Vladivostok: A History of Russia's Eastern Gateway
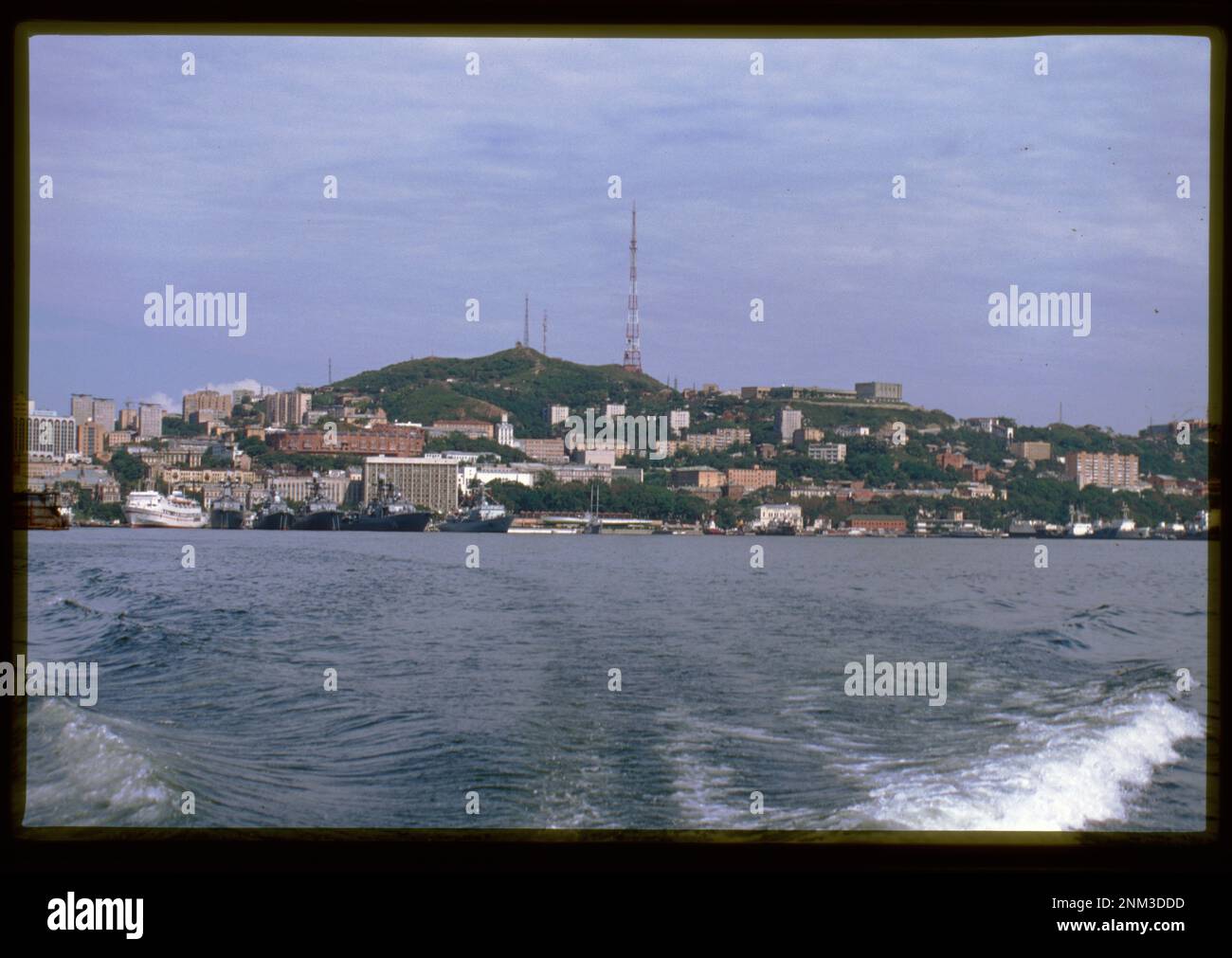
Vladivostok, the largest city in the Russian Far East, stands as a strategic and thriving hub on the Pacific coast. Located at the tip of the Kamchatka Peninsula, this city is a confluence of historical events and modern ambitions. Situated at a latitude of 43°N, Vladivostok has evolved from a small Russian settlement in the mid-19th century into a bustling metropolis with a population of over 600,000 people. Its name, first used in 1860, is derived from the Russian phrase "vladeti vostok," which means "to govern the east."
