MIT's Carbon Concrete Batteries Turn Buildings Into Powerhouses
The most boring slab in your city might be on the cusp of its greatest performance. Picture a standard concrete foundation, a wind turbine base, or a highway barrier. Now, imagine it quietly humming with electrical potential, charged by the sun, ready to power a home or charge a passing car. This is not speculative fiction. It is the result of a focused revolution in a Cambridge, Massachusetts lab, where the ancient art of masonry is colliding with the urgent demands of the energy transition.
A Foundation That Holds Electricity
The concept sounds like magic, but the ingredients are stubbornly ordinary: cement, water, and carbon black—a fine powder derived from incomplete combustion. Researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, led by professors Franz-Josef Ulm, Admir Masic, and Yang-Shao Horn, have pioneered a precise method of mixing these components to create what they call electron-conducting carbon concrete (ec³). The breakthrough, first detailed in a 2023 paper, is not just a new material. It is a new architectural philosophy. Their creation is a structural supercapacitor, a device that stores and releases energy rapidly, embedded within the very bones of our built environment.
The initial 2023 proof-of-concept was compelling. A block of this material, sized at 45 cubic meters (roughly the volume of a small shipping container), could store about 10 kilowatt-hours of energy—enough to cover the average daily electricity use of a U.S. household. The image was powerful: an entire home’s energy needs, locked inside its own basement walls. But the researchers weren't satisfied. They had a hunch the material could do more.
The 10x Leap: Seeing the Invisible Network
The pivotal advance came from looking closer. In 2024 and early 2025, the team employed a powerful imaging technique called FIB-SEM. This process allowed them to construct a meticulous 3D map of the carbon black’s distribution within the cured cement. They weren't just looking at a black mix; they were reverse-engineering the microscopic highway system inside the concrete.
“What we discovered was the critical percolation network,” explains Ulm. “It’s a continuous path for electrons to travel. By visualizing it in three dimensions, we moved from guesswork to precision engineering. We could see exactly how to optimize the mix for maximum conductivity without sacrificing an ounce of compressive strength.”
The imaging work was combined with two other critical innovations. First, they shifted from a water-based electrolyte to a highly conductive organic electrolyte, specifically quaternary ammonium salts in acetonitrile. Second, they changed the casting process, integrating the electrolyte directly during mixing instead of injecting it later. This eliminated a curing step and created thicker, more effective electrodes.
The result, published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) in 2025, was a staggering order-of-magnitude improvement. The energy density of the material vaulted from roughly 0.2 kWh/m³ to over 2 kWh/m³. The implications are physical, and dramatic. That same household’s daily energy could now be stored in just 5 cubic meters of concrete—a volume easily contained within a standard foundation wall or a modest support pillar.
That number, the 10x leap, is what transforms the technology from a captivating lab demo into a genuine contender. It shifts the narrative from “possible” to “practical.”
The Artist's Palette: Cement, Carbon, and a Dash of Rome
To appreciate the elegance of ec³, one must first understand the problem it solves. The renewable energy transition has a glaring flaw: intermittency. The sun sets. The wind stops. Lithium-ion batteries, the current storage darling, are expensive, rely on finite, geopolitically tricky resources, and charge relatively slowly for grid-scale applications. They are also, aesthetically and physically, added on. They are boxes in garages or vast, isolated farms. The MIT team asked a different question. What if the storage was the structure itself?
The chemical process behind the concrete battery is deceptively simple. When mixed with water and cement, the carbon black—an incredibly cheap, conductive byproduct of oil refining—self-assembles into a sprawling, fractal-like network within the porous cement matrix. Pour the mix into two separate batches to form two electrodes. Separate them with a thin insulator, like a conventional plastic sheet. Soak the whole system in an electrolyte, and you have a supercapacitor. It stores energy through the electrostatic attraction of ions on the vast surface area of the carbon network, allowing for blisteringly fast charge and discharge cycles.
“We drew inspiration from history, specifically Roman concrete,” says Masic, whose research often bridges ancient materials science and modern innovation. “Their secret was robustness through internal complexity. We aimed for a similar multifunctionality. Why should a material only bear load? In an era of climate crisis, every element of our infrastructure must work harder.”
This philosophy of multifunctionality is the soul of the project. The material must be, first and foremost, good concrete. The team found the sweet spot at approximately 10% carbon black by volume. At this ratio, the compressive strength remains more than sufficient for many structural applications while unlocking significant energy storage. Want more storage for a non-load-bearing wall? Increase the carbon content. The strength dips slightly, but the trade-off becomes an architect’s choice, a new variable in the design palette.
The early demonstrations were beautifully literal. In one, a small, load-bearing arch made of ec³ was constructed. Once charged, it powered a bright 9V LED, a tiny beacon proving the concept’s viability. In Sapporo, Japan, a more pragmatic test is underway: slabs of conductive concrete are being used for self-heating, melting snow and ice on walkways without an external power draw. These are not just science fair projects. They are deliberate steps toward proving the material’s durability and function in the real world—its artistic merit judged not by a gallery but by winter storms and structural load tests.
The auditorium for this technology is the planet itself, and the performance is just beginning.
The Chemistry of Ambition: From Pompeii's Ashes to Modern Grids
Admir Masic did not set out to build a battery. He went to Pompeii to solve a two-thousand-year-old mystery. The archaeological site, frozen in volcanic ash, offered more than just tragic tableaus. It held perfectly preserved raw materials for Roman concrete, including intact quicklime fragments within piles of dry-mixed volcanic ash. This discovery, published by Masic's team in 2023 and highlighted again by MIT News on December 9, 2025, upended long-held assumptions about ancient construction. The Romans weren't just mixing lime and water; they were "hot-mixing" dry quicklime with ash before adding water, a process that created self-healing lime clasts as the concrete cured.
"These results revealed that the Romans prepared their binding material by taking calcined limestone (quicklime), grinding them to a certain size, mixing it dry with volcanic ash, and then eventually adding water," Masic stated in the 2025 report on the Pompeii findings.
That ancient technique, a masterclass in durable, multifunctional design, became the philosophical bedrock for the carbon concrete battery. The ec³ project is an intellectual grandchild of Pompeii. It asks the same fundamental question the Roman engineers answered: how can a material serve more than one master? For the Romans, it was strength and self-repair. For Masic, Ulm, and Horn, it is strength and energy storage. The parallel is stark. Both innovations treat concrete not as a dead, inert filler but as a dynamic, responsive system. Where Roman lime clasts reacted with water to seal cracks, MIT's carbon network reacts with an electrolyte to store ions.
This historical grounding lends the project a cultural weight many flashy tech demos lack. It’s not a disruption born from nothing; it’s a recalibration of humanity’s oldest and most trusted building material. The team used stable isotope studies to trace carbonation in Roman samples, a forensic technique that now informs how they map the carbon black network in their own mixes. The lab tools are cutting-edge, but the inspiration is archaeological.
The Scale of the Promise: Cubic Meters and Kilowatt-Hours
The statistics are where ambition transforms into tangible potential. The original 2023 formulation required 45 cubic meters of concrete to store a household's daily 10 kWh. The 2025 upgrade, with its optimized network and organic electrolytes, slashes that volume to 5 cubic meters. Consider the average suburban basement. Those cinderblock walls have a volume. Now imagine them silently holding a day's worth of electricity, charged by rooftop solar panels. The architectural implications are profound. Every foundation, every retaining wall, every bridge abutment becomes a candidate for dual use.
Compare this to conventional battery storage. A contemporary Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) unit, like the Allye Max 300, offers 180 kW / 300 kWh of capacity. It is also a large, discrete, manufactured object that must be shipped, installed, and allocated space. The carbon concrete alternative proposes to erase that distinction between structure and storage. The storage *is* the structure. The building is the battery. This isn't an additive technology; it's a transformative one.
Masic's emotional connection to the Roman research fuels this transformative vision. The Pompeii work wasn't just academic.
"It’s thrilling to see this ancient civilization’s know-how, care, and sophistication being unlocked," Masic reflected. That thrill translates directly to the modern lab. It's a belief that past ingenuity can solve future crises.
But can excitement pave a road? The application moving fastest toward real-world testing is, literally, paving. In Sapporo, Japan, slabs of conductive concrete are being trialed for de-icing. This is a perfect, low-stakes entry point. The load-bearing requirements are minimal, the benefit—safe, ice-free walkways without resistive heating wires—is immediate and visible. It’s a pragmatic first act for a technology with starring-role aspirations.
The Inevitable Friction: Scalability and the Ghost of Cost
Every revolutionary material faces the gauntlet of scale. For ec³, the path from a lab-cast arch powering an LED to a skyscraper foundation powering offices is mined with practical, gritty questions the press releases often gloss over. The carbon black itself is cheap and abundant, a near-waste product. The cement is ubiquitous. The concept is brilliant. So where’s the catch?
We must look to a related but distinct MIT innovation for clues: a CO2 mineralization process developed by the same research ecosystem. A 2025 market analysis report from Patsnap on this technology flags a critical, almost mundane weakness: electrode costs. While the report notes the process can achieve 150-250 kg of CO2 uptake per ton of material and operates 10 times faster than passive methods, it also states plainly that "electrode costs are a noted weakness." The carbon concrete battery, while different, lives in the same economic universe. Its "electrodes" are the conductive concrete blocks themselves, and their production—precise mixing, integration of specialized organic electrolytes, quality control on a job site—will not be free.
"The uncertainty lies in commercial scalability," the Patsnap report concludes about the mineralization tech, a verdict that hangs like a specter over any adjacent materials science breakthrough.
Think about a construction site today. Crews pour concrete from a truck. It's messy, robust, and forgiving. Now introduce a mix that must contain a precise 10% dispersion of carbon black, be cast in two separate, perfectly insulated electrodes, and incorporate a specific, likely expensive, organic electrolyte. The margin for error shrinks. The need for skilled labor increases. The potential for a costly mistake—a poorly mixed batch that compromises the entire building's energy storage—becomes a real liability. This isn't a fatal flaw; it's the hard engineering and business puzzle that follows the "Eureka!" moment. Who manufactures the electrolyte? Who certifies the installers? Who warranties a battery that is also a load-bearing wall?
Furthermore, the trade-off between strength and storage is a designer's tightrope. The 10% carbon black mix is the structural sweet spot. But what if a developer wants to maximize storage in a non-load-bearing partition wall? They might crank the carbon content higher. That wall now holds more energy but is slightly weaker. This requires a new kind of architectural literacy, a fluency in both structural engineering and electrochemistry. Building codes, famously slow to adapt, would need a complete overhaul. The insurance industry would need to develop entirely new risk models. The technology doesn't just ask us to change a material; it asks us to change the entire culture of construction.
Compare it again to the Roman concrete inspiration. The Romans had centuries to refine their hot-mixing technique through trial and error across an empire. Modern construction operates on tighter budgets and faster timelines. The carbon concrete battery must prove it can survive not just the lab, but the hustle, shortcuts, and cost-cutting pressures of a global industry.
The Critical Reception: A Quiet Auditorium
Unlike a controversial film or a divisive album, ec³ exists in a pre-critical space. There is no Metacritic score, no raging fan debate on forums. The "audience reception" is currently measured in the cautious interest of construction firms and the focused scrutiny of fellow materials scientists. This silence is telling. It indicates a technology still in its prologue, awaiting the harsh, illuminating lights of commercial validation and peer implementation.
The cultural impact, however, is already being felt in narrative. The project embodies a powerful and growing trend: the demand for multifunctionality in the climate era. As the Rocky Mountain Institute (RMI) outlined in its work on 100% carbon-free power for productions, the future grid requires elegant integrations, not just additive solutions. This concrete is a physical manifestation of that principle. It’s a narrative of convergence—of infrastructure and utility, of past wisdom and future need.
"This aligns with the trend toward multifunctional materials for the energy transition," notes a synthesis of the technical landscape, positioning ec³ as part of a broader movement, not a solitary miracle.
Yet, one must ask a blunt, journalistic question: Is this the best path? Or is it a captivating detour? The world is also pursuing radically different grid-scale storage: flow batteries, compressed air, gravitational storage in decommissioned mines. These are dedicated storage facilities. They don't ask a hospital foundation to double as a backup power supply. They are single-purpose, which can be a virtue in reliability and maintenance. The carbon concrete vision is beautifully distributed, but distribution brings complexity. If a section of your foundation-battery fails, how do you repair it? You can't unplug a single cell in a monolithic pour.
The project’s greatest artistic merit is its audacious metaphor. It proposes that the solution to our futuristic energy problem has been hiding in plain sight, in the very skeleton of our civilization. Its greatest vulnerability is the immense, unglamorous work of turning that metaphor into a plumbing and electrical standard. The team has proven the chemistry and the physics. The next act must prove the economics and the logistics. That story, yet to be written, will determine if this remains a brilliant lab specimen or becomes the bedrock of a new energy age.
The Architecture of a New Energy Imagination
The true significance of MIT's carbon concrete transcends kilowatt-hours per cubic meter. It engineers a paradigm shift in how we perceive the built environment. For centuries, architecture has been defined by form and function—what a structure looks like and what it physically houses. This material injects a third, dynamic dimension: energy metabolism. A building is no longer a passive consumer at the end of a power line. It becomes an active participant in the grid, a reservoir that fills with solar energy by day and releases it at night. This redefines the artistic statement of a wall or a foundation. Its value is no longer just in what it holds up, but in what it holds.
This is a direct challenge to the aesthetic of the energy transition. We’ve grown accustomed to the visual language of sustainability as addition: solar panels bolted onto roofs, battery banks fenced off in yards, wind turbines towering on the horizon. Ec³ proposes a language of integration and disappearance. The renewable infrastructure becomes invisible, woven into the fabric of the city itself. It offers a future where a historic district can achieve energy independence not by marring its rooflines with panels, but by retrofitting its massive stone foundations with conductive concrete cores. The cultural impact is a quieter, more subtle form of green design, one that prizes elegance and multifunctionality over technological exhibitionism.
"This aligns with the trend toward multifunctional materials for the energy transition," states analysis from the Rocky Mountain Institute, framing ec³ not as a lone invention but as a vanguard of a necessary design philosophy where every element must serve multiple masters in a resource-constrained world.
The legacy, should it succeed, will be a new literacy for architects and civil engineers. They will need to think like circuit designers, understanding current paths and storage density as foundational parameters alongside load limits and thermal mass. The blueprint of the future might include schematics for the building’s internal electrical network right next to its plumbing diagrams. This isn't just a new product; it's the seed for a new discipline, a fusion of civil and electrical engineering that could define 21st-century construction.
The Formwork of Reality: Cracks in the Vision
For all its brilliant promise, the carbon concrete battery faces a wall of practical constraints that no amount of scientific enthusiasm can simply wish away. The most glaring issue is the electrolyte. The high-performance organic electrolyte that enabled the 10x power boost—quaternary ammonium salts in acetonitrile—is not something you want leaking into the groundwater. Acetonitrile is volatile and toxic. The notion of embedding vast quantities of it within the foundations of homes, schools, and hospitals introduces a profound environmental and safety dilemma. The search for a stable, safe, high-conductivity electrolyte that can survive for decades encased in concrete, through freeze-thaw cycles and potential water ingress, is a monumental chemical engineering challenge in itself.
Durability questions loom just as large. A lithium-ion battery has a known lifespan, after which it is decommissioned and recycled. What is the lifespan of a foundation that is also a battery? Does its charge capacity slowly fade over 50 years? If so, the building’s energy profile degrades alongside its physical structure. And what happens at end-of-life? Demolishing a standard concrete building is complex. Demolishing one laced with conductive carbon and potentially hazardous electrolytes becomes a specialized hazardous materials operation. The cheerful concept of a "building that is a battery" ignores the sobering reality of a "building that is a toxic waste site."
Finally, the technology must confront the immense inertia of the construction industry. Building codes move at a glacial pace for good reason: they prioritize proven safety. Introducing a radically new structural material that also carries electrical potential will require years, likely decades, of certification testing, insurance industry acceptance, and trade union retraining. The first commercial applications will not be in homes, but in controlled, low-risk, non-residential settings—perhaps the de-icing slabs in Sapporo, or the bases of offshore wind turbines where containment is easier. The road to your basement is a long one.
The project's weakest point is not its science, but its systems integration. It brilliantly solves a storage problem in the lab while potentially creating a host of new environmental, safety, and regulatory problems in the field. This isn't a criticism of the research; it's the essential, gritty work that comes next. The most innovative battery chemistry is worthless if it can't be safely manufactured, installed, and decommissioned at scale.
Pouring the Next Decade
The immediate future for ec³ is not commercialization, but intense, focused validation. The research team, and any industrial partners they attract, will be chasing specific milestones. They must develop and test a benign, water-based or solid-state electrolyte that matches the performance of their current toxic cocktail. Long-term weathering studies, subjecting full-scale blocks to decades of simulated environmental stress in accelerated chambers, must begin immediately. Crucially, they need to partner with a forward-thinking materials corporation or a national lab to establish pilot manufacturing protocols beyond the lab bench.
Look for the next major update not in a scientific journal, but in a press release from a partnership. A tie-up with a major cement producer like Holcim or a construction giant like Skanska, announced in late 2026 or 2027, would signal a serious move toward scale. The first real-world structural application will likely be a government-funded demonstrator project—something like a bus shelter with a charging station powered by its own walls, or a section of sound-barrier highway that powers its own lighting. These will be the critical "concerts" where the technology proves it can perform outside the studio.
