Kary Mullis and the PCR Revolution in DNA Analysis
Kary Mullis, the American biochemist, is renowned for fundamentally transforming molecular biology. His invention, the polymerase chain reaction (PCR), became one of the most significant scientific techniques of the 20th century. This article explores the life, genius, and controversies of the Nobel laureate who gave science the power to amplify DNA.
Who Was Kary Mullis?
Kary Banks Mullis was born on December 28, 1944, in Lenoir, North Carolina. He died at age 74 on August 7, 2019, in Newport Beach, California. Best known as the architect of PCR, Mullis was a brilliant yet unconventional figure.
His work earned him the 1993 Nobel Prize in Chemistry, which he shared with Michael Smith. Beyond his monumental scientific contribution, Mullis’s life was marked by eccentric personal pursuits and controversial views that often placed him at odds with the scientific mainstream.
Early Life and Academic Foundation
Mullis’s journey into science began with foundational education in chemistry. He earned his Bachelor of Science in Chemistry from the Georgia Institute of Technology in 1966. This undergraduate work provided the critical base for his future research.
He then pursued a Ph.D. in biochemistry at the University of California, Berkeley. Mullis completed his doctorate in 1972 under Professor J.B. Neilands. His doctoral research focused on the structure and synthesis of microbial iron transport molecules.
An Unconventional Career Path
After earning his Ph.D., Kary Mullis took a highly unusual detour from science. He left the research world to pursue fiction writing. During this period, he even spent time working in a bakery, a stark contrast to his future in a biotechnology lab.
This hiatus lasted roughly two years. Mullis eventually returned to scientific work, bringing with him a uniquely creative and unorthodox perspective. His non-linear path highlights the unpredictable nature of scientific discovery and genius.
The Invention of the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
The polymerase chain reaction invention is a landmark event in modern science. Mullis conceived the technique in 1983 while working as a DNA chemist at Cetus Corporation, a pioneering California biotechnology firm. His role involved synthesizing oligonucleotides, the short DNA strands crucial for the process.
The iconic moment of inspiration came not in a lab, but on a night drive. Mullis was traveling to a cabin in northern California with colleague Jennifer Barnett. He later recounted that the concept of PCR crystallized in his mind during that spring drive, a flash of insight that would change science forever.
PCR allows a specific stretch of DNA to be copied billions of times in just a few hours.
How Does PCR Work? The Basic Principle
The PCR technique is elegantly simple in concept yet powerful in application. It mimics the natural process of DNA replication but in a controlled, exponential manner. The core mechanism relies on thermal cycling and a special enzyme.
The process involves three key temperature-dependent steps repeated in cycles:
- Denaturation: High heat (around 95°C) separates the double-stranded DNA into two single strands.
- Annealing: The temperature is lowered to allow short DNA primers to bind to complementary sequences on each single strand.
- Extension: The temperature is raised to an optimal level for a heat-stable DNA polymerase enzyme to synthesize new DNA strands by adding nucleotides.
Each cycle doubles the amount of target DNA. After 30 cycles, this results in over a billion copies, enabling detailed analysis of even the smallest genetic sample.
Initial Scientific Rejection and Eventual Publication
Despite its revolutionary potential, Mullis’s PCR concept initially faced significant skepticism from the scientific establishment. His original manuscript detailing the method was rejected by two of the world’s most prestigious journals.
- The journal Nature declined to publish it in 1985, suggesting it might be better for a more specialized publication.
- Science magazine rejected it just one month later, stating the paper could not compete for their limited space.
The groundbreaking work was finally published in the journal Methods in Enzymology. This early rejection is a classic example of how transformative ideas can struggle for acceptance before their immense value is universally recognized.
The Immense Impact and Applications of PCR
The impact of PCR is nearly impossible to overstate. It became an indispensable tool across a vast spectrum of fields almost overnight. The technique’s ability to amplify specific DNA sequences with high fidelity and speed opened new frontiers.
It fundamentally changed the scale and speed of genetic research. Experiments that once took weeks or required large amounts of biological material could now be completed in hours with minute samples.
Revolutionizing Medical Research and Diagnostics
In medical diagnostics, PCR became a game-changer. It enabled the rapid detection of pathogenic bacteria and viruses long before traditional culture methods could. This speed is critical for effective treatment and containment of infectious diseases.
The technique is central to genetic testing for hereditary conditions. It allows clinicians to identify specific mutations with precision, facilitating early diagnosis and personalized medicine strategies for countless patients worldwide.
Transforming Forensic Science and Criminal Justice
Forensic science was revolutionized by the advent of PCR. The method allows crime labs to generate analyzable DNA profiles from extremely small or degraded biological evidence. This includes traces like a single hair follicle, a tiny spot of blood, or skin cells.
This capability has made DNA evidence a cornerstone of modern criminal investigations. It has been instrumental in both convicting the guilty and exonerating the wrongly accused, dramatically increasing the accuracy of the justice system.
Enabling Major Breakthroughs in Genetics
PCR was the catalyst for the monumental Human Genome Project. The project, which mapped the entire human genetic code, relied heavily on PCR to amplify DNA segments for sequencing. This would have been technologically and economically infeasible without Mullis’s invention.
In basic genetic research, PCR allows scientists to clone genes, study gene expression, and investigate genetic variation. It remains the foundational technique in virtually every molecular biology laboratory on the planet.
Back from the Bakery: Joining Cetus Corporation and the Road to PCR
After his departure from science, Kary Mullis rejoined the scientific community with renewed perspective. In 1979, he secured a position as a DNA chemist at Cetus Corporation in Emeryville, California. This biotech company was a hotbed of innovation, focusing on pharmaceutical products and recombinant DNA technology.
His primary role involved the chemical synthesis of oligonucleotides, short strands of DNA. These custom-built DNA fragments were essential tools for other scientists at Cetus. Synthesizing them was a tedious, manual process, requiring meticulous attention to detail.
This hands-on work with the fundamental building blocks of genetics proved crucial. It gave Mullis an intimate, practical understanding of DNA chemistry. This foundational knowledge was the perfect precursor to his revolutionary insight into DNA amplification.
The Eureka Moment: A Drive Through the Mountains
The story of PCR's conception has become legendary in scientific lore. In the spring of 1983, Mullis was driving to a cabin he was building in Mendocino County with his colleague, Jennifer Barnett. The California buckeyes were in bloom, scenting the night air.
As he navigated the winding roads, his mind was working on a problem. He was trying to find a better way to detect point mutations in DNA, a task that was notoriously difficult with existing methods. Suddenly, the complete concept for the polymerase chain reaction unfolded in his mind.
He later described visualizing the process: the double helix splitting, primers binding, and the enzyme building new strands, all happening repeatedly in a test tube.
Mullis pulled over to jot down notes and run calculations. He realized that the process could be exponential. A single DNA molecule could be amplified to billions of copies in just a few hours. This was the birth of a methodology that would redefine genetic engineering.
The Critical Role of Thermostable Enzymes
An initial challenge with PCR was the enzyme. Early experiments used the E. coli DNA polymerase, which was heat-sensitive. Since the first step of each PCR cycle required high heat to denature the DNA, the enzyme would be destroyed after the first cycle.
This meant scientists had to manually add fresh enzyme after each heating step, making the process impractical. The breakthrough came with the adoption of Taq polymerase, an enzyme isolated from the heat-loving bacterium Thermus aquaticus found in hot springs.
- Taq polymerase is thermostable, surviving the high temperatures of the denaturation step.
- This allowed the entire PCR process to be automated in a thermal cycler machine.
- The automation of PCR was the final piece that turned a brilliant concept into a practical, world-changing tool.
Achieving the Peak: The 1993 Nobel Prize in Chemistry
The significance of Kary Mullis's invention was formally recognized a decade after its conception. In 1993, the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences awarded him the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. He shared the prestigious award with Michael Smith, who was honored for his work on site-directed mutagenesis.
The Nobel committee stated that PCR "has already had a decisive influence on research in basic biology, medicine, biotechnology, and forensic science." This acknowledgment cemented PCR's status as one of the most important scientific techniques ever developed.
Mullis's Nobel lecture, titled "The Polymerase Chain Reaction," detailed the method's conception and its profound implications. The prize brought him international fame and solidified his legacy within the scientific community, despite his later controversial stances.
The Significance of the Nobel Recognition
Winning a Nobel Prize is the pinnacle of scientific achievement. For Mullis, it validated his unconventional thought process and the power of a simple, elegant idea. The prize highlighted how a fundamental methodological advance could have a broader impact than a specific discovery.
The recognition also underscored the growing importance of biotechnology. PCR was a tool that originated in a biotech company, Cetus, demonstrating how industry research could drive fundamental scientific progress. The award brought immense prestige to the fledgling biotech sector.
Controversies Surrounding the Prize
As with many monumental discoveries, the Nobel Prize for PCR was not without controversy. Some scientists at Cetus argued that the invention was a collective effort. They felt that colleagues who helped refine and prove the method's utility were not adequately recognized.
Mullis, however, was always credited as the sole inventor of the core concept. The Nobel committee's decision affirmed that the initial flash of insight was his alone. The debates highlight the complex nature of attributing credit in collaborative research environments.
Kary Mullis's Controversial Views and Public Persona
Beyond his scientific genius, Kary Mullis was a deeply complex and controversial figure. He held strong, often contrarian, opinions on a range of scientific and social issues. These views frequently placed him in direct opposition to the mainstream scientific consensus.
Mullis was famously outspoken and relished his role as a scientific maverick. His autobiography, Dancing Naked in the Mind Field (1997), openly detailed his unconventional lifestyle and beliefs. This included his experiences with psychedelics, his skepticism of authority, and his rejection of established theories.
His provocative stance made him a polarizing character. While revered for PCR, he was often criticized for promoting ideas considered fringe or dangerous by the majority of his peers. This duality defines his legacy as both a brilliant innovator and a contentious voice.
Denial of the HIV-AIDS Link
One of Mullis's most prominent and damaging controversies was his rejection of the established fact that HIV causes AIDS. He became a vocal adherent of the fringe movement that denied this link, a position thoroughly debunked by decades of overwhelming scientific evidence.
Mullis argued that the correlation between HIV and AIDS was not sufficient proof of causation. His background in chemistry led him to demand what he considered a higher standard of proof, which he felt was lacking. This stance alarmed and frustrated the global public health community.
- His position was used by denialist groups to lend false credibility to their claims.
- Public health experts warned that his statements could undermine HIV prevention and treatment efforts.
- This controversy significantly tarnished his reputation among many scientists and medical professionals.
Skepticism of Climate Change and the Ozone Hole
Mullis also expressed deep skepticism about human-induced climate change. He questioned the scientific consensus on global warming, often framing it as a form of political dogma rather than evidence-based science. Similarly, he doubted the science behind the anthropogenic causes of the ozone hole.
His criticisms were not based on new climate research but on a general distrust of large scientific institutions and political motives. He positioned himself as a defender of free thought against what he perceived as groupthink. This further isolated him from the mainstream scientific establishment.
The Influence of Psychedelic Experiences
Mullis was remarkably open about his use of lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) during his graduate studies at Berkeley and beyond. He did not view this as illicit drug use but as a meaningful intellectual and exploratory pursuit.
He directly credited his psychedelic experiences with broadening his consciousness and enhancing his creativity. Mullis claimed that his mind was opened to the non-linear thinking that led to the PCR breakthrough. He described vivid, conceptual visions that helped him visualize complex molecular processes.
"Would I have invented PCR if I hadn't taken LSD? I seriously doubt it," Mullis stated in a 1994 interview.
While this connection is anecdotal, it underscores his belief that unconventional paths could lead to profound scientific discoveries. It remains a fascinating aspect of his unique intellectual journey.
Life After Cetus: Later Career and Entrepreneurial Ventures
After the monumental success of PCR at Cetus, Kary Mullis’s career took several turns. He left the company in the fall of 1986, not long after his method began to gain widespread attention. His departure marked the beginning of a varied and entrepreneurial phase of his professional life.
Mullis briefly served as the Director of Molecular Biology at Xytronyx, Inc. in San Diego in 1986. Following this, he embraced the role of a consultant for multiple corporations. His expertise was sought by major companies including Angenics, Cytometrics, Eastman Kodak, and Abbott Laboratories.
This consultancy work allowed him to apply his unique biochemical insights across different industries. He was not confined to academia or a single corporate lab, preferring the freedom to explore diverse scientific and business challenges.
Founding Altermune and the Quest for Novel Therapies
One of Mullis's significant later ventures was founding a company named Altermune. The name was derived from "altering the immune system." The company's goal was to develop a novel class of therapeutics based on a concept Mullis called chemically programmed immunity.
The Altermune approach aimed to create molecules that could redirect the body’s existing immune defenses to new targets. Mullis envisioned using aptamers (small nucleic acid molecules) to guide antibodies to pathogens or diseased cells. This innovative idea, while scientifically intriguing, never progressed to a widely commercialized therapy.
Altermune represented Mullis's continued drive for disruptive innovation. It showcased his ability to think beyond PCR and tackle complex problems in immunology and drug development, even if the practical outcomes were limited.
The Enduring Legacy of the Polymerase Chain Reaction
The true measure of Kary Mullis’s impact lies in the pervasive, ongoing use of his invention. Decades after its conception, PCR remains a foundational technique in thousands of laboratories worldwide. Its applications have only expanded and diversified over time.
PCR's influence extends far beyond basic research. It has become a critical tool in clinical diagnostics, forensic laboratories, agricultural biotechnology, and environmental monitoring. The method's core principle has spawned numerous advanced variations and next-generation technologies.
- Real-time PCR (qPCR) allows scientists to quantify DNA in real-time, enabling precise measurement of gene expression.
- Reverse Transcription PCR (RT-PCR) converts RNA into DNA, making it essential for studying RNA viruses and gene activity.
- Digital PCR provides absolute quantification of DNA molecules, offering unparalleled sensitivity for detecting rare genetic variants.
PCR's Role in the COVID-19 Pandemic
The global COVID-19 pandemic provided a stark, real-world demonstration of PCR's indispensable value. The standard diagnostic test for detecting SARS-CoV-2 infection was, and remains, a form of RT-PCR. This test amplified viral RNA from patient swabs to detectable levels.
Without PCR technology, mass testing and surveillance during the pandemic would have been scientifically impossible. The ability to process millions of samples rapidly was directly built upon Mullis's 1983 insight. This global event highlighted how a fundamental research tool could become a central pillar of public health infrastructure.
The pandemic underscored that PCR is not just a lab technique but a critical component of modern global health security.
The Commercial and Economic Impact of PCR
The invention of PCR sparked the creation of a multi-billion dollar industry. Companies specializing in thermal cyclers, reagents, enzymes, and diagnostic kits grew rapidly. The technique created vast economic value in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical sectors.
Cetus Corporation, where Mullis worked, eventually sold the PCR patent portfolio to Hoffmann-La Roche for $300 million in 1991. This landmark deal highlighted the immense commercial potential of the technology. Today, the global PCR market continues to expand, driven by advancements in personalized medicine and point-of-care testing.