Early Settlement and Russian Influence
The origins of Vladivostok can be traced back to the 17th century when Russian explorers and hunters began to venture into the region. By the early 19th century, the area was already a significant trading post, with various Russian settlements and forts established along the coast. The site that would eventually become Vladivostok was chosen for its strategic location, both for military and economic reasons. In 1860, the town of Nakhodka was founded in the area, serving as a customs checkpoint and naval base. The next year, the name was changed to Vladivostok, marking the official establishment of the city.
Foundation and Initial Development
On June 29, 1860, the first governor of the Amur Oblast, Admiral Vasilii Pobretulin, officially founded the town of Vladivostok. The choice of this location was strategic; it was situated at the narrowest part of the Sea of Japan, making it a key point for naval operations and trade. The city's layout was planned with wide avenues and spacious parks, reflecting the aspirations of its founders.
Infrastructure and Growth
During the latter half of the 19th century, Vladivostok experienced significant growth due to its role in the Russian Empire's expanding interests in the Far East. The city's port was gradually developed, and by the early 20th century, it had become one of the most important commercial and military ports in the Russian Far East. The construction of key infrastructure, such as the Vladivostok Fortress and the Central Railway Station, furthered its development.
Role During World War I and the Russian Revolution
During World War I, Vladivostok was a crucial supply point for the Russian forces. The city hosted a large number of military units and served as a strategic location for the naval fleet. The Russian Revolution of 1917 had a profound impact on the city, as it became a focal point of opposition to the Bolsheviks. The city was under siege and was a site of intense fighting between the forces of the provisional government and the Bolsheviks. After the October Revolution, Vladivostok initially supported the white movement but was ultimately captured by the Bolsheviks in January 1918.
Interwar Period and the Russian Civil War
The years following the Russian Revolution were marked by significant changes in Vladivostok. The city became the center of the anti-Bolshevik opposition and the focus of the Japanese-backed White Army presence. The city saw periods of relative stability and conflict, with the forces of the Trans-Baikal Cossacks and the Japanese military engaging in various battles and actions. By the end of the Russian Civil War in 1920, Vladivostok had undergone a transformation, becoming a stronghold for the Red Army.
The Soviet Era and the Cold War
Entering the Soviet era, Vladivostok continued to play a vital role in the Russian Far East, serving as a key military and industrial center. The city experienced a period of economic growth during the 1920s and 1930s, with the development of heavy industry and the expansion of its port facilities. However, the Great Purge of the 1930s led to significant losses among the city's intellectuals and political leadership, as the Soviet regime intensified its repression.
World War II and the Soviet Union
During World War II, Vladivostok played a critical role as a logistics and military support base for the Soviet Union. The city's port facilities were essential in providing supplies and reinforcement to the Soviet forces fighting against the Japanese in the Far East. In response to perceived Japanese aggression, the Soviet Union began a massive program of fortification and modernization of the city and its surrounding areas.
The Soviet Industrial Revolution and Modernization
Under Soviet leadership, Vladivostok underwent a series of industrial and economic modernization projects. The city became a hub for shipbuilding, ship repair, and other heavy industries, such as metallurgy and chemical manufacturing. The Trans-Siberian Railway was extended to Vladivostok, enhancing the city's connectivity and facilitating the transfer of goods and resources.
Post-Soviet Era and Modern Vladivostok
Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, Vladivostok faced significant economic challenges as the country transitioned to a market economy. However, the city has since experienced a resurgence, particularly in recent years. The Russian government has launched major projects and investments aimed at modernizing and expanding the city's infrastructure. The 2012–2014 Russia–Korea summit, which was held in Vladivostok, highlighted the city's growing importance in regional and international affairs.