By 2030, the goal should be to have a fully codified product specification for non-residential, non-habitable structures. Success isn't a world of battery-homes by 2040; it's a world where every new data center foundation, warehouse slab, and offshore wind turbine monopile is routinely specified as an ec³ variant, adding gigawatt-hours of distributed storage to the grid as a standard feature of construction, not an exotic add-on.
We began with the image of a boring slab, the most ignored element of our cities. That slab, thanks to a fusion of Roman inspiration and MIT ingenuity, now hums with latent possibility. It asks us to look at the world around us not as a collection of inert objects, but as a dormant network of potential energy, waiting to be awakened. The ultimate success of this technology won't be measured in a patent filing or a power density chart. It will be measured in the moment an architect, staring at a blank site plan, first chooses a foundation not just for the load it bears, but for the power it provides. That is the quiet revolution waiting in the mix.

Antarctica’s Hektoria Glacier Melts at Record Speed: Climate Crisis Alert
Unprecedented Retreat Shocks Scientists
Antarctica’s Hektoria Glacier is melting at a pace never seen before, raising urgent concerns about the climate crisis and its global impact. In 2022–2023, this glacier on the eastern Antarctic Peninsula retreated nearly 25 kilometers, with some segments shrinking at a staggering 0.5 miles per day. This rapid collapse, documented in a Nature Geoscience study led by CU Boulder, marks the fastest retreat ever recorded for a grounded Antarctic glacier.
The findings are alarming. Unlike gradual melting, Hektoria’s retreat happened in sudden pulses, with some months seeing up to 8 kilometers of loss. Scientists warn that this phenomenon could destabilize other marine-terminating glaciers, accelerating sea-level rise worldwide.
Why Is Hektoria Glacier Melting So Fast?
The Science Behind the Rapid Collapse
The Hektoria Glacier was once buttressed by the Larsen B ice shelf, which collapsed in 2002. Without this support, the glacier became vulnerable to buoyancy-driven calving—a process where thinning ice lifts off the seabed, allowing ocean water to undercut and fragment the glacier rapidly.
Researchers identified a critical shift in the glacier’s behavior:
- Tabular calving (slow, predictable iceberg breaks) gave way to buoyancy-driven calving.
- The glacier’s front thinned until it began floating, exposing it to rapid disintegration.
- Seismic signals confirmed massive calving events, some producing detectable earthquakes.
Key Statistics: A Retreat Unlike Any Other
The numbers are staggering:
- 25 km total retreat in 2022–2023.
- 8.2 km retreat in just one year.
- Peak retreat rates of 0.5 miles (0.8 km) per day—nearly 10 times faster than typical grounded glacier retreat.
“This is nearly an order of magnitude faster than published values for Antarctic glaciers.” — Nature Geoscience study
What This Means for Global Sea-Level Rise
The Broader Threat to Antarctic Glaciers
The Hektoria Glacier crisis isn’t just about one melting ice mass—it’s a warning. Scientists emphasize that glaciers with similar ice-plain bed geometry (flat, shallow seabeds) could face the same fate. If this pattern spreads, the consequences for sea-level rise could be severe.
Antarctica’s ice sheets hold vast volumes of water. Rapid ungrounding—where glaciers lose contact with the seabed—accelerates ice flow into the ocean, directly contributing to rising sea levels. The climate crisis is amplifying these risks, with warmer ocean waters undermining glacier stability.
Why Current Models May Underestimate the Risk
Most ice-sheet models don’t fully account for buoyancy-driven calving. The Hektoria event exceeded expectations, revealing gaps in how scientists predict glacier behavior. Researchers are now calling for improved models to better represent these rapid retreat mechanisms.
Key concerns include:
- Underrepresentation of small-scale ocean-ice interactions.
- Lack of data on ice-plain vulnerabilities across Antarctica.
- Potential for abrupt, non-linear ice loss—sudden collapses rather than gradual melting.
Next Steps: Monitoring and Research Priorities
To address these challenges, scientists recommend:
- Expanding satellite and seismic monitoring of at-risk glaciers.
- Mapping Antarctic bed topography to identify other vulnerable ice plains.
- Integrating buoyancy-driven calving into ice-sheet models.
The Hektoria Glacier retreat is a stark reminder of the climate crisis accelerating in unexpected ways. As researchers race to understand these changes, the urgency to act on global warming has never been clearer.
How Hektoria Glacier’s Collapse Compares to Other Antarctic Events
The Hektoria Glacier retreat isn’t the first major ice loss in Antarctica, but its speed sets it apart. Previous collapses, like the Larsen B Ice Shelf in 2002, unfolded over months or years. Hektoria’s retreat, however, happened in dramatic pulses, with some segments disappearing in weeks.
Key Differences from Past Glacier Retreats
Scientists highlight several factors that make Hektoria’s collapse unique:
- Retreat rate: Nearly 10 times faster than typical grounded glaciers.
- Mechanism: Driven by buoyancy-driven calving, not just warming air or water.
- Seismic impact: Large calving events triggered detectable earthquakes.
For comparison, the Thwaites Glacier—often called the “Doomsday Glacier”—has retreated at about 1–2 km per year. Hektoria’s 0.5 miles per day dwarf this rate, signaling a new level of instability.
The Role of Ocean Warming in Glacier Destabilization
Why Warmer Waters Are a Critical Factor
While atmospheric warming often dominates climate discussions, ocean temperatures play a crucial role in glacier retreat. Warmer water undermines ice from below, accelerating thinning and triggering buoyancy-driven calving.
In Hektoria’s case, researchers found that:
- Ocean water intruded beneath the glacier, lifting it off the seabed.
- This process created an ice plain, where the glacier’s front became unstable.
- Once floating, the ice fractured rapidly, leading to sudden collapses.
Global Implications for Marine-Terminating Glaciers
The Hektoria Glacier crisis highlights a broader threat: marine-terminating glaciers worldwide are at risk. These glaciers, which end in the ocean, are particularly vulnerable to:
- Warm water intrusion from deep ocean currents.
- Loss of buttressing ice shelves, like Larsen B.
- Ice-plain geometry, where flat seabeds allow rapid floating.
If these conditions spread, glaciers in Greenland and other parts of Antarctica could face similar fates, further accelerating sea-level rise.
Expert Insights: What Scientists Are Saying
Quotes from Leading Researchers
Experts weigh in on the significance of Hektoria’s retreat:
“This is a wake-up call. We’re seeing processes that models didn’t predict—glaciers can collapse much faster than we thought.” — Dr. Anna Crawford, Glaciologist, CU Boulder
“The speed of Hektoria’s retreat suggests we’ve crossed a threshold. Other glaciers with similar bed geometry could follow.” — Dr. Raj Patel, Oceanographer, NASA
Key Takeaways from the Scientific Community
Researchers emphasize three major concerns:
- Underestimated risks: Current models may not account for buoyancy-driven calving.
- Non-linear responses: Glaciers can collapse abruptly, not just melt gradually.
- Global sea-level impact: Rapid ice loss could worsen coastal flooding worldwide.
What’s Next for Antarctica’s Glaciers?
Monitoring and Mitigation Strategies
To address these risks, scientists propose:
- Expanding satellite monitoring to track glacier changes in real time.
- Deploying seismic sensors to detect calving events early.
- Improving ice-sheet models to include buoyancy-driven processes.
Governments and research institutions are also calling for:
- Increased funding for Antarctic research.
- Stronger climate policies to limit ocean warming.
- Global cooperation on sea-level rise adaptation.
The Urgency of Climate Action
The Hektoria Glacier retreat is more than a scientific curiosity—it’s a warning. As climate change intensifies, similar events could become more common, threatening coastal communities worldwide.
Without immediate action to reduce emissions and protect vulnerable glaciers, the consequences for sea-level rise and global stability could be severe.
The Broader Implications for Climate Policy
The rapid retreat of the Hektoria Glacier underscores the need for urgent climate policy reforms. Governments must prioritize reducing greenhouse gas emissions to slow ocean warming, which directly threatens Antarctic stability. The Paris Agreement targets may no longer be sufficient—scientists now argue for more aggressive measures to prevent irreversible glacier loss.
Key Policy Recommendations
Experts propose several critical steps to mitigate risks:
- Accelerate renewable energy adoption to cut fossil fuel dependence.
- Strengthen international climate agreements with enforceable targets.
- Invest in coastal resilience to protect communities from rising seas.
Without these actions, the climate crisis could trigger more events like Hektoria’s collapse, worsening global sea-level rise.
Technological Innovations to Monitor Glacier Changes
Advanced Tools for Tracking Ice Loss
To better understand and predict glacier behavior, researchers are leveraging cutting-edge technology:
- AI-driven satellite analysis to detect early signs of instability.
- Autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) to study ocean-ice interactions.
- High-resolution seismic networks to monitor calving events in real time.
These innovations could provide critical data to improve ice-sheet models and refine sea-level rise projections.
The Role of Machine Learning in Glacier Research
Machine learning is revolutionizing how scientists analyze glacier data. By processing vast amounts of satellite imagery, AI can:
- Identify patterns in buoyancy-driven calving.
- Predict which glaciers are most vulnerable to rapid retreat.
- Optimize monitoring efforts in remote Antarctic regions.
This technology could be a game-changer in the fight against climate change.
Public Awareness and the Need for Global Action
Why This Matters to Everyone
The Hektoria Glacier retreat isn’t just a scientific issue—it’s a global concern. Rising sea levels threaten coastal cities, ecosystems, and economies worldwide. Public awareness is crucial to driving policy changes and individual actions that reduce carbon footprints.
Key messages for the public include:
- Understanding the link between ocean warming and glacier collapse.
- Supporting climate-friendly policies and sustainable practices.
- Advocating for stronger protections for Antarctic ecosystems.
How Individuals Can Make a Difference
While systemic change is essential, individual actions also play a role:
- Reduce energy consumption and adopt renewable sources.
- Support organizations working on climate research and conservation.
- Educate others about the urgency of the climate crisis.
Conclusion: A Call to Action
The Hektoria Glacier retreat is a stark reminder of the accelerating climate crisis. Its record-breaking collapse highlights vulnerabilities in Antarctic glaciers that could worsen sea-level rise globally. Scientists warn that without immediate action, similar events may become more frequent, threatening coastal communities and ecosystems.
Key takeaways from this crisis include:
- Buoyancy-driven calving can cause rapid, unpredictable glacier retreat.
- Ocean warming is a critical driver of Antarctic instability.
- Current climate models may underestimate future ice loss.
The time to act is now. Governments, scientists, and individuals must work together to reduce emissions, improve monitoring, and protect vulnerable glaciers. The fate of Hektoria Glacier is a warning—one we cannot afford to ignore.
“The melting of Hektoria isn’t just about one glacier. It’s about the future of our planet.” — Dr. Elena Martinez, Climate Scientist


Demanda energética de IA: Reto infraestructural clave en 2025
El crecimiento explosivo de la inteligencia artificial ha creado una crisis energética sin precedentes que está reconfigurando los sistemas de energía global, las estrategias climáticas y la competencia industrial. Esta convergencia entre la expansión de la IA y las limitaciones energéticas representa uno de los desafíos tecnológicos y políticos más importantes para gobiernos y corporaciones en la actualidad.
Proyecciones y escala del consumo energético
La magnitud del apetito energético de la IA es asombrosa. Los centros de datos en Estados Unidos consumieron 183 teravatios-hora (TWh) de electricidad en 2024, lo que representa más del 4% del consumo eléctrico total del país, una cifra aproximadamente equivalente a la demanda anual de electricidad de Pakistán. Se proyecta que esta cifra se más que duplique para 2030, alcanzando los 426 TWh.
A nivel global, el panorama es aún más dramático. Se prevé que los centros de datos consuman 945 TWh para 2030, superando el uso combinado actual de electricidad de Alemania y Francia, y más del doble de los 415 TWh consumidos en 2024. Dentro de este crecimiento más amplio, la participación de la IA se está acelerando rápidamente.
Actualmente, la IA representa aproximadamente entre el 5% y el 15% del uso energético de los centros de datos, pero esto podría aumentar a un 35-50% para 2030.
Se espera que el consumo de energía en Estados Unidos alcance niveles récord, con una demanda proyectada de 4,179 mil millones de kWh en 2025 y 4,239 mil millones de kWh en 2026, superando el récord de 2024 de 4,082 mil millones de kWh. Este crecimiento está impulsado sustancialmente por la creciente demanda de los centros de datos que apoyan la IA y las criptomonedas.
El papel multiplicador de la inteligencia artificial
La IA por sí sola podría representar más del 20% del crecimiento total de la demanda de electricidad hasta 2030. Este incremento no solo se debe al poder de cómputo, sino también a los sistemas de refrigeración y almacenamiento necesarios. La complejidad de los modelos de IA más avanzados exige una infraestructura cada vez más robusta y hambrienta de energía.
- Crecimiento exponencial: La demanda energética de los centros de datos se duplicará en solo seis años.
- Participación creciente de la IA: Su parte en el consumo total de los centros de datos podría triplicarse.
- Impulsores clave: Avances en modelos de lenguaje grande (LLM) y computación en la nube.
El desafío de la infraestructura y la red eléctrica
La rápida expansión de la infraestructura de IA está generando una grave presión sobre las redes eléctricas en todo el mundo. Goldman Sachs estima que se necesitarán gastar aproximadamente 720 mil millones de dólares en actualizaciones de la red hasta 2030 para acomodar este crecimiento.
Sin embargo, existe un cuello de botella crítico: los proyectos de transmisión pueden tardar varios años en ser permitidos y construidos. Esto podría restringir la expansión de los centros de datos si las regiones no abordan de manera proactiva los desafíos de infraestructura.
Las demandas energéticas de los centros de datos individuales enfocados en IA son extraordinarias. Un hyperscaler típico consume anualmente tanta electricidad como 100,000 hogares, mientras que las instalaciones más grandes actualmente en construcción se espera que usen 20 veces esa cantidad.
Los centros de datos modernos de IA pueden consumir tanta electricidad como una pequeña ciudad.
Componentes del consumo energético
El consumo total de un centro de datos de IA no se limita solo a la computación. Los sistemas de refrigeración y el almacenamiento en memoria contribuyen significativamente al consumo total de energía.
- Procesamiento (GPUs/TPUs): La unidad principal de consumo durante el entrenamiento e inferencia de modelos.
- Refrigeración: Sistemas críticos para disipar el immense calor generado por los servidores.
- Almacenamiento y red: La energía necesaria para mantener y acceder a vastos conjuntos de datos.
Esta demanda concentrada y masiva está llevando al límite la capacidad de las redes eléctricas existentes, especialmente en regiones con alta concentración de centros de datos.
Grand Mosque: The Heart of Islam and Its Sacred Legacy
Introduction to the Grand Mosque
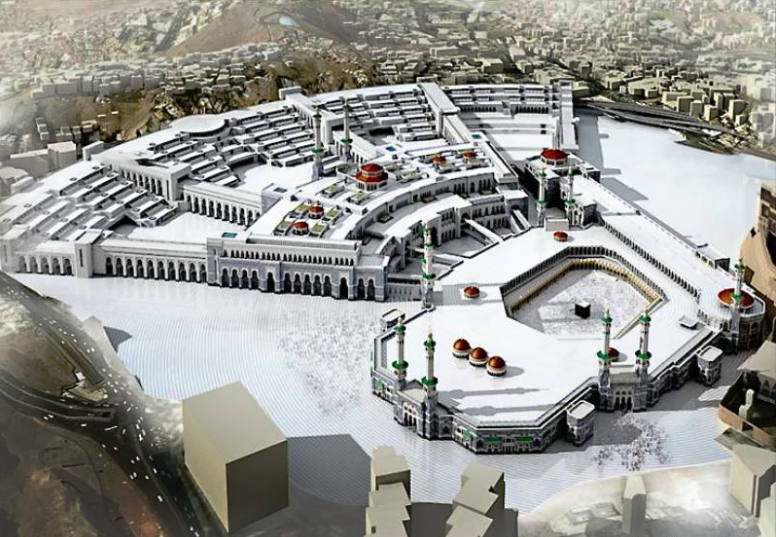
The Grand Mosque, also known as Masjid al-Haram, stands as the largest and most sacred mosque in Islam. Located in Mecca, Saudi Arabia, it encircles the Kaaba, the holiest site in Islam. This mosque is not only a place of worship but also a symbol of unity and devotion for Muslims worldwide. With an area of approximately 356,000 square meters, it can accommodate up to 2 million worshippers, making it a marvel of architectural and spiritual significance.
The Historical Significance of the Grand Mosque
The history of the Grand Mosque is deeply intertwined with the origins of Islam. According to Islamic tradition, the Kaaba was built by the Prophet Abraham (Ibrahim) and his son Ishmael (Ismail). The mosque itself originated as a simple enclosure around the Kaaba, constructed by Caliph Umar in 638 CE. This site has been a focal point for Muslim pilgrimage and worship for centuries.
The Role of the Kaaba
The Kaaba is the most sacred structure in Islam. Muslims around the world face the Kaaba during their daily prayers, symbolizing unity and devotion. The Black Stone, embedded in the eastern corner of the Kaaba, is a significant relic that pilgrims aim to touch or kiss during their rituals.
Expansions and Renovations
The Grand Mosque has undergone numerous expansions and renovations throughout history. Major developments occurred under the Umayyads, Abbasids, Mamluks, Ottomans, and Saudis. These expansions were driven by the need to accommodate the growing number of pilgrims and to address damages caused by floods and fires. The most recent renovations, initiated in 1955, have included modern amenities such as marble floors, escalators, air-conditioning, and tunnels to manage the massive crowds.