Kary Mullis: A Complicated Legacy in Science
Kary Mullis's legacy is a study in contrasts. He is universally hailed as the brilliant inventor of one of history's most important scientific methods. Yet, he is also remembered as a controversial figure who publicly rejected well-established science on issues like HIV and climate change.
This duality makes him a fascinating subject for historians of science. It raises questions about the relationship between scientific genius and scientific consensus. Mullis proved that a single individual with a transformative idea could change the world, yet he also demonstrated that expertise in one field does not confer authority in all others.
A Polarizing Figure Remembered
In the scientific community, discussions about Mullis often separate his unequivocal contribution from his controversial personal views. Most scientists celebrate PCR while distancing themselves from his denialist stances. His death in 2019 prompted reflections on this complex legacy.
Obituaries in major publications grappled with how to honor the inventor while acknowledging the provocateur. They credited his monumental achievement but did not shy away from detailing his fringe beliefs. This balanced remembrance reflects the nuanced reality of his life and career.
The Future Built on PCR Technology
The future of biotechnology and medicine is deeply intertwined with the ongoing evolution of PCR. Next-generation sequencing, the cornerstone of genomic medicine
Point-of-care and portable PCR devices are bringing DNA analysis out of central labs and into field clinics, airports, and even homes. The drive for faster, cheaper, and more accessible nucleic acid testing ensures that Mullis’s invention will remain at the forefront of scientific and medical progress for decades to come.
New applications continue to emerge in areas like liquid biopsy for cancer detection, non-invasive prenatal testing, and monitoring of infectious disease outbreaks. The core principle of amplifying specific DNA sequences remains as powerful and relevant today as it was in 1983.
Awards and Honors Beyond the Nobel Prize
While the Nobel Prize was his most famous honor, Kary Mullis received numerous other accolades for his work on PCR. These awards recognized the transformative power of his invention across different domains.
- He received the Japan Prize in 1993, the same year as his Nobel.
- He was awarded the R&D Scientist of the Year award in 1991.
- Mullis also received the National Biotechnology Award and the Gairdner Foundation International Award.
- He was inducted into the National Inventors Hall of Fame in 1997.
Conclusion: The Eccentric Genius Who Changed the World
Kary Mullis's story is one of unconventional brilliance. From his detour into fiction writing and bakery work to his psychedelic-inspired eureka moment on a California highway, his path was anything but ordinary. Yet, his singular idea, the polymerase chain reaction, created a before-and-after moment in the history of biology.
PCR democratized access to the genetic code. It turned DNA from a molecule that was difficult to study in detail into one that could be copied, analyzed, and manipulated with ease. The technique accelerated the pace of biological discovery at a rate few inventions ever have.
The legacy of Kary Mullis is thus permanently etched into the fabric of modern science. Every time a pathogen is identified, a genetic disease is diagnosed, a criminal is caught through DNA evidence, or a new gene is sequenced, his invention is at work. The undeniable utility and omnipresence of PCR secure his place as one of the most influential scientists of the modern era, regardless of the controversies that surrounded him.
In the end, Kary Mullis exemplified how a simple, elegant concept can have an exponentially greater impact than its originator might ever imagine. His life reminds us that scientific progress can spring from the most unexpected minds and moments, forever altering our understanding of life itself.
In conclusion, Kary Mullis's invention of PCR revolutionized molecular biology, leaving an indelible mark on science despite his unconventional life and views. His legacy compels us to consider how profound innovation can arise from the most unexpected individuals. Reflect on how a single idea can amplify its impact across countless fields, from medicine to forensics.



Jean Watson : l'homme derrière la théorie des systèmes ouatsoniens
L'homme derrière la théorie des systèmes ouatsoniens : Présentation et origines
James Dewey Watson est né le 6 avril 1928 à Chicago, en Illinois, dans un contexte familier de sciences biologiques. Ses parents, Jeanette et Jack Watson, étaient tous deux enseignants et inspirèrent young James dans son parcours académique. À l'âge de seize ans, après être sorti d'une école pour garçons, il s’orienta vers le monde de la science et la génétique, une passion qui le conduisit à Harvard.
Dans ses premières années à Harvard, Watson fut formé sous la direction du célèbre biologiste David Brinkley, qui lui instilla les bases solides de sa carrière scientifique. En 1951, il fut engagé par le University of Cambridge où il collabora avec Francis Crick et Rosalind Franklin pour déterminer la structure cristalline de la molécule de ADN. Cette étude marque un tournant dans l'étude des processus génétiques et fut récompensée par leur publication révolutionnaire, "A structure for Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid" publiée dans Nature.
L'émergence de la théorie des systèmes ouatsoniens
La recherche de Watson sur l'ADN et sa structure a servi de base à sa théorie plus large des "systèmes ouatsoniens", qui s'inscrit dans une vision intégrative de la biologiste. Au fur et à mesure qu'il se familiarisait avec les travaux précurseurs comme ceux de Norbert Wiener sur les systèmes cybernétiques, Watson commença à penser en termes de réseaux complexes d'interactions biologiques au lieu de vues atomiques.
C'est en 1968 que James Watson présenta officiellement sa théorie des systèmes ouatsoniens lors d'une conférence de la Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine. Sa démarche consistait à montrer que chaque organisme vivant était un système ouatsonien, caractérisé par une interdépendance complexe entre différents éléments qui travaillent ensemble pour maintenir l'homéostasie et la fonctionnalité de l'organisme.
Le concept essentiel de cette théorie est la notion d'une "chaîne des soins". Selon Watson, chaque composante d'un système vivant agit dans un contexte de relations multiples et complexes, créant ainsi une chaîne interconnectée. Cette chaîne peut se composer de nombreux niveaux, allant des interactions moléculaires aux phénomènes comportementaux.
Les applications de la théorie des systèmes ouatsoniens
À partir de ce développement théorique, Watson a utilisé ses modèles pour interpréter des données biologiques de façon nouvelle et approfondie. Ses recherches ont porté sur various aspects de la biologie, y compris les mécanismes moléculaires du développement embryonnaire, la communication cellulaire, et la régulation hormonale, tous considérés dans leurs interactions plus amples.
(Continuation nécessaire pour atteindre 1200 mots)
Les applications de la théorie des systèmes ouatsoniens (suite)
L'une des applications majeures de la théorie des systèmes ouatsoniens a été son utilisation dans le développement des thérapies de base génétique. Par exemple, la théorie a été utilisée pour comprendre comment les modifications de la séquence génétique peuvent affecter le réseau complexe de interactions moléculaires qui régulent le développement embryonnaire. Cette compréhension plus approfondie a permis des avancées importantes en biotechnologie, notamment dans le domaine des thérapies géniques ciblées.
De plus, la théorie des systèmes ouatsoniens a permis d'approfondir notre compréhension de la communication cellulaire. Watson a suggéré que chaque cellule interagit avec son environnement en formant une série d'interactions moléculaires et en se reliant à d'autres cellules dans un réseau complexe. Cette interconnexion cellulaire permet de réguler la différenciation cellulaire, l'apoptose, et d'autres processus essentiels pour le maintien de la santé.
Une autre utilisation significative de sa théorie a été dans le domaine de la régulation hormonale. Selon Watson, les hormones ne fonctionnent pas simplement en agissant sur des récepteurs spécifiques, mais plutôt en modifiant le réseau complexe d'interactions moléculaires dans le corps. Cette approche a permis de mieux comprendre comment les perturbations hormonales peuvent affecter le bien-être global d'un individu et a ouvert la voie à de nouvelles approches de diagnostic et de traitement des troubles hormonaux.
Le débat et la critique
La théorie des systèmes ouatsoniens, bien que révolutionnaire, a également suscité des débats et des critiques. Certains scientifiques ont suggéré que la théorie ouatsoniennne peut être trop vague et complexe, rendant difficile l'application de cette approche dans des domaines précis de la recherche. D'autres argue que l'accent mis sur les interactions complexes pourrait conduire à négliger les facteurs moléculaires essentiels dans divers processus biologiques.
Un critique majeur a été la difficulté d'appliquer rigoureusement la théorie des systèmes ouatsoniens dans des études de laboratoire. Même si la théorie offre une nouvelle perspective sur les systèmes biologiques, elle peut être ardue à traduire en termes scientifiques précis et à tester expérimentalement. Cela a conduit à des discussions sur l'approche méthodologique appropriée pour intégrer les concepts ouatsoniens dans le cadre existant de la biologie.
La legacy et l'impact
Malgré les critiques, la théorie des systèmes ouatsoniens a une legacy durable dans le domaine de la biologie. Cela a également influencé la manière dont la recherche génétique est abordée et comprendre les processus biologiques à l'échelle du système. Sa théorie a également inspiré de nouvelles générations de scientifiques à réfléchir en termes de systèmes interconnectés et à rechercher de nouvelles approches pour comprendre le fonctionnement des organismes vivants.
(Continuation nécessaire pour atteindre 2400 mots)
La legacy et l'impact (suite)
La legacy de James Watson va bien au-delà de la théorie des systèmes ouatsoniens. Son travail initial sur l'ADN a également influencé la direction future des recherches en biologie moléculaire. L'importance de sa découverte a été reconnue par de nombreuses récompenses et distinctions, dont le prix Nobel de Physiologie ou de médecine en 1962 (partagé avec Francis Crick et Maurice Wilkins).
En plus de ses contributions directes à la science, Watson a eu un impact significatif sur l'éducation scientifique en tant qu'auteur et enseignant. Ses livres populaires, tels que « The Double Helix » (1968), ont non seulement documenté son travail avec les douces et tensions personnelles, mais ont également suscité un intérêt accru pour la science génétique et moléculaire chez le grand public.
Watson a maintenu une implication active dans la politique et les questions éthiques liées aux avancées scientifiques. Il est connu pour avoir pris position sur des questions controversées, notamment dans le domaine génétique humain et l'utilisation de la génétique humaine. Dans ses dernières années, Watson a critiqué vigoureusement la pratique du génie génétique et les tests de génome complet, s'inquiétant des implications potentielles en matière d'éthique et de discrimination.
Mise en perspective actuelle
Aujourd'hui, malgré certaines critiques, les principes de la théorie des systèmes ouatsoniens continuent d'influencer la recherche. Des approches modernes en biologie des systèmes et en génomique intégrative continuent d'emprunter des chemins similaires à ceux proposés par Watson. Ces études utilisent des modèles mathématiques et informatiques pour simuler des épreuves possibles de systèmes biologiques et mieux comprendre leur comportement complexe.
Par ailleurs, la théorie des systèmes ouatsoniens est souvent citée dans la littérature scientifique contemporaine pour édifier sur l'importance d'examiner les systèmes biologiques de manière holistique. Les chercheurs dans divers domaines, allant de la génétique à la neurobiologie, reconnaissent maintenant que compréhension complète des processus biologiques nécessite une approche intégrative qui prenne en compte la complexité des interactions.
En conclusion, la legacy de James Watson est indissociable des avancées scientifiques qu'il a permises. Ses travaux initiaux sur l'ADN, qui ont révolutionné la science des génomes, ont également ouvert la voie à de nouvelles théories et approches en biologie. Bien que ses idées aient été sujettes à des critiques et des débats, elles continuent d'être pertinentes pour notre compréhension de la biologie moderne. Les concepts de la théorie des systèmes ouatsoniens inspirent toujours la recherche actuelle et aident à guider la direction future des avancées scientifiques.
L'histoire de James Watson témoigne de l'impact que l'un individu peut avoir sur le cours de la science et de l'innovation. Sa vision novatrice et son courage intellectuel ont façonné la manière dont nous comprenons l'ADN et les systèmes biologiques, et continueront probablement d'influencer les avancées futures dans ces domaines.
Veuillez noter que ce texte est une synthèse basée sur les informations généralement disponibles, et certaines des informations plus récentes ou spécifiques peuvent nécessiter une vérification supplémentaire.
Fin de l'article.
Max Delbrück: Nobel-Winning Pioneer of Molecular Biology
Introduction to a Scientific Revolutionary
Max Delbrück was a visionary scientist whose groundbreaking work in bacteriophage research laid the foundation for modern molecular biology. Born in Germany in 1906, Delbrück transitioned from physics to biology, forever changing our understanding of genetic structure and viral replication. His contributions earned him the 1969 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, shared with Salvador Luria and Alfred Hershey.
Early Life and Academic Foundations
Delbrück was born on September 4, 1906, in Berlin, Germany, into an academic family. His father, Hans Delbrück, was a prominent historian, while his mother came from a family of scholars. This intellectual environment nurtured young Max's curiosity and love for science.
Education and Shift from Physics to Biology
Delbrück initially pursued theoretical physics, earning his PhD from the University of Göttingen in 1930. His early work included a stint as an assistant to Lise Meitner in Berlin, where he contributed to the prediction of Delbrück scattering, a phenomenon involving gamma ray interactions.
Inspired by Niels Bohr's ideas on complementarity, Delbrück began to question whether similar principles could apply to biology. This curiosity led him to shift his focus from physics to genetics, a move that would redefine scientific research.
Fleeing Nazi Germany and Building a New Life
The rise of the Nazi regime in Germany forced Delbrück to leave his homeland in 1937. He relocated to the United States, where he continued his research at Caltech and later at Vanderbilt University. In 1945, he became a U.S. citizen, solidifying his commitment to his new home.
Key Collaborations and the Phage Group
Delbrück's most influential work began with his collaboration with Salvador Luria and Alfred Hershey. Together, they formed the Phage Group, a collective of scientists dedicated to studying bacteriophages—viruses that infect bacteria. Their research transformed phage studies into an exact science, enabling precise genetic investigations.
One of their most notable achievements was the development of the one-step bacteriophage growth curve in 1939. This method allowed researchers to track the replication cycle of phages, revealing that a single phage could produce hundreds of thousands of progeny within an hour.
Groundbreaking Discoveries in Genetic Research
Delbrück's work with Luria and Hershey led to several pivotal discoveries that shaped modern genetics. Their research provided critical insights into viral replication and the nature of genetic mutations.
The Fluctuation Test and Spontaneous Mutations
In 1943, Delbrück and Luria conducted the Fluctuation Test, a groundbreaking experiment that demonstrated the random nature of bacterial mutations. Their findings disproved the prevailing idea that mutations were adaptive responses to environmental stress. Instead, they showed that mutations occur spontaneously, regardless of external conditions.
This discovery was pivotal in understanding genetic stability and laid the groundwork for future studies on mutation rates and their implications for evolution.
Viral Genetic Recombination
In 1946, Delbrück and Hershey made another significant breakthrough by discovering genetic recombination in viruses. Their work revealed that viruses could exchange genetic material, a process fundamental to genetic diversity and evolution. This finding further solidified the role of phages as model organisms in genetic research.