Infrastructure and Development
Today, Vladivostok is a vibrant city with a mix of heritage and modernity. The city boasts a robust transportation network, including the Trans-Siberian Railway and an extensive bus system. The port, one of the largest in Russia, continues to play a crucial role in trade and maritime activities. The city is also home to several universities and cultural institutions, contributing to its educational and scientific reputation.
Future Prospects and Challenges
Vladivostok faces several challenges in its continued development. Economic growth has been uneven, and some areas of the city still lack modern amenities. The city is also grappling with issues related to environmental sustainability, particularly air and water pollution. However, the vision of transforming Vladivostok into a major economic and cultural center for the Far East remains a key government priority.
Despite these challenges, Vladivostok is poised for significant growth in the years to come. With its strategic location, modern infrastructure, and growing economic significance, the city continues to be an important player in the Russian Far East, as well as in Asia as a whole.
Okay, the user wants me to continue the article about Vladivostok. I need to make sure the second part is around 1200 words. Let me check the first part to see where I left off. The first part covered the early history up to the post-Soviet era. The second part should pick up from there, discussing the modern era, economic developments, cultural aspects, and maybe the city's role in international relations.
I should start with the post-Soviet era, which the first part already touched on. Maybe elaborate on the challenges faced after the Soviet Union dissolved. Then move into how the city has been developing in recent years, including projects like the Golden Ring development, the Russian Far East's importance, and the Primorsky Krai's role. I should mention economic initiatives, such as the Far East Development Program, and how Vladivostok serves as a key hub for Russia's integration with Asia.
Cultural and social aspects are important too. The city's multicultural population, its festivals, historical sites, and universities. Also, environmental issues and sustainability efforts. The 2022 Winter Olympics might be relevant as a recent event highlighting the city's significance. I need to ensure the flow from the first part is smooth, not repeating the same points but expanding on new areas.
I should avoid using markdown and stick to HTML tags like h2 and h3. Let me outline the structure: start with the post-Soviet era, discuss economic transformations, cultural aspects, modern infrastructure, international relations, environmental challenges, and conclude with future prospects. Each section can be a subheading with a few paragraphs. Need to check the word count as I go to stay around 1200 words. Make sure to use formal language suitable for a journalistic article, keeping it informative and engaging without any markdown. Alright, time to draft the second part.
Economic Transformers: Vladivostok in the 21st Century
The post-Soviet years marked a turbulent but transformative period for Vladivostok. In the early 1990s, the city, like much of Russia, grappled with hyperinflation, political instability, and a sudden withdrawal of Soviet-era subsidies. The collapse of the USSR left the Russian Far East economically isolated, as trade routes that had once connected the region to the rest of the Soviet Union faltered. Vladivostok’s port, once the gateway for goods flowing through the Trans-Siberian Railway, faced a steep decline in activity. However, the city’s resilience became evident in the 2000s, as the Russian government began to reorient its economic and foreign policy strategies toward the Asia-Pacific region. Vladivostok emerged as a linchpin in this new vision, tasked with revitalizing Russia’s eastern corridor and reasserting its presence in a rapidly evolving geopolitical landscape.
The Far East Development Program
Key to Vladivostok’s resurgence was the Russian government’s Far East Development Program, launched in the early 2000s. This initiative aimed to ease the economic stagnation of Russia’s eastern territories by offering tax breaks, land incentives, and infrastructure investments to attract both domestic and foreign capital. Vladivostok, as the administrative center of the Primorsky Krai, became the flagship of this program. The city’s strategic location—closer to China, Japan, and South Korea than to Moscow—made it an ideal candidate for economic integration with the Asian continent. The program spurred the construction of modern residential complexes, industrial zones, and transportation hubs, gradually transforming Vladivostok into a financial and logistical hub for the Far East.
