continually evolving, and new threats emerge regularly. Staying informed about emerging threats is essential to staying one step ahead of scammers. Here are some sources to keep you updated:
- Crypto News Websites: Follow reputable crypto news sites like CoinDesk, Coindesk, and The Block for regular updates on market developments and scams.
- Industry Reports: Keep an eye on industry reports and whitepapers that discuss emerging technologies and security measures.
- Security Blogs: Security-focused blogs and newsletters from experts in the field provide valuable insights into new threats and countermeasures.
Additionally, participating in webinars, conferences, and workshops focused on crypto security can offer direct access to industry experts and cutting-edge knowledge.
Final Thoughts
Facing scams in the crypto space is an ongoing challenge, but with the right strategies and tools, you can minimize the risks. Educating yourself about common scams, using secure practices, engaging with the community, and leveraging available security tools can significantly enhance your safety and security.
Remember, the crypto world is dynamic, and staying informed is key to navigating it safely. Continuously educate yourself, remain vigilant, and take proactive steps to protect your investments. By doing so, you can enjoy the many benefits of crypto while minimizing the associated risks.
Happy crypto trading, and may you remain secure!


The Benefits of Using Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies have made significant inroads into the financial landscape over the past decade, transforming the way individuals and businesses transact across the globe. From facilitating cross-border payments without the need for intermediaries to offering secure and anonymous transactions, cryptocurrencies provide a plethora of benefits that go beyond traditional fiat currencies.
Decentralization and Transparency
The decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum is one of their most appealing features. Unlike traditional financial systems where central banks or governments control the issuance and regulation of currency, cryptocurrencies operate on blockchain networks. This decentralization ensures that there is no single point of failure or manipulation, making the system more resistant to fraud, corruption, and censorship.
Moreover, blockchain technology provides a level of transparency not usually found in traditional financial systems. Every transaction on the blockchain is recorded and visible to all participants within the network. While the identity of participants can be anonymized, every transaction is traceable and immutable, providing a transparent yet secure record of all financial activities.
Cost Efficiency
Cryptocurrencies offer significant cost savings compared to traditional payment methods. For instance, sending payments internationally using traditional bank transfers often involves high transaction fees and long processing times. Cryptocurrencies, on the other hand, typically enable faster transactions and lower fees, especially when conducted via peer-to-peer networks on platforms like Paxful and Binance.
In addition, businesses that adopt cryptocurrencies can reduce the overhead costs associated with traditional banking services. They can avoid the need for extensive physical infrastructure to support cash transactions and automate many aspects of their operations. The lower operational costs can translate into higher profit margins, making it easier for businesses to maintain competitiveness in the global marketplace.
Accessibility and Financial Inclusion
Cryptocurrencies have the potential to revolutionize financial inclusion by providing access to financial services to those who traditionally have been excluded. In many developing countries, a large portion of the population lacks access to traditional banking services due to factors such as distance, poverty, and lack of identification. Cryptocurrencies can bypass these barriers and provide a simple and fast way to transact.
Furthermore, cryptocurrencies can enable microtransactions that are challenging with traditional financial systems. For example, content creators can receive instant payments for their work through platforms like Steemit, while small businesses can accept micropayments from customers making small purchases using cryptocurrencies.
Anonymity and Privacy
While anonymity and privacy are often misunderstood as synonymous with illegal activity, they can play a significant role in protecting individual freedoms and personal information. Cryptocurrencies offer users the ability to transact without revealing their identities, which can be crucial in regions with restrictive laws or where identity theft is prevalent.
For instance, cryptocurrencies like Monero provide advanced privacy features that make it difficult for third parties to track the movement of funds. This enhances user privacy and security, ensuring that personal financial data remains confidential. Additionally, cryptocurrencies can be a valuable tool for individuals and organizations looking to conduct transactions without fear of surveillance or government interference.
Flexibility and Scalability
Cryptocurrencies offer unparalleled flexibility and scalability, allowing users and businesses to adapt to changing market conditions quickly. Traditional financial systems can take time to process transactions, approve loans, or issue payments, whereas cryptocurrencies often allow for near-instantaneous execution, regardless of geographic location.
Furthermore, blockchain technology can support a wide range of use cases beyond simple payments. Smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps) built on blockchain platforms can automate complex financial processes, reducing the need for intermediaries and increasing efficiency. This flexibility makes cryptocurrencies a versatile tool for various industries, from real estate to supply chain management.
Resilience and Stability
Cryptocurrencies are known for their inherent resilience against inflation, which can negatively impact traditional fiat currencies, especially in countries with high inflation rates. Unlike national currencies, cryptocurrencies like gold or silver can act as a store of value without the risk of devaluation due to monetary policies.
Additionally, blockchain technology's decentralized nature helps protect against economic shocks and systemic risks that can cripple traditional financial systems. If one entity fails, the rest of the network can continue operating, ensuring the continuity of financial transactions. This stability can be particularly beneficial during economic crises, providing a resilient alternative to conventional finance.
Conclusion
The benefits of using cryptocurrencies are numerous and far-reaching, offering advantages in terms of decentralization, cost efficiency, accessibility, anonymity, flexibility, and resilience. As more individuals and businesses adopt cryptocurrencies, it is likely that we will see a shift towards a more decentralized, transparent, and efficient financial system.
However, it is important to note that cryptocurrencies also come with risks, including volatility, regulatory uncertainty, and cybersecurity threats. It is crucial for users and businesses to understand these risks and take appropriate measures to mitigate them.
As the technological landscape evolves, cryptocurrencies are likely to play an increasingly prominent role in shaping the future of finance. Whether through direct monetary transactions or supporting broader technological advancements, cryptocurrencies offer a world of possibilities and opportunities for individuals and businesses alike.
Regulatory Clarity and Innovation
One of the challenges facing cryptocurrencies is regulatory clarity. While some countries have taken steps to regulate cryptocurrencies, others remain ambivalent, leading to legal uncertainties that can deter widespread adoption. However, as more nations implement specific regulations, the industry is beginning to find a balance between innovation and compliance.
New regulations can also accelerate the development and adoption of cryptocurrencies. For example, jurisdictions like Japan and Singapore have established clear guidelines that encourage financial institutions to engage with cryptocurrencies, leading to increased innovation and investment in the sector. These regulatory frameworks often outline how cryptocurrencies should be classified, taxed, and integrated into existing financial systems.
Besides, regulatory clarity fosters a stable environment for startups and established companies to innovate and experiment with new financial products and services. Companies like Ripple, which specializes in cross-border payments, have gained regulatory approval in certain markets, thereby enabling more institutional participation in the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Economic Diversification
Cryptocurrencies offer a chance for economic diversification, particularly in regions where traditional economies are struggling. In Venezuela, for instance, where hyperinflation is rampant, the use of cryptocurrencies like stablecoins backed by fiat currency has provided a means of preserving purchasing power and conducting transactions without the risk of losing value rapidly.
Mining cryptocurrencies, especially in areas with abundant natural resources like renewable energy, can also contribute to local economic growth. Countries like Iceland and Norway, endowed with vast geothermal and hydropower resources, have leveraged these assets to become major cryptocurrency mining hubs. This not only provides employment opportunities but also attracts foreign investment, contributing to the overall economic development of these nations.
User Experience Enhancements2>
The user experience in using cryptocurrencies has significantly improved over the years. Today, users can easily buy, sell, and trade cryptocurrencies through a multitude of exchanges, custodians, and wallets. Mobile apps like Coinbase and Binance have made trading more accessible to a global audience, allowing users to manage their investments from their smartphones.
Moreover, user-friendly interfaces and educational resources have addressed one of the main hurdles—lack of knowledge. Online communities, forums, and social media platforms offer guidance, tutorials, and support, helping new users navigate the complexities of cryptocurrencies. These resources are critical for fostering a more informed and engaged user base.
Enterprise Solutions and Blockchain Technology2>
Cryptocurrencies have found applications beyond individual transactions. Enterprises are increasingly leveraging blockchain technology to streamline internal processes and enhance transparency. For example, supply chain management has seen significant improvements with the implementation of blockchain-based solutions that reduce fraud, improve traceability, and increase efficiency.
Smart contracts, automated agreements that execute when predefined conditions are met, are being adopted in various sectors such as real estate, finance, and healthcare. These smart contracts eliminate intermediaries, lower costs, and ensure compliance, thus enhancing trust among parties involved in these transactions.
Many large corporations, including IBM, Walmart, and Maersk, have already implemented blockchain solutions to improve their supply chain operations. These initiatives demonstrate the potential of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology to disrupt traditional business models and drive innovations.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency2>
The environmental impact of cryptocurrencies, particularly those requiring significant computational power (like Bitcoin), has been a topic of concern. Concerns about energy consumption have led some cryptocurrency projects to focus on more sustainable alternatives. For example, Cardano has implemented a proof-of-stake consensus mechanism that significantly reduces energy usage compared to proof-of-work systems.
Innovations like zero-knowledge proofs, which allow for private transactions without revealing transaction details, further enhance sustainability by minimizing the computational resources needed for secure transactions. Additionally, initiatives like the Token Charity Foundation and the Blockchain Sustainability Alliance are working to promote eco-friendly practices within the cryptocurrency community.
Emerging Trends and Future Prospects2>
As the cryptocurrency ecosystem continues to evolve, several emerging trends are worth noting. Decentralized Finance (DeFi) platforms are gaining traction, offering users a range of financial tools and services without the need for traditional financial institutions. DeFi protocols like Compound and Uniswap allow users to earn interest on deposited assets, lend to others, and engage in token swaps, all on a decentralized network.
Additionally, non-fungible tokens (NFTs) represent a significant trend, with artists, musicians, and gamers utilizing NFTs to create unique digital assets that can be traded and owned. Platforms like OpenSea and Rarible have emerged as marketplaces for NFTs, facilitating transactions and promoting digital creativity.
Futuristically, we can expect rapid advancements in blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies. Quantum computing, for instance, could potentially solve some of the current limitations faced by blockchain networks, enhancing security and processing speed. Blockchain interoperability, allowing different blockchain networks to coexist and communicate seamlessly, is another area ripe for innovation.
Conclusion2>
The benefits of using cryptocurrencies are manifold and continue to grow as the technology matures and more use cases emerge. From enhancing financial inclusivity and cost efficiency to promoting innovation and sustainability, cryptocurrencies offer a promising alternative to traditional financial systems. However, to fully realize these benefits, the cryptocurrency industry needs to address regulatory challenges, foster user education, and promote environmental sustainability.
As the landscape continues to evolve, cryptocurrencies are poised to play an even more significant role in shaping the future of finance and beyond. By embracing the potential of this revolutionary technology, we can unlock new opportunities and contribute to a more innovative and inclusive global economy.
Addressing Challenges and Ensuring Security2>
Despite the numerous benefits offered by cryptocurrencies, several challenges remain, primarily related to security, regulation, and mass adoption. Ensuring the safety and integrity of transactions is crucial for the sustained growth of the crypto ecosystem. One of the primary concerns is the risk of hacking and theft, especially with exchanges and wallet providers that hold large amounts of user funds.