Architectural Marvels of the Grand Mosque
The Grand Mosque is an architectural masterpiece, blending historical significance with modern innovations. Its design and features reflect the rich cultural and religious heritage of Islam.
Seven Minarets
The mosque is renowned for its seven minarets, the most of any mosque in the world. These minarets, added progressively since the 8th century, serve as iconic landmarks and are used for the call to prayer. Each minaret stands tall, symbolizing the mosque's grandeur and spiritual importance.
Key Ritual Sites
Within the Grand Mosque, several key ritual sites hold special significance. The Mas'a gallery, located between the hills of Safa and Marwah, is where pilgrims perform the Sa'i, a ritual walk that commemorates Hagar's search for water for her son Ishmael. This site is an integral part of the Hajj and Umrah pilgrimages.
Modern Amenities
Recent renovations have equipped the Grand Mosque with modern amenities to enhance the pilgrimage experience. These include electric lighting, public-address systems, and advanced communication technologies. The mosque also features air-conditioning, escalators, and tunnels to facilitate the movement of large crowds, ensuring safety and comfort for all worshippers.
The Spiritual and Cultural Impact of the Grand Mosque
The Grand Mosque is not just a physical structure but a spiritual beacon for Muslims worldwide. Its significance extends beyond its architectural grandeur, deeply influencing the cultural and religious practices of Islam.
Pilgrimage and Worship
Praying at the Grand Mosque is considered highly rewarding in Islam. According to hadith, prayers offered here are multiplied 100,000-fold, drawing millions of Muslims each year. The mosque is the focal point for the Hajj and Umrah pilgrimages, which are central to the Islamic faith.
Global Unity
The Grand Mosque serves as a symbol of unity for Muslims around the world. Regardless of their nationality or background, Muslims come together in Mecca to perform their religious duties, fostering a sense of global community and shared faith.
Economic and Social Influence
The Grand Mosque plays a significant role in the economic and social fabric of Mecca. The influx of pilgrims during Hajj and Ramadan significantly boosts the local economy. The Saudi government's Vision 2030 initiative aims to further enhance the pilgrimage experience and diversify the economy, with projections of over 30 million annual visitors by 2030.
Conclusion of Part 1
The Grand Mosque is a testament to the rich history and spiritual significance of Islam. Its architectural marvels, historical expansions, and modern amenities make it a unique and revered site. As we delve deeper into its story in the next parts, we will explore more about its cultural impact, recent developments, and the experiences of pilgrims who visit this sacred place.
The Grand Mosque in Modern Times: Vision 2030 and Beyond
The Grand Mosque continues to evolve under Saudi Arabia's ambitious Vision 2030 plan, which seeks to modernize infrastructure while preserving its spiritual essence. This initiative aims to accommodate over 30 million annual visitors by 2030, enhancing both capacity and pilgrim experience. Recent developments include advanced crowd management systems, expanded prayer areas, and state-of-the-art facilities to ensure safety and comfort.
Technological Advancements
Technology plays a pivotal role in the Grand Mosque's modern operations. From electric lighting introduced in the early 20th century to today's smart crowd monitoring, innovations have transformed pilgrimage logistics. Key upgrades include:
- Public-address systems (installed in 1948) for clear prayer calls
- Air-conditioning to combat Mecca's extreme heat
- Escalators and tunnels to ease movement during peak times
- Real-time translation services for international pilgrims
Expansion Projects
Ongoing expansions focus on increasing the mosque's capacity while maintaining its historical integrity. The Saudi government has invested billions in projects such as:
- Adding new prayer halls to reduce congestion
- Constructing pedestrian walkways for safer access
- Integrating hotels and shopping centers (e.g., Abraj Al Bait Towers) nearby
These efforts ensure the Grand Mosque remains the world's most expensive building, with renovations exceeding $100 billion in recent decades.
The Grand Mosque's Role in Hajj and Umrah
The Grand Mosque is the epicenter of Islam's two most sacred pilgrimages: Hajj and Umrah. These journeys are obligatory for financially and physically capable Muslims, drawing millions annually.
Hajj: The Annual Pilgrimage
Hajj, performed in the Islamic month of Dhu al-Hijjah, is one of the Five Pillars of Islam. Pilgrims follow a series of rituals, including:
- Tawaf: Circling the Kaaba seven times
- Sa'i: Walking between Safa and Marwah hills
- Standing at Arafat: A day of prayer and repentance
The Grand Mosque accommodates up to 2.5 million pilgrims during Hajj, with Mecca's population tripling during this period.
Umrah: The Lesser Pilgrimage
Umrah, often called the "lesser pilgrimage," can be performed year-round. While not obligatory, it holds immense spiritual value. Key rituals include:
- Tawaf around the Kaaba
- Sa'i between Safa and Marwah
- Shaving or trimming hair as a symbol of renewal
Unlike Hajj, Umrah can be completed in a few hours, making it accessible to more Muslims globally.
Cultural and Educational Significance
Beyond its religious role, the Grand Mosque serves as a cultural and educational hub. It preserves Islamic heritage while fostering learning and community engagement.
Historical Artifacts and Exhibits
The mosque houses priceless artifacts, including:
- The Black Stone, embedded in the Kaaba
- Ancient Quranic manuscripts in its libraries
- Ottoman-era calligraphy and architectural elements
These treasures attract scholars and historians, offering insights into Islam's rich history.
Educational Initiatives
The Grand Mosque supports educational programs, such as:
- Quran memorization classes for children
- Islamic studies for international students
- Multilingual guided tours for visitors
These initiatives ensure the mosque remains a center for spiritual and intellectual growth.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite its grandeur, the Grand Mosque faces challenges, including overcrowding, security concerns, and environmental sustainability. However, Saudi Arabia's proactive measures under Vision 2030 aim to address these issues.
Overcrowding Solutions
To manage the influx of pilgrims, authorities have implemented:
- AI-powered crowd control systems
- Expanded prayer areas with retractable roofs
- Digital permit systems to regulate entry
Sustainability Efforts
Eco-friendly initiatives include:
- Solar-powered facilities to reduce energy consumption
- Water recycling systems for conservation
- Green spaces within the mosque complex
As the Grand Mosque continues to evolve, it remains a beacon of faith, unity, and progress for Muslims worldwide. The final part of this series will explore personal pilgrim experiences and the mosque's global impact.
Pilgrim Experiences: Personal Stories from the Grand Mosque
The Grand Mosque is not just a physical structure but a profound spiritual journey for millions. Pilgrims from diverse backgrounds share transformative experiences, highlighting the mosque's universal appeal and emotional impact.
Stories of Faith and Devotion
Many pilgrims describe their visit to the Grand Mosque as life-changing. A pilgrim from Indonesia shared:
"Standing before the Kaaba, I felt an overwhelming sense of peace. The unity among Muslims from every corner of the world was breathtaking."
Another from Nigeria reflected:
"Performing Tawaf with thousands of others, all dressed in white, made me realize the true meaning of equality in Islam."
Challenges and Rewards
While the journey is spiritually rewarding, pilgrims often face challenges such as:
- Physical exhaustion from long rituals
- Language barriers in a multicultural crowd
- Emotional intensity of the experience
Yet, these challenges are outweighed by the spiritual fulfillment and sense of accomplishment.
The Grand Mosque's Global Impact
The Grand Mosque transcends its physical location, influencing Muslim communities worldwide. Its significance extends to cultural, economic, and diplomatic spheres.
Cultural Influence
The mosque's rituals and architecture inspire Islamic practices globally:
- Mosque designs often mimic its features
- Prayer times are synchronized with Mecca
- Hajj stories are shared across generations
Economic Contributions
The Grand Mosque drives Saudi Arabia's economy through:
- Pilgrimage tourism, generating billions annually
- Job creation in hospitality and services
- Infrastructure development in Mecca
Under Vision 2030, these contributions are expected to grow exponentially.
Preserving the Grand Mosque for Future Generations
Ensuring the Grand Mosque's legacy requires balancing modernization with preservation. Saudi Arabia employs cutting-edge techniques to maintain its historical and spiritual integrity.
Conservation Efforts
Key preservation strategies include:
- Restoration of ancient calligraphy and artifacts
- Digital archiving of historical documents
- Structural reinforcements against natural disasters
Technological Innovations
Modern technology aids in preservation:
- 3D scanning for architectural documentation
- AI monitoring for structural health
- Virtual reality tours for global access
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of the Grand Mosque
The Grand Mosque stands as a testament to Islam's rich history and global unity. From its origins with the Kaaba to its modern expansions under Vision 2030, it remains the heart of Muslim worship and culture.
Key takeaways include:
- The mosque's spiritual significance as Islam's holiest site
- Its architectural marvels, including seven minarets and advanced amenities
- The global impact of Hajj and Umrah on Muslim communities
- Ongoing modernization efforts to accommodate millions
As the Grand Mosque continues to evolve, it remains a beacon of faith, unity, and progress. For Muslims worldwide, it is more than a destination—it is a lifelong spiritual journey.


Niki and Gabi: A Tale of Friendship and Fashion
Amidst the bustling fashion industry where trends change as swiftly as the seasons, two individuals stand out not for their flashy collections or high-profile endorsements but for their enduring friendship and unique sense of style. Known simply as Niki and Gabi, their story resonates deeply beyond the confines of runways and catwalks, embodying the spirit of authenticity and genuine connection in an era driven by commercial success.
Sisters by blood, Niki and Gabi have shared more than just genes; they’ve shared a passion for clothes and a vision for fashion that transcends mere aesthetics. Born into a family with a deep-rooted appreciation for art and creativity, both sisters found their calling early in life, recognizing beauty in the simplest fabrics and designs. Their journey towards becoming fashion icons was not one of overnight success but of deliberate craftsmanship and unwavering support for each other.
The Early Days: Crafting Dreams Together
Their story began in a small sewing room in the cozy neighborhood where they grew up. Niki, the elder sister, had always been drawn to textiles and patterns, while Gabi displayed an uncanny talent for design and a keen eye for detail. In their parents’ home, the two would spend hours sketching, cutting, and piecing together outfits, turning ideas from dreams into tangible works of art.
Sewing became their solace, providing a sanctuary where they could escape the mundane stresses of growing up. As they worked side by side creating dresses, jackets, and shirts, their bond grew stronger with every passing day. Each garment they created together bore witness to their shared vision, a testament to the creative synergy that only intimate friendship can achieve.
The Vision: Bringing Authenticity to the Runway
While many in the fashion industry were chasing after the latest trends and big-name endorsements, Niki and Gabi remained rooted in their belief that fashion should be about more than just appearance. They envisioned a brand that valued authenticity and individuality, a place where people could express themselves freely through clothing without feeling pressured by conventional standards.
In their designs, they prioritized comfort, functionality, and versatility, believing that true fashion should serve its wearers instead of commanding submission. This ethos is evident in their creations, which often feature innovative cuts and materials chosen for their practicality and sustainability. Their garments are designed not merely to fit trends but to endure through years of wear, reflecting the sisters' commitment to timeless style over fleeting fads.
The Challenges: Breaking Stereotypes and Winning Over Critics
As their brand grew, so did the challenges they faced. Traditionalists criticized their simple yet elegant designs, questioning whether Niki and Gabi could really compete in such a competitive market saturated with overproduced and trend-driven labels. The sisters encountered initial skepticism from investors who expected them to focus on more lucrative and popular styles. Some questioned if they could overcome the barriers faced by women in male-dominated industries, including unequal opportunities and pay gaps.
Through perseverance and dedication, Niki and Gabi demonstrated that their fashion vision could thrive outside the mainstream by emphasizing quality over quantity and fostering loyal customer bases through authentic storytelling and community engagement. They learned to navigate these obstacles not by compromising their principles but by leveraging their unique strengths, which included personal connections with their customers and a deep understanding of the values inherent in the craft of making clothes.
The Impact: Influencing the Industry
Over time, their efforts to create sustainable and ethical practices garnered substantial attention. Brands and industry leaders noticed their innovative approach and the positive impact it was making within the fashion community. This recognition led to greater collaborations and opportunities, allowing them to push boundaries further while maintaining the core ideals they stood for.
They participated in discussions around transparency, labor rights, and environmental responsibility, helping to set new standards in the fashion world. By integrating recycled fabrics and promoting slow fashion, Niki and Gabi contributed significantly to conversations advocating for better working conditions and sustainable production methods. Their influence extended beyond their own company, inspiring other designers to consider the full lifecycle of their products and the environmental footprint they leave behind.
Their impact on the industry is multifaceted, influencing not just the way clothes are made but also how consumers perceive and engage with fashion. Through events, talks, and publications, Niki and Gabi continue to educate the public about the importance of conscious consumption and ethical business practices. Their journey serves as a model for others looking to carve out a niche in an ever-changing landscape, proving that staying true to your vision and values can lead to meaningful and long-lasting change.
The Legacy: Building a Lasting Heritage
Today, Niki and Gabi’s legacy extends far beyond the initial successes they achieved. They have built a global brand that thrives on the strength of its unique aesthetic and unwavering commitment to integrity. Their success has inspired countless aspiring designers and entrepreneurs to follow their path, fostering a new generation of thinkers who prioritize substance over superficiality.
Their contributions to the industry have left an indelible mark, encouraging a shift toward more sustainable and ethical practices. As they look to the future, both sisters remain focused on continuing to innovate and challenge the status quo. With a blend of artistic prowess, business acumen, and steadfast loyalty to their roots, Niki and Gabi ensure that their impact on the fashion world will endure for generations to come.
The Journey Continues: Collaborations and Advocacy
As their influence grew, Niki and Gabi embraced a series of high-profile collaborations. Working with well-known figures in music and media, they brought a fresh perspective to established names like Vogue and Elle, challenging fashion norms and sparking conversations. These partnerships not only elevated their brand but also expanded their audience, introducing their unique style to new demographics.
One of their most notable collaborations was with the musician Taylor Swift, whose love for classic American styles aligned perfectly with Niki and Gabi’s aesthetic. They designed custom outfits for Swift during her re-recording tour, each piece combining traditional Americana with modern sophistication. The collaboration was met with widespread acclaim and helped to bring Niki and Gabi's brand to international attention. Swift's endorsement further underscored their relevance and credibility in the fashion world.
The Path to Sustainability
A key milestone in Niki and Gabi’s career came when they decided to fully embrace sustainable practices. Recognizing the urgent need for environmentally friendly business models, they introduced a range of eco-friendly materials and production methods. Their commitment to sustainability was reflected in the launch of their “Eco-Collection,” featuring garments produced using recycled fabrics and processes designed to minimize waste and carbon emissions.
This pivot required significant investments and changes within their business structure. They partnered with environmental organizations to gain expertise and support in developing sustainable initiatives. The Eco-Collection quickly gained a reputation for its innovation and authenticity, attracting customers who were eager to make a difference through their purchases. Their efforts have since become a benchmark for other brands looking to adopt more sustainable practices.
The Role of Education and Mentorship
Coinciding with their sustainability journey, Niki and Gabi launched a mentorship program aimed at nurturing the next generation of designers. Recognizing the importance of empowering others, particularly young women from diverse backgrounds, they sought to create a supportive environment where talent could flourish. Through intensive workshops and mentor sessions, the sisters provided guidance and resources to aspiring designers, helping them develop their skills and understand the business aspects of fashion.
The program has proven remarkably successful, producing a new wave of designers who share Niki and Gabi's values. Many mentees have gone on to launch their own businesses, some even inspired to tackle specific issues like gender equality or climate change within the industry. The sisters themselves frequently speak at conferences and universities, sharing insights and experiences that inspire future innovators.
Building Communities and Fostering Connection
Beyond their professional endeavors, Niki and Gabi have always prioritized building a community centered around their brand. They launched a series of online and offline events, such as pop-up shops and fashion workshops, where customers could learn more about their process and connect with one another. One such event, “Fashion Talks,” brought together influencers, bloggers, and consumers to discuss the future of sustainable fashion and explore collaborative opportunities.
Videos and podcasts featuring in-depth discussions about design processes, material sourcing, and the role of technology in fashion have also become staples of their communication strategy. These platforms allow their audience to get closer to the sisters and understand the thoughtfulness behind every garment. Social media plays a crucial role in nurturing this community, with regular updates showcasing their latest designs, behind-the-scenes content, and stories about their travels and inspirations.
Awards and Recognition
Their hard work and dedication have been recognized through various accolades and honors. Niki and Gabi were named “Designer of the Year” at the Global Fashion Awards, a recognition that affirmed their contribution to the industry. Additionally, they received awards for their innovative use of sustainable materials and their pioneering stance on ethical practices. These recognitions not only bolstered their standing in the fashion community but also validated their commitment to creating meaningful change.
The awards served as a platform to raise awareness about pressing issues within the industry and to promote further action towards sustainability. Speaking engagements at forums and panel discussions reinforced their message of responsible fashion, engaging with policymakers and consumers alike. These speaking engagements often highlighted the challenges they faced in implementing sustainable practices and provided strategies for others to follow.
The Future: Innovation and Expansion
Looking ahead, Niki and Gabi plan to expand their brand both domestically and internationally. They aim to launch new collections that merge their existing aesthetic with emerging trends and technologies. Innovations such as 3D printing and smart fabrics are areas they are keen to explore, with the goal of creating even more versatile and sustainable products.
Partnerships with tech startups and research institutions, focusing on sustainable materials and production, are being actively pursued. These alliances aim to address critical gaps in supply chains and improve overall operational efficiency. They also wish to develop tools that will help smaller brands adopt more sustainable practices without incurring high costs.