One of the most symbolic projects under this program was the city’s Golden Ring development—a sprawling urban renewal initiative that proposed building a ring of modern infrastructure around the historic center of Vladivostok. Though not fully realized, the Golden Ring inspired significant investments in the city’s transportation network, including the expansion of the Vladivostok Metro and the modernization of the city’s international airport. These upgrades not only improved connectivity within Russia but also positioned Vladivostok as a key stop for international trade routes linking Europe and Asia.
Vladivostok as a Gateway to Asia
The city’s role as a gateway to Asia has deepened in the 21st century, particularly with the rise of the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) and Russia’s renewed emphasis on strengthening economic ties with China. Vladivostok is the westernmost terminus of the China-Europe Railway Express, a high-speed freight network that connects China’s coastal cities to European markets. The port of Vladivostok, now a critical node in this network, has seen a resurgence in container traffic, with goods flowing between the Far East, Europe, and Asia. The city’s harbor, equipped with modern facilities and expanded logistics infrastructure, can now handle large volumes of trade, rivaling other Russian ports like Murmansk and St. Petersburg.
This economic integration has also translated into cultural and diplomatic exchanges. Vladivostok has become a melting pot of Eastern and Western influences, with its streets reflecting a mix of Russian, Chinese, Korean, and Japanese cultures. The city hosts numerous international conferences, business forums, and cultural festivals, further cementing its status as a crossroads of East and West. The annual Vladivostok International Economic Forum, launched in 2012, has become a cornerstone event for business leaders, scientists, and policymakers from across Eurasia, showcasing the city’s role in shaping the future of regional cooperation.
Challenges of Urbanization and Modernization
Despite its economic strides, Vladivostok faces significant challenges in its quest to modernize. The city’s population has grown steadily over the years, driven by migration incentives and improved living standards, but this growth has placed strain on housing, healthcare, and education systems. The pace of suburbanization has outstripped the development of infrastructure, leading to traffic congestion and housing shortages in the city center. Additionally, the disparity between the wealth of new developments and the underfunded institutions in older parts of the city has sparked social and political tensions, with locals questioning whether the benefits of economic growth are being evenly distributed.
Another pressing issue is environmental sustainability. Vladivostok’s coastal location makes it vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, including rising sea levels and more frequent extreme weather events. The city’s harbor, while critical to its economy, has been linked to pollution concerns, with industrial runoff and shipping activities affecting the local marine ecosystem. Efforts to address these challenges have included stricter environmental regulations and the promotion of renewable energy projects, but progress has been slow amid competing priorities and limited funding.
Cultural Revival and the Arts
Beyond its economic and strategic importance, Vladivostok has also experienced a cultural renaissance. The city’s arts scene, once overshadowed by the political and economic upheavals of the past century, has gained momentum in the 21st century. Contemporary art galleries, music festivals, and historical museums have flourished, attracting both local and international visitors. The Central Museum of the Far East, for example, houses an extensive collection of artifacts showcasing the region’s multicultural heritage, from ancient indigenous artifacts to Soviet-era propaganda materials.
Modern architects and urban designers have also played a role in revitalizing the city’s cultural landscape. The revitalization of the historic district, including the restoration of the Vladivostok Fortress and the creation of open-air museums, has transformed the city into a living archive of its past. These efforts have not only preserved the city’s architectural legacy but also reinforced its identity as a place where history and modernity coexist.
Education has become another pillar of Vladivostok’s development. The city is home to several prestigious universities, including the Far East Federal University, which offers programs in engineering, medicine, and international relations. These institutions have attracted students from across Russia and beyond, contributing to a more educated and globally connected local workforce. The presence of these academic institutions has also spurred research and innovation, with Vladivostok emerging as a hub for scientific collaboration in fields such as maritime technology and environmental studies.
Geopolitical Significance: Vladivostok in a New Era
As Russia navigates an increasingly multipolar world, Vladivostok’s strategic importance has only grown. The city has become a focal point for Russia’s enhanced engagement with the Asia-Pacific region, a shift that has been underscored by the nation’s military buildup in the Far East. The Pacific Fleet, headquartered in Vladivostok, has seen increased modernization, with the deployment of advanced naval vessels and submarines designed to project Russian power into the Pacific Ocean. This military presence has reinforced Vladivostok’s role as a key player in regional security dynamics, particularly in the context of rising tensions between Russia and Western nations.