To address these issues, both consumers and businesses are turning to multi-factor authentication (MFA), cold storage wallets, and insurance products. Multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security to logins, while cold storage wallets keep cryptocurrencies offline, thereby reducing the risk of online hacks. Insurance products help mitigate losses caused by security breaches, providing financial protection to users.
In addition to individual security measures, there is a growing emphasis on improving the security of blockchain networks themselves. Innovations like zk-SNARKs and zk-STARKs are being developed to enhance privacy while maintaining strong security. These technologies allow for zero-knowledge proofs, enabling users to prove possession of certain data without revealing the actual data itself. This not only improves security but also enhances privacy and user satisfaction.
Regulatory Environment and Legal Frameworks2>
While regulatory clarity is crucial for the long-term success of cryptocurrencies, the current regulatory landscape varies widely across countries. Some jurisdictions, such as Switzerland and Malta, have established favorable environments for cryptocurrency businesses, attracting innovative fintech companies and attracting investments. In contrast, other regions face stricter regulations or outright bans, which can hinder adoption and investment.
Effective regulatory frameworks strike a balance between preventing illicit activities and fostering innovation. They include measures such as anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) requirements, tax regulations, and consumer protection rules. The US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has played a significant role in defining the regulatory status of cryptocurrencies, with classifications like security tokens (STOs) and utility tokens (UTOS).
Collaboration between governments and the crypto industry is essential for creating robust legal frameworks. Industry groups like the Crypto Association in the US and industry consortia like the Global Blockchain Business Council (GBBC) work to advocate for fair regulations and promote responsible growth. As the industry matures, more comprehensive and harmonized regulatory approaches are expected to emerge, paving the way for greater acceptance and widespread adoption.
Mass Adoption Strategies2>
To achieve broader adoption, cryptocurrencies must overcome barriers such as complexity and user awareness. Simplifying the user experience and making cryptocurrencies more accessible are key strategies. Initiatives such as integrating cryptocurrencies into everyday payments and creating more user-friendly wallets can make cryptocurrencies a viable option for individuals who currently do not use digital currencies.
Promoting financial literacy and education is also crucial. Schools and universities can incorporate blockchain and cryptocurrency topics into their curricula, helping students understand the technology and its implications. Public awareness campaigns can demystify complex concepts and highlight the real-world benefits of cryptocurrencies, fostering a more informed and engaged user base.
Incentivizing early adopters through loyalty programs and partnerships with traditional financial institutions can drive initial demand. For example, major banks and payment processors partnering with cryptocurrency firms can integrate blockchain technology into their existing services, making it more appealing for consumers who already rely on these institutions.
Conclusion2>
Cryptocurrencies offer a wide array of benefits, from increased financial flexibility to enhanced security and reduced costs. As the technology continues to mature, it presents a promising future for both individuals and businesses. However, addressing ongoing challenges such as security, regulation, and user education is paramount for widespread adoption and long-term success.
By adopting best practices in security, advocating for sound regulatory frameworks, and implementing strategies to educate and incentivize users, the crypto industry can overcome current obstacles and unlock its full potential. As more people and businesses embrace cryptocurrencies, the financial landscape is set to undergo transformative changes, ushering in a new era of innovation and opportunity.
Looking forward, cryptocurrencies are likely to play an integral role in shaping the future of finance. Whether through financial inclusion, economic diversification, or disruptive technological advancements, cryptocurrencies present a world of possibilities that are only beginning to be realized. Embracing this technology with an understanding of its benefits and challenges is essential for navigating the coming era of digital finance.
In conclusion, cryptocurrencies are not just about money; they represent a fundamental shift in how we perceive and interact with financial systems. As we continue to explore and harness their potential, we move closer to a future defined by greater transparency, efficiency, and empowerment.
As technological innovation advances, the journey ahead promises exciting developments and transformative changes. The benefits of cryptocurrencies extend far beyond their current applications, opening doors to new possibilities and opportunities. With continued effort and collaboration, cryptocurrencies can become a cornerstone of a robust and equitable global financial system.


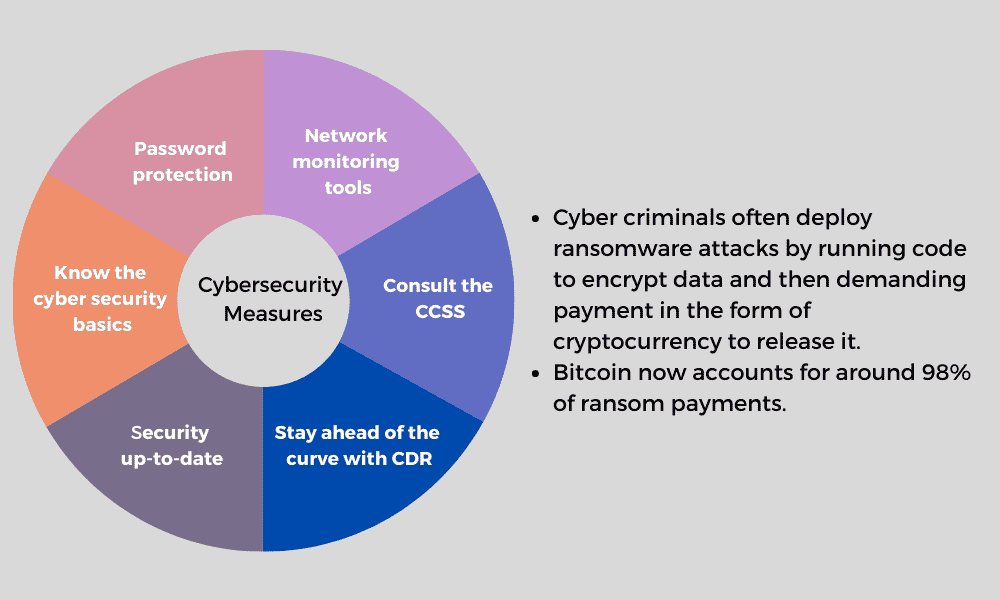

Risks Involved in Investing in Cryptocurrency
Introduction
Cryptocurrency has emerged as one of the most talked-about investment opportunities in recent years. With the rise of Bitcoin, Ethereum, and thousands of alternative coins (altcoins), many investors are eager to dive into digital assets in hopes of high returns. However, while cryptocurrencies offer potential rewards, they also come with significant risks that every investor must understand before committing their funds.
Unlike traditional investments like stocks or bonds, cryptocurrencies operate in a largely unregulated, highly volatile, and technologically complex environment. This article explores the key risks involved in cryptocurrency investments, helping you make informed decisions before entering this unpredictable market.
1. Extreme Market Volatility
One of the most notable risks in cryptocurrency investing is extreme price volatility. Digital assets can experience dramatic price swings in very short periods. For example, Bitcoin has seen both meteoric rises and devastating crashes, sometimes losing or gaining more than 20% of its value in a single day.
Why Is Cryptocurrency so Volatile?
Several factors contribute to cryptocurrency volatility:
- Speculation: Many investors buy cryptocurrencies based on hype rather than fundamentals, leading to bubbles and sharp corrections.
- Market Liquidity: Compared to traditional markets, crypto markets have lower liquidity, meaning large trades can cause significant price movements.
- Regulatory News: Government crackdowns or endorsements can trigger massive price swings.
- Technological Developments: Updates, hacks, or security flaws in blockchain networks can impact prices drastically.
For investors, this volatility means potential for high gains but also severe losses. Unlike stable assets, cryptocurrencies require strong risk tolerance and an ability to withstand rapid value fluctuations.
2. Lack of Regulation and Investor Protections
Unlike traditional financial institutions, most cryptocurrency markets operate without stringent regulatory oversight. This exposes investors to several dangers:
Potential Fraud and Scams
The decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies makes them an attractive target for scammers. Common fraudulent schemes include:
- Pump-and-Dump Schemes: Groups artificially inflate a coin's price before selling off their holdings, leaving others with worthless assets.
- Fake ICOs (Initial Coin Offerings): Fraudsters create fraudulent fundraising projects and disappear with investors' money.
- Phishing Attacks: Hackers trick users into revealing private keys or login credentials.
No Government Backing or Insurance
Traditional bank accounts often benefit from government insurance (e.g., FDIC in the U.S.), protecting deposits up to a certain limit. Cryptocurrencies lack such safeguards—if an exchange collapses or funds are stolen, investors may have no recourse.
Legal and Tax Uncertainties
Cryptocurrency regulations vary widely across countries, and sudden legal changes can disrupt markets. Additionally, tax reporting for crypto gains can be complex, leading to potential compliance risks.
3. Security Risks and Hacking Threats
Cybersecurity is a major concern in the cryptocurrency space. Even though blockchain technology itself is secure, exchanges, wallets, and individual users are vulnerable to attacks.
Exchange Hacks
Cryptocurrency exchanges are prime targets for hackers. Several high-profile breaches, such as the Mt. Gox hack (2014) and the Coincheck theft (2018), led to losses worth hundreds of millions of dollars. Investors storing funds on exchanges risk losing everything if security measures fail.
Wallet Vulnerabilities
Crypto wallets, whether hardware or software-based, can be compromised if not properly secured. Private keys—necessary for accessing funds—can be stolen through malware, phishing, or physical theft.
Smart Contract Exploits
Cryptocurrencies like Ethereum rely on smart contracts, self-executing agreements written in code. Flaws in these contracts can lead to exploits, as seen in the infamous DAO hack, where $60 million in Ether was stolen.
4. Liquidity Risks
While major cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum enjoy high liquidity, smaller altcoins may suffer from thin trading volumes. This can make it difficult to buy or sell large amounts without impacting the price.
Illiquid Markets and Price Slippage
In low-liquidity markets, executing large trades can lead to significant price slippage—where the executed price differs from the expected price due to lack of buyers or sellers. This can result in unexpected losses.
Exchange Shutdowns and Withdrawal Freezes
Some exchanges, especially smaller or less reputable ones, may suddenly halt withdrawals or shut down entirely, trapping investors' funds.
5. Technological Risks
Blockchain technology is still evolving, and cryptocurrencies face several technological challenges that can affect their viability.
Network Congestion and High Fees
During peak usage, blockchain networks like Bitcoin or Ethereum can become congested, leading to slow transactions and high fees. This reduces usability and can negatively impact investor confidence.
Potential for Obsolescence
With thousands of cryptocurrencies in existence, many may fail due to competition, lack of development, or technological inferiority. Investors risk holding coins that eventually become obsolete.
---End of Part 1---
6. Regulatory and Legal Risks
Cryptocurrency operates in a legal gray area in many jurisdictions, making it susceptible to sudden regulatory crackdowns. Governments worldwide are still figuring out how to classify and regulate digital assets, which creates uncertainty for investors.
Government Bans and Restrictions
Some countries, including China and India, have imposed strict restrictions or outright bans on cryptocurrencies. These actions can drastically reduce market liquidity and sever access to exchanges, leaving investors with limited options to trade or sell their holdings.