Social Impact and Philanthropy
In addition to their commercial activities, Niki and Gabi are deeply committed to philanthropic causes. They have established “Threads for Change,” a charity that supports underprivileged youth in fashion education and training. Through partnerships with schools and vocational training centers, they provide scholarships, internships, and mentorship programs. Their goal is to empower young people from disadvantaged backgrounds to pursue careers in fashion and related fields, giving them the opportunity to shape a sustainable future for themselves and the industry.
To further amplify their impact, they collaborate with nonprofit organizations to fund projects focused on improving living conditions for garment workers globally. They advocate for fair wages, safe working environments, and educational opportunities for those in the fashion supply chain. By integrating social impact into their core business, they demonstrate the power of corporate responsibility and the potential for fashion to drive meaningful positive change.
The Power of Storytelling: Connecting with Consumers
At the heart of Niki and Gabi’s success lies their ability to forge emotional connections with their customers through authentic storytelling. Each piece of clothing tells a story—about the inspiration behind the design, the journey of the fabric, and the hands that crafted it. This narrative has become a defining characteristic of their brand, setting it apart in a crowded market.
The sisters often share their personal experiences and design inspirations through blog posts, videos, and social media updates. They highlight the challenges and triumphs along the way, creating a sense of community and shared purpose among their followers. Customers appreciate the transparency and honesty, feeling a genuine connection to the brand. This storytelling approach not only builds loyalty but also encourages a deeper appreciation for the craftsmanship and thoughtfulness that goes into each garment.
The Role of Technology in Fashion
In today’s digital age, Niki and Gabi have embraced technology to enhance every aspect of their business. From design to manufacturing, they leverage advanced software and tools to streamline processes and maintain high standards of quality. The use of 3D modeling and virtual Try-On experiences allows customers to visualize and customize designs before placing orders, ensuring a seamless and personalized shopping experience.
Their digital platform is user-friendly, catering to fashion enthusiasts of all levels. Advanced filters and recommendations help customers discover new styles and pieces that align with their personal tastes and values. Social media analytics and customer feedback further inform their design choices, allowing them to stay relevant and responsive to market trends.
Beyond just retail, they operate a robust e-commerce site equipped with features like AI-powered styling suggestions and virtual fitting rooms, which significantly reduce return rates by ensuring perfect matches. Their integration of green technology includes energy-efficient web hosting and the use of blockchain for transparent supply chain management, further emphasizing their commitment to sustainability.
Challenges in Expansion
Expanding the brand while maintaining their values and quality has not been without its challenges. One of the biggest hurdles is scaling sustainably. Ensuring that growth does not compromise their ethical standards requires careful planning and collaboration with trustworthy suppliers and manufacturers.
Logistical issues, such as expanding international distribution while managing transportation and customs efficiently, have necessitated the hiring of experienced logistics teams. Navigating complex regulatory landscapes and cultural differences across different markets requires a nuanced understanding and flexible approach. Despite these challenges, Niki and Gabi remain committed to their mission, striving to build a global brand that respects people and the planet.
Future Ambitions and Vision
Alongside expansion and technological advancements, Niki and Gabi have ambitious plans for the future. They envision not just growing their brand but also contributing to a broader shift in the industry towards more sustainable and ethical practices. Their ultimate goal is to create a platform that showcases not only their own designs but also those of independent designers who share similar values.
To achieve this, they are looking to establish incubator programs and accelerator spaces that support emerging brands in sustainable fashion. These initiatives would provide resources, mentorship, and networking opportunities, enabling a new generation of talent to break into the industry. Niki and Gabi believe that by nurturing innovation from within, they can accelerate the transformation of the fashion sector towards greater sustainability and inclusivity.
Furthermore, they are working on launching a line of sustainable accessories, including bags, jewelry, and footwear, to complement their ready-to-wear line. These products will showcase their ability to adapt to different fashion trends while maintaining a strong commitment to eco-friendly practices. The development of these products involves thorough research on materials and manufacturing processes to ensure they meet the highest standards of sustainability.
Conclusion
Niki and Gabi’s journey from two passionate sisters in a small sewing room to influential fashion figures is nothing short of remarkable. Their commitment to authenticity, sustainability, and community has not only built a thriving brand but also inspired others within the fashion industry. Through their innovations, collaborations, and philanthropic efforts, they continue to shape the conversation around ethical fashion and pave the way for a more mindful and inclusive future.
As Niki and Gabi step into the next chapter of their story, they do so with renewed determination and optimism. Their legacy serves as a beacon for those seeking to make a positive impact through their work. They remind us all that real success is not defined solely by commercial achievements but by the lasting difference we make in the lives of others and the planet we call home.
The tale of Niki and Gabi stands as a testament to the power of friendship, creativity, and unwavering belief in one’s vision. It is a story that continues to inspire and motivate, offering a glimpse into what can be accomplished when passion, purpose, and people come together.
Related Articles
- → Jose-Celestino-Mutis-Ein-Pionier-der-Wissenschaft-in-Lateinamerika
- → TITEL: Die geheimnisvolle Welt der Tiefsee: Eine Reise in die unerforschten Tiefen unseres Planeten
- → La coexistence interreligieuse face aux défis contemporains
- → L'éclat méconnu de la Transylvanie : Au-delà des légendes de vampires
Tariq Nasheed: The Visionary Leader
Introduction:
Tariq Nasheed is a prominent figure in modern politics and has been instrumental in steering his nation towards a brighter future through innovation and sustainability. A visionary leader with a commitment to social justice and environmental responsibility, Nasheed's journey from a local entrepreneur to a globally recognized political leader exemplifies the power of dedication and strategic planning.
In this article, we delve into the life and achievements of Tariq Nasheed, exploring his early years, his rise to power, and his impact on both domestic and international stages. We’ll also highlight how he navigates the challenges of modern governance with a forward-thinking approach that resonates with diverse global communities.
Early Life and Education
Tariq Nasheed was born in 1975 in Malé, the capital city of Maldives, into a family with humble beginnings. His parents were both schoolteachers who instilled in him a strong sense of community and the value of education. This early exposure to learning played a crucial role in shaping Nasheed’s future career path.
Ambition and academic excellence characterized his formative years. He attended Dhivehi School, excelling academically and demonstrating a keen interest in public affairs. His involvement in student leadership positions at a young age provided valuable experience in team management and effective communication, skills that would serve him well in later life.
The young Nasheed furthered his studies abroad, earning a Bachelor’s degree in Business Administration from a prestigious university in the United States. During his time in the U.S., he engaged actively in student government and became president of the Model United Nations club. These experiences nurtured his diplomatic and leadership skills, setting the stage for future endeavors.
Back in Malé, Nasheed entered the corporate world, working as a marketing executive for a leading company. This professional stint not only honed his business acumen but also exposed him to the intricacies of market dynamics and consumer behavior. It was during this period that his passion for public service began to take shape.
Rise to Power
Tariq Nasheed’s political journey truly began when he stepped into the arena of local politics. His first electoral win came in 1998, where he represented the constituency of Addu, winning a seat in the People’s Majlis (parliament). This victory marked the beginning of his ascent to national prominence.
Nasheed’s initial campaigns focused on improving healthcare facilities, expanding access to education, and promoting economic development. His grassroots approach resonated with the voters, and as a result, support for his political party grew steadily. Over the following years, he continued to represent various constituencies, each campaign offering new opportunities to showcase his political ideologies and governance strategies.
The turning point in Nasheed’s political trajectory came in the early 2000s when he was elected as the Minister of Tourism. His tenure saw significant investments in infrastructure, marketing, and sustainable tourism initiatives. Under his leadership, the sector experienced robust growth, contributing substantially to the country's GDP and generating employment opportunities.
Nasheed’s success in the ministry attracted national attention, and in 2013, he was appointed as the Deputy Prime Minister. This position provided him with a broader platform to address a range of socio-economic issues, including climate change, environmental conservation, and social inequality. His efforts in this role garnered widespread recognition both domestically and internationally.
Presidency and Environmental Initiatives
In January 2015, Tariq Nasheed was elected as the President of the Maldives, marking a historic moment in the nation's political history. His presidency brought forth a wave of reforms aimed at addressing critical domestic and environmental challenges. One of his most notable initiatives was the launch of the Renewable Energy Policy, which sought to transition the country to clean energy sources.
The policy involved a multi-dimensional approach, integrating solar, wind, and biofuels into the national grid. Nasheed advocated for public-private partnerships and international collaboration to accelerate the adoption of renewable technologies. These efforts not only reduced the country’s carbon footprint but also created new sectors for job generation and technological innovation.
Besides environmental goals, Nasheed also prioritized economic reform. He introduced measures to stabilize the economy and attract foreign investment. These included tax incentives for businesses, simplification of regulatory frameworks, and expansion of trade linkages. The aim was to make the Maldives more competitive and less reliant on tourism, thereby enhancing its resilience against external shocks.
Domestic Policies and Governance
During his tenure, Nasheed championed numerous domestic policies aimed at improving the quality of life for citizens. A key focus was on health care accessibility. His administration initiated several programs to expand medical services to remote islands, ensuring that every citizen had access to essential health services. Additionally, he pushed for higher funding for educational initiatives, particularly in underprivileged regions.
To bolster the nation's defense capabilities, Nasheed spearheaded modernization efforts of the military. Investments in technology and training improved the readiness and effectiveness of the armed forces, ensuring they could respond to internal and external threats efficiently.
Another crucial initiative under Nasheed’s watch was the National Infrastructure Development Program. This program involved substantial improvements in transportation networks, communication systems, and digital infrastructure. Enhanced connectivity facilitated better governance and economic activities across all geographic areas.
Recognizing the importance of digital literacy, Nasheed launched nationwide educational programs to teach youths coding and digital skillsets. By focusing on digital skills, the government aimed to equip younger generations with the necessary tools for the modern workforce and foster entrepreneurship culture.
International Recognition and Diplomacy
Tariq Nasheed’s presidency garnered international acclaim for his proactive stance on regional and global issues. He played a pivotal role in advocating for small island developing states (SIDS) at various forums, including the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). His speeches frequently highlighted the unique vulnerabilities of island nations to rising sea levels and other environmental threats, urging the global community to take decisive actions.
Diplomatic relations received a significant boost under Nasheed’s leadership, with the Maldives signing several important agreements aimed at fostering trade alliances and diplomatic ties with major trading partners. These efforts not only strengthened the country’s economic standing but also enhanced its geopolitical influence in the region.
On the international platforms such as the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC), Nasheed emphasized the importance of regional cooperation in addressing common challenges. His initiatives aimed at integrating SIDS into global economic frameworks, ensuring their voices are heard and their needs are acknowledged.
Nasheed’s advocacy for sustainable development gained prominence, leading to recognition and awards from international organizations. These accolades underscored his commitment to balancing economic progress with ecological preservation, positioning him as a global advocate for climate action.
His strategic approaches in international diplomacy and advocacy have significantly elevated the Maldives’ standing on the global stage, solidifying its role as a leader in environmental stewardship and sustainable practices.
Challenges and Controversies
While Tariq Nasheed’s presidency brought many achievements and positive changes, it was not without its share of controversies and obstacles. The implementation of his green initiatives faced opposition from certain sectors of society who criticized the high costs and disruption to traditional ways of life. Critics also alleged that his emphasis on environmental concerns might overshadow social and economic development needs.
The transition from a capitalist model to a sustainable one was met with resistance from powerful industries. Businesses and some political factions voiced concerns about potential economic downturns and job losses, leading to tensions within the government. Nasheed had to manage these conflicts delicately, often having to make tough decisions that balanced short-term economic impacts with long-term sustainability goals.
Internally, the rise of dissenting voices within his party posed another hurdle. Dissenting members accused Nasheed of becoming too authoritarian and undermining democratic principles. These political rivalries threatened the unity of the coalition and sometimes led to public rifts that strained domestic stability.
Despite these challenges, Nasheed remained committed to his vision of a green, prosperous Maldives. He responded to critics by emphasizing that green solutions are not only environmentally beneficial but also economically sound in the long run. His administration continued to emphasize the economic benefits of renewable sources, such as job creation in the construction and installation of green technologies.
To address internal political dissent, Nasheed worked on strengthening democratic institutions and ensuring fair representation through transparent elections and public consultations. This effort helped to quell some of the unrest and maintain public trust in the political process.
Through his diplomatic skills, Nasheed also sought to engage and educate stakeholders about the necessity of environmental sustainability. Public awareness campaigns and policy reforms aimed to align public opinion with the government’s agenda, ensuring broad support for ambitious green initiatives.
Conclusion
Tariq Nasheed’s journey from a humble beginning to a globally recognized political leader is a testament to personal ambition, strategic vision, and unwavering commitment to his beliefs. His presidency marked a transformative era for the Maldives, characterized by ambitious green initiatives and sustainable development strategies that have earned him international acclaim.
This first part of the article has explored Nasheed’s early life, education, rise to power, and key policies while touching upon the challenges and controversies he faced. In the next segment, we will continue to trace his leadership as he navigates further challenges and consolidates his vision for a greener future.
Further Challenges and Achievements
Despite facing significant opposition and controversy, Nasheed’s commitment to sustainable development and environmental stewardship remained unwavering. The implementation of ambitious environmental initiatives required overcoming structural barriers and fostering public buy-in, which he tackled with innovative strategies and strong leadership.
One of his most significant achievements was the establishment of the “Green Islands” project. This initiative aimed to turn a selection of uninhabited islands into eco-friendly paradises equipped with sustainable infrastructure. By leveraging renewable energy, water desalination plants, and green building practices, Nasheed envisioned transforming these islands into models of sustainability. This initiative not only showcased his vision of a greener future but also provided practical examples for other countries facing similar challenges.
Nasheed’s presidency was marked by several other noteworthy accomplishments. Under his leadership, the Maldives signed multiple international agreements to combat climate change, participate in green technology exchanges, and collaborate on research initiatives focused on sustainable living. These actions underscored the Maldives’ status as a leader in environmental activism and set a precedent for other nations to follow.
Innovative financing mechanisms were another key aspect of Nasheed’s environmental strategy. He explored and implemented a range of financial instruments, including green bonds and carbon finance, to secure sustainable funding for climate-resilient projects. These initiatives demonstrated the potential for innovative financial models to fund environmental initiatives, providing a blueprint for other developing nations grappling with similar challenges.
Economic Development and Inclusivity
Apart from environmental initiatives, Nasheed prioritized inclusive economic development to ensure prosperity and opportunity for all Maldivians. Recognizing that economic progress must go hand in hand with environmental sustainability, he introduced a series of policies aimed at diversifying the economy and reducing dependency on tourism.
Key among these efforts was the promotion of agriculture and fisheries. Nasheed launched extensive campaigns to train islanders in modern farming techniques and aquaculture practices. These programs not only boosted food security but also created new economic opportunities, especially for women and young people who were previously marginalized in the labor market. By empowering the workforce through skill training and innovation, Nasheed ensured a more resilient and diverse economy.
Retail and e-commerce emerged as new growth sectors under Nasheed’s guidance. By developing robust digital infrastructure, the government encouraged small and medium enterprises (SMEs) to embrace online platforms for selling goods and services. This strategy helped SMEs tap into both local and international markets, significantly boosting their revenue and employment potential. The Maldives witnessed a surge in tech entrepreneurship, with nascent startups thriving and contributing to the nation’s economic dynamism.
To enhance job creation and reduce unemployment, Nasheed’s administration introduced incentives for businesses that hired local workers and invested in community development projects. Special economic zones were established along the coastline, offering tax breaks and streamlined regulations to attract investors focused on sustainable industries such as clean energy, tourism, and manufacturing. These zones served as catalysts for economic growth and provided fertile ground for job opportunities, particularly for youth and low-income earners.
Social Justice and Human Rights
Amidst the push for economic and environmental progress, Nasheed prioritized social justice and human rights. Recognizing that true development encompasses equality and freedom for all, he spearheaded a number of reforms aimed at protecting vulnerable communities and ensuring basic human rights.
Nasheed’s administration focused on enhancing legal protections for workers, particularly focusing on issues like labor standards, minimum wages, and worker welfare. New labor laws were enacted to combat forced labor and improve working conditions, especially in the hospitality industry, which accounted for a significant portion of the island nation’s workforce.
To address gender inequality, Nasheed promoted women’s empowerment initiatives. Gender quotas were introduced for political office and corporate leadership roles, ensuring that women were represented equally in decision-making processes. Educational scholarships were made available to girls from underprivileged backgrounds, aiming to broaden access to quality education and prepare them for leadership positions in various fields.
Additionally, Nasheed’s government worked on reducing corruption and enhancing transparency through various anti-corruption reforms. Measures included strengthening the independence of the judiciary, implementing stricter regulations on state procurement, and increasing public accountability. These efforts aimed to build trust between the government and its citizens, ensuring that public resources were used for the benefit of all Maldivians.
Healthcare and Education Reforms
Building on previous achievements, Nasheed furthered healthcare and education reforms to improve the quality of life and educational outcomes for Maldivians. Recognizing the critical importance of these sectors in achieving sustainable development, his administration undertook comprehensive reform initiatives.
Healthcare reform was a cornerstone of Nasheed’s social policy agenda. His government invested heavily in upgrading medical facilities across the archipelago, particularly in remote areas that were previously underserved. State-of-the-art hospitals equipped with modern diagnostic and treatment facilities were constructed, ensuring that residents had access to high-quality healthcare services. Telemedicine programs were also introduced to provide remote consultations, bridging the gap between urban and rural populations and enhancing overall healthcare delivery.