The Arctic and Pacific Strategic Balance
Vladivostok’s significance extends beyond its immediate vicinity. As part of Russia’s broader strategy to balance its Arctic and Pacific maritime interests, the city serves as a vital logistical and operational base for naval forces. The Arctic, while rich in natural resources and increasingly accessible due to climate change, has long been a source of strategic concern for Moscow. Vladivostok’s position allows the Russian navy to maintain a presence in both the Pacific and Arctic theaters, acting as a bridge between Russia’s two maritime zones. This dual focus has made the city a critical asset in shaping Russia’s national defense posture.
Moreover, the Russian government has invested heavily in infrastructure projects aimed at improving connectivity between Vladivostok and the Arctic. The Northern Sea Route, a vital trade corridor that circumvents the traditional Suez Canal, has been modernized to accommodate increased shipping traffic. Vladivostok, as the eastern terminus of this route, plays a key role in facilitating the movement of goods between Russia’s Arctic ports and global markets. This development has the potential to further cement the city’s status as a global trade node, enhancing its economic and geopolitical influence.
Regional Rivalries and Diplomatic Tensions
Vladivostok’s position at the crossroads of East Asia has also made it a site of growing diplomatic tensions. The city’s proximity to China, Japan, and South Korea has placed it at the center of regional disputes, particularly regarding territorial claims and maritime boundaries. The disputed islands between Russia and Japan, known as the South Kuril Islands or the Northern Territories, have long been a source of friction, with Vladivostok serving as a key administrative and strategic hub for Russian claims in the area. Similarly, tensions with South Korea over Russian naval activities in the Sea of Japan have occasionally led to regional standoffs, highlighting the complex geopolitical chessboard in which Vladivostok operates.
Despite these tensions, the city has also been a platform for dialogue and cooperation. Bilateral agreements between Russia and its neighbors have focused on economic partnerships, such as joint ventures in energy, infrastructure, and tourism. The 2022 Winter Olympics, hosted in Beijing, marked a rare instance of collaboration between Russia and China, with Vladivostok playing a supporting role in logistics and international outreach. These efforts underscore the city’s dual role as both a symbol of regional rivalry and a potential bridge for reconciliation.
The challenges posed by geopolitical rivalries have not diminished Vladivostok’s ambition to become a regional leader. As the Russian government continues to invest in its military and economic capabilities, the city’s strategic value is likely to grow. Its continued development will depend on its ability to navigate these complex relationships while maintaining its unique identity as a cultural and economic hub in the Far East.
Conclusion: A City for the Future
Vladivostok’s journey from a small Russian outpost to a modern metropolis reflects the broader story of Russia’s engagement with the world. The city has weathered the storms of history, from imperial ambitions to revolutionary upheavals and post-Soviet reinvention. Today, it stands at the forefront of Russia’s efforts to reassert its influence in the Asia-Pacific region, balancing economic aspirations with strategic imperatives. While the road ahead is fraught with challenges—whether economic, environmental, or geopolitical—Vladivostok’s resilience and resourcefulness offer hope for its continued ascent as a vital center in the 21st century.
A Sustainable Future for Vladivostok
As Vladivostok looks to the future, the question of sustainability remains at the forefront. The city faces significant environmental challenges, including climate change, pollution, and the need to develop sustainable practices in its economic activities. Addressing these issues requires a multifaceted approach involving both public and private sectors, government policies, and community engagement.
Climate Change and Ecosystem Conservation
The effects of climate change are already being felt in Vladivostok. Rising sea levels, increasing temperatures, and more frequent extreme weather events pose serious threats to the city’s infrastructure and natural environment. To mitigate these risks, the city has developed comprehensive climate adaptation plans, focusing on measures such as improving stormwater management, reinforcing coastal defenses, and promoting green infrastructure.