KYC & AML Compliance Risks
Many exchanges now enforce Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations. If investors fail to comply with these requirements, their accounts may be frozen or seized. Additionally, regulatory scrutiny could force platforms to delist certain cryptocurrencies, causing price crashes.
Changing Tax Policies
Tax authorities worldwide are tightening cryptocurrency taxation rules. Investors may face unexpected capital gains taxes, reporting obligations, or audits. Misunderstanding tax requirements could result in legal penalties.
7. Market Manipulation
Due to lower liquidity and less oversight compared to traditional markets, cryptocurrency is highly prone to manipulation. Large holders, known as "whales," can influence prices by executing coordinated buy or sell orders.
Wash Trading and Spoofing
Some exchanges engage in wash trading—fake transactions designed to inflate trading volumes and attract investors. Similarly, spoofing (placing fake orders to manipulate prices) is prevalent in crypto markets, misleading traders into making poor decisions.
Whale Influence
A small number of entities hold significant portions of certain cryptocurrencies. If these whales decide to sell their holdings, prices can plummet, harming smaller investors.
8. Limited Adoption and Utility Concerns
Despite growing interest, cryptocurrencies still face adoption barriers that could hinder long-term growth. Many projects promise real-world utility but fail to deliver, leading to disillusionment and price drops.
Merchant Acceptance
While some companies accept Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies as payment, widespread adoption remains limited. If businesses do not embrace crypto payments, demand may stagnate, negatively affecting prices.
Dependence on Speculation
Most cryptocurrencies derive their value from speculation rather than actual utility. If investor sentiment shifts due to negative news, prices can collapse rapidly without underlying fundamentals to support them.
9. Emotional and Psychological Risks
Investing in cryptocurrency can be emotionally taxing due to extreme volatility and rapid market shifts. Many investors fall into psychological traps that lead to poor decision-making.
FOMO (Fear of Missing Out)
Investors often buy into cryptocurrencies during price surges out of fear of missing profits. This can lead to buying at inflated prices before inevitable corrections.
Panic Selling
Conversely, sharp price declines can trigger panic selling, causing investors to lock in losses instead of holding for potential recoveries.
Addiction to Trading
The 24/7 nature of cryptocurrency markets can encourage compulsive trading behaviors, resulting in excessive risk-taking and financial losses.
10. Dependence on Third-Party Services
While blockchain itself is decentralized, many investors rely on centralized services that introduce counterparty risks.
Custodial Exchange Risks
Using exchanges to store funds means trusting a third party with security. If the exchange is hacked, goes bankrupt, or freezes withdrawals (as seen with FTX), users can lose access to their assets permanently.
Staking and Lending Platform Vulnerabilities
Decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms offer staking and lending opportunities but also carry risks of smart contract exploits or platform collapses, as witnessed in the Celsius and Terra (LUNA) crashes.
11. Scams and Ponzi Schemes
The anonymous and pseudonymous nature of cryptocurrency makes it a breeding ground for fraudulent investment schemes.
High-Yield Investment Programs (HYIPs)
Many scams promise unrealistic weekly or monthly returns, only to vanish with investors’ deposits.
Rug Pulls
Developers of new tokens may abandon projects abruptly (rug pulls), selling off liquidity and leaving investors with worthless coins.
12. Concentration Risk in Crypto Portfolios
Many investors focus heavily on a single cryptocurrency, increasing their exposure to that asset’s specific risks.
Overexposure to Bitcoin or Altcoins
While Bitcoin is dominant, its performance isn’t guaranteed. Similarly, altcoins can experience extreme volatility or total failure.
Lack of Portfolio Diversification
Crypto investors often neglect traditional asset allocation, making their portfolios highly susceptible to market downturns.
13. Environmental and Sustainability Concerns
Bitcoin and other proof-of-work cryptocurrencies face criticism for high energy consumption, leading to potential regulatory backlash.
Green Policies Impacting Mining
Countries may impose stricter environmental regulations on mining operations, increasing costs and reducing profitability for miners.
Investor Sentiment Shift Toward Eco-Friendly Blockchains
As sustainability becomes a priority, investors may favor proof-of-stake coins (e.g., Ethereum post-Merge), causing declines in energy-intensive cryptocurrencies.
---End of Part 2---
14. Operational Risks in Blockchain Networks
While blockchain itself is designed to be secure, cryptocurrency networks are still susceptible to operational risks that can threaten both functionality and value.
51% Attacks on Proof-of-Work Networks
Smaller proof-of-work cryptocurrencies risk "51% attacks," where a single entity gains majority control of the network’s mining power. This allows bad actors to reverse transactions, double-spend coins, and destabilize the blockchain—potentially rendering the cryptocurrency worthless.
Node Centralization Issues
Ironically, many blockchains that promote decentralization have seen increasing node centralization. If a handful of entities control most validation nodes, the network becomes vulnerable to collusion or coercion, undermining trust in the system.
15. Smart Contract and Protocol Risks
Ethereum and other smart contract platforms introduce unique risks tied to code execution and governance models.
Unintended Code Execution
Smart contracts are immutable once deployed. If a bug exists—even a minor one—it can be exploited indefinitely unless the network agrees on a manual override (as seen in Ethereum’s DAO hack reversal).
Protocol Upgrade Risks
Hard forks (major upgrades) can fragment communities if consensus isn’t reached. Bitcoin’s 2017 split into BTC and Bitcoin Cash illustrates how contentious upgrades can create competing chains, diluting value and trust.
16. Privacy and Anonymity Myths
Many investors mistakenly believe cryptocurrency transactions are fully anonymous, exposing themselves to legal and tracking risks.
Pseudonymity ≠ Anonymity
Most blockchains are pseudonymous, meaning transactions link to public wallet addresses indefinitely. Sophisticated chain analysis tools, used by firms like Chainalysis, can often trace activity back to real-world identities.
Regulatory Pressure on Privacy Coins
Privacy-focused coins like Monero (XMR) or Zcash (ZEC) face increasing scrutiny and delistings from exchanges due to regulatory concerns about money laundering, reducing liquidity and accessibility.
17. Inflation Risks in Stablecoins
Stablecoins—cryptocurrencies pegged to fiat currencies—are marketed as "safe havens," but carry hidden risks.
Collateralization Failures
Algorithmic stablecoins (e.g., Terra’s UST) rely on complex mechanisms to maintain pegs. If confidence falters, a death spiral can occur, as seen when UST collapsed alongside LUNA in May 2022.
Centralized Stablecoin Trust Issues
Fiat-backed stablecoins like Tether (USDT) require faith in the issuer’s reserves. If auditors or regulators uncover insufficient backing, a "bank run" scenario could trigger mass redemptions and destabilize markets.
18. Long-Term Viability and Technological Redundancy
The crypto space evolves rapidly, and today’s leading projects risk obsolescence due to innovation or shifting paradigms.
Quantum Computing Threats
Future quantum computers could theoretically break elliptic curve cryptography, jeopardizing Bitcoin and other networks’ security. While post-quantum cryptography is in development, proactive upgrades are uncertain.
Blockchain’s "Innovator’s Dilemma"
First-generation blockchains may struggle to adapt to superior Layer 2 solutions or entirely new architectures, leaving early investors stuck with depreciating legacy assets.
19. Cultural and Generational Risks
Cryptocurrency’s adoption hinges on sociocultural factors that remain unpredictable.
Generational Wealth Transfer Effects
If younger, crypto-friendly generations inherit significant wealth, adoption may surge. Conversely, distrust among older demographics or institutional investors could slow mainstream acceptance.
Ideological Conflicts Within Communities
Decentralized governance often leads to infighting (e.g., Bitcoin’s block size wars). Protracted disputes can stall development, fracture communities, and erode investor confidence.
20. Geopolitical and Macroeconomic Risks
Global events increasingly influence cryptocurrency markets in unpredictable ways.
Sanctions and Capital Controls
Authoritarian regimes may ban or co-opt cryptocurrencies to bypass sanctions (e.g., Russia) or enforce capital controls (e.g., Nigeria), creating regulatory arbitrage dangers for international investors.
Correlation With Traditional Markets
Once touted as "uncorrelated assets," major cryptocurrencies now often move in tandem with Nasdaq or risk-on assets. A global recession could trigger synchronized selloffs across crypto and traditional markets.
21. Psychological and Behavioral Pitfalls
Investor psychology plays an outsized role in crypto markets, often amplifying risks.
Overconfidence in Technical Analysis (TA)
Unlike traditional charts, crypto TA frequently fails due to extreme volatility and manipulation. Retail traders relying on indicators like RSI or Fibonacci retracements may suffer unexpected losses.
"HODL" Culture and Sunk Cost Fallacy
The meme-driven "HODL" mentality discourages rational profit-taking, leading investors to hold through bear markets despite fundamental deterioration.
22. Insurance and Recovery Challenges
Cryptocurrency’s irreversible transactions create unique recovery dilemmas.
Lost Private Keys
An estimated 20% of all mined Bitcoin is permanently inaccessible due to lost keys. Unlike bank accounts, no customer service exists to restore access.
Limited Insurance Coverage
While some exchanges offer partial insurance on custodial holdings, most DeFi protocols lack protections. The burden of security falls entirely on users.
Conclusion: Navigating Crypto Risks Strategically
Cryptocurrency investing isn’t inherently reckless—but it demands heightened due diligence. Unlike traditional finance, crypto markets lack safety nets, making risk management non-negotiable. Diversification, cold storage solutions, skepticism towards "guaranteed returns," and continuous education are essential. Regulatory clarity may eventually reduce some risks, but volatility and technological uncertainty will persist. Investors must honestly assess their risk tolerance before allocating capital to this dynamic but perilous asset class.
For those willing to embrace both the opportunities and hazards, cryptocurrencies remain a fascinating frontier—but one where vigilance is the price of participation.
---End of Part 3 / Final---



Understanding Different Types of Cryptocurrencies
The realm of cryptocurrencies has revolutionized how we perceive and utilize money, breaking conventional boundaries in the financial sector. As digital currencies continue to gain traction, it's essential to understand the diverse array of cryptocurrencies that comprise this dynamic digital landscape. This article explores some of the most prominent types and categories of cryptocurrencies, from pioneers like Bitcoin to innovative newcomers that are redefining blockchain applications.
Bitcoin: The Trailblazer
When discussing cryptocurrencies, Bitcoin often emerges as the first—and sometimes the only—name people recognize. Created in 2009 by an anonymous figure or group known as Satoshi Nakamoto, Bitcoin was the first decentralized cryptocurrency. Its primary innovation was the introduction of blockchain technology—a decentralized ledger that ensures the integrity of the financial transactions conducted with Bitcoin.
Bitcoin's design is inherently deflationary with its capped supply of 21 million coins. This scarcity model has contributed significantly to its value and positions Bitcoin not just as a currency but as a store of value, akin to "digital gold." Its decentralized nature is further reinforced by its network of miners, who validate and record transactions through complex problem-solving processes known as proof-of-work.