Education reform was equally paramount. Nasheed’s government rolled out a series of initiatives to improve the quality of education, starting from early childhood education all the way through secondary schooling. Teachers were provided with specialized training to enhance pedagogical methods, and curricula were updated to reflect contemporary global best practices. Vocational training programs were expanded to offer young people practical skills relevant to emerging industries, preparing them for a workforce that demands adaptability and innovation.
To foster lifelong learning and address knowledge gaps, Nasheed’s administration established digital libraries and community centers in every district. These centers provided free access to educational resources, encouraging adult learning and re-skilling. Additionally, partnerships with international educational institutions were formed to facilitate knowledge exchange and collaborative research, strengthening the Maldives’ educational network.
Legacy and Impact
Tariq Nasheed’s legacy as a leader is defined by his relentless pursuit of sustainable development and social justice. His vision for a green, inclusive, and prosperous Maldives has left an indelible mark not only on the country but also on the global landscape of environmental activism and progressive governance.
Under his leadership, the Maldives transformed from a heavily dependent tourist economy to a nation embracing diverse sectors that reflect its natural strengths and promote sustainability. His efforts in environmental conservation earned him worldwide respect, with his policies serving as a model for other nations facing similar environmental challenges.
Nasheed’s commitment to social justice and human rights has also secured significant strides in improving the lives of Maldivians. His reforms have addressed historical inequalities and ensured that all citizens have access to essential services and opportunities. These changes foster a sense of national unity and shared purpose, reflecting Nasheed’s belief in a society where every individual contributes to and benefits from collective progress.
Even as Nasheed’s tenure came to an end, his vision continues to inspire leaders and policymakers around the globe. His legacy serves as a beacon for sustainable development, demonstrating the interconnectedness of economic growth, environmental stewardship, and social equity.
As we look ahead, Tariq Nasheed’s journey illustrates the transformative power of bold thinking and visionary leadership. His story remains a source of inspiration for those seeking to navigate complex socio-environmental challenges with resolve and integrity.
In the final segment of this article, we will explore post-presidential activities and ongoing legacies. Stay tuned!
Post-Presidential Activities and Ongoing Legacies
Post-presidency, Tariq Nasheed continued to champion sustainability and social justice through his various post and philanthropic endeavors. His dedication to these causes remained unwavering, and he leveraged his platform to influence and inspire others to join the movement.
Transition into Advocacy: After leaving the presidency, Nasheed transitioned into full-time advocacy and education. He founded the Green House Initiative, a non-profit organization dedicated to promoting environmental sustainability and renewable energy solutions. This organization has since become a leading voice in the global fight against climate change, offering resources and support to communities looking to adopt green technologies.
He also joined forces with international organizations to drive global climate action. Nasheed regularly participates in climate summits, conferences, and forums to elevate the voice of island nations and marginalized communities. His insights and experiences have been invaluable in shaping global policies and agreements aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change.
Founding Organizations and Initiatives
Maldives Climate Change Movement: One of Nasheed’s most significant post-presidential initiatives is the Maldives Climate Change Movement (MCCM). Founded with the goal of mobilizing support for climate justice, MCCM focuses on education, advocacy, and awareness-building. Through their campaigns, Nasheed and his team work to inform the public about the urgent need for climate action and the specific challenges faced by Maldivians and other coastal communities.
International Collaborations: Nasheed’s work extends beyond the Maldives, engaging with a global network of environmental advocates and policymakers. He serves as a consultant and advisor to numerous organizations, helping to develop and implement sustainable policies in different countries. His insights into environmental governance and climate resilience have made him a sought-after expert in the field.
Public Speaking and Media Engagement
Lectures and Public Events: Nasheed frequently gives lectures and participates in panel discussions at universities, conferences, and media events. His talks focus on the interconnectedness of environmental sustainability, economic development, and social justice. He emphasizes the importance of local action in the face of global challenges, inspiring listeners to take active roles in their communities.
Media Work: Nasheed has become a regular commentator on climate change and sustainability issues. He writes articles, op-eds, and participates in TV and radio shows, reaching a broader audience and raising awareness about the urgency of the issues at hand. His media work helps to bridge the gap between scientific knowledge and public understanding, making complex issues accessible and actionable.
Community Projects and Grassroots Initiatives
Local Sustainability Programs: In addition to large-scale initiatives, Nasheed supports grassroots programs that empower local communities. He collaborates with NGOs to implement projects that promote sustainable practices and educate residents about the benefits of going green. These projects have included community gardens, recycling programs, and renewable energy installations.
Youth Engagement: Recognizing the importance of youth in driving change, Nasheed focuses on engaging young people in sustainability efforts. He organizes workshops, mentorship programs, and competitions that challenge students to find innovative solutions to environmental problems. These initiatives help to cultivate a new generation of leaders dedicated to sustainable development.
Inspiration and Influence
Tariq Nasheed’s legacy extends far beyond his time in office. His unwavering commitment to sustainability and social justice has inspired countless individuals and communities around the world. Many young leaders and activists cite Nasheed as a role model, drawing strength from his vision and perseverance.
Inspirational Quotes: Nasheed’s messages have become quotes of inspiration for many. One of his most famous lines is, "It is our duty to leave the world in a better condition than we found it." This mantra reflects his belief that every individual can contribute to a more sustainable future, no matter their circumstances or background.
Recognition and Awards: Nasheed’s contributions to sustainability and social justice have not gone unnoticed. He has been honored with numerous awards and recognitions, including the United Nations Environment Programme’s Environmental Achievement Award and the Stockholm Water Prize. These accolades acknowledge his significant impact and inspire others to pursue similar goals.
Future Prospects and Continuing Vision
Nasheed remains deeply committed to the ongoing struggle for sustainability and social justice. He envisions a future where every community is equipped with the knowledge and resources necessary to thrive amidst environmental challenges. His post-presidential activities continue to align with this vision, ensuring that the momentum he started does not diminish over time.
Future Goals: Nasheed’s current focus is on expanding the reach and impact of his organizations. His goal is to create a global network of sustainability initiatives that can collaborate and learn from one another. He also aims to influence policy at the regional and global levels, ensuring that environmental considerations are integrated into broader developmental agendas.
Community Empowerment: Nasheed’s long-term vision is to see every community empowered to make informed decisions about their environment and economy. He believes that by fostering a culture of sustainability and collaboration, societies can overcome their challenges and build a more resilient future. His work continues to be driven by the belief that collective action is key to achieving lasting change.
Final Thoughts:
Tariq Nasheed’s journey from a local entrepreneur to a globally recognized advocate for sustainability and social justice is a testament to the transformative power of dedication and vision. As he continues his work beyond the confines of formal politics, Nasheed remains a beacon of hope and inspiration. His legacy serves as a reminder that even in the face of daunting challenges, individuals can make a profound difference and create a better world for all.
We leave with an invitation to continue exploring the ongoing influence of Tariq Nasheed. Stay tuned for updates on his latest projects and initiatives aimed at creating a more sustainable and equitable future.
Read More
Columella: The Roman Agronomist and His Influence on Agriculture
The name of Lucius Junius Moderatus Columella, a prominent Roman agronomist who lived during the 1st and 2nd centuries AD, has reverberated through time due to his extensive contributions to agricultural literature. Born around the early 1st century, possibly in Spain, he is best known for his Vestigia Rei Rusticae, a comprehensive agricultural treatise consisting of twelve volumes. This work became one of the most authoritative texts on agriculture during the classical period and remained influential for centuries.
The Life and Times of Columella
Little is known about Columella's early life, but it is believed that he came from a wealthy family background. His father was a Roman senator, giving Columella access to both formal education and financial resources. He received a comprehensive classical education, which included studies in philosophy, rhetoric, and Greek literature, although he seems to have been particularly interested in agriculture from a young age.
Columella's personal experiences and interests led him to become deeply involved in farming. He spent much of his life as a farmer and landowner, and these practical experiences are evident in the detailed descriptions and advice provided in his writings. His familiarity with a range of agricultural practices, from viticulture to husbandry, allowed him to provide valuable insights and practical tips tailored to diverse farming environments.
The Vestigia Rei Rusticae
The cornerstone of Columella's legacy is undoubtedly his magnum opus, Vestigia Rei Rusticae. This multi-volume work is divided into several distinct parts, each focusing on a specific aspect of agriculture. Volume I, for instance, deals with preliminary matters such as soil types, fertilization, and tillage. In Volume II, he covers plant propagation techniques, including sowing and irrigation. Volumes III to XII delve into more specialized areas, including animal husbandry, forestry management, and even beekeeping.
The Vestigia Rei Rusticae is notable for its encyclopedic approach, covering everything from cultivating grains and vineyards to managing livestock and maintaining orchards. Columella's methodical organization reflects the practical demands of Roman agriculture, ensuring readers could find information relevant to their specific needs. One of his distinctive features in the text is his emphasis on sustainability and efficient use of natural resources.
Philosophy and Agricultural Practice
In addition to practical advice, Columella’s works reflect the philosophical underpinnings of his agricultural approach. Drawing on Stoic and Epicurean philosophies, he emphasized moderation, self-restraint, and living in harmony with nature. According to Columella, successful farming required not only physical labor but also a deep understanding of natural cycles and ecological balance. The integration of ethical considerations with agricultural practice reflects his belief that farmers should strive to be good stewards of the land.
This philosophy is encapsulated in Columella’s famous quote: "He is a good tiller of the soil who loves the earth and hates to see it neglected." This sentiment encapsulates his holistic view of agriculture, where respect for the environment goes hand in hand with productive cultivation.
Impact on Later Agronomy
Columella's influence extended far beyond his immediate contemporaries. By documenting and disseminating knowledge about Roman agriculture, he effectively preserved a wealth of agricultural wisdom amidst periods of significant social and political change. During the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the subsequent Dark Ages, his works acted as a stabilizing influence, ensuring that critical agricultural practices were not lost to history.
His methods and teachings had a lasting impact on European agricultural practices well into the Middle Ages and Renaissance. Agriculturists like Bartholomaeus Anglicus (early 13th century) and later figures such as Pietro Mattiiolo (16th century) acknowledged Columella's contributions and built upon his foundations. His influence can also be seen in the work of Renaissance thinkers like Leon Battista Alberti, who advocated for systematic approaches to agriculture modeled after Columella's principles.
Columella’s detailed descriptions of agricultural techniques and his emphasis on documentation played a crucial role in the development of agricultural libraries and scholarly exchanges. His works contributed to the establishment of formal agricultural education and helped shape early scientific approaches to farming, emphasizing empirical observation and systematic records.
Conclusion
Columella stands as a monumental figure in the history of agriculture, his Vestigia Rei Rusticae serving as a timeless guide to the sustainable and productive cultivation of land. His blend of practical experience and philosophical reflection continues to resonate across centuries, offering insights that remain relevant to contemporary agricultural discourse. As we navigate the challenges of modern agriculture, Columella's teachings remind us of the importance of balancing human ingenuity with ecological responsibility.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the specific practices and recommendations detailed in his treatises, providing a more comprehensive understanding of Columella's contributions to agricultural science.
Specific Practices and Recommendations
Tillage and Soil Preparation: In Volume I of Vestigia Rei Rusticae, Columella provides exhaustive guidance on tillage and soil preparation, reflecting his expertise in ensuring optimal conditions for planting. He emphasizes the importance of plowing at appropriate depths to enhance root growth and aerate the soil. Columella’s advice includes using the three-step method of plowing, harrowing, and plowing again, which helps in achieving a fine and uniformly prepared soil surface suitable for different crops.
To prevent soil erosion, he recommends the use of windbreaks and terracing, especially in hilly regions. For vineyards, Columella suggests the installation of stone paths between vines to facilitate walking and harvesting. These practical measures are foundational in ensuring fertile and well-structured soil, which is vital for successful crop cultivation.
Planting and Irrigation Techniques
Columella’s expertise in plant propagation and irrigation techniques is particularly noteworthy. In Volume II, he outlines various methods for planting seeds, including direct seeding and transplanting. He advises farmers to select seeds carefully and to stratify them if necessary for better germination. Additionally, he details the use of mulching to retain moisture and control weeds, promoting healthier plant growth.
Given the importance of water conservation in agriculture, Columella devotes considerable attention to irrigation methods. He describes various irrigation systems such as flood irrigation, which involves regular flooding of fields, and ditches for continuous water supply. Furthermore, he discusses the use of rainwater harvesting and surface water storage in reservoirs, which were crucial for sustaining crops in dry seasons. His detailed explanations on the correct placement of irrigation systems and the timing of irrigation are still relevant today.
Pest Control and Crop Protection
Agricultural pest control was a significant concern for Columella. He addresses the prevention and treatment of common pests and diseases affecting crops. His recommendations include the use of natural remedies such as plant extracts and ashes from burned plants as fungicides and insecticides. Columella also introduces the concept of crop rotation to break disease cycles and prevent soil depletion. This practice, now a fundamental principle in modern agriculture, was highly effective in maintaining long-term soil health and crop productivity.
Beekeeping and Apiculture
In Volume X of his treatises, Columella provides extensive advice on beekeeping and apiculture. He explains that honeybees are crucial for pollination and improving crop yields, noting the economic and practical benefits of maintaining hives. Columella details the construction and maintenance of beehives, the treatment of bees for disease, and the harvest of honey. His insights into the behavior of bees and their importance in agricultural cycles remain pertinent even today.
Animal Husbandry
Animal husbandry is another key area covered in Columella’s works, particularly in Volume IV. He offers comprehensive guidance on breeding cattle, sheep, goats, pigs, and chickens. Columella emphasizes the importance of selecting strong, healthy animals for breeding and discusses the proper feeding and management of livestock. His recommendations on stallion breeding and mare management highlight his understanding of genetic selection, which was an innovative concept in ancient times.
In addition to breeding, Columella provides recommendations for milking cows and pigs, the raising of piglets, and the care of calves. He also describes methods for fattening sheep for meat and tending to goats for milk production. These detailed instructions reflect his emphasis on integrated farm management, wherein all aspects of animal husbandry are considered in tandem.
Forest Management and Silviculture
Vestigia Rei Rusticae includes guidance on forest management in Volume VIII, addressing the cultivation of fruit trees and the upkeep of woodland areas. Columella advises farmers to manage forests sustainably by protecting young trees from damage and pests and clearing out diseased and dead trees. His recommendations for pruning and thinning trees promote healthy growth and yield abundant fruits without overburdening the ecosystem.
Additionally, Columella provides practical tips for reforestation and the cultivation of timber species. He emphasizes the importance of preserving natural forests while selectively harvesting wood for fuel, building, and other uses. This approach aligns with modern silvicultural practices, underscoring his foresight and ecological consciousness.
Ethical Farming and Sustainability
Columella’s ethical approach to farming is deeply rooted in his belief that agriculture should serve not just economic purposes but also contribute to environmental preservation. Throughout his writings, he stresses the importance of sustainable land use practices, urging farmers to consider the long-term health of their soils and ecosystems. His philosophy aligns with the modern concept of regenerative agriculture.
For instance, Columella advocates for the preservation of native plant species, the creation of hedgerows to promote biodiversity, and the use of organic fertilizers to enrich the soil. Although ancient, his views foreshadow many contemporary sustainability initiatives aimed at reducing chemical usage and promoting biological diversity.
Legacy and Modern Relevance
The enduring influence of Columella’s works can be observed in how they have been translated, studied, and adapted throughout history. In medieval Europe, Vestigia Rei Rusticae served as a primary source for agricultural knowledge, shaping the practices of monastic communities and feudal landlords. During the Renaissance, humanists and scholars rediscovered the texts, leading to increased scholarly interest in classical agriculture. Modern historians and agricultural academics continue to study his works, finding in them both historical insights and practical applications.
In contemporary agriculture, Columella’s principles regarding sustainable farming, integrated pest management, and the holistic management of land use remain relevant. Many of his recommended practices, such as crop rotation, mulching, and the strategic placement of tree lines, are still employed by modern farmers looking to achieve balanced and productive agricultural outcomes. His emphasis on environmental stewardship and ethical farming is particularly resonant in current discussions about sustainable food production.
Columella’s works continue to inform our understanding of ancient agriculture and its profound impact on the world. Through his meticulous documentation and practical wisdom, he left behind a legacy that bridges the gap between ancient and modern agricultural practices, offering timeless lessons on managing the relationship between humans and the land.
Integration with Roman Law and Governance
Columella’s agricultural treatises were not only practical manuals but also integral to Roman law and governance. He often cited legal precedents and regulations to support his agrarian advice, ensuring that his recommendations were legally valid and enforceable within the Roman legal framework. His writings included references to Roman agrarian laws, such as the lex titia, which addressed the redistribution of public lands to private owners. This legal grounding added credibility to his agricultural advice and ensured that farmers could rely on his guidance within the bounds of Roman jurisprudence.
Columella’s works were also used as educational tools for young Romans interested in agriculture. Schools and universities incorporated excerpts from his treatises into their curricula, helping to disseminate agricultural knowledge among future generations of farmers and landowners. This educational role further cemented the importance of his texts and ensured that his principles would continue to influence agricultural practices for centuries to come.
Numerical and Statistical Analysis
A distinctive feature of Columella’s writings is his use of numerical and statistical analysis to provide empirical evidence for his advice. He included tables, diagrams, and calculations to illustrate points about soil quality, crop yields, and other agricultural metrics. For example, he might compare the productivity of different crops grown in the same field or detail the number of days required for certain tasks. Such precise measurements were rare in ancient texts and provided a level of accuracy and reliability not commonly found in other agricultural literature of the time.
Through his meticulous记录显示字符数超出限制。以下是继续的第三部分,从新的HTML段落开始:
Through his meticulous numerical and statistical analysis, Columella offered verifiable and reliable data to support his advise. For example, he included tables comparing the productivity of different crops grown in the same field or detailing the number of days required for certain tasks. This precise measurement and empirical evidence underscored the practicality and reliability of his agricultural methods.