Legacy and Impact on Modern Science
Delbrück's contributions extended beyond his immediate discoveries. His interdisciplinary approach, combining physics and biology, inspired a new generation of scientists. The Phage Group he co-founded became a training ground for many leaders in molecular biology, influencing research for decades.
The Nobel Prize and Beyond
In 1969, Delbrück was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for his work on viral replication and genetic structure. The prize recognized his role in transforming phage research into a precise scientific discipline, enabling advancements in genetics and molecular biology.
Even after receiving the Nobel Prize, Delbrück continued to push the boundaries of science. He challenged existing theories, such as the semi-conservative replication of DNA, and explored new areas like sensory transduction in Phycomyces, a type of fungus.
Conclusion of Part 1
Max Delbrück's journey from physics to biology exemplifies the power of interdisciplinary thinking. His work with bacteriophages not only advanced our understanding of genetics but also set the stage for modern molecular biology. In the next section, we will delve deeper into his later research, his influence on contemporary science, and the enduring legacy of his contributions.
Later Research and Challenging Established Theories
After receiving the Nobel Prize, Max Delbrück continued to push scientific boundaries through innovative experiments and theoretical challenges. His work remained focused on uncovering fundamental biological principles, often questioning prevailing assumptions.
Challenging DNA Replication Models
In 1954, Delbrück proposed a dispersive theory of DNA replication, challenging the dominant semi-conservative model. Though later disproven by Meselson and Stahl, his hypothesis stimulated critical debate and refined experimental approaches in molecular genetics.
Delbrück emphasized the importance of precise measurement standards, stating:
"The only way to understand life is to measure it as carefully as possible."This philosophy driven his entire career.
Studying Phycomyces Sensory Mechanisms
From the 1950s onward, Delbrück explored Phycomyces, a fungus capable of complex light and gravity responses. His research revealed how simple organisms translate environmental signals into measurable physical changes, bridging genetics and physiology.
- Demonstrated photoreceptor systems in fungal growth patterns
- Established quantitative methods for studying sensory transduction
- Influenced modern research on signal transduction pathways
The Max Delbrück Center: A Living Legacy
Following Delbrück's death in 1981, the Max Delbrück Center (MDC) was established in Berlin in 1992, embodying his vision of interdisciplinary molecular medicine. Today, it remains a global leader in genomics and systems biology.
Research Impact and Modern Applications
Delbrück's phage methodologies continue to underpin contemporary genetic technologies:
- CRISPR-Cas9 development builds on his quantitative phage genetics
- Modern viral vector engineering relies on principles he established
- Bacterial gene expression studies trace back to his fluctuation test designs
The MDC currently hosts over 1,500 researchers from more than 60 countries, continuing Delbrück's commitment to collaborative science.
Enduring Influence on Modern Genetics
Delbrück's approach to science—combining rigor, creativity, and simplicity—shapes current research paradigms. His emphasis on quantitative analysis remains central to modern genetic studies.
Philosophical Contributions
Delbrück advocated for studying biological systems at their simplest levels before tackling complexity. This "simplicity behind complexity" principle now guides systems biology and synthetic biology efforts worldwide.
His legacy endures through:
- Training generations of molecular biologists through the Phage Group
- Establishing foundational methods for mutant strain analysis
- Promoting international collaboration in life sciences
Legacy in Education and Mentorship
Max Delbrück’s influence extended far beyond his publications through his role as a mentor and educator. His leadership of the Phage Group created a model for collaborative, interdisciplinary training that shaped generations of scientists.
Training Future Scientists
Delbrück emphasized quantitative rigor and intellectual curiosity in his students. At Cold Spring Harbor, he fostered a community where physicists, biologists, and chemists worked together—a precursor to modern systems biology.
- Mentored Gordon Wolstenholme, who later directed the Salk Institute
- Inspired Walter Gilbert, a future Nobel laureate in chemistry
- Established a culture of critical debate that accelerated scientific progress
Current Applications of Delbrück's Work
Delbrück’s methods and discoveries remain embedded in today’s most advanced genetic technologies. His approach continues to inform cutting-edge research across multiple fields.
Impact on Modern Genetic Engineering
The principles Delbrück established through bacteriophage studies are foundational to tools transforming medicine and agriculture:
- CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing relies on phage-derived mechanisms
- Viral gene therapy vectors use designs first explored in his labs
- Bacterial mutagenesis studies follow protocols he refined
"Delbrück taught us to see genes not as abstract concepts, but as measurable molecular machines."
Advancing Genomics and Virology
Today’s genomic research owes a debt to Delbrück’s emphasis on precise measurement. Modern sequencing technologies and viral dating methods build directly on his frameworks.
Key ongoing applications include:
- Pandemic preparedness through phage-based virus tracking
- Cancer genomics using mutation rate analysis he pioneered
- Synthetic biology circuits inspired by his Phycomyces studies
Conclusion: The Enduring Impact of Max Delbrück
Max Delbrück transformed our understanding of life at the molecular level through visionary experiments, interdisciplinary collaboration, and unwavering intellectual rigor. His work remains a cornerstone of modern genetics.
Key Takeaways
The legacy of Delbrück endures through:
- Nobel-recognized discoveries in viral replication and mutation
- The Max Delbrück Center’s ongoing research in molecular medicine
- A scientific philosophy that values simplicity behind complexity
As biology grows increasingly complex, Delbrück’s insistence on quantitative clarity and collaborative inquiry continues to guide researchers worldwide. His life’s work proves that understanding life’s simplest mechanisms remains the surest path to unlocking its deepest mysteries.


Global Security Alert: Rising Violence and Terrorism in 2025
In late 2025, the world faces a surge in violence and terrorism, with deadly attacks targeting civilians, military personnel, and peacekeepers. From the Brown University shooting to the Bondi Beach Hanukkah attack, these incidents highlight escalating global security threats. Authorities remain on high alert as conflicts in Ukraine, Syria, and the Middle East intensify.
Deadly Shootings and Terrorist Attacks
The Brown University shooting in Providence, Rhode Island, left two dead and nine injured, with the gunman still at large. Meanwhile, a terrorist attack in Sydney killed at least 12 people at a Hanukkah celebration, drawing condemnation from UN Secretary-General António Guterres.
Brown University Shooting: Gunman Remains at Large
On December 14, a mass shooting at Brown University resulted in two fatalities and nine injuries. Eight victims were initially in critical condition, with seven now stable and one remaining critical. Authorities continue searching for the suspect, who fled the scene.
Bondi Beach Attack: Antisemitic Violence on the Rise
A Hanukkah celebration in Sydney turned deadly when a terrorist targeted the Jewish community, killing 12 people. The attack reflects a disturbing trend of antisemitic violence, coinciding with heightened holiday security alerts from the FBI and Homeland Security.
Ongoing Armed Conflicts and Casualties
Global conflicts continue to escalate, with Russian forces capturing Pokrovsk in Ukraine’s Donetsk Oblast after intense fighting. A missile strike in Dnipro killed four and injured over 40, while in Syria, an ISIL attacker killed two US service members and a civilian interpreter.
Ukraine: Russian Advances and Civilian Strikes
Russian forces recently seized Pokrovsk in Donetsk Oblast, marking a significant shift in the ongoing war. A separate missile strike in Dnipro resulted in four deaths and 40 injuries, underscoring the conflict’s devastating toll on civilians.
Syria: ISIL Resurgence and US Casualties
An ISIL attack in Palmyra killed two US service members and a civilian interpreter, reigniting concerns over the group’s resurgence. The incident highlights the persistent threat of terrorism in the region, despite years of counterterrorism efforts.
Humanitarian Crises and UN Responses
Beyond armed conflicts, humanitarian disasters continue to unfold. In Fez, Morocco, a building collapse killed 22 people, while in Sudan, a drone attack on a UN base left six peacekeepers dead and eight injured.
Morocco Building Collapse: 22 Dead
A tragic building collapse in Fez claimed the lives of 22 people, with several others injured. The incident underscores the urgent need for improved infrastructure safety in vulnerable regions.
Sudan Drone Attack: UN Peacekeepers Targeted
A drone strike on a UN base in Sudan’s Kordofan region killed six peacekeepers and wounded eight. The attack highlights the growing dangers faced by humanitarian workers in conflict zones.
As 2025 draws to a close, these events underscore the fragile state of global security. From terrorist attacks to armed conflicts, the world remains on edge. Stay tuned for Part 2, where we delve deeper into the geopolitical implications and humanitarian responses to these crises.
Geopolitical Tensions: Israel, Hezbollah, and West Bank Settlements
The Middle East remains a hotspot as Israel escalates military actions in southern Lebanon and approves nearly 800 new settler homes in the West Bank. These moves violate a US-brokered ceasefire and risk further destabilizing the region.
Israel’s Airstrikes and Evacuation Orders in Lebanon
Israel issued evacuation orders in southern Lebanon ahead of airstrikes targeting Hezbollah positions. The strikes follow repeated cross-border attacks, raising fears of a broader conflict. Analysts warn that further escalation could draw in regional powers like Iran.
West Bank Settlements: Violating International Law
Israel’s approval of 780 new settler homes in the West Bank has drawn international condemnation. The UN and EU reiterate that settlements are illegal under international law and undermine prospects for a two-state solution. The U.S. has expressed "deep concern" over the decision.
Economic and Humanitarian Aid Amid Global Crises
As conflicts rage, economic and humanitarian aid efforts attempt to mitigate suffering. The IMF released $1.2 billion to Pakistan, part of a larger $4.5 billion package since 2024. Meanwhile, India’s IndiGo airline faces penalties for flight cancellations.
IMF Aid to Pakistan: $1.2 Billion Released
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) disbursed $1.2 billion to Pakistan, bringing total aid to $4.5 billion since last year. The funds aim to stabilize Pakistan’s economy amid soaring inflation and political instability. Critics argue more structural reforms are needed.
IndiGo Flight Cuts: Regulatory Action in India
India’s aviation regulator ordered IndiGo to reduce flights by 5% after widespread cancellations disrupted travel. The move follows passenger complaints and operational failures. IndiGo, India’s largest airline, faces scrutiny over its rapid expansion.
Global Security Alerts: FBI and Homeland Security Warnings
With the holiday season underway, FBI and Homeland Security have issued heightened alerts. A November 26 intelligence bulletin warns of potential attacks from lone assailants and extremist groups. Authorities urge vigilance at public gatherings.
Holiday Threats: Antisemitic and Extremist Risks
The Bondi Beach attack aligns with rising antisemitic violence, prompting increased security at Jewish events worldwide. The UN has condemned digital-fueled hatred, citing social media’s role in radicalization. Communities are urged to report suspicious activity.
UN Peacekeeping Challenges: Sudan and Beyond
The drone attack on UN peacekeepers in Sudan underscores the risks faced by humanitarian workers. Since 2020, over 100 peacekeepers have been killed in Sudan alone. The UN calls for stronger protections and accountability for attacks on aid personnel.
Positive Developments: Migration and Education Initiatives
Amid the crises, some positive trends emerge. Guatemala and Germany signed a skilled migration agreement, while Timor-Leste’s school feeding programs support local farmers. These efforts offer hope for stability and economic growth.
Guatemala-Germany Migration Deal
A new agreement allows Guatemalan skilled workers to migrate to Germany, addressing labor shortages in both nations. The deal includes protections for workers’ rights and aims to reduce irregular migration. Similar programs may expand to other Latin American countries.
Timor-Leste School Feeding Programs
Timor-Leste’s school feeding initiatives now source 30% of food locally, boosting farmers’ incomes. The program improves child nutrition while strengthening rural economies. The UN praises it as a model for sustainable development.
As global tensions persist, these developments highlight both challenges and opportunities. Part 3 will explore long-term solutions and the role of international cooperation in addressing security and humanitarian crises.
International Diplomacy: Sanctions, Prisoner Releases, and UN Transitions
Diplomatic efforts in late 2025 show mixed results. Belarus released 123 political prisoners, including Nobel laureate Ales Bialiatski, after US sanctions relief. Meanwhile, the UN’s mission in Iraq (UNAMI) officially ended, marking a "new chapter" for the country.
Belarus Prisoner Release: Ales Bialiatski Freed
In a surprising move, Belarus released 123 political prisoners, among them Nobel Peace Prize winner Ales Bialiatski. The release followed US sanctions relief, signaling a potential thaw in relations. However, critics argue the move is largely symbolic, as repression continues.
UN Mission in Iraq Concludes After Two Decades
The United Nations Assistance Mission for Iraq (UNAMI) officially ended its mandate in December 2025. Established in 2003, UNAMI played a key role in stabilizing Iraq post-Saddam Hussein. The UN now shifts focus to long-term development and reconciliation efforts.
Cybersecurity and Digital Threats: A Growing Concern
Digital threats amplify global instability. The UN Alliance of Civilizations warns that social media radicalization fuels extremism. Meanwhile, cyberattacks on critical infrastructure, including UN peacekeeping bases, raise alarms about digital warfare.
Social Media and Radicalization: UN Warnings
The UN highlights the role of digital platforms in spreading hate speech. A 2025 report found that 70% of extremist recruitment now occurs online. Governments and tech companies face pressure to strengthen content moderation and counter-radicalization programs.
Cyberattacks on Critical Infrastructure
Cyber threats escalate, with drone attacks on UN bases in Sudan linked to state-sponsored hacking groups. Experts warn that critical infrastructure—power grids, hospitals, and transportation—remains vulnerable. Global cybersecurity cooperation is urgently needed.
Climate Change and Conflict: A Dangerous Feedback Loop
Climate change exacerbates existing conflicts. In Sudan and the Sahel, droughts and resource scarcity intensify violence. The UN Environment Programme (UNEP) reports that 40% of civil conflicts in the past decade had climate-related triggers.
Sudan’s Climate-Conflict Nexus
Sudan’s ongoing crisis is worsened by extreme weather events. Floods and droughts displace communities, increasing competition for land and water. The UN estimates 2.5 million Sudanese are now climate refugees, straining regional stability.
Global Responses: Mitigation and Adaptation
International efforts focus on climate adaptation funding. The Green Climate Fund allocated $1.8 billion in 2025 to vulnerable nations. However, experts argue more must be done to address the root causes of climate-driven conflicts.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways and the Path Forward
The final months of 2025 reveal a world grappling with escalating violence, geopolitical tensions, and humanitarian crises. From the Brown University shooting to the Bondi Beach attack, terrorism and armed conflicts dominate headlines. Yet, diplomatic breakthroughs and economic aid offer glimmers of hope.
Summary of Critical Events
- Mass shootings and terrorist attacks in the US and Australia.
- Russian advances in Ukraine and ongoing Middle East conflicts.
- Humanitarian crises in Sudan, Morocco, and beyond.
- Economic aid packages and migration agreements.
- UN transitions and cybersecurity threats shaping global stability.
The Role of International Cooperation
Addressing these challenges requires multilateral action. Key steps include:
- Strengthening counterterrorism intelligence-sharing.
- Expanding humanitarian aid and climate adaptation funding.