Ethereum: Beyond Currency
While Bitcoin was the first to introduce the concept of a decentralized currency, Ethereum emerged in 2015 to expand on blockchain technology. Founded by Vitalik Buterin and a team of developers, Ethereum introduced the idea of smart contracts—self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code.
Ethereum’s native cryptocurrency, Ether (ETH), fuels transactions and smart contracts on its platform. What sets Ethereum apart is its flexibility as a platform capable of supporting decentralized applications (dApps). This functionality has made Ethereum the foundation for a wide array of projects, including decentralized finance (DeFi) services and non-fungible tokens (NFTs).
Ripple: Engineered for Banks
Ripple challenges the concept of cryptocurrencies purely being for individuals by aiming at financial institutions. Created by Ripple Labs in 2012, Ripple functions not just as a digital currency (XRP) but also as a digital payment protocol. Unlike Bitcoin or Ethereum, Ripple isn’t based on blockchain technology but utilizes a consensus ledger and validating servers.
XRP's primary use is in international money transfers, where it helps reduce the friction and costs associated with cross-border transactions. Its appeal lies in its speed and scalability, making it particularly attractive to banks and financial service companies seeking more efficient alternatives to traditional SWIFT systems.
Litecoin: The Silver to Bitcoin’s Gold
Litecoin is often referred to as "the silver to Bitcoin's gold." Created by Charlie Lee in 2011, Litecoin was one of the earliest spinoffs of Bitcoin, or "altcoins." It was designed to serve as a lightweight, faster alternative for everyday transactions. Litecoin’s block time of just 2.5 minutes—significantly faster than Bitcoin's 10-minute block time—enables quicker transaction confirmations.
Litecoin employs a different proof-of-work algorithm called Scrypt, which makes it less complex to mine compared to Bitcoin. This design choice was intended to make mining more accessible to individuals using standard consumer hardware, promoting decentralization and user participation across a wide audience.
Stablecoins: Stability in the Volatile
In the world of cryptocurrencies, where volatility is a defining feature, stablecoins offer a refuge by pegging their value to stable assets, such as the US dollar or gold. Popular stablecoins like Tether (USDT), USD Coin (USDC), and Binance USD (BUSD) are valued one-to-one with the US dollar, ensuring that users can avoid the price fluctuations typical in the crypto space.
Stablecoins serve multiple roles: they act as safe havens during times of market volatility, serve as mediums of exchange, and facilitate trading on cryptocurrency exchanges by allowing lower-cost cross-border transactions. The demand for stablecoins demonstrates a significant step toward integrating crypto into mainstream financial systems by ensuring certainty and reliability in value transfer.
Conclusion
These cryptocurrencies represent just a snapshot of the ever-evolving digital currency ecosystem. While each offers unique features and serves different purposes—from digital gold like Bitcoin to transactional assets like XRP and Ether's innovative platform for decentralized applications—the core premise remains the same: leveraging technology to create secure, decentralized means of value exchange.
In the next part, we will delve deeper into other types of cryptocurrencies, exploring those with unique use-cases, and discussing innovative developments in this fascinating domain. Stay tuned to learn more about privacy coins, utility tokens, and how meme-inspired coins are reshaping the cryptocurrency world.
Privacy Coins: Ensuring Anonymity
As the adoption of cryptocurrencies continues to grow, so too does the focus on privacy and anonymity in transactions. This is where privacy coins come into play. Unlike other cryptocurrencies, privacy coins are designed to provide enhanced security by obscuring transaction details to protect the identities of the parties involved.
One of the most well-known privacy coins is Monero (XMR). Monero employs advanced cryptographic techniques, such as ring signatures and stealth addresses, to ensure the sender, receiver, and transaction amount remain confidential. This focus on privacy makes Monero an attractive option for individuals and entities seeking to conduct transactions without prying eyes.
Another significant privacy coin is Zcash (ZEC). Zcash offers the option of "shielded" transactions, leveraging a technology called zk-SNARKs (zero-knowledge succinct non-interactive arguments of knowledge), which ensures complete privacy by proving the transaction's validity without revealing any sensitive information.
Privacy coins, however, face regulatory scrutiny due to their potential misuse in illicit activities. This ongoing debate highlights the balance between individual privacy rights and the need for regulatory oversight in the financial ecosystem.
Utility Tokens: Empowering Digital Ecosystems
Utility tokens are a distinct class of cryptocurrencies that go beyond mere financial transactions. These tokens are intended to provide users with access to products or services within a specific blockchain ecosystem. They play a vital role in facilitating functionality and interactions on decentralized platforms.
Ethereum’s Ether (ETH) is a prime example, as it acts both as a cryptocurrency and a utility token, powering transactions and computational services on the Ethereum network. Similarly, Binance Coin (BNB) is used for reducing trading fees on the Binance Exchange and powering the Binance Smart Chain's numerous decentralized applications.
Another notable utility token is Chainlink (LINK), which bridges the gap between smart contracts and real-world data. Chainlink enables smart contracts to securely interact with external data sources, facilitating services ranging from weather data to financial information.
These tokens not only provide specific utilities within their ecosystems but also often represent a way for projects to raise capital through initial coin offerings (ICOs). The versatility and functionality of utility tokens have garnered them substantial attention, leading to their proliferation across diverse blockchain projects.
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs): Bridging Traditional and Digital Finance
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) have emerged as a concept that blends traditional fiat currencies with the technological advancements of digital currencies. Unlike cryptocurrencies, CBDCs are issued and regulated by central banks, representing the digital form of a nation's fiat currency.
Numerous countries, including China with its Digital Yuan and Sweden with the E-krona, are actively exploring or piloting CBDCs. These digital currencies aim to improve payment efficiency, reduce costs associated with cash handling, and promote financial inclusion. For instance, the Digital Yuan is designed to enhance the speed and security of domestic transactions while supporting the development of China's digital economy.
CBDCs can fundamentally transform how monetary policy is implemented, offering a direct channel between central banks and citizens. However, their introduction raises questions about privacy, cybersecurity, and the potential impact on the existing banking system. The global discourse around CBDCs signifies a pivotal shift in the way nations approach and adapt to the digitalization of their currencies.
Meme Coins: The Culture Drivers
While most cryptocurrencies serve practical purposes, meme coins are a whimsical yet significant part of the crypto ecosystem. These coins, often lacking any substantial technological innovation, gain value primarily through cultural virality and community momentum.
Dogecoin (DOGE) is the most prominent example of a meme coin. Originally created as a joke in 2013, featuring the Shiba Inu dog from the “Doge” meme, it has gained substantial popularity, fueled by internet culture and endorsements from high-profile figures like Elon Musk. Despite its humorous origins, Dogecoin has achieved mainstream acceptance and is used for tipping and charitable causes.
The success of Dogecoin has inspired the creation of other meme coins, such as Shiba Inu (SHIB), which further capitalizes on pop culture references and the power of community-driven speculation. Although these coins are primarily driven by humor, they underscore the influence of social media and digital culture in shaping the financial landscape.
Conclusion
The diversity among cryptocurrencies reflects the multifaceted nature of blockchain technology and digital finance. From privacy coins safeguarding anonymity to utility tokens enabling decentralized ecosystems, each type plays a unique role in advancing the goals and capabilities of the crypto space. Meanwhile, CBDCs illustrate the convergence of traditional finance with digital innovation, and meme coins highlight the cultural dimension of cryptocurrencies.
Understanding these different types of cryptocurrencies equips individuals and institutions with the knowledge to navigate this rapidly evolving landscape. In the concluding section of this article, we will explore upcoming trends and future outlooks for cryptocurrencies, delving into the technologies and innovations likely to shape the next era of finance. Stay tuned to uncover how emerging developments are poised to redefine our interaction with money.
The Rise of DeFi Tokens: Decentralizing Finance
Decentralized Finance, or DeFi, represents a transformative wave in the cryptocurrency sphere, aiming to recreate traditional financial systems like lending, insurance, and exchanges using blockchain technology. DeFi tokens serve as the backbone of these innovative financial services, allowing users to engage in activities once confined to centralized institutions, all while maintaining control over their assets.
One notable DeFi token is Uniswap (UNI), which powers the Uniswap protocol—a decentralized trading platform used for swapping various ERC-20 tokens on Ethereum. Uniswap's automated market maker (AMM) model and liquidity pools eliminate the need for traditional intermediaries, fostering a more open and accessible trading environment.
Another key player in the DeFi space is Maker (MKR). The Maker platform functions as a decentralized credit system on Ethereum, allowing users to lock in Ether as collateral to generate the Dai stablecoin. This process is governed by MKR holders, who vote on changes to the protocol, exemplifying decentralized governance in action.
DeFi tokens have not only democratized access to financial services but have also introduced novel concepts like yield farming and liquidity mining. These trends have attracted significant capital and interest, reflecting a growing appetite for financial autonomy and innovation.
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): Unique Digital Assets
In recent years, Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) have taken the digital world by storm, representing a distinct category within the cryptocurrency space. Unlike fungible cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum, each NFT is unique and cannot be exchanged on a one-to-one basis with another.
NFTs are typically used to certify ownership of digital assets, including art, music, videos, and even virtual real estate. The Ethereum blockchain is the leading platform for NFTs due to its robust support for smart contracts. Through smart contracts, creators can embed metadata describing the NFT's attributes and ownership details, making them viable for verifying authenticity and provenance.
CryptoPunks and Bored Ape Yacht Club are among the most iconic NFT collections, known for their distinctive art and exclusivity. Beyond collectibles, NFTs have expanded into domains like gaming and ticketing, allowing for new models of ownership and revenue streams for creators.
Despite their popularity, NFTs are not without controversy. Issues related to environmental impact, copyright infringement, and market volatility have sparked debates on their long-term sustainability. Nevertheless, NFTs represent an exciting frontier at the intersection of art, technology, and finance.
Crypto Futures: What Lies Ahead?
As the landscape of cryptocurrencies continues to evolve, several trends and developments are likely to shape its future trajectory. One such trend is the ongoing expansion of blockchain scalability solutions. Projects like Ethereum 2.0 aim to improve transaction throughput through mechanisms like sharding and Proof of Stake consensus, addressing current limitations of speed and cost.
Interoperability is another crucial area of focus. With numerous blockchains existing independently, solutions that facilitate seamless communication and transfer of assets across different networks are gaining importance. Polkadot and Cosmos are leading projects in this field, striving to create a more connected and cohesive blockchain ecosystem.
Moreover, regulatory clarity will play a pivotal role in determining the future of cryptocurrencies. As governments navigate the complexities of digital currencies, collaboration between industry stakeholders and regulators will be essential in establishing frameworks that protect investors while encouraging innovation.
Finally, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) with blockchain technology presents exciting possibilities. AI algorithms can enhance decision-making, security, and personalization in blockchain applications, opening new avenues for growth and creativity.
Conclusion
The vast array of cryptocurrencies available today reflects the innovation and diversity inherent in the blockchain space. From foundational coins like Bitcoin and Ethereum to specialized tokens driving DeFi, NFTs, and cross-border solutions, each type serves a distinct purpose and caters to varying user needs and preferences.