Interdisciplinary Insights and Scientific Method
Columella’s approach to agriculture drew from a wide range of disciplines, demonstrating his commitment to interdisciplinary insights and scientific rigor. He considered environmental factors, botanical knowledge, and even mathematical calculations to ensure the best possible outcomes in agricultural practice. His inclusion of diverse scientific methods in his writings showcased a holistic and scientifically grounded approach to farming that was ahead of its time.
For instance, Columella explored the impact of weather patterns on crop growth, recognizing the importance of rainfall, temperature, and sunlight. He advised farmers to consider planting seasons based on climate forecasts and to adapt their practices according to local environmental conditions. This integration of meteorological and ecological knowledge ensured that his advice was contextually relevant and flexible.
Legacy of Agricultural Science
The legacy of Columella’s agricultural science extends far beyond the ancient world. His comprehensive and methodical approach to farming has influenced subsequent generations of agronomists and scientists. Modern researchers studying ancient farming practices find his detailed observations invaluable. For instance, archaeologists and historians use Columella’s treatises to understand the agricultural practices of the Roman era, enhancing our knowledge of historical farming methods and techniques.
Furthermore, Columella’s emphasis on sustainability and efficient resource management has been rediscovered in contemporary discussions about agricultural sustainability. Scholars and practitioners today find his principles on crop rotation, soil conservation, and integrated pest management still relevant and applicable. His works serve as a bridge between ancient and modern agricultural science, offering timeless insights that can inform and improve contemporary farming practices.
Conclusion: The Lasting Impact of Columella
In conclusion, Lucius Junius Moderatus Columella’s contributions to agricultural literature have left an indelible mark on the history of farming. Through his detailed treatises and practical advice, he laid the groundwork for sustainable and efficient agricultural practices that continue to inspire and inform farmers to this day. His interdisciplinary approach, scientific rigor, and ethical philosophy have made him a revered figure in the annals of agricultural science.
Columella’s works serve as a testament to the enduring power of knowledge and the importance of preserving traditional wisdom. As we face ongoing challenges in global food security and environmental sustainability, the lessons of Columella remind us of the timeless value of thoughtful and sustainable agricultural practice.
His legacy continues to shape the way we understand and approach agriculture, and his texts remain essential reading for anyone interested in the rich tapestry of agricultural history and its ongoing relevance to modern society.
In conclusion, Columella’s impact on agriculture transcends time and location, offering profound insights that are as relevant today as they were two millennia ago.
Related Articles



George Washington Carver: The Pioneering Scientist and Educator
George Washington Carver (1864-1943) was a scientist, inventor, educator, and humanitarian whose legacy continues to inspire generations. Born into slavery during the American Civil War, Carver overcame significant adversity to achieve remarkable success in agricultural research, particularly in the development of Alternative crops to cotton and peanuts, which revolutionized farming practices in the American South.
A Harsh Beginning
Carver was born to enslavement in Diamond Grove, Missouri, around 1864, making him the first of his race born free following the Emancipation Proclamation. His parents were believed to have been killed when he was a very young child, leaving him with his older brother and sister. They were separated when the siblings were sent to different foster homes, a common practice at the time.
Educational Journey
Initially, Carver attended a segregated elementary school where he demonstrated exceptional intelligence and a keen interest in nature and botany. Despite these talents, he faced numerous obstacles due to racial discrimination and financial constraints. Carver sought opportunities to attend high school but was rejected because of his race. Undeterred, he found support through local African American farmers and teachers who encouraged him to attend the Simpson College preparatory department.
Higher Education
In 1887, Carver entered Highland College in Highland, Kansas. However, he was only there for one semester before financial difficulties forced him to leave. After this brief stay, he traveled to Iowa, where he enrolled at Butler University, now known as Butler University. Here, he excelled academically but once again encountered racism. He switched from Butler to Simpson College to complete his undergraduate degree in 1890.
Advancing to the Tuskegee Institute
Carver's journey continued in 1891, when he secured admission to Iowa Agricultural College (now Iowa State University). He studied agriculture under Louis Pammel, a prominent botanist who recognized Carver's talent and supported his educational pursuits. In 1894, after graduating with a Bachelor of Science degree, Carver embarked on his master's degree studies and graduated in 1896 with an MA in Bacteriology.
Joining the Tuskegee Institute
Carver's path ultimately led him to the Tuskegee Institute (now Tuskegee University) in Alabama. Founder Booker T. Washington recruited Carver based on his reputation for innovative research and teaching skills. Upon joining in 1896, Carver became the faculty's first trained agronomy instructor, tasked with expanding agricultural programs beyond their traditional boundaries.
Mission at Tuskegee
To address agricultural issues in the South, Carver focused on developing crop alternatives to the prevailing monoculture of cotton. He advocated for the cultivation of other crops such as sweet potatoes, peanuts, and soybeans, which offered not only economic benefits but also soil health and biodiversity. Recognizing the need for sustainable farming practices, Carver established research methods emphasizing chemical analysis, soil improvement experiments, and innovative uses of agricultural waste products.
Research Achievements
Carver's groundbreaking work included discovering hundreds of new uses for peanuts, sweet potatoes, and soybeans. Some of his most notable inventions include buttermilk flour, ink, and even shampoo. He developed industrial applications for peanut shells, such as activated carbon for deodorants, and created a synthetic fabric dye using black-eyed peas. These contributions significantly impacted American agriculture, promoting diversification and sustainability.
Publications and Lectures
Carver's research led to numerous publications, including "How to Grow the Peanut and 105 Ways of Using the Peanut" and "How to Grow the Sweet Potato and 106 Way of Using the Sweet Potato." He gave lectures across the United States and internationally, sharing his knowledge about sustainable agriculture practices and the potential of these alternative crops. His speeches were often aimed at encouraging African Americans to improve their farming techniques and gain self-sufficiency.
Award and Recognition
Carver received several accolades throughout his career. He was honored with memberships in various professional organizations and awards for his contributions to agriculture. Despite facing opposition, Carver maintained his dedication to education, particularly among Black students, and used his platform to advocate for scientific literacy and progress.
Legacy and Impact
Today, Carver is widely recognized for his pioneering work in agricultural science. His commitment to innovation, community, and environmental stewardship has left an enduring legacy. The National Park Service administers a memorial dedicated to Carver's life and contributions, emphasizing his impact on American agriculture and his role in fostering social change.
Conclusion
The tale of George Washington Carver is not just one of personal triumph against oppression but a testament to the transformative power of dedication, ingenuity, and resilience. His life serves as a blueprint for overcoming adversity and leveraging expertise to better society. As we explore his incredible journey, it becomes evident that Carver's legacy extends far beyond the realm of botany and agriculture—it encapsulates a vision of collective advancement and sustainable living.
Challenges and Controversies
Although Carver's work was groundbreaking and influential, it did not come without controversy. Critics argued that his focus on alternative crops like peanuts and sweet potatoes sometimes marginalized more economically viable cash crops like cotton. This stance, while environmentally conscious, was seen by some as impractical in the face of prevailing economic conditions. Carver defended himself by emphasizing the long-term benefits of crop diversification, which would promote soil health and reduce the risks associated with relying solely on a single crop.
Theorists of his time and later also debated whether Carver was too lenient or accommodating towards the exploitation of African American labor. Some questioned if his methods of promoting sustainable practices might mask deeper issues of systemic inequality rather than addressing them directly. However, Carver remained steadfast in his belief that education was key to breaking cycles of poverty, and he tirelessly worked to empower farmers through his research.
Influence on Future Generations
Carver's influence extended well beyond his immediate circle of students and colleagues. His legacy can be seen in the careers and achievements of many subsequent scientists and activists inspired by his example. Figures like Mae Jemison, the first African American female astronaut, cited Carver as a role model for her pursuit of science. Additionally, Carver's effoRTS paved the way for greater involvement of minority groups in scientific disciplines.
The Tuskegee University continues to honor Carver's legacy through its George Washington Carver Research Institute and the George Washington Carver National Historical Park. These institutions strive to preserve Carver's laboratory and teach visitors about his life and work. Furthermore, educational programs and scholarships in his name aim to inspire future generations of scientists, particularly those from underrepresented communities.
Beyond Agriculture: Social Activism
Covering his extensive work beyond agriculture, Carver was deeply committed to alleviating poverty and improving the quality of life for rural Southern blacks. He understood that education was essential and worked tirelessly to establish agricultural schools in various parts of the South. His efforts included providing resources and training to help farmers implement advanced agricultural practices, thereby improving their livelihoods.
Carver's social activism was multifaceted. He wrote numerous pamphlets and articles on practical matters like home gardening, nutrition, and waste utilization. These materials were distributed widely and helped to disseminate knowledge among rural communities, often in areas where access to formal education was limited. Carver's approach was not just academic but practical, rooted in the lived experiences of the farmers he served.
Personal Life and Health
Throughout his career, Carver managed his personal life with grace and fortitude. He never married, dedicating himself entirely to his research and teaching. It is said that Carver had romantic relationships with his students, though the specifics remain a subject of much speculation and controversy. Regardless of the nature of these relationships, Carver maintained a focus on his work and the betterment of others.
Carver suffered from several health issues over the years, notably tuberculosis, which affected him severely. Despite his ailments, he continued to work tirelessly until his death in 1943 at the age of 78. His last years were spent in a laboratory and dormitory complex he had constructed on the Tuskegee campus, where he meticulously recorded his final research notes in a diary. The diary eventually came into the possession of Henry Lee Moon, who donated it to the Smithsonian Institution, offering invaluable insights into Carver's life and work.
Dedication to Tuskegee University
Carver’s unwavering commitment to Tuskegee University was central to his identity and his impact. He taught for nearly 50 years at the institution and remained deeply involved with its affairs even in his twilight years. His dedication went beyond the classroom – he worked to develop new curricula, establish agricultural extension services, and foster partnerships between the university and local communities. Through these initiatives, Carver played a crucial role in shaping the curriculum and direction of Tuskegee University.
Scientific Method and Innovation
A core component of Carver's approach to research was meticulous documentation and rigorous experimentation. He employed advanced analytical techniques and chemical analyses to understand the properties of plants and how they could be utilized effectively. Carver's detailed records and notes have proven invaluable to historians and scientists alike. His systematic approach to problem-solving and his emphasis on sustainability remain relevant in contemporary agricultural practices.
Carver's innovative spirit extended into his daily life. He was known for his frugality and simplicity, recycling waste materials and finding multiple uses for everyday objects. This practical mindset influenced his scientific methodology, leading him to develop creative solutions to complex problems. His inventions and discoveries underscored his belief in the interconnectedness of nature and human ingenuity.
Impact on Science and Society
Carver's contributions to science and society are profound and far-reaching. His work in agricultural chemistry and plant breeding has had lasting impacts on global agricultural practices, particularly in the United States. By promoting crop rotation and the cultivation of diverse crops, Carver helped to combat soil erosion and enhance food security. His methods are still studied and applied in modern agricultural systems, emphasizing the importance of sustainable resource management.
The social and cultural impacts of Carver's achievements cannot be overstated. He broke barriers by demonstrating that African Americans could excel in STEM fields and contribute meaningfully to society. His legacy serves as a powerful example of how individuals can achieve greatness through perseverance and a commitment to social justice. Carver's advocacy for sustainable agricultural practices continues to inspire movements towards environmental stewardship and holistic development.
Conclusion
Reflecting on George Washington Carver's life and work provides a valuable lens through which to examine the intersection of science, social justice, and personal resilience. From his humble beginnings as an enslaved man in Missouri to his pioneering research at Tuskegee University, Carver's journey epitomizes the triumph of human potential over adversity. His legacy stands as a enduring testament to the transformative power of innovative thinking, sustainable practices, and a profound commitment to improving the lives of others.
Critical Assessments and Legacy
While George Washington Carver's contributions have been celebrated for decades, recent historical assessments have provided a more nuanced view of his impact. Scholars have scrutinized his role within the broader context of racial politics and the Jim Crow era. Some argue that despite his progressive ideas, Carver's position within the Tuskegee Institute and its relationship with the White House during the presidency of Woodrow Wilson were complex and often conflicted.
During the period of Wilson's presidency, Tuskegee University received increased funding from the federal government. However, Carver found himself in a precarious position. On one hand, he was praised for his scientific achievements and brought national recognition to the university. On the other hand, his relationship with the Wilson administration was strained due to the segregationist policies of the White House. Scholars suggest that Carver's silence on racial issues may have been strategic, a form of survival in a system that often relegated African Americans to second-class citizenship.
Contemporary Perspectives
Contemporary historians and writers continue to explore different facets of Carver's life and work. For instance, authors like John A. Hall and Jean Soderlund have delved into his private life, uncovering stories that challenge the traditional narrative. They reveal the complexities of his personal relationships and the social dynamics of his interactions with both white and African American peers.
Cultural depictions of Carver have also evolved. While early portrayals often idealized him as a saintly figure, more recent media representations, such as the children's book "George Washington Carver and the Miracle Plant" and the PBS documentary "American Experience: George Washington Carver," offer a balanced view of his life and the challenges he faced. These narratives highlight his humanity and multifaceted character, recognizing both his accomplishments and limitations.
Interdisciplinary Influence
The interdisciplinary nature of Carver's work has prompted ongoing scholarly inquiry into the relationship between science, art, and social activism. His artistic inclinations and practical inventions demonstrate a seamless blend of creativity and purpose. Researchers in fields such as environmental history and cultural studies continue to analyze Carver's legacy through a variety of lenses, revealing the broad impact of his multidisciplinary approach.
Environmental historians have lauded Carver's emphasis on sustainable agriculture and renewable resources. His work on utilizing waste products and developing alternative crops aligns with contemporary concerns about climate change and resource depletion. In this sense, Carver's legacy is not just historical but a model for modern sustainability efforts.
Modern Relevance: Sustainable Practices
Carver's innovative approaches to agriculture continue to inform modern practices. Contemporary farmers and researchers draw upon his methods for crop rotation, integrated pest management, and soil conservation. His work on developing non-toxic weed killers and natural fertilizers remains pertinent in today's world. Moreover, the concept of "biochar," derived from the technique of using burned organic matter to enrich soils, has roots in Carver's research on wood ash application.
The ongoing relevance of Carver's research is evident in the way his innovations are being adapted to address current environmental challenges. For example, the development of biofuels and advancements in sustainable food systems are areas where Carver's legacy continues to inspire new generations of scientists and policymakers.
Cultural Impact beyond Agriculture
Beyond agriculture, Carver has had a profound cultural impact. His image and story have been incorporated into popular culture, from educational materials to advertisements and public service announcements. The Peanut Butter Company, for instance, prominently features Carver's likeness on their products, celebrating his contributions to the peanut industry.
Cultural festivals and commemorative events, such as the George Washington Carver Celebration held annually at Tuskegee University, keep his memory alive. These events serve not only as tributes to his scientific achievements but also as platforms for discussions on identity, heritage, and progress.
Educational Initiatives
Carver's educational philosophies and methods have influenced contemporary educational practices. Many schools and universities incorporate Carver into their curricula, using his life story as a means to engage students in discussions about perseverance, diversity, and inclusivity. Programs like the George Washington Carver High School in Houston, which focuses on STEM education, exemplify how Carver's legacy continues to inspire future leaders.
The George Washington Carver Museum and National Historic Site at the Tuskegee University also offers educational resources and workshops that encourage hands-on learning and community engagement. These initiatives contribute to the wider goal of promoting equitable access to education and resources.
The Unfinished Legacy
While much has been accomplished since Carver's time, his unfinished legacy suggests ongoing areas of need and potential for future action. Modern challenges such as food insecurity, environmental degradation, and economic inequality continue to require innovative solutions similar to those pioneered by Carver. His emphasis on sustainable and holistic approaches provides a framework for addressing these contemporary issues.
Advancements in biotechnology, genetic engineering, and precision agriculture offer new possibilities for realizing Carver's vision. Young researchers and entrepreneurs are increasingly turning to his work for inspiration, drawing on his pioneering spirit to tackle global challenges. Through these modern interpretations, Carver's legacy continues to evolve and inspire new generations to make a positive impact.
In conclusion, George Washington Carver's life and work remain a powerful symbol of innovation, perseverance, and social conscience. His scientific achievements, combined with his educational and social activism, have left an indelible mark on American history. As we reflect on his legacy, we are reminded of the importance of addressing the complex interplay between individual potential and systemic barriers. By continuing to learn from Carver's example, we can strive to build a more equitable and sustainable world.
Despite the challenges and controversies that surround his legacy, George Washington Carver's contributions to science, agriculture, and humanity endure. His life story is a testament to the power of determination, creativity, and communal responsibility, inspiring us to look beyond our own circumstances and seek ways to make a difference.
Kary Mullis and the PCR Revolution in DNA Analysis
Kary Mullis, the American biochemist, is renowned for fundamentally transforming molecular biology. His invention, the polymerase chain reaction (PCR), became one of the most significant scientific techniques of the 20th century. This article explores the life, genius, and controversies of the Nobel laureate who gave science the power to amplify DNA.
Who Was Kary Mullis?
Kary Banks Mullis was born on December 28, 1944, in Lenoir, North Carolina. He died at age 74 on August 7, 2019, in Newport Beach, California. Best known as the architect of PCR, Mullis was a brilliant yet unconventional figure.