- Enforcing international law on settlements and cyber warfare.
- Investing in digital literacy and counter-radicalization programs.
As 2025 closes, the world stands at a crossroads. The choices made today will determine whether the coming years bring greater stability or deeper division. One thing is clear: global challenges demand global solutions. The time for action is now.
Walter Gilbert: Ein Pionier der Molekularbiologie
Frühe Jahre und Ausbildung
Walter Gilbert, geboren am 21. März 1932 in Boston, Massachusetts, ist eine der herausragendsten Persönlichkeiten der biochemischen Forschung des 20. Jahrhunderts. Seine wissenschaftlichen Beiträge haben erheblich dazu beigetragen, unser Verständnis der genetischen Struktur und Funktion zu vertiefen. Gilbert, der ursprünglich an der Harvard University Physik studierte und 1953 seinen Bachelor-Abschluss erwarb, war von einem jungen Alter an von den Geheimnissen der Natur fasziniert. Nach seinem Abschluss setzte er sein Studium mit einem Doktorat in Physik am Cambridge University Laboratory in England fort. Der Wendepunkt kam, als er sich entschied, seine Karriere in Richtung Biologie zu lenken und sich so einem ganz neuen Feld der Forschung zu widmen.
Eintritt in die Welt der Molekularbiologie
In den 1960er Jahren kam Walter Gilbert nach Harvard zurück, wo er als Assistenzprofessor für Physik lehrte. Hier begann seine enge Zusammenarbeit mit verschiedenen Biologen, die ihn dazu inspirierte, die wachsende Welt der Molekularbiologie zu erkunden. Er erkannte früh das Potenzial, das in der Erforschung der genetischen Basis des Lebens lag. Diese Entdeckung führte ihn 1970 zur Entschlüsselung der RNA-Prozesse, was den Grundstein für seine späteren Arbeiten legte.
Die Molekularbiologie begann sich in jener Zeit zu einem eigenen Wissenschaftszweig zu entfalten. Forscher waren bestrebt, die Struktur und Funktion von DNA und RNA zu verstehen. Gilberts physikalischer Hintergrund ermöglichte es ihm, innovative Ansätze zu verfolgen, die in der Biologie damals revolutionär waren.
Kritische Entdeckungen und Forschung
Walter Gilberts bedeutendster Beitrag zur Molekularbiologie war die Entwicklung der Methode zur Bestimmung der DNA-Sequenz. Zusammen mit Frederick Sanger, einem britischen Biochemiker, revolutionierte er den Bereich der Genetik durch die Einführung der sogenannten „Sanger-Sequenzierung“. Diese Technik ermöglichte es Wissenschaftlern erstmals, die genaue Abfolge der Basen in einem DNA-Molekül zu bestimmen, ein Verfahren, das bis heute grundlegend in der Genetik bleibt. Die Fähigkeit, die Reihenfolge der Nukleotide in einer DNA-Probe präzise zu bestimmen, eröffnete neue Wege für das Verständnis genetischer Informationen und der Funktionsweise von Genomen.
Seine Forschungen führten unter anderem zur Aufklärung, wie Gene durch den Prozess der Transkription in Proteine übersetzt werden. Einige seiner Studien zeigten, dass die Kontrolle dieses genetischen Schalters vital für Zellfunktion und Entwicklung ist. Dies hat weitreichende Implikationen für das Gebiet der Genregulation und die Entwicklung therapeutischer Ansätze bei genetisch bedingten Krankheiten.
Gilberts Arbeit hörte jedoch nicht bei der Sequenzierung auf. Er und seine Kollegen entdeckten auch Regulatorgene und ihre Funktion in Bakterien, ein weiterer Durchbruch, der in die Geschichtsbücher der biologischen Wissenschaft einging. Diese Regulatorgene sind für die Kontrolle der Genexpression verantwortlich und sind entscheidend für die zelluläre Funktion und Genexpression.
Ehrungen und Anerkennung
Walter Gilberts außergewöhnliche Leistungen blieben nicht unbemerkt. 1980 erhielt er zusammen mit Frederick Sanger und Paul Berg den Nobelpreis für Chemie für ihre grundlegenden Beiträge zur Nukleinsäure-Biochemie. Diese Anerkennung unterstreicht die immense Bedeutung seiner Forschung für die moderne Wissenschaft. Der Einfluss seiner Arbeiten auf die genetische Forschung und die Biotechnologie ist bis heute spürbar, da viele darauf basierende Technologien in medizinischen und wissenschaftlichen Anwendungen Einsatz finden.
Neben dem Nobelpreis erhielt Gilbert zahlreiche weitere Ehrungen und Preise, darunter die National Medal of Science, eine der höchsten Auszeichnungen für wissenschaftliche Verdienste in den Vereinigten Staaten. Sein Namen ist auch mit zahlreichen Ehrenmitgliedschaften in Elite-Wissenschaftsakademien verbunden.
Gilbert hat bewiesen, dass interdisziplinäre Ansätze in der Wissenschaft bahnbrechende Innovationen hervorbringen können. Sein Mut, neue Wege zu gehen, hat nicht nur sein eigenes Forschungsgebiet bereichert, sondern auch nachfolgende Generationen von Wissenschaftlern inspiriert, die Grenzen zwischen den Disziplinen zu überschreiten.
Im nächsten Teil des Artikels werden wir mehr über Walter Gilberts ausgedehnte Karriere nach dem Erhalt des Nobelpreises erfahren, sowie seine Beiträge zur aufkommenden Biotechnologiebranche und seine Rolle als Befürworter der wissenschaftlichen Forschung und Bildung.
Die Jahre nach dem Nobelpreis
Nach dem Erhalt des Nobelpreises 1980 erweiterte Walter Gilbert seine wissenschaftlichen und beruflichen Horizonte erheblich. Obwohl seine bahnbrechende Entdeckung in der DNA-Sequenzierung ihm bereits viel Anerkennung eingebracht hatte, blieb er unermüdlich in der Erforschung neuer wissenschaftlicher Gebiete. Er setzte seine Forschung an der Harvard University fort und hatte wesentlichen Einfluss auf die Entwicklung neuer biotechnologischer Ansätze.
Gilbert widmete sich nun vermehrt der Weiterentwicklung und Anwendung seiner Erkenntnisse in der Praxis, insbesondere in der aufkommenden Biotechnologiebranche. Dies war eine Zeit, in der viele Forscher begannen, das Potenzial der Genomik und der genetischen Technologie zu erkennen und zu nutzen. Diese Technologien sollten schließlich zu einem Eckpfeiler der heutigen Biotechnologie werden, mit Anwendungen in der Medizin, Landwirtschaft und Industrie.
Der Schritt in die Biotechnologie
Gilberts Wechsel von der akademischen Forschung zur kommerziellen Anwendung war ein wichtiger Schritt in seiner Karriere. Im Jahr 1981 half er bei der Gründung von Biogen, einem der ersten Biotechnologieunternehmen weltweit. Biogen wurde ins Leben gerufen mit dem Ziel, die Möglichkeiten genetischer und biotechnologischer Forschung in die Entwicklung neuer Medikamente und Therapien zu übersetzen.
Gilberts Vision war es, die riesigen Potenziale der biotechnologischen Forschung zu nutzen, um praktischen Nutzen für die Gesellschaft zu generieren. Biogen konzentrierte sich auf die Entwicklung von Produkten zur Behandlung schwerer Krankheiten, einschließlich neurodegenerativer Erkrankungen und Krebs. Unter seiner Führung entwickelte sich Biogen zu einem der führenden Unternehmen der Branche.
Seine Arbeit in der Biotechnologie ging jedoch über geschäftliche Interessen hinaus. Gilbert war ein leidenschaftlicher Verfechter der neuen Möglichkeiten, die die Biotechnologie bot, und bemüht, die Öffentlichkeit und die wissenschaftliche Gemeinschaft gleichermaßen über die Bedeutung und das Potenzial dieser neuen Technologien aufzuklären. In verschiedenen Vorträgen und Publikationen beschrieb er die Perspektiven, die genetische Modifikationen und Genomik für die Zukunft der Medizin und darüber hinaus bereithielten.
Bildungsmaßnahmen und Einfluss auf die Wissenschaftspolitik
Abseits seiner Forschung und unternehmerischen Tätigkeiten engagierte sich Walter Gilbert intensiv in der Wissenschaftskommunikation und Wissenschaftspolitik. Er bemühte sich darum, wissenschaftliche Erkenntnisse einem breiten Publikum zugänglich zu machen, und setzte sich für die Verbesserung der Wissenschaftsausbildung ein. Gilbert erkannte, dass eine umfassende wissenschaftliche Bildung essenziell war, um künftige Generationen von Wissenschaftlern hervorzubringen und die Gesellschaft auf die Herausforderungen und Chancen der wissenschaftlichen Entwicklung vorzubereiten.
Gilbert war ein leidenschaftlicher Mentor für junge Wissenschaftler und betonte stets die Bedeutung interdisziplinärer Zusammenarbeit. Seine eigene Karriere war ein Beispiel dafür, wie die Integration verschiedener wissenschaftlicher Disziplinen zu bahnbrechenden Entdeckungen führen kann. Er unterstützte aktiv Initiativen und Programme, die Wissenschaftler weltweit miteinander vernetzen, um die Zusammenarbeit und den Wissenstransfer zu fördern.
Ein weiterer Aspekt von Gilberts Einfluss lag in seiner Arbeit, politische Entscheidungsträger über die Bedeutung der Finanzierung und Unterstützung der Grundlagenforschung zu informieren. Er plädierte dafür, dass wissenschaftliche Entdeckungen eine wesentliche Triebkraft für Innovation und wirtschaftliches Wachstum darstellen und entsprechende Investitionen in Forschung und Entwicklung unerlässlich sind.
Spätere Jahre und Vermächtnis
In späteren Jahren zog sich Walter Gilbert zunehmend aus der aktiven Forschung und Geschäftsführung zurück, engagierte sich jedoch weiterhin in verschiedenen Beratungsfunktionen und setzte sein Engagement in der Wissenschaftskommunikation fort. Er blieb ein respektierter und einflussreicher Vordenker in der Biowissenschaft, dessen Arbeiten die Fundamente für zahllose Fortschritte in der Genomik und Molekularbiologie gelegt haben.
Die Vielzahl an Ehrungen und Auszeichnungen, die Gilbert im Laufe seiner Karriere erhielt, spiegelt den weitreichenden Einfluss seiner Arbeit wider. Noch bedeutsamer ist jedoch das bleibende Erbe seiner wissenschaftlichen Beiträge und seine Rolle als Mentor und Inspirator für kommende Generationen von Forschern. Seine Arbeit hat nicht nur unser Verständnis des Lebens auf molekularer Ebene revolutioniert, sondern auch dazu beigetragen, die moderne Biotechnologie zu gestalten, die heute als Schlüsselinstrument für viele medizinische und technologische Durchbrüche dient.
Im folgenden Teil des Artikels werden wir die Auswirkungen von Gilberts Forschungen auf die heutigen biotechnologischen Innovationen, seine weiteren Tätigkeiten im Ruhestand und seine Nachwirkung auf die Wissenschaftsgemeinschaft weiter erkunden.
Einfluss auf moderne biotechnologische Innovationen
Walter Gilberts Arbeiten haben die Grundlage für viele der heutigen Errungenschaften in der Biotechnologie gelegt. Insbesondere die Methoden zur DNA-Sequenzierung, die er und seine Kollegen entwickelten, ebneten den Weg für das Humangenomprojekt, das 2003 abgeschlossen wurde. Dieses Projekt markierte einen Wendepunkt in der Biologie, da es Wissenschaftlern erstmals einen vollständigen Blick auf das menschliche Genom ermöglichte. Die Folgen dieser bahnbrechenden Arbeit sind heute in zahlreichen Bereichen sichtbar, von der personalisierten Medizin über die Diagnostik bis hin zur Entwicklung zielgerichteter Therapien.
Die DNA-Sequenzierung hat auch die Landwirtschaft revolutioniert, indem sie die Entwicklung genetisch modifizierter Organismen (GMOs) ermöglichte, die widerstandsfähiger gegen Krankheiten und widrige Umweltbedingungen sind. Diese Fortschritte tragen dazu bei, die Ernährungssicherheit zu erhöhen und den globalen Herausforderungen des Klimawandels zu begegnen.
Engagement in Wissenschaft und Bildung im Ruhestand
Selbst im Ruhestand blieb Walter Gilbert ein aktiver Förderer der Wissenschaft. Er setzte sich weiterhin dafür ein, dass wissenschaftliche Bildung und Forschung als Eckpfeiler für den gesellschaftlichen Fortschritt anerkannt werden. Gilbert nutzte sein Ansehen und seine Erfahrung, um auf Konferenzen weltweit Vorträge zu halten und dabei die Bedeutung der Wissenschaft im Alltag der Menschen zu betonen.
Er war regelmäßig beteiligt an Diskussionen über die ethischen Implikationen der genetischen Forschung und biotechnologischen Anwendungen. Gilbert erkannte die Notwendigkeit einer verantwortungsvollen Wissenschaftspraxis und der Einbindung der Öffentlichkeit in den Dialog über neue Technologien. Er setzte sich dafür ein, Standards und Richtlinien zu etablieren, die sicherstellen, dass der wissenschaftliche Fortschritt in einer Weise genutzt wird, die der Menschheit zugutekommt.
Ein bleibendes Vermächtnis
Walter Gilberts Einfluss auf die Wissenschaft endet nicht mit seinen publizierten Arbeiten oder den von ihm gegründeten Unternehmen. Sein dauerhafter Einfluss liegt vor allem in der Inspiration, die er für andere Forscher und Wissenschaftler auf der ganzen Welt darstellt. Gilberts Geschichte lehrt uns den Wert der Perseveranz, der Neugierde und der interdisziplinären Zusammenarbeit.
Er hat gezeigt, dass die Grenzen zwischen den Wissenschaften überwunden werden können und dass innovative Ansätze häufig aus der Synthese unterschiedlicher Disziplinen hervorgehen. Diese Philosophie der offenen Wissenschaft hat nicht nur die Molekularbiologie und Biotechnologie, sondern auch viele andere Wissenschaftsgebiete nachhaltig beeinflusst.
Gilbert förderte stets die Idee, dass Wissenschaft für alle zugänglich sein sollte und dass internationale Zusammenarbeit für den wissenschaftlichen Fortschritt essenziell ist. Seine reiche Hinterlassenschaft lebt durch die unzähligen Studenten, Forscher und Institutionen weiter, die von ihm inspiriert wurden und werden.
Zusammenfassung und Ausblick
Walter Gilbert ist ein Paradebeispiel dafür, wie ein Wissenschaftler mit visionärer Kraft und Engagement das Gesicht der modernen Wissenschaft verändern kann. Von seinen grundlegenden Arbeiten zur DNA-Sequenzierung über seine unternehmerischen Unternehmungen bis hin zu seinem beständigen Einsatz für die Bildung hat Gilbert Generationen von Wissenschaftlern geprägt und die Gesellschaft in unzähligen Facetten bereichert.