As the industry matures, these cryptocurrencies will continue to influence and reshape financial landscapes across the globe. Whether fostering financial inclusion, disrupting traditional systems, or crafting new cultural paradigms, cryptocurrencies are at the frontier of a revolution that transcends money, touching on technology, governance, and society.
Staying informed and adaptable will be crucial for anyone navigating the complexities of the cryptocurrency world. As innovations unfold and new concepts inevitably emerge, maintaining a forward-thinking perspective will be vital in harnessing the full potential of this transformative digital phenomenon.

Understanding Crypto Tokens: A Comprehensive Guide
In recent years, digital currencies have taken the financial world by storm, with Bitcoin and Ethereum often dominating the conversation. However, the burgeoning field of blockchain technology is not just restricted to these well-known cryptocurrencies. The realm of crypto tokens is equally dynamic and holds immense potential for reshaping how we interact with financial assets.
In this guide, we will delve into the complex yet fascinating world of crypto tokens. We'll demystify what they are, how they function, their varying types, and the crucial role they play within the broader blockchain ecosystem.
What Are Crypto Tokens?
Crypto tokens are a type of cryptocurrency, typically representing an asset or a utility. They are often built on an existing blockchain and can represent ownership of a resource, participation in a network, or access to specific services. Unlike traditional cryptocurrencies, which primarily serve as a medium of exchange, tokens are more versatile and can be programmed with unique functionalities.
Tokens are predominantly created through the process of an Initial Coin Offering (ICO), a method reminiscent of a traditional Initial Public Offering (IPO) but specific to the crypto world. During an ICO, a company or project offers tokens for sale to raise capital. These tokens can later be traded on various cryptocurrency exchanges, making them accessible to a global audience.
How Crypto Tokens Work
To understand how crypto tokens operate, it’s essential to recognize their dependency on smart contracts and blockchain technology. Most tokens are issued on blockchains like Ethereum, which supports smart contracts. Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. This code manages the transfer of tokens between parties, ensuring transparency and security without the need for a middleman.
When you purchase or receive a token, your transaction is recorded on the blockchain, an immutable and distributed ledger. The ownership of tokens and their associated rights or functions are thus guaranteed through blockchain technology, which ensures that records are tamper-proof and reliable.
Types of Crypto Tokens
Crypto tokens fall into several categories based on their intended use and functionality. Here are a few predominant types:
1. Utility Tokens
Utility tokens provide holders with future access to a product or service. These tokens are not meant for investment purposes but rather as a mechanism to facilitate services within a platform. A prominent example of a utility token is Binance Coin (BNB), which users leverage for fee reductions and other benefits within the Binance cryptocurrency exchange platform.
2. Security Tokens
Security tokens represent ownership in a real-world asset, such as shares in a company, real estate, or other valuable resources. They are subject to federal securities regulations and are designed to offer investors a degree of legal protection and oversight akin to traditional securities. Security tokens are a bridge between traditional finance and the dynamic world of blockchain.
3. Tokenized Assets
Tokenized assets are converted from their real-world form to a digital token on the blockchain. For example, physical assets like gold, real estate, or artwork can be tokenized, allowing fractional ownership and improved liquidity.
4. Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
Non-fungible tokens are unique and indivisible tokens that represent ownership of a specific item or piece of content, such as digital art, music, or collectibles. Unlike regular cryptocurrencies or other fungible tokens, NFTs cannot be exchanged on a one-to-one basis and track ownership and provenance of a single item on the blockchain.
The Importance of Crypto Tokens in the Blockchain Ecosystem
Crypto tokens play a pivotal role in the broader blockchain narrative by expanding its application beyond simple financial transactions. They are the building blocks for decentralized applications (DApps), allowing developers to create complex ecosystems with varied functionalities.
For businesses and entrepreneurs, tokens offer an innovative way to engage with investors and consumers. They facilitate fundraising through mechanisms like ICOs, enabling projects to gather capital while allowing early adopters a chance to partake in future successes.
Moreover, tokens empower decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, which are reshaping traditional financial services by offering new ways to lend, borrow, and grow investments without intermediaries. As tokens trade in decentralized exchanges, they contribute to liquidity and fluidity in the cryptocurrency markets.
As the digital world continues to evolve, understanding the intricacies of crypto tokens becomes essential for anyone interested in technology, finance, or innovation. Their applications are boundless, capable of disrupting industries and creating opportunities for new forms of economic interaction.
In the following sections, we will further explore the challenges facing crypto tokens and their potential future trajectory within a rapidly shifting landscape.
Challenges and Risks Associated with Crypto Tokens
While the prospects of crypto tokens are indeed captivating, they are not without inherent challenges and risks. Understanding these issues is crucial for anyone looking to invest in or develop projects centered around tokens.
1. Regulatory Uncertainty
One of the foremost concerns regarding crypto tokens is regulatory ambiguity. Different jurisdictions have varied stances on cryptocurrencies and tokens, leading to a patchwork of laws and regulations. This uncertainty can impact the development and distribution of tokens. In some regions, stringent regulations classify certain tokens as securities, subjecting them to the same rules as traditional financial instruments. This necessitates thorough legal compliance and can deter smaller projects due to cost constraints.
2. Security Concerns
The digital nature of crypto tokens makes them susceptible to various cyber threats. Smart contract vulnerabilities, improper coding, and sophisticated hacking techniques can lead to the loss of tokens. Frequent high-profile attacks on crypto exchanges and DeFi projects highlight the importance of robust security measures and audits. Consequently, token issuers need to prioritize these measures to safeguard investors and their projects.
3. Market Volatility
Crypto markets are notoriously volatile, and tokens are no exception. Prices can swing dramatically based on market sentiment, regulatory news, or technological advancements. Such volatility can pose a risk for investors, who must be prepared for the roller-coaster-like fluctuations. While this volatility can lead to significant gains, it can also result in steep losses, underscoring the importance of research and risk management.
4. Lack of Awareness and Understanding
The crypto industry is still in its infancy for many, and understanding the nuances of crypto tokens can be challenging. This knowledge gap creates a breeding ground for misinformation and fraudulent schemes. For wider adoption and acceptance, it's vital that educational resources are developed to bridge this gap. Educating potential investors and users about token functionalities and risks is crucial for informed decision-making.
The Evolution of Crypto Tokens
Despite the challenges, the evolution of crypto tokens continues unabated, driven by technological advancements and increased interest in decentralized ecosystems. Several trends are shaping the future of crypto tokens:
1. Rise of Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
DeFi represents a revolutionary shift within the financial industry. Utilizing crypto tokens, DeFi platforms offer traditional financial services including lending, borrowing, and trading with enhanced efficiency and accessibility. DeFi tokens often power these platforms, providing liquidity, governance rights, and other functionalities. As DeFi grows, tokens play a vital role in facilitating an inclusive financial system that transcends borders.
2. Tokenomics and Governance
Tokenomics, the study of the economics of tokens, is a critical aspect of token design and functionality. Projects now focus on creating well-balanced ecosystems where token supply, demand, and utility are aligned. Additionally, decentralized governance models are increasingly adopted, allowing token holders to participate in decision-making processes. This democratic approach brings a significant level of transparency and community engagement to projects.
3. Increased Tokenization of Assets
Asset tokenization is gaining traction as more industries recognize the benefits of blockchain technology. From real estate to commodities, tokenization simplifies ownership, reduces transaction costs, and enhances liquidity. As this trend expands, the traditional barriers surrounding illiquid assets will continue to erode, offering investors unique opportunities for diversification.
4. Integration with Internet of Things (IoT) and Other Technologies
The integration of crypto tokens with IoT and other emerging technologies presents exciting possibilities. Tokens can facilitate machine-to-machine transactions, creating a seamless interaction between smart devices and blockchain networks. This fusion promises to automate processes and improve efficiency across various sectors, from supply chain management to energy distribution.
The Future of Crypto Tokens
The landscape of crypto tokens is poised for continued innovation and adaptation, as new use cases emerge and existing structures mature. Key factors that will shape their future include:
1. Enhanced Regulation
Greater regulatory clarity and uniformity are anticipated to encourage wider adoption and investment in token projects. Constructive regulations can foster innovation, protect investors, and lend legitimacy to the crypto space. This will lead to increased confidence and participation from traditional financial institutions.
2. Interoperability Solutions
Interoperability remains a significant hurdle in the blockchain sector. As solutions develop to link different blockchain networks, crypto tokens will gain broader utility and acceptance. Efforts to standardize token protocols are underway, promising a future where tokens can seamlessly move between disparate systems.
3. Evolution of Smart Contracts
Advancements in smart contract technology will redefine token functionalities, enhancing their efficiency and security. Smarter, more intuitive contracts can foster complex interactions, allowing for unique applications that are beyond the current scope. These developments will open new avenues for the use of tokens in different sectors.
As the intrigue surrounding crypto tokens grows, so does the necessity for awareness and education. The continued evolution of this digital asset class will undeniably impact traditional business models and consumer interactions. Staying informed and embracing these emerging trends will be essential for capitalizing on the opportunities presented by crypto tokens.
Case Studies: Successful Crypto Token Applications
To illustrate the transformative potential of crypto tokens, examining real-world case studies can offer valuable insights. These examples showcase the diversity and impact of token applications across different sectors.
1. Chainlink (LINK)
Chainlink is a prominent player in the realm of decentralized oracles, connecting smart contracts with real-world data. The Chainlink Network relies on LINK tokens to incentivize nodes to provide reliable data inputs and outputs, ensuring the integrity of smart contracts. By bridging the gap between blockchain networks and real-world data, Chainlink has enabled a host of DeFi applications and highlighted the critical role of tokens in securing and facilitating these ecosystems.
2. Uniswap (UNI)
Uniswap is a decentralized exchange (DEX) that leverages the Ethereum blockchain to facilitate the swapping of various tokens without relying on a centralized authority. The introduction of the UNI token added a governance layer, granting holders voting rights to influence the platform's development and fee structures. This democratization of decision-making has reinforced community involvement, showcasing how governance tokens can empower users and drive platform improvements.
3. Basic Attention Token (BAT)
BAT has fundamentally changed the digital advertising industry by integrating blockchain with internet browsing. Through the Brave browser, users are rewarded with BAT tokens for viewing privacy-respecting ads. Advertisers benefit from more engaged and authentic interactions while users can monetize their attention. This ecosystem is a testament to how utility tokens can revamp traditional models, fostering a fairer value exchange between consumers and businesses.
Community Impact and Social Responsibility
Beyond their economic and technological implications, crypto tokens have the potential to foster substantial community impact and promote social responsibility. As the cryptocurrency landscape evolves, integrating ethical considerations into token projects can yield significant social benefits.
1. Financial Inclusion
Crypto tokens can lower barriers to financial services, providing access to underbanked populations globally. By offering more inclusive financial products and services, tokens empower individuals in regions where traditional banking services are limited or non-existent. Projects focusing on micro-lending, remittances, and savings mechanisms demonstrate the potential of tokens to address socio-economic challenges and promote financial equity.