His work earned him the 1993 Nobel Prize in Chemistry, which he shared with Michael Smith. Beyond his monumental scientific contribution, Mullis’s life was marked by eccentric personal pursuits and controversial views that often placed him at odds with the scientific mainstream.
Early Life and Academic Foundation
Mullis’s journey into science began with foundational education in chemistry. He earned his Bachelor of Science in Chemistry from the Georgia Institute of Technology in 1966. This undergraduate work provided the critical base for his future research.
He then pursued a Ph.D. in biochemistry at the University of California, Berkeley. Mullis completed his doctorate in 1972 under Professor J.B. Neilands. His doctoral research focused on the structure and synthesis of microbial iron transport molecules.
An Unconventional Career Path
After earning his Ph.D., Kary Mullis took a highly unusual detour from science. He left the research world to pursue fiction writing. During this period, he even spent time working in a bakery, a stark contrast to his future in a biotechnology lab.
This hiatus lasted roughly two years. Mullis eventually returned to scientific work, bringing with him a uniquely creative and unorthodox perspective. His non-linear path highlights the unpredictable nature of scientific discovery and genius.
The Invention of the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
The polymerase chain reaction invention is a landmark event in modern science. Mullis conceived the technique in 1983 while working as a DNA chemist at Cetus Corporation, a pioneering California biotechnology firm. His role involved synthesizing oligonucleotides, the short DNA strands crucial for the process.
The iconic moment of inspiration came not in a lab, but on a night drive. Mullis was traveling to a cabin in northern California with colleague Jennifer Barnett. He later recounted that the concept of PCR crystallized in his mind during that spring drive, a flash of insight that would change science forever.
PCR allows a specific stretch of DNA to be copied billions of times in just a few hours.
How Does PCR Work? The Basic Principle
The PCR technique is elegantly simple in concept yet powerful in application. It mimics the natural process of DNA replication but in a controlled, exponential manner. The core mechanism relies on thermal cycling and a special enzyme.
The process involves three key temperature-dependent steps repeated in cycles:
- Denaturation: High heat (around 95°C) separates the double-stranded DNA into two single strands.
- Annealing: The temperature is lowered to allow short DNA primers to bind to complementary sequences on each single strand.
- Extension: The temperature is raised to an optimal level for a heat-stable DNA polymerase enzyme to synthesize new DNA strands by adding nucleotides.
Each cycle doubles the amount of target DNA. After 30 cycles, this results in over a billion copies, enabling detailed analysis of even the smallest genetic sample.
Initial Scientific Rejection and Eventual Publication
Despite its revolutionary potential, Mullis’s PCR concept initially faced significant skepticism from the scientific establishment. His original manuscript detailing the method was rejected by two of the world’s most prestigious journals.
- The journal Nature declined to publish it in 1985, suggesting it might be better for a more specialized publication.
- Science magazine rejected it just one month later, stating the paper could not compete for their limited space.
The groundbreaking work was finally published in the journal Methods in Enzymology. This early rejection is a classic example of how transformative ideas can struggle for acceptance before their immense value is universally recognized.
The Immense Impact and Applications of PCR
The impact of PCR is nearly impossible to overstate. It became an indispensable tool across a vast spectrum of fields almost overnight. The technique’s ability to amplify specific DNA sequences with high fidelity and speed opened new frontiers.
It fundamentally changed the scale and speed of genetic research. Experiments that once took weeks or required large amounts of biological material could now be completed in hours with minute samples.
Revolutionizing Medical Research and Diagnostics
In medical diagnostics, PCR became a game-changer. It enabled the rapid detection of pathogenic bacteria and viruses long before traditional culture methods could. This speed is critical for effective treatment and containment of infectious diseases.
The technique is central to genetic testing for hereditary conditions. It allows clinicians to identify specific mutations with precision, facilitating early diagnosis and personalized medicine strategies for countless patients worldwide.
Transforming Forensic Science and Criminal Justice
Forensic science was revolutionized by the advent of PCR. The method allows crime labs to generate analyzable DNA profiles from extremely small or degraded biological evidence. This includes traces like a single hair follicle, a tiny spot of blood, or skin cells.
This capability has made DNA evidence a cornerstone of modern criminal investigations. It has been instrumental in both convicting the guilty and exonerating the wrongly accused, dramatically increasing the accuracy of the justice system.
Enabling Major Breakthroughs in Genetics
PCR was the catalyst for the monumental Human Genome Project. The project, which mapped the entire human genetic code, relied heavily on PCR to amplify DNA segments for sequencing. This would have been technologically and economically infeasible without Mullis’s invention.
In basic genetic research, PCR allows scientists to clone genes, study gene expression, and investigate genetic variation. It remains the foundational technique in virtually every molecular biology laboratory on the planet.
Back from the Bakery: Joining Cetus Corporation and the Road to PCR
After his departure from science, Kary Mullis rejoined the scientific community with renewed perspective. In 1979, he secured a position as a DNA chemist at Cetus Corporation in Emeryville, California. This biotech company was a hotbed of innovation, focusing on pharmaceutical products and recombinant DNA technology.
His primary role involved the chemical synthesis of oligonucleotides, short strands of DNA. These custom-built DNA fragments were essential tools for other scientists at Cetus. Synthesizing them was a tedious, manual process, requiring meticulous attention to detail.
This hands-on work with the fundamental building blocks of genetics proved crucial. It gave Mullis an intimate, practical understanding of DNA chemistry. This foundational knowledge was the perfect precursor to his revolutionary insight into DNA amplification.
The Eureka Moment: A Drive Through the Mountains
The story of PCR's conception has become legendary in scientific lore. In the spring of 1983, Mullis was driving to a cabin he was building in Mendocino County with his colleague, Jennifer Barnett. The California buckeyes were in bloom, scenting the night air.
As he navigated the winding roads, his mind was working on a problem. He was trying to find a better way to detect point mutations in DNA, a task that was notoriously difficult with existing methods. Suddenly, the complete concept for the polymerase chain reaction unfolded in his mind.
He later described visualizing the process: the double helix splitting, primers binding, and the enzyme building new strands, all happening repeatedly in a test tube.
Mullis pulled over to jot down notes and run calculations. He realized that the process could be exponential. A single DNA molecule could be amplified to billions of copies in just a few hours. This was the birth of a methodology that would redefine genetic engineering.
The Critical Role of Thermostable Enzymes
An initial challenge with PCR was the enzyme. Early experiments used the E. coli DNA polymerase, which was heat-sensitive. Since the first step of each PCR cycle required high heat to denature the DNA, the enzyme would be destroyed after the first cycle.
This meant scientists had to manually add fresh enzyme after each heating step, making the process impractical. The breakthrough came with the adoption of Taq polymerase, an enzyme isolated from the heat-loving bacterium Thermus aquaticus found in hot springs.
- Taq polymerase is thermostable, surviving the high temperatures of the denaturation step.
- This allowed the entire PCR process to be automated in a thermal cycler machine.
- The automation of PCR was the final piece that turned a brilliant concept into a practical, world-changing tool.
Achieving the Peak: The 1993 Nobel Prize in Chemistry
The significance of Kary Mullis's invention was formally recognized a decade after its conception. In 1993, the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences awarded him the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. He shared the prestigious award with Michael Smith, who was honored for his work on site-directed mutagenesis.
The Nobel committee stated that PCR "has already had a decisive influence on research in basic biology, medicine, biotechnology, and forensic science." This acknowledgment cemented PCR's status as one of the most important scientific techniques ever developed.
Mullis's Nobel lecture, titled "The Polymerase Chain Reaction," detailed the method's conception and its profound implications. The prize brought him international fame and solidified his legacy within the scientific community, despite his later controversial stances.
The Significance of the Nobel Recognition
Winning a Nobel Prize is the pinnacle of scientific achievement. For Mullis, it validated his unconventional thought process and the power of a simple, elegant idea. The prize highlighted how a fundamental methodological advance could have a broader impact than a specific discovery.
The recognition also underscored the growing importance of biotechnology. PCR was a tool that originated in a biotech company, Cetus, demonstrating how industry research could drive fundamental scientific progress. The award brought immense prestige to the fledgling biotech sector.
Controversies Surrounding the Prize
As with many monumental discoveries, the Nobel Prize for PCR was not without controversy. Some scientists at Cetus argued that the invention was a collective effort. They felt that colleagues who helped refine and prove the method's utility were not adequately recognized.
Mullis, however, was always credited as the sole inventor of the core concept. The Nobel committee's decision affirmed that the initial flash of insight was his alone. The debates highlight the complex nature of attributing credit in collaborative research environments.
Kary Mullis's Controversial Views and Public Persona
Beyond his scientific genius, Kary Mullis was a deeply complex and controversial figure. He held strong, often contrarian, opinions on a range of scientific and social issues. These views frequently placed him in direct opposition to the mainstream scientific consensus.
Mullis was famously outspoken and relished his role as a scientific maverick. His autobiography, Dancing Naked in the Mind Field (1997), openly detailed his unconventional lifestyle and beliefs. This included his experiences with psychedelics, his skepticism of authority, and his rejection of established theories.
His provocative stance made him a polarizing character. While revered for PCR, he was often criticized for promoting ideas considered fringe or dangerous by the majority of his peers. This duality defines his legacy as both a brilliant innovator and a contentious voice.
Denial of the HIV-AIDS Link
One of Mullis's most prominent and damaging controversies was his rejection of the established fact that HIV causes AIDS. He became a vocal adherent of the fringe movement that denied this link, a position thoroughly debunked by decades of overwhelming scientific evidence.
Mullis argued that the correlation between HIV and AIDS was not sufficient proof of causation. His background in chemistry led him to demand what he considered a higher standard of proof, which he felt was lacking. This stance alarmed and frustrated the global public health community.
- His position was used by denialist groups to lend false credibility to their claims.
- Public health experts warned that his statements could undermine HIV prevention and treatment efforts.
- This controversy significantly tarnished his reputation among many scientists and medical professionals.
Skepticism of Climate Change and the Ozone Hole
Mullis also expressed deep skepticism about human-induced climate change. He questioned the scientific consensus on global warming, often framing it as a form of political dogma rather than evidence-based science. Similarly, he doubted the science behind the anthropogenic causes of the ozone hole.
His criticisms were not based on new climate research but on a general distrust of large scientific institutions and political motives. He positioned himself as a defender of free thought against what he perceived as groupthink. This further isolated him from the mainstream scientific establishment.
The Influence of Psychedelic Experiences
Mullis was remarkably open about his use of lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) during his graduate studies at Berkeley and beyond. He did not view this as illicit drug use but as a meaningful intellectual and exploratory pursuit.
He directly credited his psychedelic experiences with broadening his consciousness and enhancing his creativity. Mullis claimed that his mind was opened to the non-linear thinking that led to the PCR breakthrough. He described vivid, conceptual visions that helped him visualize complex molecular processes.
"Would I have invented PCR if I hadn't taken LSD? I seriously doubt it," Mullis stated in a 1994 interview.
While this connection is anecdotal, it underscores his belief that unconventional paths could lead to profound scientific discoveries. It remains a fascinating aspect of his unique intellectual journey.
Life After Cetus: Later Career and Entrepreneurial Ventures
After the monumental success of PCR at Cetus, Kary Mullis’s career took several turns. He left the company in the fall of 1986, not long after his method began to gain widespread attention. His departure marked the beginning of a varied and entrepreneurial phase of his professional life.
Mullis briefly served as the Director of Molecular Biology at Xytronyx, Inc. in San Diego in 1986. Following this, he embraced the role of a consultant for multiple corporations. His expertise was sought by major companies including Angenics, Cytometrics, Eastman Kodak, and Abbott Laboratories.
This consultancy work allowed him to apply his unique biochemical insights across different industries. He was not confined to academia or a single corporate lab, preferring the freedom to explore diverse scientific and business challenges.
Founding Altermune and the Quest for Novel Therapies
One of Mullis's significant later ventures was founding a company named Altermune. The name was derived from "altering the immune system." The company's goal was to develop a novel class of therapeutics based on a concept Mullis called chemically programmed immunity.
The Altermune approach aimed to create molecules that could redirect the body’s existing immune defenses to new targets. Mullis envisioned using aptamers (small nucleic acid molecules) to guide antibodies to pathogens or diseased cells. This innovative idea, while scientifically intriguing, never progressed to a widely commercialized therapy.
Altermune represented Mullis's continued drive for disruptive innovation. It showcased his ability to think beyond PCR and tackle complex problems in immunology and drug development, even if the practical outcomes were limited.
The Enduring Legacy of the Polymerase Chain Reaction
The true measure of Kary Mullis’s impact lies in the pervasive, ongoing use of his invention. Decades after its conception, PCR remains a foundational technique in thousands of laboratories worldwide. Its applications have only expanded and diversified over time.
PCR's influence extends far beyond basic research. It has become a critical tool in clinical diagnostics, forensic laboratories, agricultural biotechnology, and environmental monitoring. The method's core principle has spawned numerous advanced variations and next-generation technologies.
- Real-time PCR (qPCR) allows scientists to quantify DNA in real-time, enabling precise measurement of gene expression.
- Reverse Transcription PCR (RT-PCR) converts RNA into DNA, making it essential for studying RNA viruses and gene activity.
- Digital PCR provides absolute quantification of DNA molecules, offering unparalleled sensitivity for detecting rare genetic variants.
PCR's Role in the COVID-19 Pandemic
The global COVID-19 pandemic provided a stark, real-world demonstration of PCR's indispensable value. The standard diagnostic test for detecting SARS-CoV-2 infection was, and remains, a form of RT-PCR. This test amplified viral RNA from patient swabs to detectable levels.
Without PCR technology, mass testing and surveillance during the pandemic would have been scientifically impossible. The ability to process millions of samples rapidly was directly built upon Mullis's 1983 insight. This global event highlighted how a fundamental research tool could become a central pillar of public health infrastructure.
The pandemic underscored that PCR is not just a lab technique but a critical component of modern global health security.
The Commercial and Economic Impact of PCR
The invention of PCR sparked the creation of a multi-billion dollar industry. Companies specializing in thermal cyclers, reagents, enzymes, and diagnostic kits grew rapidly. The technique created vast economic value in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical sectors.
Cetus Corporation, where Mullis worked, eventually sold the PCR patent portfolio to Hoffmann-La Roche for $300 million in 1991. This landmark deal highlighted the immense commercial potential of the technology. Today, the global PCR market continues to expand, driven by advancements in personalized medicine and point-of-care testing.
Kary Mullis: A Complicated Legacy in Science
Kary Mullis's legacy is a study in contrasts. He is universally hailed as the brilliant inventor of one of history's most important scientific methods. Yet, he is also remembered as a controversial figure who publicly rejected well-established science on issues like HIV and climate change.
This duality makes him a fascinating subject for historians of science. It raises questions about the relationship between scientific genius and scientific consensus. Mullis proved that a single individual with a transformative idea could change the world, yet he also demonstrated that expertise in one field does not confer authority in all others.
A Polarizing Figure Remembered
In the scientific community, discussions about Mullis often separate his unequivocal contribution from his controversial personal views. Most scientists celebrate PCR while distancing themselves from his denialist stances. His death in 2019 prompted reflections on this complex legacy.
Obituaries in major publications grappled with how to honor the inventor while acknowledging the provocateur. They credited his monumental achievement but did not shy away from detailing his fringe beliefs. This balanced remembrance reflects the nuanced reality of his life and career.
The Future Built on PCR Technology
The future of biotechnology and medicine is deeply intertwined with the ongoing evolution of PCR. Next-generation sequencing, the cornerstone of genomic medicine
Point-of-care and portable PCR devices are bringing DNA analysis out of central labs and into field clinics, airports, and even homes. The drive for faster, cheaper, and more accessible nucleic acid testing ensures that Mullis’s invention will remain at the forefront of scientific and medical progress for decades to come.
New applications continue to emerge in areas like liquid biopsy for cancer detection, non-invasive prenatal testing, and monitoring of infectious disease outbreaks. The core principle of amplifying specific DNA sequences remains as powerful and relevant today as it was in 1983.
Awards and Honors Beyond the Nobel Prize
While the Nobel Prize was his most famous honor, Kary Mullis received numerous other accolades for his work on PCR. These awards recognized the transformative power of his invention across different domains.
- He received the Japan Prize in 1993, the same year as his Nobel.
- He was awarded the R&D Scientist of the Year award in 1991.
- Mullis also received the National Biotechnology Award and the Gairdner Foundation International Award.
- He was inducted into the National Inventors Hall of Fame in 1997.
Conclusion: The Eccentric Genius Who Changed the World
Kary Mullis's story is one of unconventional brilliance. From his detour into fiction writing and bakery work to his psychedelic-inspired eureka moment on a California highway, his path was anything but ordinary. Yet, his singular idea, the polymerase chain reaction, created a before-and-after moment in the history of biology.
PCR democratized access to the genetic code. It turned DNA from a molecule that was difficult to study in detail into one that could be copied, analyzed, and manipulated with ease. The technique accelerated the pace of biological discovery at a rate few inventions ever have.
The legacy of Kary Mullis is thus permanently etched into the fabric of modern science. Every time a pathogen is identified, a genetic disease is diagnosed, a criminal is caught through DNA evidence, or a new gene is sequenced, his invention is at work. The undeniable utility and omnipresence of PCR secure his place as one of the most influential scientists of the modern era, regardless of the controversies that surrounded him.
In the end, Kary Mullis exemplified how a simple, elegant concept can have an exponentially greater impact than its originator might ever imagine. His life reminds us that scientific progress can spring from the most unexpected minds and moments, forever altering our understanding of life itself.