One prominent initiative is the restoration of the coastal wetlands, which serve as a natural buffer against storm surges and help to filter pollutants. The city has also implemented greener building codes, encouraging the construction of energy-efficient and eco-friendly structures. The development of a green belt around downtown Vladivostok has helped to preserve green spaces, reduce urban heat islands, and provide recreational areas for residents.
Environmental Regulations and Industry Sustainability
To tackle pollution, the city has implemented stringent environmental regulations targeting key industries such as shipbuilding, chemical processing, and waste management. Efforts to reduce industrial emissions and improve waste disposal practices have significantly reduced the city’s carbon footprint. Collaboration with international organizations has helped Vladivostok adopt best practices in environmental management, fostering a more sustainable industrial sector.
The introduction of eco-tourism initiatives has also promoted sustainable practices. Vladivostok’s commitment to preserving its natural beauty has led to the development of eco-friendly tours and outdoor recreation activities that educate residents and visitors about the importance of conservation. Initiatives such as the annual Environmental Festival highlight the city’s dedication to sustainable development and raise awareness among residents about their role in protecting the environment.
Community Engagement and Education
Engaging the community in sustainability efforts is crucial for long-term success. Vladivostok’s local schools and universities have integrated environmental education into their curricula, fostering a culture of sustainability among young people. Community-based cleanup campaigns, tree-planting drives, and recycling initiatives have engaged citizens in practical environmental stewardship.
The city’s cultural institutions, such as museums and historical societies, play a vital role in promoting environmental awareness through exhibitions and educational programs. Public art projects that celebrate the city’s natural landscapes and promote eco-conscious behaviors have become a hallmark of Vladivostok’s cultural identity. The annual Green Walk, a community-run event, draws thousands of participants who walk through the city’s parks and green spaces, raising awareness about environmental issues.
Strategic Partnerships and International Collaboration
Vladivostok’s strategic position in the Far East makes it a natural platform for international collaboration on environmental issues. The city has established partnerships with similar cities in Northeast Asia, such as Shanghai and Busan, to share best practices and coordinate responses to shared environmental challenges. These collaborations have facilitated joint research initiatives, technology transfers, and knowledge exchange, enhancing Vladivostok’s position as a model for sustainable urban development.
The city’s participation in the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) forum has also provided a venue for discussing regional environmental issues. Vladivostok has championed proposals for green infrastructure, renewable energy projects, and sustainable transportation networks, contributing to the broader goal of environmental stewardship in the Asia-Pacific region.
Investment in Green Projects and Technological Innovation
To further drive sustainability, Vladivostok has invested in green projects that leverage technological innovation. The city’s port, for instance, has adopted advanced technologies to reduce its carbon footprint. Investments in electric and hydrogen fuel cell-powered vessels have helped to minimize emissions, while modernization of harbor facilities has improved efficiency and reduced waste.
The development of renewable energy sources is another key focus. Wind farms and solar parks, strategically located on the outskirts of the city, provide clean electricity to local businesses and residences. Vladivostok’s commitment to green technology has attracted investment from international firms, further cementing its status as a hub for sustainable innovation.
Conclusion: Vladivostok’s Path Forward
In conclusion, Vladivostok’s journey from a small frontier town to a dynamic metropolis with global ambitions underscores its potential to lead in the realm of sustainable urban development. While the city faces significant challenges, its proactive approach to climate adaptation, stringent environmental regulations, and community engagement demonstrate a commitment to a sustainable future. As Vladimir Putin envisions transforming Vladivostok into a major economic and cultural center, the city’s sustainability efforts ensure that its growth is both prosperity-bringing and environmentally responsible.
As Vladivostok continues to thrive, its future is intertwined with the global quest for sustainable development. By embracing green innovation, fostering international partnerships, and engaging its community, Vladivostok is poised to set an example for other cities seeking to balance economic growth with environmental stewardship. As the dawn of the 21st century approaches, Vladivostok stands ready to embrace its role as a beacon of sustainable progress, not just for Russia but for the world at large.























Comments