2. Environmental Considerations
As awareness of the environmental impact of blockchain technology grows, there is a push towards developing eco-friendly solutions. Some token projects are actively looking to mitigate their carbon footprints by optimizing consensus mechanisms, investing in renewable energy sources, and promoting sustainability initiatives. The development of green blockchain technology and eco-conscious tokens reflects a broader commitment to minimizing environmental impacts.
3. Charitable Contributions and Social Causes
Tokens are being increasingly leveraged to support charitable causes, enabling direct contributions to nonprofits and social enterprises through blockchain-based platforms. These initiatives eliminate intermediaries, ensuring that more funds reach their intended target. Tokenized fundraising campaigns present a transparent and effective way to support humanitarian efforts and community development projects worldwide.
Guidelines for Engaging with Crypto Tokens
To successfully navigate the complex landscape of crypto tokens, it is essential to approach them with informed caution and strategic foresight. Here are some guidelines for individuals and businesses considering engaging with tokens:
1. Conduct Thorough Research
Understand the project's vision, team, and use case before investing in or developing a token. Due diligence involves evaluating the project's whitepaper, market potential, and its alignment with your own financial goals or business objectives. Knowing the competitive landscape and assessing the project's unique value proposition is crucial.
2. Diversify and Manage Risk
Avoid concentrated positions in a single token or project by diversifying your holdings across multiple assets. A diversified portfolio can mitigate risk and optimize potential returns. Additionally, adopting sound risk management strategies, such as setting stop-loss orders and understanding market trends, is vital for maintaining portfolio health.
3. Stay Updated on Regulation and Compliance
As regulatory environments evolve, keeping abreast of changes is vital to ensure compliance and legality in your token activities. Understanding local and international regulations can safeguard against unforeseen legal issues and enhance long-term stability.
4. Engage with the Community
Joining communities related to specific tokens or broader cryptocurrency discourse can provide valuable insights and foster collaboration. These engagements can further understanding, keep you informed about project developments, and support collective growth and innovation.
Conclusion: The Ongoing Journey of Crypto Tokens
Crypto tokens represent one of the most versatile and dynamic innovations emerging from the blockchain revolution. As their utility expands across various sectors, from finance and advertising to art and social enterprise, the importance of understanding and engaging with tokens cannot be overstated.
Despite the hurdles of regulatory ambiguity, security threats, and market volatility, the trajectory of crypto tokens is promising. With ongoing advancements in technology and a growing focus on ethical considerations, the future of crypto tokens looks bright, holding the potential to reshape industries and empower individuals worldwide.
As this journey continues, those who navigate the space with knowledge and strategic foresight will find themselves at the forefront of a new digital economy, where crypto tokens are integral to everyday interactions and opportunities.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/crypto-token.asp-v5-6774f213bd3b4deaac537f196990edff.png)

Риски инвестирования в криптовалюту: что нужно знать
Введение в мир криптовалют
Инвестирование в криптовалюту за последние годы приобрело значительную популярность благодаря своим высоким потенциальным доходам и возможности децентрализованного управления. Тем не менее, это направление финансовых вложений сопровождается рядом рисков, которые следует учитывать как опытным инвесторам, так и начинающим энтузиастам. В этой статье мы рассмотрим основные риски, связанные с криптовалютными инвестициями, и дадим рекомендации о том, как минимизировать возможные потери.
1. Высокая волатильность курса
Одним из самых заметных рисков при инвестировании в криптовалюты является их высокая волатильность. Курс биткойна или любой другой цифровой валюты может колебаться в течение одного дня на десятки процентов как в плюс, так и в минус. Это может быть как преимуществом для опытных трейдеров, умеющих зарабатывать на короткосрочных изменениях, так и серьезной опасностью для долгосрочных инвесторов.
Волатильность криптовалют обусловлена несколькими факторами: отсутствием регулирования, новостными событиями, манипуляциями на рынке и низкой ликвидностью. Для защиты своих инвестиций от влияния волатильности рекомендуется распределять средства между разными активами и сохранять только ту долю портфеля в криптовалютах, которую вы готовы рискнуть.
2. Риски мошенничества и безопасности
Криптовалютный рынок на сегодняшний день привлекает множество мошенников, которые пользуются недостатками системы и неопытностью инвесторов. Фейковые ICO, мошеннические биржи и схемы Понци — далеко не полный список проблем, с которыми может столкнуться инвестор в поисках крупной прибыли.
Кроме этого, важным аспектом остается проблема безопасности личных данных и средств. Хакеры часто атакуют биржи и электронные кошельки, чтобы похитить криптовалюту. Даже в случае надежного хранения средств на аппаратных кошельках, пользователи могут стать жертвами фишинга или социальной инженерии. Регулярное обновление средств защиты и использование надежных платформ поможет минимизировать данные риски.
3. Отсутствие регулирования
Хотя многие страны пытаются разрабатывать и вводить в действие законы, регулирующие криптовалютный рынок, в большинстве юрисдикций он до сих пор остается мало регулируемым. Это может привести к непредвиденным изменениям законодательства, которые могут кардинально изменить условия инвестирования, как это было, например, в Китае или Индии.
Отсутствие регулирования также способствует распространению мошенничества, увеличивает риски участия в недобросовестных проектах и делает рынок более уязвимым к манипуляциям. Инвесторы должны быть готовы к внезапным изменениям правовой среды и тщательно проверять легитимность платформ и проектов.
4. Технические сложности и риск потери средств
Криптовалютные технологии, такие как блокчейн, достаточно сложны для понимания. Неправильное использование кошельков, ошибочные транзакции или простая потеря ключей могут привести к безвозвратной потере средств. Даже опытные пользователи иногда совершают ошибки, которые приводят к утрате доступа к цифровым активам.
Эти технические сложности не только отпугивают новичков, но и повышают вероятность случайной потери. Чтобы избежать подобных рисков, стоит потратить время на изучение блокчейн-технологий, внимательно следить за проведением транзакций и регулярно создавать резервные копии ключей.
Заключение
Инвестирование в криптовалюту предлагает как большие возможности, так и значительные риски. Волатильность, вероятность мошенничества, отсутствие регулирования и технические сложности — это лишь часть проблем, с которыми могут столкнуться инвесторы. Понимание и анализ этих рисков, а также следование рекомендациям по их минимизации помогут сделать инвестиции более безопасными и успешными. Продолжение в следующей части статьи...
5. Регуляторные риски и правовая неопределенность
На сегодняшний день правовое регулирование криптовалют остается одной из наиболее спорных тем в мировой экономике. В то время как некоторые страны уже внедрили определенные нормы и правила для криптоактивов, значительная часть мировых держав еще только разрабатывает законодательство в этой области. Этот процесс сопровождается значительными правовыми непредсказуемостями.
Регуляторная неопределенность может существенно повлиять на стоимость криптовалют и уровень доверия к ним. Например, введение запретов на использование или добычу криптовалют может в одночасье обвалить их стоимость или сделать их незаконными в определенной юрисдикции. Инвесторы в таких условиях обязаны внимательно следить за новостями в области законодательства и быть готовыми к оперативным действиям в случае внезапных изменений правовой среды.
6. Навигация по рискам ликвидности
Ликвидность криптовалют сменяется от абсолютной доступности до трудностей с реализацией активов, особенно для менее известных токенов. Высокая ликвидность позволяет инвестору в любой момент продать активы по рыночной цене, однако на практике это не всегда возможно для ряда криптоактивов с малым объемом торгов.
Проблемы с ликвидностью делают рынок более уязвимым к манипуляциям, когда крупные игроки могут значительно воздействовать на рынок путем крупных транзакций. Инвесторам рекомендуется ориентироваться на крупные криптовалюты с устойчивым объемом торгов или тщательно анализировать малоликвидные активы перед вложениями, чтобы не попасть в ситуацию, когда продать актив будет крайне сложно или невозможно без значительных потерь.
7. Психологические и поведенческие риски
Психология играет не меньшую роль в инвестировании в криптовалюты, чем фактический анализ риска. Фома (страх упущенных возможностей) часто толкает инвесторов на совершение необдуманных действий: покупка активов на пике их стоимости или продажа в момент паники.
Поскольку криптовалютный рынок работает круглосуточно и непрерывно предлагает информацию о колебаниях курсов, инвестора может охватить неконтролируемый стресс, приводящий к скоропалительным инвестиционным решениям. Практика осознанного инвестирования, хладнокровный расчет и дисциплина помогут избежать ошибок, связанных с психологическим давлением рынка, и выработать успешную стратегию долгосрочных инвестиций.
8. Экологические риски
Криптовалюты, особенно такие как биткойн, подвергаются критике за значительное воздействие на окружающую среду. Процесс майнинга требует колоссального количества электроэнергии, что вызывает обеспокоенность экологов и привлекает внимание регуляторов к этому вопросу.
Экологические дебаты могут повлиять на индустрию в будущем, так как государства могут вводить ограничения на использование энергозатратных методов добычи или вводить дополнительные налоги, что существенно повлияет на общую экономику и стоимость криптоактивов. Эти факторы необходимо учитывать при планировании долгосрочных стратегий инвестирования.
Подведение итогов и рекомендации
Криптовалютные инвестиции, несмотря на всех описанных рисков, остаются привлекательными для множества инвесторов благодаря их потенциалу возврата. Однако для успешных вложений необходимо комбинировать финансовое чутье с глубоким пониманием всех возможных угроз и грамотным управлением инвестиционным портфелем.
- Регулярно обучайтесь и следите за новостями в мире криптовалют и блокчейн-технологий.
- Используйте стратегии диверсификации и распределяйте активы между различными формами инвестиций.
- Работайте с надежными и проверенными биржами и криптовалютными кошельками.
- Составьте для себя строгий план инвестиций и придерживайтесь его, не поддаваясь эмоциям.
Осознанный подход к инвестированию в криптовалюты позволит не только минимизировать риски, но и извлечь максимальную выгоду от данного формата вложений. Продолжение в следующей части статьи...
9. Конкуренция и инновации в криптоиндустрии
На фоне бурного развития криптовалютной индустрии появилось множество новых проектов, что создает серьёзную конкуренцию внутри рынка. Новые и альтернативные криптовалюты, инновации в блокчейн-технологиях и появление децентрализованных финансовых инструментов (DeFi) ведут к изменению ландшафта криптоэкономики.
Инвесторы должны учитывать, что не все проекты, которые кажутся перспективными, смогут выдержать конкуренцию и технические испытания. Многие из них исчезают, не успев набрать обороты, что приводит к потере инвестиций. Успех инвестирования во многом зависит от умения анализировать технологические инновации и оценивать их долгосрочную устойчивость и конкурентоспособность.
10. Ограниченная адаптация и принятие на рынке
Несмотря на рост интереса к криптовалютам, их распространение и интеграция в традиционные финансовые системы по-прежнему остаются относительно ограниченными. Возможности использования криптовалют для покупок товаров и услуг, вложения средств или банковского обслуживания пока что узки.