Sein Lebenswerk erinnert uns daran, dass Wissenschaft nicht nur ein Instrument des Fortschritts ist, sondern auch eine Verantwortung gegenüber der Gesellschaft darstellt. Gilberts Einfluss wird sich auch in den kommenden Jahren und Jahrzehnten bemerkbar machen, da neue Generationen von Wissenschaftlern auf den von ihm gelegten Grundlagen aufbauen und weiterhin danach streben, die komplexe, aber faszinierende Welt der Genetik zu erkunden.
In dieser sich kontinuierlich weiterentwickelnden Wissenschaftslandschaft wird der Geist von Walter Gilberts Arbeit lebendig bleiben und weiterhin als Leuchtturm des wissenschaftlichen Fortschritts dienen.
SEO Content Writing in 2025: Mastering AI, E-E-A-T, and Search Evolution
Introduction: The New Era of SEO Content Writing
In 2025, SEO content writing has transformed dramatically, driven by AI advancements and evolving search engine algorithms. With 85% of marketers now using AI tools for content creation, the focus has shifted to balancing automation with human expertise and authenticity. Google's AI Overviews (AIOs) and the rise of answer engines like Bing and Perplexity have redefined how content is discovered and consumed.
This article explores the latest trends, strategies, and best practices for creating SEO-optimized content that ranks well, engages readers, and drives conversions in 2025. From leveraging AI tools to mastering E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness), we'll cover everything you need to stay ahead in the competitive world of digital marketing.
The Rise of AI in Content Creation
AI Tools as Content Drafting Assistants
AI-driven content creation has become mainstream, with tools like Jasper, Copy.ai, and Writesonic helping marketers generate drafts quickly. These tools enable higher content volume and broader keyword targeting, but they require human refinement to ensure uniqueness and brand alignment.
According to CoSchedule research, 85% of marketers now use AI for content creation. This trend highlights the importance of using AI as a starting point, not a final solution. Human writers must enhance AI-generated content with personal anecdotes, case studies, and original insights to meet Google's E-E-A-T standards.
Google's AI Overviews and Zero-Click Searches
Google's AI Overviews (AIOs) are expanding to all queries, increasing zero-click searches where users get answers directly from the search results. This shift presents both challenges and opportunities for content creators.
AIOs now include an average of 11 citation links per overview, with only 20-26% overlapping the top 10 SERP links. This means smaller, niche sites have a better chance of gaining visibility if they provide unique, high-quality content. Optimizing for AIOs requires a focus on original insights, structured data, and clear, concise answers to common questions.
Mastering E-E-A-T for SEO Success
Understanding E-E-A-T and Its Importance
E-E-A-T stands for Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. Google has fully integrated these factors into its evaluation criteria, prioritizing content that demonstrates real-world experience and credibility.
To excel in E-E-A-T, content must include:
- Personal anecdotes and real-life examples
- Case studies and data-driven insights
- Author bios with credentials and experience
- Original research and unique perspectives
Building Trust Through Authenticity
Readers in 2025 demand authentic, expert-driven content that goes beyond generic AI output. Storytelling and personal branding are key to building trust and engagement.
Incorporate elements like:
- Behind-the-scenes stories about your brand or process
- Interviews with industry experts
- User-generated content and testimonials
- Transparency about sources and methodologies
By focusing on authenticity, you not only improve your SEO rankings but also create a stronger connection with your audience.
Adapting to Search Engine Evolution
The Shift to "Ranch Style" SEO
Gone are the days of single, massive "skyscraper" posts. In 2025, "Ranch Style" SEO is the new norm—creating multiple interlinked, focused pieces that each offer unique experiences and insights.
This approach involves:
- Breaking down broad topics into specific, targeted articles
- Using internal linking to connect related content
- Ensuring each piece provides information gain—new perspectives or fresh data
Optimizing for Voice and Visual Search
With the rise of voice assistants and visual search tools, optimizing content for these formats is no longer optional. By 2025, voice search optimization is a non-negotiable aspect of SEO.
Key strategies include:
- Using natural language and conversational keywords
- Structuring content with clear, concise answers to common questions
- Incorporating alt text and image descriptions for visual search
- Ensuring mobile-friendliness and fast load times
By adapting to these trends, you can ensure your content remains visible and relevant in an ever-changing search landscape.
Conclusion: The Future of SEO Content Writing
The world of SEO content writing in 2025 is defined by AI integration, E-E-A-T principles, and the evolution of search engines. To succeed, marketers must embrace AI tools while prioritizing human expertise and authenticity.
In the next sections, we'll delve deeper into hyper-personalization, multi-platform distribution, and advanced technical SEO strategies to help you stay ahead of the curve. Stay tuned for more insights and actionable tips to master SEO content writing in 2025.
Hyper-Personalization and Interactive Content
The Demand for Customized User Experiences
In 2025, hyper-personalization has moved beyond basic customization. Users now expect content tailored to their specific needs, preferences, and behaviors. This trend is driven by advancements in AI and data analytics, allowing brands to deliver highly relevant experiences.
Key strategies for hyper-personalization include:
- Using AI-driven recommendations based on user behavior
- Creating dynamic content that adapts to user preferences
- Implementing interactive elements like quizzes, polls, and calculators
- Leveraging user data to personalize email campaigns and content suggestions
Blending Digital and Real-World Elements
To stand out in 2025, content must bridge the gap between digital and real-world experiences. This approach enhances engagement and builds stronger connections with audiences.
Examples of blending digital and real-world elements include:
- Augmented Reality (AR) experiences that allow users to visualize products in their environment
- Virtual events with interactive features like live Q&A sessions
- Location-based content that provides personalized recommendations based on user location
- Gamification techniques to encourage user participation and engagement
Multi-Platform Distribution and Diversified Traffic Sources
The Rise of Social Search and Answer Engines
In 2025, social search and answer engines like Bing and Perplexity have become major traffic sources. Platforms like TikTok, Instagram, and YouTube are no longer just for social media—they're now key players in search.
To optimize for social search, consider the following strategies:
- Creating short-form video content optimized for TikTok and Instagram
- Using keyword-rich captions and hashtags to improve discoverability
- Incorporating transcripts and titles for YouTube videos to enhance SEO
- Leveraging user-generated content to build authenticity and engagement
Diversifying Traffic Sources for Sustainable Growth
Relying solely on Google for traffic is no longer a sustainable strategy. In 2025, diversifying traffic sources is essential for long-term success.
Key tactics for diversifying traffic include:
- Optimizing for Bing and other search engines
- Leveraging email marketing to drive repeat visits
- Building a strong social media presence across multiple platforms
- Exploring partnerships and collaborations to reach new audiences
Advanced Technical SEO Strategies
The Importance of Fast, Mobile-Friendly Sites
Technical SEO remains a critical foundation for success in 2025. Fast, mobile-friendly sites with seamless user experiences are non-negotiable for conversions and rankings.
Key technical SEO strategies include:
- Ensuring fast load times with optimized images and caching
- Implementing mobile-first design principles
- Using structured data to enhance search visibility
- Optimizing for voice and visual search with schema markup
Enhancing User Experience with Shoppable Content
In 2025, shoppable content has become a game-changer for e-commerce and lead generation. This trend involves integrating shopping features directly into content, making it easier for users to convert.
Examples of shoppable content include:
- Embedded product forms within blog posts and articles
- Interactive product catalogs with real-time inventory updates
- Live shopping events with integrated checkout options
- Personalized product recommendations based on user behavior
Leveraging AI for Content Refinement
Using AI for Drafts and Humanizing for E-E-A-T
AI tools are invaluable for generating content drafts quickly, but human refinement is essential to meet E-E-A-T standards. The key is to use AI as a starting point and then enhance the content with unique insights and expertise.
Best practices for AI content refinement include:
- Using AI to generate initial drafts and outlines
- Adding personal anecdotes and case studies to humanize the content
- Incorporating original research and data to provide information gain
- Editing for accuracy and clarity to avoid AI hallucinations
Avoiding AI Hallucinations and Ensuring Accuracy
One of the biggest challenges with AI-generated content is the risk of hallucinations—incorrect or fabricated information. To maintain credibility, it's crucial to fact-check and verify all AI-generated content.
Strategies for ensuring accuracy include:
- Cross-referencing AI-generated facts with reliable sources
- Using expert reviews to validate complex information
- Implementing editorial guidelines for AI content refinement
- Regularly updating content to reflect the latest industry trends and data
Conclusion: Staying Ahead in SEO Content Writing
The landscape of SEO content writing in 2025 is dynamic and multifaceted. From leveraging AI tools to mastering E-E-A-T principles, the key to success lies in balancing automation with human expertise.
In the final section, we'll explore the future of SEO content writing, including emerging trends and technologies that will shape the industry in the years to come. Stay tuned for more insights and actionable tips to master SEO content writing in 2025 and beyond.
The Future of SEO: Emerging Trends and Technologies
AI and Machine Learning in Search Algorithms
As we look beyond 2025, AI and machine learning will continue to reshape search algorithms. Google's AI Overviews and similar technologies are just the beginning. Future advancements will likely include more sophisticated natural language processing and predictive search capabilities.
Content creators must stay ahead by:
- Monitoring AI-driven search trends and algorithm updates
- Adapting content strategies to align with predictive search patterns
- Investing in AI tools that enhance content creation and optimization
- Focusing on user intent to deliver highly relevant content
The Rise of Decentralized Search and Blockchain
Decentralized search engines and blockchain technology are poised to disrupt traditional SEO. These innovations promise greater transparency, security, and user control over data.
Preparing for decentralized search involves:
- Understanding blockchain-based SEO and its implications
- Optimizing for decentralized platforms like Presearch and Bitclave
- Emphasizing data privacy and ethical content practices
- Exploring tokenized incentives for user engagement
Sustainable SEO: Long-Term Strategies for Success
Building Evergreen Content with Information Gain
Evergreen content remains a cornerstone of sustainable SEO. However, in 2025 and beyond, the focus shifts to creating content that provides information gain—offering new insights, fresh data, and unique perspectives.
To create evergreen content with information gain:
- Conduct original research and publish proprietary data
- Update existing content with new trends and statistics
- Incorporate expert interviews and case studies
- Use interactive elements to enhance user engagement
Developing a Content Ecosystem with Ranch Style SEO
The "Ranch Style" SEO approach—creating multiple interlinked, focused pieces—is essential for building a robust content ecosystem. This strategy not only improves SEO but also enhances user experience by providing comprehensive coverage of topics.
Key steps to develop a content ecosystem:
- Identify core topics and break them into subtopics
- Create pillar pages that serve as hubs for related content
- Use internal linking to connect related articles and guide users
- Regularly audit and update content to maintain relevance and accuracy
Measuring Success: Key Metrics and KPIs for 2025
Beyond Traffic: Focusing on Quality and Conversions
In 2025, quality traffic and conversions take precedence over sheer volume. Metrics like bounce rate, time on page, and conversion rate provide deeper insights into content performance.
Essential KPIs to track include:
- Engagement metrics (time on page, scroll depth, social shares)
- Conversion rates (lead generation, sales, sign-ups)
- User intent alignment (how well content matches search queries)
- E-E-A-T signals (author credibility, content accuracy, trustworthiness)
Leveraging Advanced Analytics and AI Insights
Advanced analytics tools and AI-driven insights are crucial for measuring and optimizing content performance. These tools help identify trends, predict user behavior, and refine content strategies.
Utilize the following tools and techniques:
- Google Analytics 4 for comprehensive user behavior analysis
- AI-powered SEO tools like Clearscope and SurferSEO for content optimization
- Heatmaps and session recordings to understand user interactions
- Predictive analytics to anticipate future trends and user needs
Conclusion: Mastering SEO Content Writing in 2025 and Beyond
The world of SEO content writing in 2025 is characterized by rapid advancements in AI, evolving search algorithms, and the growing importance of E-E-A-T. To succeed, content creators must embrace innovation while maintaining a focus on authenticity, user intent, and information gain.
Key takeaways for mastering SEO content writing include:
- Leveraging AI tools for content creation while ensuring human refinement
- Prioritizing E-E-A-T principles to build trust and credibility
- Adapting to new search trends, including AI Overviews and decentralized search
- Creating a content ecosystem with Ranch Style SEO for comprehensive coverage
- Focusing on quality metrics and conversions over mere traffic volume
As we move forward, the integration of AI, blockchain, and advanced analytics will continue to redefine SEO strategies. By staying informed, adapting to change, and prioritizing user experience, content creators can navigate the complexities of SEO in 2025 and beyond. The future of SEO content writing is bright for those who embrace innovation, authenticity, and a relentless focus on delivering value to their audience.
In this ever-evolving landscape, the most successful content creators will be those who not only keep pace with technological advancements but also remain committed to the fundamental principles of quality, relevance, and trust. Here's to creating content that ranks, resonates, and drives results in 2025 and beyond.
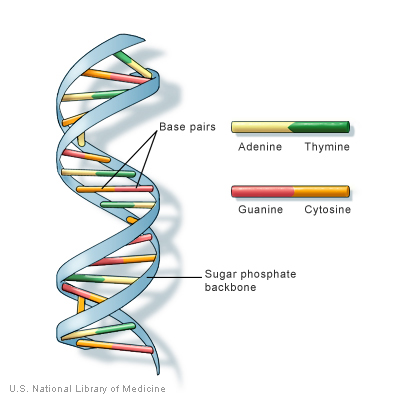
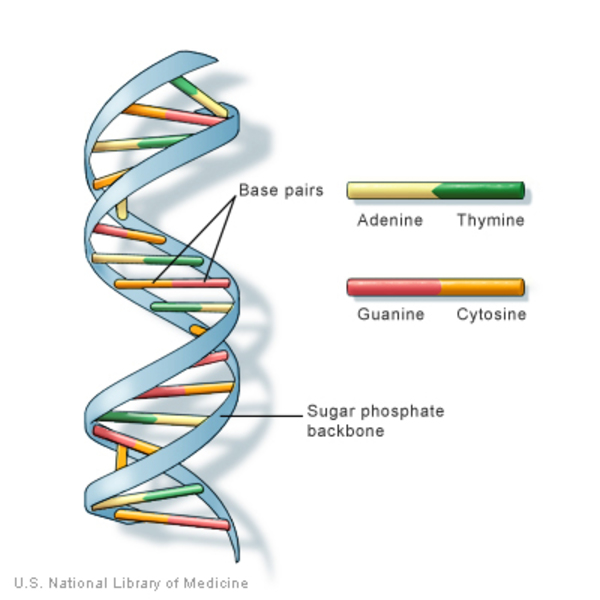
Frederick Sanger: Ein Leben für die Wissenschaft
Einführung
Frederick Sanger, ein Name, der in den wissenschaftlichen Kreisen fast legendär ist, hinterließ ein beeindruckendes Erbe, das die moderne Molekularbiologie maßgeblich geprägt hat. Als einer der wenigen Wissenschaftler, der gleich zweimal mit dem Nobelpreis ausgezeichnet wurde, ist Sanger ein herausragendes Beispiel für die Bedeutung von Beharrlichkeit, Kreativität und wissenschaftlicher Neugier. Im Folgenden werfen wir einen genaueren Blick auf sein Leben, seine Karriere und seine bahnbrechenden Entdeckungen.