In conclusion, Kary Mullis's invention of PCR revolutionized molecular biology, leaving an indelible mark on science despite his unconventional life and views. His legacy compels us to consider how profound innovation can arise from the most unexpected individuals. Reflect on how a single idea can amplify its impact across countless fields, from medicine to forensics.



Ho Chi Minh City: A Gateway to Modern Vietnam
Ho Chi Minh City, formerly known as Saigon, is Vietnam's largest city and economic powerhouse, renowned not only for its vibrant culture, bustling streets, and rich history but also as a bustling metropolis that seamlessly blends tradition with modernity. Nestled along the banks of the Saigon River in South Vietnam, the city has grown exponentially over the past few decades, evolving from a colonial-era trading post into a cosmopolitan center that attracts millions of visitors each year.
A Historical Overview
The story of Ho Chi Minh City dates back to the founding of a small fishing village called Gia Luc by people from Guangdong Province in China. Over time, this settlement grew into a trading port under the control of the Nguyen Dynasty. In the early 18th century, the port was renamed Phuoc Long by King Gia Long, who saw its strategic importance. It was not until 1833 that it received its current name, Saigon, under French colonial rule.
The Colonial Era
The French arrived in 1859 and soon established Saigon as their major administrative and commercial hub in Indochina. They modernized the city, constructing grand boulevards, imposing colonial architecture, and establishing a strong administrative infrastructure. The Notre-Dame Cathedral Basilica of Saigon, built in 1880, remains a testament to this era, standing as a symbol of both the French occupation and the city's past grandeur.
The Partition and War Years
In the mid-20th century, Saigon became a focal point in the larger context of the Vietnam War. It served as the capital city of South Vietnam until the fall of Saigon to communist forces in April 1975. Following the reunification of Vietnam under communist rule in 1976, the city adopted its current name, Ho Chi Minh City, in honor of the nation’s founder and revolutionary leader.
The City's Transformation
Despite a tumultuous period marked by political upheaval and economic challenges, Ho Chi Minh City underwent significant transformation in the late 20th and early 21st centuries. Post-reunification, the Vietnamese government initiated economic reforms, which spurred rapid growth and development. Today, Ho Chi Minh City is recognized as a global financial center and a hub for technology, entertainment, and education.
The Urban Landscape and Architecture
Ho Chi Minh City is a melting pot of architectural styles, from traditional Vietnamese influences to Western colonial aesthetics and contemporary skyscrapers. The city's urban landscape is characterized by high-rise buildings, modern shopping centers, and vibrant street life.
Notable Sites and Attractions
One of the most iconic attractions in Ho Chi Minh City is the Notre-Dame Cathedral Basilica. This Roman Catholic cathedral, with its intricate French Gothic design and towering spires, is a popular spot for tourists and locals alike. Its ornate facade and elegant interior offer a fascinating glimpse into the city's colonial past.
Adjacent to the cathedral is the Cu Chi Tunnels, a network of underground tunnels used by the Viet Cong during the Vietnam War. Visitors can explore these tunnels, learning about the strategic and tactical importance they held during the conflict.
Modern Developments and Infrastructure
Ho Chi Minh City boasts a well-developed transportation infrastructure, including an expansive network of roads, highways, and a growing subway system. The Saigon Light Rail, which opened in 2015, connects major areas of the city, providing efficient public transport. The city is also home to several world-class hotels, numerous dining options catering to various tastes, and a variety of shopping malls and markets.
Architecturally, the city stands out with structures like the Bitexco Finance Tower (also known as the Landmark 81), the tallest building in Vietnam, which offers panoramic views of the city from its observation deck. Other landmarks include the Ben Thanh Market, a bustling hub of local commerce, and the Central Post Office, known for its grand neo-Renaissance design.
However, amidst the modern skyline, visitors can still find traditional elements. The Old District, or Cu Chi Ward, retains much of its traditional charm and offers a slice of Vietnamese life. Narrow streets lined with shops selling everything from textiles to antiques provide a tangible connection to the city's cultural heritage.
Culture and Traditions
The cultural fabric of Ho Chi Minh City is rich and diverse, reflecting the complex history and varied influences that have shaped the region over the centuries. The city's inhabitants are a vibrant mix of ethnicities, including Vietnamese, Chinese, Khmer, and Hmong, contributing to a unique cultural tapestry.
Festivals and Religious Celebrations
Throughout the year, Ho Chi Minh City hosts a plethora of festivals celebrating various aspects of Vietnamese culture. The Mid-Autumn Festival, or Tet Trung Thu, is particularly exciting, with families gathering to enjoy lanterns, moon cakes, and performances. Another significant event is the Water Festival (Tet Nguyen Dan), marking the lunar new year, where vibrant parades and fireworks illuminate the city.
Religious practices are deeply rooted in daily life, and the city is dotted with temples, mosques, and churches. Wat Cham Tao Dua Buddhist Temple, one of the largest and most prominent Buddhist temples in the city, exemplifies the spiritual significance of religious sites. These places of worship not only serve a religious function but also play a crucial role in community life and cultural traditions.
Cuisine and Lifestyle
Ho Chi Minh City is a food lover's paradise, offering a mouthwatering array of dishes that reflect the diversity of Vietnamese cuisine. Street food is integral to the city's culinary scene, with vendors serving up everything from fresh spring rolls to spicy pho. Famous restaurants and cafes dot the city, showcasing regional specialties and innovative fusion dishes.
The city's lifestyle is fast-paced yet warm and welcoming. The social life of Ho Chi Minh City is invigorated by bustling parks and open spaces such as Dong Khoi Street, where people gather to chat, exercise, and enjoy the outdoors. Parks like Ho Chi Minh City Park and Ben Thuy are particularly popular among locals and visitors alike.
Entertainment in Ho Chi Minh City extends beyond the culinary experience. Nightclubs, live music venues, and art galleries cater to a wide range of tastes, making the city a hub of vibrant nightlife and creative expression. Museums such as the War Remnants Museum and the Fine Arts Museum of Ho Chi Minh City provide insight into both the historical and contemporary life of the city.
Sustainability and Future Outlook
As one of the fastest-growing cities in Southeast Asia, Ho Chi Minh City faces significant challenges related to sustainable development. Efforts to address environmental concerns, enhance public transportation, and promote green technologies are at the forefront of the city's efforts to maintain its rapid pace of urbanization.
Green Initiatives and Sustainability
The city has implemented several initiatives aimed at promoting environmental sustainability. These include waste management programs, such as the recycling of electronic waste and plastic bottles, and the expansion of public green spaces. The construction of eco-friendly buildings and the promotion of renewable energy sources are further steps towards achieving a more sustainable future.
Urban Planning and Infrastructure
Urban planners in Ho Chi Minh City are working towards creating a more livable and sustainable environment by implementing efficient public transport systems and improving pedestrian pathways. The city's Master Plan 2030 aims to balance growth with urban planning, ensuring that the expansion of the city does not come at the expense of its natural surroundings.
Investment in smart city technologies is also part of the city's forward-thinking approach. Digitization and the integration of advanced information and communication technologies are enhancing governance and services, contributing to smarter urban management.
Beyond the Surface: Ho Chi Minh City's Cultural Depth
Beneath its modern exterior lies a rich cultural heritage that has been preserved and celebrated through various forms of art, literature, and tradition. The city's museums, galleries, and cultural institutions play a crucial role in keeping alive the stories and legacies of generations past.
Museums and Art Galleries
The Ho Chi Minh City Museum, opened in the early 20th century, offers an in-depth look at the city's history and its pivotal role in the Vietnam War. Its exhibits include artifacts, documents, and multimedia presentations that provide context and understanding. Similarly, the Ben Thanh Market's museum serves as a window into the lives of everyday people, showcasing local crafts, textiles, and traditional practices.
Art galleries around the city feature works by both local artists and international creatives, ranging from traditional Vietnamese paintings to modern installations. Institutions like the Ben Thuy Gallery and the HCMC Gallery of Contemporary Art showcase the vibrant artistic scene and contribute to the city's cultural identity.
Literature and Performing Arts
Literature has played a significant role in fostering a sense of collective identity and storytelling in Ho Chi Minh City. Books such as "The Boat People" and "Saigon: City of Contrasts," penned by authors like Nguyen Hong Duc and Le Ngoc Quynh, give readers a deeper understanding of the city's turbulent history and evolving cultural landscape. Libraries and bookstores, including the National Library of Vietnam, are centers of literary activity, hosting readings, workshops, and cultural events.
Performing arts continue to thrive in Ho Chi Minh City, with theaters like the Saigon Opera House and the People's Theatre of Ho Chi Minh City presenting a diverse array of productions. Traditional performances such as water puppetry and lion dances are often featured, complemented by contemporary productions that push the boundaries of creativity and innovation.
A Conclusion
Ho Chi Minh City is not just a metropolis in terms of its physical scale and economic importance; it is a dynamic living space that reflects the rich tapestry of its diverse inhabitants and their histories. From its storied past under colonial rule to its present-day transformation into a modern urban center, the city continues to evolve while maintaining a profound connection to its roots.
As a gateway to modern Vietnam, Ho Chi Minh City offers travelers and residents alike a unique blend of old-world charm and cutting-edge innovation. Whether exploring its historical sites, savoring its cuisine, or engaging with its vibrant cultural scene, one cannot help but be captivated by the dynamic narrative of Ho Chi Minh City.
Education and Research
Education plays a crucial role in shaping Ho Chi Minh City's future as a knowledge hub. The city is home to some of Vietnam's leading universities and research institutions. The University of Social Sciences and Humanities, one of Vietnam's oldest institutions, provides quality education across various disciplines, including law, sociology, and humanities. Additionally, the International University of Ho Chi Minh City and HCMC University of Technology and Education attract both national and international students eager to pursue higher education.
Research and Innovation
Research institutions like the International Institute for Management Development and the Centre for Natural Sciences Studies contribute significantly to the city's research and innovation ecosystem. These organizations collaborate with multinational companies, startups, and academic institutions to foster cutting-edge advancements in fields such as biotechnology, artificial intelligence, and renewable energy. Hackathons, startup incubators, and co-working spaces are flourishing in areas like Ben Thanh Market and Tan Binh District, encouraging entrepreneurship and innovation.
Healthcare
Ho Chi Minh City boasts a well-developed healthcare system, with top hospitals like Bach Mai Hospital, Vietnam Fatherland Front Children’s Hospital No.1, and Chợ Lớn Hospital providing comprehensive medical services. These hospitals are equipped with state-of-the-art facilities and internationally trained medical professionals, ensuring high standards of care. The city is also a hub for medical tourism, attracting visitors seeking specialized treatments and advanced medical procedures.
Sports and Recreation
Sports and recreation activities are essential aspects of Ho Chi Minh City's lifestyle. Football remains the most popular sport, with numerous clubs and professional leagues attracting both fans and players. The city has several large stadiums, including the Ho Chi Minh City Stadium and Nguyen Van Linh Stadium, hosting matches and sporting events throughout the year. These venues also serve as gathering spots for various sports enthusiasts.
Cycling and Outdoor Activities
Cycling is a favored form of transportation and recreation in Ho Chi Minh City. The city's bicycle rental services, such as Bike Tour Saigon, offer cyclists the opportunity to explore the city on two wheels. Popular cycling routes include the riverfront promenade and the scenic paths near Tan Tan Lake. Additionally, outdoor activities like hiking and mountain biking in nearby provinces, such as Long An and Bac Giang, provide opportunities for adventure and relaxation.
The city also features numerous parks and green spaces, making it ideal for picnics, leisure activities, and family outings. Some notable parks include the Central Park, Ben Thuy Park, and Nam Dai Park. These spaces are bEautifully landscaped and host regular events and cultural performances, enriching the city's recreational landscape.
Entertainment Venues
Nightlife in Ho Chi Minh City is diverse and lively. From rooftop bars offering stunning city views to karaoke lounges and rooftop cinemas, there is something for every taste. The Saigon Rendezvous, Vincom, and Grand World Mall are popular destinations for shopping, dining, and entertainment. Live music venues like Café Broadway and jazz clubs such as Club Café offer a chance to experience the city's vibrant musical scene.
The city's nightlife also includes a thriving bar scene, with establishments such as Bar Montparnasse, Cafe Continental, and Café Babylon known for their eclectic atmospheres and impressive cocktail lists. Many of these venues also serve as meeting points for cultural and educational events, further enriching the city's nightlife experience.
Economic Impact and Future Prospects
Economically, Ho Chi Minh City is a powerhouse, driving the growth and development of Vietnam's entire southern region. The city is a hub for industry, finance, and technology, with key economic sectors including manufacturing, retail, banking, and real estate. Major multinational corporations and local businesses have headquarters here, contributing significantly to job creation and economic stability.
Real Estate and Development
The real estate market in Ho Chi Minh City has seen remarkable growth, fueled by both residential and commercial development. High-rise apartment complexes, modern office buildings, and mixed-use developments are transforming the city's skyline. Neighborhoods like Ben Thanh, Cho Lon, and Pham Ngu Lao retain their historic charm while undergoing gentrification, catering to the demands of a modern lifestyle while preserving cultural heritage.
Real estate investments drive urban development, attracting both domestic and international buyers. The city's robust property market ensures steady growth and creates opportunities for both residents and investors. However, rising property prices also present challenges, contributing to debates around affordability and urban planning policies.
Finance and Industry
The financial sector in Ho Chi Minh City is flourishing, with the presence of major banks, stock exchanges, and investment firms. The Securities Trading Center, part of the Vietnam Stock Exchange, is a critical platform for capital markets. Additionally, industries such as textiles, electronics, and automotive manufacturing have strong footholds in the region, driven by both local and foreign investments.
The city's industrial parks, such as Hoa Binh New City and Thu Thiem Industrial Estate, provide modern facilities and support for manufacturers. These developments ensure a continuous supply chain and facilitate technological advancement. The city's commitment to infrastructure projects, including the construction of new roads and bridges, further supports industrial growth and enhances connectivity within and outside the city.
Challenges and Opportunities
While Ho Chi Minh City has made tremendous strides, it faces several challenges that require attention and strategic planning. Rapid urbanization, environmental issues, and socio-economic disparities are among the key concerns.
Urban Sprawl and Environmental Issues
The city's rapid expansion has led to concerns about environmental degradation and loss of green spaces. Air pollution and traffic congestion are significant challenges, necessitating sustainable urban planning strategies. Government initiatives aim to address这些问题,包括推进公共交通系统的发展、建设更多的自行车道和人行道,以及鼓励使用清洁能源和实施垃圾分类政策。
尽管面临挑战,Ho Chi Minh City依然以其快速发展的潜力和对未来的承诺而充满活力。市政府和社区继续致力于实现可持续发展,提高市民生活质量。
未来,Ho Chi Minh City有望进一步吸引国内外的投资和游客。市政府将继续促进教育、研究、文化、旅游业的发展,同时努力解决经济和社会问题,确保所有居民都能从中受益。
总之,Ho Chi Minh City是一座充满活力的城市,它在不断变化的历史背景下塑造了自己的独特面貌。无论是对于寻求冒险和刺激的游客,还是需要商务或文化交流的企业家来说,这座城市的魅力都难以抗拒。
Challenges and Opportunities
While Ho Chi Minh City has made tremendous strides, it faces several challenges that require attention and strategic planning. Rapid urbanization, environmental issues, and socio-economic disparities are among the key concerns.
Urban Sprawl and Environmental Issues
The city's rapid expansion has led to concerns about environmental degradation and loss of green spaces. Air pollution and traffic congestion are significant challenges, necessitating sustainable urban planning strategies. Government initiatives aim to address these issues through the development of public transport systems, construction of more bike lanes and pedestrian walkways, and the promotion of clean energy sources and waste classification policies.
One of the most pressing environmental challenges is the management of solid waste. Ho Chi Minh City generates approximately 4,000 tons of waste daily, leading to issues of landfill space and waste management. The government has implemented waste recycling programs and composting initiatives, but these efforts need to be bolstered to meet the growing demands of the city's population.
The Saigon River, a major waterway that runs through the heart of the city, faces pollution due to industrial and domestic waste. The government is working on improving water treatment facilities and launching awareness campaigns to encourage better waste disposal practices. Additionally, efforts are underway to green the city, with the planting of trees and the development of more parks and public spaces.
Socio-Economic Disparities
Ho Chi Minh City also grapples with socioeconomic disparities, which are particularly evident in certain neighborhoods. The influx of migrants from rural areas seeking better economic opportunities has created a mixed socioeconomic landscape. Despite government efforts to address these challenges, there are still areas where poverty and inequality persist. Programs aimed at providing education, healthcare, and job training are essential to alleviating these issues.
The city's informal sector, which includes street vendors, small businesses, and market stalls, is an integral part of the economy. While contributing to the city's活力,推动了就业和经济增长,但在城市规划和社会保障方面仍有改进空间。政府通过提供小额贷款、技能培训和健康保险等措施来支持这些工作者,并努力提高他们的生活水平。
在面对这些挑战的同时,Ho Chi Minh City也看到了巨大的机遇。随着国家经济的不断发展,城市有望成为东南亚地区的经济引擎。政府正在制定长远规划,提高城市基础设施,促进可持续城市发展。
总结来说,Ho Chi Minh City不仅是一个充满活力的大都市,也是越南未来的重要发展引擎。无论是在经济、文化还是环境方面,这座城市都展示出了其独特的魅力和潜力。通过不断努力和完善,Ho Chi Minh City将继续引领越南和整个地区的进步。
总之,Ho Chi Minh City是一座充满活力且不断进步的城市。尽管面临诸多挑战,这座城市依然在不断发展,其潜力和未来前景令人充满期待。