Ограниченная адаптация может сдерживать рост стоимости криптовалют в долгосрочной перспективе. Инвесторы должны быть готовы к возможным задержкам в распространении и адаптации криптоактивов в различных сферах и планировать свои инвестиции с учетом этого фактора.
11. Влияние макроэкономических факторов
Криптовалюты, учитывая их тесную связь с глобальной экономикой, подвержены воздействию макроэкономических факторов, включая изменения процентных ставок, мировые экономические кризисы и колебания валютных курсов традиционных фиатных денег.
Неожиданные изменения на мировом финансовом рынке могут привести к нестабильности криптовалют, изменяя инвестиционные планы и предсказываемые доходы. Инвесторам необходимо следить за глобальными экономическими тенденциями и быть готовыми адаптировать свои стратегии в соответствии с изменяющейся экономической обстановкой.
Заключительные соображения
Криптовалюты представляют собой уникальный класс активов с высокими потенциальными доходами, но и значительными рисками. Важно помнить, что успех в таких инвестициях требует не только финансовых вложений, но и знаний, терпения и умений анализировать быстро меняющуюся информацию.
- Перед началом инвестиций изучите основы блокчейн-технологий и принципы функционирования криптовалют.
- Уделите внимание изучению макроэкономических тенденций и паттернов рыночного поведения.
- Разработайте гибкий инвестиционный план с учетом возможных изменений как в вашем личном хозяйственном положении, так и в экономической среде.
Осознанный подход и строгий контроль над своими инвестициями помогут не только минимизировать риски, но и извлечь максимальную пользу из динамично развивающегося криптовалютного рынка. С течением времени рынок будет продолжать развиваться, и понимание основных принципов и тенденций станет ключом к успеху в этой захватывающей сфере финансового инвестиционного мира.
Zcash Price Analysis and Privacy-Focused Cryptocurrency Future
The cryptocurrency Zcash (ZEC) is a pioneering digital asset designed for financial privacy in an era of increasing surveillance. Launched in October 2016, Zcash offers users a unique choice between transparent and fully shielded transactions through advanced cryptographic technology. This article provides a comprehensive Zcash price prediction and explores the key developments fueling its recent surge, institutional adoption trends, and long-term potential in the evolving digital finance landscape.
Introduction to Zcash: Privacy by Choice
Zcash (ZEC) was developed by the Electric Coin Company (ECC), founded by Zooko Wilcox-O’Hearn, and is based on groundbreaking academic research from Johns Hopkins University. It represents a significant innovation in the blockchain space by implementing zk-SNARKs (Zero-Knowledge Succinct Non-Interactive Arguments of Knowledge). This technology allows for "shielded" transactions where the sender, receiver, and transaction amount are encrypted on the blockchain.
Unlike some privacy coins that mandate anonymity, Zcash's model of optional privacy provides flexibility. Users can choose transparent transactions for auditing or compliance purposes while opting for shielded transactions when confidentiality is required. This hybrid approach has become a critical factor in its appeal to institutional investors and its strategy for navigating regulatory landscapes.
Recent Zcash Price Surge and Market Performance
Late 2025 witnessed an extraordinary rally for Zcash, with the price surging over 700% since September of that year. This dramatic increase was not merely speculative; it was underpinned by tangible on-chain growth and broadening adoption. The price reached an all-time high of $748.1 in November 2025, a stark contrast to its all-time low of $15.75 in July 2024.
Key metrics from Q4 2025 show that over 30% of ZEC's circulating supply was held in shielded addresses, a clear signal of growing demand for its core privacy features.
This surge reflects a broader market trend where privacy-centric cryptocurrencies are gaining traction. Analysts point to increased institutional interest, proactive regulatory engagement by the ECC, and significant network upgrades as primary catalysts. The momentum has positioned Zcash as a frontrunner in the so-called "institutional crypto era," where privacy and compliance coexist.
On-Chain Strength and Network Security
The fundamentals of the Zcash network have demonstrated remarkable strength, supporting its price appreciation. Key on-chain metrics hit record highs in 2025, enhancing the network's security and decentralization.
- Network Hashrate and Mining Difficulty: Both achieved all-time highs, indicating robust participation from miners and a more secure Proof-of-Work consensus.
- Node Count: A growing number of full nodes strengthens network resilience and decentralization.
- Shielded Transaction Growth: The use of privacy features saw explosive adoption. Sapling shielded outputs grew from 154,000 in 2019 to over 2 million in 2025.
This data suggests that Zcash's price movement is increasingly driven by real utility and adoption, rather than pure speculation. The rising volume of shielded transactions validates the project's core value proposition and user demand for financial privacy.
Core Technology: How Zcash Ensures Privacy
At the heart of Zcash's functionality is its innovative use of zero-knowledge cryptography. Understanding this technology is crucial for evaluating the project's long-term viability and its comparative advantage.
The Power of zk-SNARKs
zk-SNARKs enable one party to prove to another that a statement is true without revealing any information beyond the validity of the statement itself. In Zcash, this allows the network to verify that a shielded transaction is valid—that the sender has sufficient funds and the transaction rules are followed—without revealing the addresses or amounts involved.
This technology provides a level of privacy and fungibility that is difficult to achieve on transparent blockchains like Bitcoin, where transaction histories are publicly visible and traceable. Fungibility, the property where each unit of a currency is interchangeable, is enhanced because the history of a shielded ZEC token cannot be tainted.
Unified Addresses and Protocol Upgrades
To improve user experience and interoperability, Zcash has implemented Unified Addresses (UAs). A UA is a single address that can receive both transparent and shielded funds, simplifying the process for users and services. This innovation removes complexity and reduces the risk of user error when dealing with different address types.
Furthermore, the network has undergone significant upgrades. The Q4 2025 Sapling upgrade improved proof generation speed by 90%, making shielded transactions faster and more efficient. The development of the Orchard shielded pool introduced even more advanced cryptographic primitives, paving the way for better scalability and mobile wallet support. These continuous improvements demonstrate a committed development roadmap focused on scalability and usability.
Zcash Halving and Economic Model
Similar to Bitcoin, Zcash incorporates a halving event approximately every four years to control its inflation rate. The most recent halving occurred in 2024, reducing the block reward for miners. This event is designed to create digital scarcity over time.
The halving mechanism reduces the rate at which new ZEC enters circulation. Following the 2024 halving, Zcash's inflation rate is projected to fall to 4% by late 2025. This decreasing supply, coupled with rising demand, is a classic economic driver that can positively influence price, assuming adoption continues to grow. The predictable, diminishing issuance schedule makes Zcash's monetary policy transparent and algorithmically enforced.
The Upcoming Shift to Proof-of-Stake
Looking ahead, one of the most significant planned changes for Zcash is its transition from a Proof-of-Work (PoW) to a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism. This shift, anticipated in the coming years, aims to address several key areas:
- Energy Efficiency: PoS eliminates the need for energy-intensive mining, aligning with broader sustainability trends.
- Staking Rewards: It will enable ZEC holders to earn rewards by participating in network validation, creating a new yield-generating use case for the asset.
- Enhanced Security and Governance: A PoS system can potentially offer different security guarantees and more formalized on-chain governance.
This fundamental evolution could substantially alter the investment thesis for Zcash, attracting a new cohort of investors interested in staking yields while maintaining exposure to a leading privacy asset.
Institutional Adoption and Regulatory Landscape for Zcash
The institutional adoption of Zcash has become a major narrative driving its growth and price stability. Major financial analysis firms, including Grayscale, have highlighted privacy protocols like Zcash as integral to the future of mainstream finance integration in 2026. This shift marks a maturation from being a niche privacy coin to an asset with recognized institutional utility.
Zcash's optional privacy model is a key factor in this institutional appeal. Unlike fully anonymous coins, Zcash allows for selective disclosure. This means that institutions can use shielded transactions for internal confidentiality while having the ability to provide transaction details to regulators or auditors when legally required. This compliance-friendly feature mitigates one of the largest risks associated with privacy-focused cryptocurrencies.
Analysts note that Zcash's hybrid transparency model is a strategic advantage for navigating the complex global regulatory landscape, making it a more viable candidate for traditional finance portfolios.
Tools Driving Adoption: Zashi Wallet and CrossPay
Technological advancements have lowered the barrier to using Zcash's privacy features. The development of the Zashi mobile wallet and CrossPay tools has been instrumental. These user-friendly applications simplify the process of creating and managing shielded transactions, moving privacy from a technically complex feature to an accessible consumer product.
- Zashi Wallet: A mobile-focused wallet designed for ease of use, bringing shielded transactions to everyday users.
- CrossPay: A suite of tools that facilitates seamless interactions between transparent and shielded pools, enhancing interoperability.
These tools directly contributed to the milestone where 30% of the circulating ZEC supply was held in shielded addresses by Q4 2025. This metric is a powerful indicator of real-world use, not just speculative holding.
Zcash Price Prediction and Market Analysis
Forecasting the future price of Zcash involves analyzing a complex interplay of technological upgrades, adoption metrics, regulatory shifts, and broader market sentiment. The wide range of predictions reflects the high-volatility, high-potential nature of the cryptocurrency asset class, especially for privacy coins.
Short-Term and Mid-Term Price Forecasts
Based on algorithmic models and technical analysis from late 2025, several short-term predictions were made. These models incorporate factors like moving averages, trading volume, and historical volatility.
The 50-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) was reported at $472.11, while the 200-day SMA was significantly lower at $175.20, indicating a strong upward trend over the medium term. Other key technical indicators included a Neutral Relative Strength Index (RSI) of 42.88 and a market volatility of 20.56% over the previous month.
- Conservative 2025 Prediction: $45 – $75. This scenario assumes moderate adoption and ongoing regulatory challenges.
- Moderate 2025 Prediction: $75 – $120. Driven by sustained institutional interest and successful network upgrades.
- Bullish 2025 Prediction: $120 – $200. Predicated on a surge in privacy demand and favorable regulatory clarity.
Long-Term Outlook and Analyst Consensus
Looking beyond 2025, the long-term outlook for Zcash is intrinsically tied to the value society places on financial privacy and the project's ability to execute its roadmap. The planned shift to Proof-of-Stake is a significant future catalyst that could redefine its economic model.
The average analyst price prediction for Zcash in 2025 ranged from $155 to $544, according to aggregated forecasts. This wide band underscores the uncertainty and high-stakes nature of the market.
Specific model-based forecasts from late 2025 projected a price of $549.95 by January 2026, representing a potential increase of over 42%. These models weigh on-chain strength, such as the rising count of Orchard shielded transactions from 302,300 in 2022 to nearly 914,000 in 2025, as a positive fundamental indicator.
Ultimately, long-term price appreciation will depend on Zcash maintaining its technological edge in the privacy sector, continuing to grow its shielded transaction volume, and successfully onboarding more institutional users into its ecosystem.
Zcash in the Competitive Privacy Coin Landscape
Zcash does not exist in a vacuum; it operates within a competitive sector of privacy-focused cryptocurrencies. Its unique value proposition and strategic choices differentiate it from key rivals like Monero (XMR) and Dash (DASH).