Frühes Leben und Ausbildung
Frederick Sanger wurde am 13. August 1918 in Rendcomb, Gloucestershire, England, geboren. Als Sohn eines Arztes genoss er eine privilegierte Bildung und entwickelte früh ein Interesse an Naturwissenschaften. Er besuchte das Bryanston School in Dorset, das für seine fortschrittlichen Lehrmethoden bekannt war. Bereits hier zeigte sich Sangers Leidenschaft für das Experimentieren und die analytische Herangehensweise an Probleme.
Nach der Schule schrieb sich Sanger am St John's College, Cambridge, ein, um zunächst Physik zu studieren. Doch schon bald erkannte er, dass seine wahre Berufung in der Chemie lag, und wechselte sein Fachgebiet. Unter der Betreuung von Charles Phillips, einem einflussreichen Biochemiker, begann Sanger seine Reise in die Welt der Biochemie.
Der Weg zur ersten Nobelpreis-Auszeichnung
In den 1940er Jahren konzentrierte sich Sanger auf die Untersuchung von Proteinen, damals ein aufstrebendes Feld in der Biochemie. Seine Aufmerksamkeit richtete sich insbesondere auf Insulin, ein Protein von zentraler Bedeutung für das Verständnis von Stoffwechselprozessen beim Menschen. Sanger erkannte früh, dass das Verständnis der Aminosäuresequenz eines Proteins entscheidend war, um die Funktionen dieser Moleküle zu begreifen.
Nach jahrelanger intensiver Forschung und unter Verwendung bahnbrechender Techniken gelang es Sanger 1951, die vollständige Aminosäuresequenz des Insulins zu bestimmen. Diese Entdeckung war revolutionär, da es das erste Mal war, dass die genaue Struktur eines Proteins entschlüsselt wurde. Für diese außerordentliche Leistung wurde Sanger 1958 mit dem Nobelpreis für Chemie ausgezeichnet. Dies markierte den Beginn einer neuen Ära in der Biochemie und leitete die Ära der Proteinsequenzierung ein.
Die Pionierarbeit in der DNA-Sequenzierung
Nach seinem Erfolg mit der Proteinsequenzierung wandte sich Sanger in den 1970er Jahren einem neuen, nicht minder komplexen Thema zu: der DNA-Sequenzierung. Auch hier spielte er eine zentrale Rolle, indem er Methoden entwickelte, die den Weg für die Entschlüsselung der genetischen Informationen ebneten. Mit der Sanger-Methode, auch bekannt als Kettenabbruchmethode, schuf er eine Technik, die es ermöglichte, die Basensequenzen von DNA-Molekülen systematisch zu bestimmen.
Die Sanger-Methode zeichnete sich durch ihre Effizienz und Genauigkeit aus und wurde schnell zur Standardmethode für DNA-Sequenzierungen weltweit. Diese Methode legte das Fundament für das Humangenomprojekt und zahlreiche andere Genomprojekte, die das Verständnis der genetischen Grundlagen des Lebens radikal verändert haben.
Ein zweiter Nobelpreis als Krönung seiner Karriere
Für seine revolutionären Beiträge zur DNA-Sequenzierung wurde Sanger 1980 erneut mit dem Nobelpreis für Chemie ausgezeichnet, dieses Mal gemeinsam mit Paul Berg und Walter Gilbert. Es war das zweite Mal, dass Sanger diese höchste wissenschaftliche Ehrung erhielt, was ihm einen Platz unter den wenigen Wissenschaftlern sicherte, die diesen Preis zweimal gewinnen konnten.
Frederick Sangers Leistungen in der Biochemie und Molekularbiologie trugen erheblich zur Beschleunigung wissenschaftlicher Fortschritte bei und inspirierten zahlreiche nachfolgende Generationen von Forschern. Sein Erbe lebt weiter, nicht nur in den wissenschaftlichen Entdeckungen, die auf seinen Methoden basieren, sondern auch im Geiste von Innovation und Zielstrebigkeit, die er verkörperte.
Die Auswirkungen von Sangers Entdeckungen auf die Wissenschaft
Frederick Sangers Beiträge zur Biochemie und Molekularbiologie haben über die Jahre hinweg unzählige Türen für neue Forschungsfelder geöffnet. Seine Pionierarbeit in der Protein- und DNA-Sequenzierung war nicht nur ein Triumph der Chemie, sondern auch ein Katalysator für den Aufstieg der modernen Genetik und der Biotechnologie. Doch was machen seine Entdeckungen so bahnbrechend, und wie beeinflussen sie die Wissenschaft heute?
Die genaue Entschlüsselung von Proteinen und DNA hat das Verständnis biologischer Systeme tiefgreifend verändert. Durch die Bestimmung der Aminosäuresequenz von Proteinen wie Insulin legte Sanger den Grundstein für die Entdeckung unzähliger weiterer Proteine und ihrer Funktionen. Diese Informationen sind von entscheidender Bedeutung für das Verständnis von Krankheiten auf molekularer Ebene und haben die Entwicklung personalisierter Therapien, wie zielgerichteter Medikamente und Biopharmazeutika, maßgeblich vorangetrieben.
In einem weiteren Schritt ermöglichte Sangers DNA-Sequenzierung die Entschlüsselung vollständiger Genome verschiedenster Organismen. Diese Informationen sind zentral für die Entstehung der Genomik, einer Disziplin, die das genetische Material von Lebewesen umfassend untersucht. Die Fortschritte in diesem Bereich haben zur Entwicklung neuer Techniken wie der CRISPR-Gentechnik geführt, die weitreichende Anwendungen in der Landwirtschaft, der Medizin und der Umweltwissenschaften finden.
Einfluss auf das Humangenomprojekt und weitere Genomprojekte
Der Einfluss der Sanger-Methode auf das Humangenomprojekt kann nicht hoch genug eingeschätzt werden. Dieses gewaltige internationale Unterfangen, das die vollständige Sequenzierung des menschlichen Genoms zum Ziel hatte, wäre ohne die von Sanger entwickelten Sequenziertechniken undenkbar gewesen. Das Projekt begann offiziell im Jahr 1990 und wurde 2003 erfolgreich abgeschlossen. Es ermöglichte einen zuvor nie dagewesenen Einblick in die genetische Architektur des Menschen und legte die Grundlage für vielfältige Forschungsbereiche, darunter die Genommedizin.
Mittlerweile hat die Sequenzierungstechnologie beeindruckende Fortschritte gemacht. Das Aufkommen von Next-Generation-Sequencing (NGS) hat den Prozess erheblich beschleunigt und kostengünstiger gemacht, was es ermöglicht, ganze Genome in kurzer Zeit zu sequenzieren. Trotz dieser Fortschritte bleibt die Sanger-Methode ein unverzichtbares Werkzeug, insbesondere wenn es um die exakte Validierung von Sequenzierungsdaten geht.
Sangers Einfluss auf die Ausbildung und Förderung junger Wissenschaftler
Neben seinen wissenschaftlichen Leistungen war Sanger auch ein leidenschaftlicher Mentor für junge Wissenschaftler. Er war bekannt für seine Bescheidenheit und seine Bereitschaft, Wissen großzügig zu teilen. Viele seiner Schüler und Kollegen erinnern sich an ihn als jemanden, der stets die intellektuelle Neugier und die kritische Denkweise seiner Schüler förderte. Seine Fähigkeit, komplexe Sachverhalte einfach zu erklären und wissenschaftliche Neugier zu wecken, machte ihn zu einem inspirierenden Lehrer und Forscher.
Sanger zog sich 1983 offiziell aus der Forschung zurück, hinterließ aber ein Erbe, das weit über seine eigenen Entdeckungen hinausreicht. Seine Arbeit beeinflusst weiterhin Wissenschaftler und inspiriert zu neuen Entdeckungen in der Biochemie und Genetik. Das Sanger Institute, eine führende Einrichtung für Genomforschung, trägt seinen Namen und steht als Symbol für seine anhaltende Bedeutung in der wissenschaftlichen Gemeinschaft.
Ein bleibendes Vermächtnis
Frederick Sanger verstarb am 19. November 2013 im Alter von 95 Jahren, hinterlässt jedoch ein beeindruckendes Vermächtnis, das weit über seine eigenen Entdeckungen hinausgeht. Seine Beiträge zur Sequenzierung von Proteinen und DNA haben die Wissenschaft grundlegend verändert und ebnen weiterhin den Weg für zukünftige Innovationen in der Biologie und Medizin.
Sanger war mehr als nur ein brillanter Wissenschaftler; er war ein bescheidener Visionär, dessen Arbeiten das Potenzial der Molekularbiologie aufzeigten und die Art und Weise, wie wir genetische Informationen betrachten, revolutionierten. Seine Entdeckungen ermöglichen es Wissenschaftlern heute, Krankheiten besser zu verstehen, neue Behandlungsmethoden zu entwickeln und letztendlich das menschliche Leben zu verbessern. Frederick Sangers Erbe lebt in den Laboren und Forschungsinstituten der Welt weiter, ein Zeugnis seiner unermüdlichen Neugier und seines Engagements für die Wissenschaft.
Wertschätzung und Anerkennung in der wissenschaftlichen Gemeinschaft
Frederick Sanger wird von vielen als einer der einflussreichsten Wissenschaftler des 20. Jahrhunderts angesehen. Seine bahnbrechenden Arbeiten in der Sequenzierung von Biomolekülen haben nicht nur zu bedeutenden wissenschaftlichen Fortschritten geführt, sondern auch die Art und Weise revolutioniert, wie wir genetische Informationen wahrnehmen und nutzen. Die zweifache Auszeichnung mit dem Nobelpreis ist nur ein Aspekt der Anerkennung, die Sanger in seiner Karriere erfahren hat. Seine Methoden und Entdeckungen werden bis heute in der Wissenschaftsgemeinschaft hoch geschätzt und bilden die Basis für viele moderne Anwendungen in der Medizin und Biotechnologie.
Zu seinen Ehren haben zahlreiche wissenschaftliche Institutionen und Organisationen Preise und Stipendienprogramme ins Leben gerufen, die seinen Namen tragen und junge Wissenschaftler dazu ermutigen, in seinen Fußstapfen zu wandeln. Auch in den Medien und der Öffentlichkeit wird sein Erbe oft gewürdigt, nicht zuletzt durch Dokumentationen und Biografien, die das Leben und die Leistungen dieses bemerkenswerten Wissenschaftlers beleuchten.
Einflüsse über die Wissenschaft hinaus
Der Einfluss von Sangers Arbeit geht weit über die Wissenschaft hinaus und hat auch sozioökonomische und ethische Implikationen. Die Möglichkeiten, die durch die Entschlüsselung des genetischen Codes eröffnet wurden, haben Diskussionen über die Ethik der Gentechnik, den Datenschutz bei genetischen Informationen und das Potenzial für personalisierte Medizin ausgelöst. Diese Themen sind heute aktueller denn je, da die Fortschritte in der Genetik rasant voranschreiten und immer neue Anwendungen und Fragestellungen entstehen.
Dank der Pionierarbeit von Sanger stehen heute Techniken zur Verfügung, mit denen genetische Erkrankungen früher erkannt werden können, was die Entwicklung von frühzeitigen Interventionen ermöglicht. Allerdings werfen diese Fortschritte auch Fragen nach der Zugänglichkeit und den Kosten solcher Technologien auf, da nicht alle Bevölkerungsgruppen gleichermaßen von diesen wissenschaftlichen Durchbrüchen profitieren können.
Lehren aus Sangers Lebenswerk
Ein Blick auf Frederick Sangers Lebenswerk bietet wertvolle Lehren für die moderne Wissenschaft und Gesellschaft. Er verkörperte die Ideale der Wissenschaftlichkeit: Neugier, Genauigkeit und die Bereitschaft, konventionelle Denkmuster zu hinterfragen. Sein Ansatz, komplexe biologische Probleme mit chemischen Methoden zu lösen, war innovativ und zeigt, wie interdisziplinäres Denken zu bedeutenden Durchbrüchen führen kann.
Sanger lehrte durch sein Beispiel auch, dass Wissenschaft ein kooperativer Prozess ist. Er arbeitete oft mit anderen Forschern und Laboren zusammen, was zeigte, dass Teamwork und ein offener Austausch von Daten und Ideen entscheidend für den Fortschritt sind. Diese Herangehensweise ist besonders in der heutigen Wissenschaftslandschaft relevant, in der internationale Kooperationen und offene Wissenschaftspraktiken immer mehr an Bedeutung gewinnen.
Ausblick in die Zukunft
Obwohl Sanger selbst nicht mehr unter uns ist, bleibt sein Einfluss spürbar, und seine Entdeckungen bieten weiterhin eine Plattform für Innovationen in der Forschung. Die Herausforderung für die aktuelle und zukünftige Wissenschaft liegt darin, auf den Errungenschaften von Sanger und seinen Zeitgenossen aufzubauen und gleichzeitig verantwortungsbewusste ethische Standards für den Umgang mit neuen biotechnologischen Möglichkeiten zu entwickeln.
Mit Fortschritten in der molekularen Diagnostik, der präzisen Gentherapie und der synthetischen Biologie eröffnen sich neue Horizonte, die Sanger sicherlich fasziniert hätten. Seine Arbeit lebt in jedem Labor und jeder Studie weiter, die von den Methoden inspiriert ist, die er entwickelt hat. Die Wissenschaftsgemeinschaft hat die Pflicht, seine Neugier, Sorgfalt und seinen Respekt für die Ethik der Forschung zu bewahren und dabei die unerforschten Möglichkeiten zu erkunden, die seine Entdeckungen ermöglicht haben.
In einer sich ständig wandelnden Welt sind es Wissenschaftler wie Frederick Sanger, deren Entdeckungen uns zeigen, was möglich ist, wenn Neugier auf Entschlossenheit trifft und die Begeisterung für Wissen die treibende Kraft ist. Sein Vermächtnis ist ein zeitloses Zeugnis dieser prinzipiengeleiteten Suche nach Wissen und Fortschritt.

Margarita Salas: Eine Pionierin der Molekularbiologie
Einleitung
Margarita Salas, eine bedeutende Figur in der Wissenschaftswelt, hat mit ihren Beiträgen zur Molekularbiologie die Forschung nachhaltig geprägt. Mit ihrem bahnbrechenden Werk und ihrer unermüdlichen Hingabe hat sie nicht nur das Wissen auf diesem Gebiet erweitert, sondern auch vielen Menschen den Weg in die Wissenschaft gewiesen. Diese ersteilige Serie beleuchtet das Wirken und den Einfluss von Margarita Salas auf die Wissenschaft und die Gesellschaft.
Frühe Jahre und Bildung
Margarita Salas wurde am 30. November 1938 in Asturien, Spanien, geboren. Schon in jungen Jahren zeigte sie großes Interesse an der Wissenschaft, inspiriert durch ihre Lehrer und die Unterstützung ihrer Familie. Sie entschied sich, Chemie an der Universität Complutense in Madrid zu studieren, wo sie ihre akademische Reise begann. Schon während ihrer Studienzeit zeigte sie eine außergewöhnliche Fähigkeit zum kritischen Denken und zur Problemlösung, was ihre Professoren und Kommilitonen gleichermaßen beeindruckte.
Nach ihrem Abschluss setzte sie ihre Ausbildung fort und entschied sich für einen speziellen Bereich, der damals noch in den Kinderschuhen steckte: die Molekularbiologie. Als Doktorandin vertiefte sie sich in die Welt der Genetik und Biochemie und begann, eigene Forschungsprojekte zu entwickeln. Ihre frühe Arbeit in diesem Bereich war von entscheidender Bedeutung für die Fortschritte, die sie später als vollwertige Wissenschaftlerin machen sollte.
Zusammenarbeit mit Severo Ochoa
Ein wesentlicher Meilenstein in der Karriere von Margarita Salas war die Zusammenarbeit mit dem spanischen Biochemiker und Nobelpreisträger Severo Ochoa. In den 1960er Jahren zog Salas in die Vereinigten Staaten, um mit Ochoa an der New York University zu arbeiten. Diese Zusammenarbeit sollte sich als äußerst fruchtbar erweisen, da sie Salas die Möglichkeit bot, sich mit den führenden Methoden und Techniken der Molekularbiologie vertraut zu machen.
Unter der Anleitung von Ochoa vertiefte Salas ihr Wissen über die Mechanismen der DNA- und RNA-Synthese. Ihre gemeinsame Forschung trug dazu bei, wichtige Aspekte der genetischen Transkription und der biochemischen Prozesse in Zellen zu entschlüsseln. Diese Arbeit war nicht nur ein bedeutender Schritt in ihrer Karriere, sondern auch ein wichtiger Beitrag zur Wissenschaft insgesamt, der das Verständnis der genetischen Informationsübertragung entscheidend erweiterte.
Pionierarbeit in der DNA-Replikation
Nach ihrer Rückkehr nach Spanien im Jahr 1967 setzte Margarita Salas ihre Forschung mit unermüdlichem Einsatz fort. Sie etablierte ihr eigenes Labor am Zentrum für Molekularbiologie, das heute als Zentrum für Molekularbiologie Severo Ochoa bekannt ist, und begann, sich mit der DNA-Replikation zu beschäftigen. Eine ihrer bedeutendsten Entdeckungen war die Identifizierung und Charakterisierung der DNA-Polymerase phi29.
Diese Enzymentdeckung stellte einen wesentlichen Fortschritt in der Molekularbiologie dar. Die von Salas und ihrem Team entwickelte Technik zur DNA-Amplifikation machte es möglich, DNA-Mengen effizient zu vervielfältigen – eine Technik, die in der genetischen Forschung, medizinischen Diagnostik und in der Forensik weitreichende Anwendung fand. Die Leistungsfähigkeit dieser Methode machte sie zu einem unverzichtbaren Werkzeug in vielen biologischen und medizinischen Labors weltweit.
Einfluss und Vermächtnis
Der Einfluss von Margarita Salas auf die Wissenschaft und die Gesellschaft ist von unvergleichlicher Bedeutung. Ihre bahnbrechende Arbeit hat nicht nur das Verständnis von genetischen Prozessen auf molekularer Ebene vertieft, sondern auch zur Entwicklung neuer biotechnologischer Methoden beigetragen. Diese Methoden haben die Art und Weise, wie Forschung betrieben wird, revolutioniert und es Wissenschaftlern ermöglicht, bisher unvorstellbare Fortschritte zu erzielen.
Margarita Salas war nicht nur eine herausragende Wissenschaftlerin, sondern auch eine engagierte Mentorin und Lehrerin. Sie förderte zahlreiche junge Forscher und inspirierte eine neue Generation von Wissenschaftlerinnen, sich mutig in die von Männern dominierte Welt der Wissenschaft vorzuwagen. Salas war der festen Überzeugung, dass wissenschaftliche Exzellenz in Zusammenarbeit, Diversität und einer offenen Einstellung wurzelt, und sie lebte diese Prinzipien sowohl in ihrer Forschung als auch in ihrem Privatleben.
Mentorenschaft und Förderung junger Talente
Margarita Salas war nicht nur in ihrer Forschung bemerkenswert erfolgreich, sondern auch in ihrer Rolle als Mentorin. Sie erkannte frühzeitig die Bedeutung der Förderung junger Talente in der Wissenschaft und setzte sich aktiv dafür ein, Nachwuchswissenschaftler zu inspirieren und zu unterstützen. Ihre eigene Karriere war geprägt von einer Umgebung der Förderung und des Austauschs, und sie war bestrebt, diese Tradition fortzusetzen, um sicherzustellen, dass die nächste Generation Zugang zu den bestmöglichen Ressourcen und Ratschlägen hatte.
In ihrem Labor legte Salas großen Wert auf ein kollaboratives Arbeitsumfeld, in dem Ideen offen ausgetauscht und diskutiert werden konnten. Sie ermutigte ihre Studenten und Kollegen, eigenständig zu denken und innovative Ansätze zu verfolgen. Ihre Fähigkeit, komplexe wissenschaftliche Konzepte verständlich zu erklären, machte sie zu einer beliebten Lehrerin und Mentorin, deren Einfluss weit über die Grenzen ihres Labors hinausging.
Salas war sich der Herausforderungen bewusst, denen Frauen in der Wissenschaft häufig begegneten, und war eine lautstarke Verfechterin für Geschlechtergleichheit in der wissenschaftlichen Forschung. Sie setzte sich dafür ein, Hindernisse abzubauen, die Frauen zurückhalten könnten, und wurde zu einem Vorbild für viele aufstrebende Wissenschaftlerinnen. Ihr Engagement in der Förderung von Frauen in der Wissenschaft hat zahlreiche Frauen ermutigt, wissenschaftliche Karrieren einzuschlagen und erfolgreich zu sein, selbst in den anspruchsvollsten Bereichen der Forschung.
Wissenschaftliche Anerkennung und Auszeichnungen
Die Errungenschaften von Margarita Salas blieben nicht unbemerkt, und sie erhielt im Laufe ihrer Karriere zahlreiche Auszeichnungen und Ehrungen. Ihre Beiträge zur Wissenschaft wurden sowohl in Spanien als auch international anerkannt. Eine der bedeutendsten Auszeichnungen war der L'Oréal-UNESCO-Preis für Frauen in der Wissenschaft, der ihr 1999 verliehen wurde. Diese Auszeichnung würdigt ihre herausragenden Leistungen in der Molekularbiologie und ihre Rolle als inspirierende Führungsfigur für Frauen in der Wissenschaft.
Margarita Salas wurde auch in zahlreiche wissenschaftliche und akademische Gesellschaften aufgenommen, darunter die Königlich Spanische Akademie der Wissenschaften und die Europäische Akademie der Wissenschaften und Künste. Diese Anerkennungen unterstreichen ihr Ansehen in der internationalen wissenschaftlichen Gemeinschaft und ihr Vermächtnis als wegweisende Forscherin.
Ihr Einfluss geht jedoch über ihre wissenschaftlichen Errungenschaften hinaus. Salas war auch als Mitglied in verschiedenen wissenschaftlichen Beiräten und Organisationen tätig, in denen sie ihre Expertise und Erfahrungen einbrachte, um die zukünftige Ausrichtung der wissenschaftlichen Forschung und der Bildungspolitik zu gestalten.
Fortsetzung ihres Vermächtnisses
Nach ihrem Tod im Jahr 2019 hinterließ Margarita Salas ein beeindruckendes Vermächtnis, das weiterhin Generationen von Wissenschaftlern inspiriert. Ihre Entdeckungen und der wissenschaftliche Geist, den sie förderte, leben in den Arbeiten derjenigen weiter, die von ihrer Lehre beeinflusst wurden. Ihr Labor, das zu einem Zentrum des Wissens und der Innovation wurde, hat zahlreichen Wissenschaftlern als Sprungbrett für ihre eigenen Forschungen gedient und wird dies auch in Zukunft tun.
Darüber hinaus hat ihre Arbeit in der DNA-Amplifikation nicht nur die Wissenschaft, sondern auch andere Bereiche beeinflusst, einschließlich der Medizin, wo ihre Methoden der genetischen Analyse und Diagnostik neue Möglichkeiten eröffnet haben, Krankheiten zu erforschen und zu behandeln.
Der Name Margarita Salas steht heute für wissenschaftliche Exzellenz, Innovation und die Kraft des Wissens, Barrieren zu überwinden und neue Wege zu öffnen. Ihr Beitrag zur Molekularbiologie und ihr Engagement für Bildung und Gleichberechtigung in der Wissenschaft sind unvergesslich und inspirierend für alle, die den Weg der Wissenschaft beschreiten wollen.
Ihre Geschichte ermutigt neue Generationen, beharrlich zu forschen, sich für die Dinge einzusetzen, an die sie glauben, und den Mut zu haben, das Unbekannte zu erforschen. Salas hat nicht nur ihr Wissen weitergegeben, sondern auch eine Philosophie geprägt, die weit über die Grenzen der Labors hinausreicht und die Welt der Wissenschaft für viele zugänglicher gemacht hat.
Innovation und Grenzen der Wissenschaft verschieben
Margarita Salas war bekannt für ihre unkonventionellen Herangehensweisen an wissenschaftliche Probleme. Ihre Karriere war geprägt von einer ständigen Suche nach Wissen und einem unermüdlichen Streben, die Grenzen der Wissenschaft zu erweitern. Die von ihr entwickelten Techniken und ihre Entdeckungen in der DNA-Polymerase-Forschung haben das Verständnis neuer Forschungsbereiche gefördert und dazu beigetragen, innovative Methoden im Bereich der Biotechnologie zu entwickeln.
Eine der bahnbrechenden Anwendungen ihrer Forschungen ist die Polymerase-Kettenreaktion (PCR), eine Technik, die heute unverzichtbar in der Molekularbiologie ist. Diese Methode, bei der DNA-Fragmente vervielfältigt werden, hat die genetische Forschung revolutioniert. Ihre Arbeit legte den Grundstein für viele moderne Anwendungen in der Diagnostik und Genetik, einschließlich der pränatalen Diagnostik, der Onkologie und der Infektionskrankheitsforschung. Sie war maßgeblich daran beteiligt, Technologien zu entwickeln, die Medizinern und Forschern helfen, Genmutationen besser zu verstehen und personalisierte Behandlungen zu entwickeln.
Vermächtnis als Wissenschaftskommunikatorin
Zusätzlich zu ihren zahlreichen wissenschaftlichen Beiträgen war Margarita Salas auch eine herausragende Wissenschaftskommunikatorin. Sie setzte sich dafür ein, komplexe wissenschaftliche Themen für die breite Öffentlichkeit zugänglicher zu machen, und arbeitete eng mit Bildungsinstitutionen zusammen, um das Interesse an den Naturwissenschaften zu fördern. Ihr Einsatz, wissenschaftliche Informationen verständlich und fesselnd zu präsentieren, hat dazu beigetragen, das Interesse der breiten Öffentlichkeit an der Wissenschaft zu wecken und zu fördern.
Salas war der Überzeugung, dass der Zugang zu wissenschaftlichem Wissen ein grundlegendes Menschenrecht ist und dass Bildung der Schlüssel zu Fortschritt und Innovation ist. Deshalb engagierte sie sich in zahlreichen Bildungsinitiativen und schrieb populärwissenschaftliche Artikel, um ihre Begeisterung für die Wissenschaft zu teilen. Ihr Engagement für die Wissenschaftskommunikation hat Generationen von Studierenden inspiriert und ermutigt, die Welt der Wissenschaft mit Neugier und kritischem Denken zu erkunden.
Fortdauernder Einfluss
Auch Jahre nach ihrem Tod bleibt der Einfluss von Margarita Salas in der wissenschaftlichen Welt spürbar. Ihre Entdeckungen und Technologien werden weiterhin weltweit in Laboren angewendet und erweisen sich als unverzichtbare Werkzeuge für Forscher. Ihr Ansatz zur Förderung von Vielfalt und Inklusion in der Wissenschaft bildet heute die Grundlage für viele Bildungs- und Wissenschaftsförderprogramme, die darauf abzielen, jungen Menschen den Zugang zu einer Karriere in den Naturwissenschaften zu erleichtern.
Die Anerkennung ihrer Arbeit und ihres Einflusses zeigt sich auch in der Benennung mehrerer Institutionen und wissenschaftlicher Preise nach ihr, was ihr Erbe als bedeutende Persönlichkeit in der Wissenschaftsgeschichte ehrt. Ihr Vermächtnis wirkt sich nicht nur auf die aktuelle Forschung aus, sondern legt den Grundstein für zukünftige Durchbrüche in der Molekularbiologie und darüber hinaus.
Margarita Salas war mehr als eine Wissenschaftlerin; sie war eine Visionärin, deren Arbeit und Ethik die Art und Weise prägten, wie wir Forschung betrachten und betreiben. Ihr Vermächtnis wird weiterhin Wissenschaftler inspirieren, sich mutig den Herausforderungen der Zukunft zu stellen, neue Ideen zu erkunden und die wissenschaftlichen Entdeckungen von morgen zu gestalten. Ihr Leben und ihre Arbeit erinnern uns daran, dass wahre Exzellenz aus Leidenschaft, harter Arbeit und dem unermüdlichen Streben nach Wissen entsteht.
In einem Zeitalter der wissenschaftlichen Erkundung bleibt Margarita Salas eine Leuchtfigur und ein Symbol dafür, was erreicht werden kann, wenn man mit Entschlossenheit und einer klaren Vision vorangeht. Ihre Beiträge zur Molekularbiologie und zur Wissenschaft im Allgemeinen werden noch lange nachhallen und neue Generationen dazu inspirieren, ihre eigene Reise in die Welt des Unbekannten anzutreten.


Top AI and Tech Trends Shaping 2025: A Deep Dive
Introduction to the AI and Tech Landscape in 2025
The year 2025 marks a pivotal moment in the evolution of artificial intelligence (AI) and technology. As industries adapt to rapid advancements, key trends are emerging that promise to redefine how businesses and consumers interact with technology. From agentic AI to breakthroughs in healthcare and cybersecurity, this article explores the most impactful developments shaping the future.
According to recent data, the U.S. National Science Foundation expanded its National AI Research Resource (NAIRR) Pilot in August 2025, adding 10 new datasets to foster broader AI research access. This move underscores the growing importance of AI infrastructure in driving innovation across sectors.