Zcash vs. Monero: Optional vs. Mandatory Privacy
The most direct comparison is often between Zcash and Monero. Monero uses ring signatures and stealth addresses to provide mandatory privacy on all transactions. This design prioritizes maximum anonymity but can draw sharper regulatory scrutiny.
Zcash, with its optional privacy features, offers a different philosophy. It provides the tools for strong privacy but allows users—particularly institutions—to operate within existing financial transparency frameworks when necessary. This key difference is why Zcash is often seen as more palatable for regulated financial entities exploring blockchain privacy solutions.
Zcash vs. Dash: Focus and Technology
Dash offers a feature called PrivateSend, which provides a mixing service for obfuscating transaction trails. However, its primary focus has expanded to include fast, low-cost payments. Zcash remains singularly focused on providing the strongest possible cryptographic privacy through zero-knowledge proofs.
The underlying technology sets them apart. Dash's privacy is an optional feature based on a mixing protocol, while Zcash's shielded pools use advanced zk-SNARKs to cryptographically conceal data. This technological depth gives Zcash a reputation for having one of the most robust privacy guarantees in the industry, albeit with a higher computational cost that is being addressed through upgrades like Sapling.
Market Position and Future Competitiveness
Zcash's position is strengthened by its academic foundations and ongoing research and development by the Electric Coin Company. Its proactive engagement with regulators and focus on creating compliance tools like viewing keys for selective disclosure are strategic advantages.
As the digital asset market matures, the demand for privacy is likely to grow, but so will regulatory pressure. Zcash's hybrid model may allow it to capture market share from both sides: users seeking uncompromising privacy and institutions requiring auditable compliance. Success will depend on executing its PoS transition, maintaining its security, and continuing to improve user experience to drive mainstream adoption of shielded transactions.
Risks, Challenges, and Investment Considerations for Zcash
Investing in Zcash, like any cryptocurrency, carries significant risks alongside its potential rewards. Understanding these challenges is crucial for any investor considering exposure to this privacy-focused digital asset. The primary risks stem from regulatory uncertainty, technological complexity, and intense market competition.
The regulatory environment for privacy coins remains a major concern. Governments and financial watchdogs worldwide are scrutinizing anonymous transactions due to potential misuse. While Zcash's optional privacy model offers a compliance pathway, some jurisdictions may still impose restrictions on its use. This creates a persistent overhang of regulatory risk that can impact price volatility and exchange listings.
Technological reliance on zk-SNARKs also presents challenges. The initial "trusted setup" for the system, while a monumental cryptographic achievement, has been a point of discussion. Furthermore, shielded transactions are computationally intensive, though recent upgrades like Sapling have dramatically improved performance. The ongoing development and security of these complex protocols are vital to the network's integrity and user trust.
Market Volatility and Sentiment Analysis
Zcash exhibits high volatility, characteristic of the broader cryptocurrency market. Data from late 2025 showed a 30-day volatility of 20.56%. The market sentiment at that time was measured as neutral, with a Relative Strength Index (RSI) of 42.88 and approximately 43% green trading days in the previous month.
- Price Sensitivity: ZEC price is highly sensitive to broader crypto market trends, Bitcoin's performance, and news related to privacy regulation.
- Adoption Cycle: Value is heavily tied to the adoption cycle of its privacy features, not just general crypto bull markets.
- Liquidity: While listed on major exchanges, its liquidity can be lower than top-tier assets like Bitcoin or Ethereum, potentially leading to sharper price swings.
Investors must be prepared for significant price fluctuations and should consider Zcash as a high-risk, high-potential-return component of a diversified portfolio, not a core holding.
The Future Roadmap: Proof-of-Stake and Beyond
The planned transition from Proof-of-Work (PoW) to Proof-of-Stake (PoS) represents the most significant upcoming change to the Zcash ecosystem. This shift is not merely a technical upgrade; it is a fundamental transformation of the network's economic and security model with profound implications.
Implications of the Proof-of-Stake Transition
The move to PoS is designed to address several critical areas. First, it will drastically reduce the network's energy consumption, aligning with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria that are increasingly important to institutional investors. Second, it will introduce staking rewards, allowing ZEC holders to earn yield by participating in network validation.
This creates a new, powerful use case for the token. Instead of just being a medium of exchange or store of value, ZEC becomes a productive asset. This could attract a different class of long-term investors and potentially reduce sell pressure as holders stake their coins. However, the transition itself is a complex engineering challenge that carries execution risk.
Continued Protocol Development and Ecosystem Growth
Beyond the PoS shift, the Electric Coin Company and the broader Zcash community continue to drive innovation. Future upgrades will likely focus on further improving the efficiency and user experience of shielded transactions, enhancing mobile wallet integration, and exploring new cryptographic advancements.
The growth of the Zcash ecosystem is also critical. This includes the development of decentralized applications (dApps) that leverage its privacy features, integration with DeFi protocols in a privacy-preserving manner, and partnerships with financial service providers. The success of tools like Zashi and CrossPay demonstrates the importance of building accessible gateways to Zcash's core technology.
Zcash Price Prediction Summary and Final Analysis
Synthesizing the various data points, analyst forecasts, and fundamental factors provides a multi-faceted view of Zcash's potential trajectory. Price predictions vary widely based on assumptions about adoption, regulation, and technological execution.
The most optimistic scenarios, projecting prices in the $500+ range, assume a "perfect storm" of favorable conditions: widespread institutional adoption, a benign regulatory climate for optional privacy, and a successful transition to an efficient Proof-of-Stake network that attracts stakers. These scenarios also factor in a sustained surge in demand for financial privacy tools globally.
More conservative forecasts, in the $75 to $150 range, anticipate moderate growth. They assume Zcash continues to develop its technology and user base but faces ongoing regulatory headwinds and competitive pressure. These models often view Zcash as a successful niche player rather than a mainstream financial asset.
The fundamental takeaway is that Zcash's value proposition is unique and increasingly relevant in a digitally surveilled world. Its future price will be a direct function of how successfully it can translate its technological superiority in privacy into broad-based, practical adoption.
Conclusion: The Strategic Value of Privacy in Crypto
Zcash stands at a unique crossroads between the foundational cypherpunk ideal of financial privacy and the practical realities of modern, regulated finance. Its journey from an academic concept to a cryptocurrency with a multi-billion dollar market cap and growing institutional interest validates the enduring demand for private transactional capability.
The project's recent performance, marked by a 700%+ price surge in late 2025, was not an isolated event. It was fueled by tangible metrics: record highs in shielded transaction outputs, a significant portion of the supply moving into private pools, and all-time highs in network security measures like hashrate. This indicates a maturation from speculative asset to a network with demonstrable utility.
The key strengths of Zcash are clear: its cutting-edge zk-SNARK technology, its flexible optional privacy model that enables compliance, a committed development team driving upgrades, and a clear roadmap including the transition to Proof-of-Stake. These factors combine to make it a leading contender in the privacy coin sector.
Final Investment Takeaways
For investors and observers, several critical points should be emphasized:
- Privacy is a Feature, Not a Bug: In an era of data monetization and surveillance, the demand for financial privacy is likely to grow, not diminish.
- Adoption is the Key Metric: Monitor on-chain data, especially the growth in shielded transactions and the percentage of supply in shielded addresses, as true indicators of value.
- Regulation is a Double-Edged Sword: While a risk, clear regulation could also legitimize compliant privacy tools like Zcash, separating it from fully anonymous alternatives.
- Execution is Everything: The successful delivery of the PoS transition and continued protocol improvements are non-negotiable for long-term success.
In conclusion, Zcash (ZEC) represents a sophisticated bet on the future of private digital finance. Its path forward is complex, navigating technological hurdles, regulatory landscapes, and market dynamics. However, its foundational technology, strategic positioning, and recent growth metrics suggest it is more than just another cryptocurrency. It is a pivotal project testing whether strong, user-controlled privacy can coexist with the transparency often demanded by the modern financial world. As the digital asset ecosystem evolves, Zcash's hybrid approach may well prove to be not just viable, but essential.
How to Buy Cryptocurrency: A Comprehensive Guide
The world of cryptocurrency is fast-paced and exciting, with countless opportunities for investment and financial growth. However, for those new to the arena, the process of buying cryptocurrency can seem daunting. This guide aims to simplify the process, providing clear and concise steps to help you buy cryptocurrency confidently and safely.
Understanding Cryptocurrency
Before delving into the purchase of cryptocurrency, it is crucial to understand what it is. Cryptocurrency is a decentralized digital currency that uses cryptographic techniques for secure transactions. Unlike traditional currencies, cryptocurrencies operate independently of a central bank, relying on a technology called blockchain to record and verify transactions.
Step 1: Choose a Reputable Cryptocurrency Exchange
The first step in purchasing cryptocurrency is selecting a reliable cryptocurrency exchange. An exchange is a platform that facilitates the buying, selling, and exchanging of cryptocurrencies. There are many exchanges available, each offering various features, fees, and levels of security.
Popular exchanges such as Coinbase, Binance, and Kraken are widely used for their user-friendly interfaces and robust security measures. When selecting an exchange, consider factors such as ease of use, supported currencies, fees, and security features. Performing thorough research and reading user reviews will help you make an informed decision.
Step 2: Set Up Your Account
Once you have selected a cryptocurrency exchange, the next step is to set up your trading account. This process typically involves registering with your email address and creating a secure password. After registering, you will likely need to complete a Know Your Customer (KYC) verification process. This process requires you to provide personal information and identification documents to comply with regulatory standards and ensure the security of the platform.
Step 3: Secure a Cryptocurrency Wallet
A cryptocurrency wallet is an essential tool for storing your digital assets safely. Wallets come in various forms, including software wallets (online or mobile applications) and hardware wallets (physical devices). While most exchanges provide integrated wallets, it is generally safer to use a separate wallet for enhanced security.
Software wallets are convenient for frequent trading and accessibility, while hardware wallets offer an additional layer of security by storing your private keys offline. Popular wallets include MetaMask, Trust Wallet, and Ledger for a range of security options and functionalities.
Step 4: Fund Your Account
With your account set up and a wallet secured, you are ready to fund your exchange account. Most platforms allow you to fund your account using fiat currencies such as USD, EUR, or GBP via bank transfer, credit/debit card, or online payment systems. Each method may have varying fees and processing times, so choose the one that best suits your needs.
Ensure that you are familiar with any deposit fees or minimum funding requirements before initiating a transaction. Once your account is funded, you will have the purchasing power to explore the cryptocurrency market.
Conclusion
By choosing a reputable exchange, setting up a secure account and wallet, and funding your account, you lay the foundation for entering the exciting world of cryptocurrency. These initial steps are crucial to ensure that your journey into cryptocurrency investment is secure and successful. In the next section, we will explore how to actually buy your chosen cryptocurrency and navigate the nuances of trading on the exchange. Stay tuned!









:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Primary_Images-421ad583334747108aab43b54152822f.jpg)