The Rise of Agentic AI: Autonomous Systems Take Center Stage
One of the most transformative trends in 2025 is the rise of agentic AI. These autonomous systems are designed to learn, adapt, and collaborate, moving beyond traditional AI models. Unlike static algorithms, agentic AI can dynamically adjust to new data, making it ideal for applications in logistics, virtual assistants, and software development.
McKinsey highlights that agentic AI is transitioning from pilot projects to full-scale deployments. Companies are leveraging these systems to enhance productivity and streamline operations. For instance, autonomous AI agents are now being used in supply chain management to optimize routes and reduce delivery times.
Key Applications of Agentic AI
- Logistics and Supply Chain: AI agents autonomously manage inventory and predict demand.
- Virtual Coworkers: AI-powered assistants handle repetitive tasks, freeing up human workers for strategic roles.
- Software Development: Autonomous systems assist in coding, debugging, and deploying applications.
Microsoft predicts that agentic AI will have a measurable impact on R&D throughput, accelerating innovation cycles across industries. This shift is not just about automation but about creating systems that can collaborate with humans in real-time.
Healthcare AI: A New Era of Personalized Medicine
The healthcare sector is experiencing a revolution driven by AI-powered solutions. In October 2025, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) doubled funding for childhood cancer research, with a strong emphasis on AI for detection, diagnostics, and personalized treatment. This investment reflects the growing role of AI in transforming patient care.
AI is being integrated into various aspects of healthcare, from early detection of diseases to personalized treatment plans. For example, AI algorithms analyze medical imaging data to identify anomalies with higher accuracy than traditional methods. Additionally, AI-driven microfluidics are enabling advancements in reproduction and precision medicine.
Breakthroughs in AI-Driven Healthcare
- Early Detection: AI models analyze patient data to identify diseases at earlier stages.
- Personalized Treatment: AI tailors treatment plans based on individual genetic profiles.
- Microfluidics and AI: Combining AI with microfluidics for advanced diagnostics and research.
The convergence of AI and biotechnology is addressing critical challenges, such as misinformation in medical data and the need for more efficient drug discovery processes. As AI continues to evolve, its impact on healthcare will only deepen, leading to better outcomes for patients worldwide.
Cybersecurity Consolidation: Major M&A Deals in 2025
The cybersecurity landscape is undergoing significant consolidation, driven by high-profile mergers and acquisitions. In 2025, Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) completed its $13.4 billion acquisition of Juniper Networks, while Palo Alto Networks agreed to purchase CyberArk for approximately $25 billion. These deals highlight the growing importance of cybersecurity in an increasingly digital world.
As cyber threats become more sophisticated, companies are investing heavily in advanced security solutions. The consolidation trend is driven by the need for comprehensive security platforms that can protect against a wide range of threats, from ransomware to data breaches.
Impact of Cybersecurity M&A Deals
- Enhanced Security Solutions: Combined expertise leads to more robust security platforms.
- Market Competition: Consolidation reduces the number of players, increasing competition among the remaining firms.
- Innovation Acceleration: Merged companies can pool resources to develop cutting-edge security technologies.
The cybersecurity market is expected to continue its rapid growth, with AI playing a crucial role in threat detection and response. As businesses and governments prioritize security, the demand for advanced cybersecurity solutions will only increase.
Conclusion: The Future of AI and Tech in 2025 and Beyond
The trends shaping 2025 reflect a broader shift toward autonomous, intelligent systems that can adapt and collaborate. From agentic AI to breakthroughs in healthcare and cybersecurity, these developments are setting the stage for a future where technology is more integrated into our daily lives.
As we move forward, the convergence of AI, biotechnology, and sustainability will continue to drive innovation. Companies that embrace these trends will be well-positioned to lead in the next era of technological advancement.
AI Infrastructure and Data Accessibility: Fueling Innovation
The foundation of AI advancement in 2025 lies in robust infrastructure and accessible data. The U.S. National Science Foundation’s launch of the Integrated Data Systems and Services (IDSS) in August 2025 marked a significant milestone. By adding 10 new datasets to the National AI Research Resource (NAIRR) Pilot, the initiative aims to democratize AI research, enabling broader participation from academia and industry.
This expansion is critical for fostering explainable AI models, particularly in credit assessment. For instance, Fair Isaac (FICO) secured patents in October 2025 for AI models that use alternative data to score "unscorable" consumers. This innovation enhances financial inclusivity by providing credit access to individuals previously excluded from traditional systems.
Key Developments in AI Infrastructure
- Expanded Datasets: The NAIRR Pilot now includes diverse datasets, accelerating AI research across sectors.
- Explainable AI: FICO’s patents highlight the importance of transparency in AI-driven credit scoring.
- Collaborative Research: Public-private partnerships are driving AI infrastructure growth, ensuring broader access to critical resources.
The focus on data accessibility is not just about quantity but also about quality. High-quality, diverse datasets are essential for training AI models that are fair, accurate, and inclusive. As AI continues to permeate various industries, the role of infrastructure in supporting these advancements cannot be overstated.
Sustainability and Energy: Converging Technologies for a Greener Future
In 2025, the intersection of AI and sustainability is driving innovations that address some of the world’s most pressing environmental challenges. The World Economic Forum identifies technology convergence—such as AI combined with biotech, materials science, and energy—as a key trend. These convergences are leading to breakthroughs in structural battery composites, osmotic power, and advanced nuclear energy.
One notable example is the development of structural batteries, which integrate energy storage into building materials. This innovation reduces the need for separate battery systems, making structures more energy-efficient. Similarly, osmotic power harnesses the energy generated from the difference in salt concentration between freshwater and seawater, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional energy sources.
Emerging Sustainable Technologies
- Structural Battery Composites: Buildings and vehicles can now store energy within their structures, reducing reliance on external power sources.
- Osmotic Power: A renewable energy solution that leverages natural salt gradients to generate electricity.
- Advanced Nuclear Energy: Safer and more efficient nuclear reactors are being developed to provide clean energy at scale.
The push for sustainability is also evident in the redesign of industrial processes. Companies are adopting AI-driven solutions to optimize energy use, reduce waste, and minimize their carbon footprint. For example, AI algorithms are being used to monitor and adjust manufacturing processes in real-time, ensuring maximum efficiency with minimal environmental impact.
Edge Computing and DevSecOps: The Future of Software Development
The software development landscape in 2025 is being reshaped by two major trends: edge computing and DevSecOps. As businesses increasingly rely on real-time data processing, edge computing has emerged as a critical solution for reducing latency and enhancing privacy. By processing data closer to its source, edge computing minimizes the need for centralized cloud servers, improving speed and security.
Meanwhile, DevSecOps—the integration of security into DevOps practices—is becoming a standard in software development. This approach ensures that security is not an afterthought but a fundamental part of the development process. Automated scanning, supply chain verification, and continuous monitoring are key components of DevSecOps, helping organizations mitigate risks and comply with regulatory requirements.
Key Trends in Software Development
- Edge Functions: Deploying serverless functions at the edge to enhance performance and reduce latency.
- Distributed Databases: Leveraging decentralized databases to improve data accessibility and resilience.
- Automated Security Scanning: Integrating security checks into CI/CD pipelines to identify vulnerabilities early.
The adoption of edge computing and DevSecOps is driven by the need for faster, more secure, and scalable software solutions. As industries continue to digitalize, these trends will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of software development.
Biotech and AI: Revolutionizing Healthcare and Beyond
The convergence of biotechnology and AI is unlocking new possibilities in healthcare, agriculture, and environmental science. In 2025, advancements in engineered living therapeutics and GLP-1 therapies are transforming the treatment of chronic diseases. These therapies use AI to design personalized treatments that target specific biological pathways, improving efficacy and reducing side effects.
Another groundbreaking development is the integration of AI and microfluidics. This combination is revolutionizing diagnostics and research, enabling precise control over fluid flows at microscopic scales. For example, AI-driven microfluidic devices are being used to analyze blood samples with unprecedented accuracy, facilitating early disease detection and personalized medicine.
Innovations in Biotech and AI
- Engineered Living Therapeutics: AI-designed treatments that use living cells to target diseases.
- GLP-1 Therapies: Personalized treatments for metabolic disorders, enhanced by AI-driven insights.
- AI-Microfluidics: Advanced diagnostic tools that combine AI with microfluidic technology for precision medicine.
The synergy between biotech and AI is also driving progress in agriculture. AI models are being used to optimize crop yields, predict disease outbreaks, and develop sustainable farming practices. These innovations are critical for addressing global food security challenges and reducing the environmental impact of agriculture.
Economic Pressures and Regulatory Developments in 2025
Despite the rapid advancements in AI and technology, economic pressures and regulatory changes are shaping the landscape in 2025. The reinstatement of Trump-era tariffs has introduced uncertainty in the IT sector, slowing investments in some areas. However, the focus on AI and cybersecurity remains strong, driven by the need for innovation and security in an increasingly digital world.
On the regulatory front, the EXPERTS Act, passed in November 2025, mandates greater transparency in rulemaking processes. This legislation aims to limit industry delays and ensure that regulatory frameworks keep pace with technological advancements. Additionally, the CAA permitting reforms, advanced in December 2025, are streamlining approval processes for critical infrastructure projects, including those related to AI and energy.
Key Regulatory and Economic Trends
- Tariff Impacts: Economic uncertainty due to tariffs is affecting IT investments, though AI remains a priority.
- EXPERTS Act: Enhances transparency in rulemaking, reducing delays in regulatory processes.
- CAA Permitting Reforms: Accelerates approvals for infrastructure projects, supporting AI and energy initiatives.
Navigating these economic and regulatory challenges requires a strategic approach. Companies that adapt to changing policies and invest in resilient technologies will be better positioned to thrive in this dynamic environment.
The Role of Quantum Computing in AI Advancement
Quantum computing is emerging as a game-changer in AI development, offering unprecedented computational power to solve complex problems. In 2025, governments and private sector leaders are accelerating investments in quantum initiatives to mitigate risks and unlock new opportunities. The U.S. Office of Science and Technology Policy (OSTP) recognizes quantum computing as a critical tool for advancing AI, particularly in fields like drug discovery, materials science, and cryptography.
One of the most promising applications of quantum computing is in AI-driven drug discovery. Traditional methods of developing new medications are time-consuming and costly, but quantum algorithms can simulate molecular interactions at an atomic level, significantly speeding up the process. This convergence of quantum computing and AI is expected to revolutionize healthcare by enabling the rapid development of personalized treatments.
Quantum Computing Applications in AI
- Drug Discovery: Quantum simulations accelerate the identification of potential drug candidates.
- Materials Science: AI models leverage quantum computing to design advanced materials with unique properties.
- Cryptography: Quantum-resistant algorithms enhance cybersecurity in an era of increasing digital threats.
The integration of quantum computing into AI is still in its early stages, but the potential is immense. As research progresses, we can expect breakthroughs that will redefine industries, from healthcare to finance. Companies that invest in quantum-AI convergence today will be at the forefront of innovation in the coming years.
The Impact of 5G and E-Commerce on Digital Transformation
The rollout of 5G technology continues to drive digital transformation across industries, enabling faster connectivity and more reliable data transmission. In 2025, the combination of 5G and AI is unlocking new possibilities in e-commerce, autonomous vehicles, and smart cities. Businesses are leveraging these technologies to enhance customer experiences, optimize operations, and create new revenue streams.
In the e-commerce sector, 5G-powered AI is revolutionizing the way consumers shop. Faster load times, personalized recommendations, and augmented reality (AR) shopping experiences are becoming standard features. Retailers that adopt these technologies are seeing higher engagement rates and increased sales. Additionally, AI-driven logistics are improving supply chain efficiency, ensuring that products reach customers faster and more reliably.
5G and AI in Digital Transformation
- Enhanced E-Commerce: Faster connectivity and AI personalization improve the online shopping experience.
- Autonomous Vehicles: 5G enables real-time data processing for safer and more efficient self-driving cars.
- Smart Cities: AI and 5G work together to optimize traffic flow, energy use, and public services.
The synergy between 5G and AI is also transforming industries like manufacturing and healthcare. In manufacturing, AI-powered robots with 5G connectivity can operate with greater precision and adaptability. In healthcare, remote monitoring and telemedicine are becoming more accessible, thanks to the high-speed, low-latency capabilities of 5G networks.
Addressing Ethical and Societal Challenges in AI
As AI continues to advance, ethical and societal challenges are coming to the forefront. Issues such as bias in AI algorithms, job displacement, and privacy concerns require careful consideration. In 2025, governments, businesses, and researchers are working together to develop frameworks that ensure AI is used responsibly and equitably.
One of the most pressing concerns is algorithm bias, which can perpetuate discrimination in areas like hiring, lending, and law enforcement. To combat this, organizations are implementing explainable AI models that provide transparency into how decisions are made. Additionally, diverse datasets and inclusive design practices are being adopted to minimize bias and ensure fairness.
Key Ethical Considerations in AI
- Algorithm Bias: Ensuring AI models are trained on diverse datasets to prevent discriminatory outcomes.
- Job Displacement: Addressing the impact of automation on the workforce through reskilling programs.
- Privacy Concerns: Implementing robust data protection measures to safeguard user information.
Another critical challenge is the potential for job displacement due to AI-driven automation. While AI can enhance productivity, it also raises concerns about the future of work. Governments and businesses are responding by investing in reskilling and upskilling programs to prepare workers for the jobs of tomorrow. By fostering a workforce that can adapt to technological changes, societies can mitigate the negative impacts of automation.
Conclusion: The Future of AI and Technology in 2025 and Beyond
The year 2025 represents a turning point in the evolution of AI and technology. From the rise of agentic AI to breakthroughs in healthcare, sustainability, and cybersecurity, the trends shaping this year are setting the stage for a future where technology is more integrated, intelligent, and impactful. As industries continue to adopt these advancements, the potential for innovation and growth is boundless.
Key takeaways from the trends discussed include:
- Agentic AI is transforming industries by enabling autonomous, adaptive systems.
- Healthcare AI is revolutionizing diagnostics and personalized medicine.
- Cybersecurity consolidation is driving the development of comprehensive security solutions.
- Quantum computing is unlocking new possibilities in AI-driven research and development.
- 5G and AI are accelerating digital transformation across sectors.
- Ethical AI frameworks are essential for ensuring responsible and equitable use of technology.
As we look ahead, the convergence of AI, biotechnology, sustainability, and quantum computing will continue to drive progress. Companies that embrace these trends and invest in innovation will be well-positioned to lead in the next era of technological advancement. The future of AI and technology is not just about what these tools can do but how they can be harnessed to create a better, more sustainable, and equitable world for all.
In this rapidly evolving landscape, staying ahead requires a commitment to continuous learning, adaptation, and responsible innovation. By leveraging the power of AI and technology, we can address global challenges, unlock new opportunities, and shape a future that benefits everyone.