Unveiling the Myriad Benefits of Probiotics Beyond Gut Health
The human body is a complex ecosystem, home to trillions of microorganisms that coexist in harmony. Among them, probiotics, often referred to as "good bacteria," have been traditionally celebrated for their role in maintaining gut health. However, burgeoning research has begun to shed light on the far-reaching impacts of probiotics that extend well beyond the confines of our digestive tracts.
Probiotics are live microorganisms that, when administered in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit on the host. These benefits are not only grounded in supporting digestive health but also in their potential to influence systemic conditions. Over the years, the realm of probiotic application has expanded considerably, making these microbial allies a topic of interest across various domains of health and medicine.
The immune system, the body's natural defense against pathogens, is profoundly influenced by the state of the gut microbiota. Probiotics can exert a modulatory effect on the immune system. They have been shown to enhance immune responses, therefore, potentially reducing the risk or duration of infections. This is not just limited to the common cold or flu; probiotics could also play a role in the body’s defense against more serious infections.
Another burgeoning area of probiotic research is the gut-brain axis, a bi-directional communication network that connects the enteric and central nervous systems. This axis suggests that the state of the gut can influence mental states and behaviors. Probiotics are being studied for their potential role in the management of disorders such as depression and anxiety. While they are not a substitute for conventional treatments, they could become part of a more integrative approach to managing mental well-being.
Furthermore, skin health can reflect what happens inside the body, including the balance of the gut microbiome. Studies have investigated the usage of probiotics to manage skin conditions such as eczema, acne, and rosacea with promising results. Although the skin and the gut may seem unrelated, the influence of systemic inflammation and the release of certain biochemicals due to gut microflora suggest otherwise.
Cardiovascular health is yet another area benefiting from probiotics investigation. Certain strains of probiotics may help to lower cholesterol levels and blood pressure, suggesting that they could be incorporated into lifestyle strategies aimed at reducing cardiovascular disease risk. The mechanism may involve the breakdown of bile in the gut, thus preventing its reabsorption as cholesterol in the blood.
Furthermore, evidence is growing in support of the role of probiotics in weight management and metabolic disorders such as diabetes. Some research indicates that the gut microbiome composition correlates with the body's metabolism and fat storage, and probiotics might help in modulating these aspects for a beneficial outcome.
To delve deeper into the benefits of probiotics, one must also consider the issue of antibiotic resistance, a towering global health crisis. Probiotics can help support the body during and after antibiotic treatment, not only by mitigating some of the gastrointestinal side effects but also by maintaining a diverse and stable microbiome, which is crucial in the fight against resistant bacteria.
Additionally, probiotics are being scrutinized for their potential anticancer properties. Though research is in its early stages, there is some evidence that probiotics can produce compounds that might induce the death of cancer cells or enhance the efficacy of certain cancer treatments.
Despite the promise that probiotics hold in managing various health issues, it is essential to approach their use with a note of caution. Not all probiotics are created equal, and the effects may vary based on strain specificity, dosage, and individual host factors. Furthermore, the regulatory landscape regarding probiotics is complex; with products ranging from dietary supplements to medically prescribed probiotics, each differs in its oversight and claims of efficacy.
As we continue to explore the benefits of probiotics, it's critical to engage with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and to keep abreast of ongoing research deciphering the precise roles of these microscopic benefactors in our overall health. With each scientific stride, we uncover more layers of the symbiotic relationship between humans and their resident microorganisms, embarking on a future where probiotics may become fundamental components of preventive and therapeutic healthcare.As the scientific community delves deeper into the myriad effects of probiotics, it becomes clear that the advantages of these microorganisms could span a wide array of health issues, potentially transforming how we approach prevention and treatment.
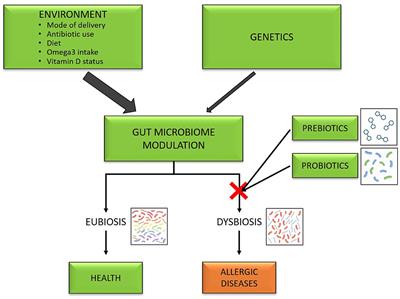
One striking observation is the potential interplay between probiotics and the onset of various allergies. With allergies on the rise globally, researchers are examining how early exposure to beneficial bacteria might affect the immune system's development, possibly preventing allergic reactions. This insight stems from the 'hygiene hypothesis,' which postulates that a lack of exposure to microbes at an early age can lead to an increased risk for allergies. Some studies suggest that certain probiotics, when administered to pregnant women and young children, may reduce the incidence of eczema and other allergic conditions.
In the domain of gastrointestinal health, beyond the widely recognized impact on digestive balance and function, scientists are examining probiotics' role in managing serious conditions such as inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) like Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. While not a cure, certain strains of probiotics have been shown to induce remission and maintain it in some patients. This suggests that modulation of the gut microbiome might play a pivotal role in managing chronic inflammatory gastrointestinal conditions.
Another promising avenue is the exploration of probiotics in maintaining liver health. Preliminary studies have shown that certain probiotics may help manage liver function in individuals suffering from conditions like non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). This is thought to be through reducing liver inflammation and possibly improving insulin sensitivity, highlighting a fascinating nexus between microbiome health and metabolic pathways.
Moreover, the potential role of probiotics in improving dental health is gaining traction. Evidence suggests that certain strains can help combat oral pathogens responsible for tooth decay, gum disease, and even bad breath. As oral health significantly impacts systemic health, integrating probiotics into daily dental care could have far-reaching benefits.
The way probiotics may affect athletic performance has also stirred interest. Athletes are prone to intense physical stress, which can affect the immune system and gut health. Probiotics might offer an edge by potentially enhancing recovery, reducing the incidence of respiratory tract infections, and mitigating gut disturbances often experienced during endurance activities.
But despite the expanding pool of knowledge, one must acknowledge the complexities involved in the application of probiotics. The challenge lies in deciphering the specific strains and dosages that would be most efficacious for different conditions. Probiotic research is, by necessity, highly detailed – a probiotic that shows promise for one condition may be entirely ineffective for another, and some probiotics might even be contraindicated in certain populations, such as immunocompromised individuals.
The interindividual variability also plays a critical role in the effectiveness of probiotics. Differences in genetics, existing microbiome composition, diet, and overall health can all influence how one might respond to a given probiotic treatment. Personalized probiotics, tailored to an individual's unique microbiome, might become a future possibility as we learn more about the specific mechanisms of action and interactions within our body's ecosystems.
Moreover, the safety profile of probiotics is a subject of ongoing analysis. While generally considered safe for healthy individuals, there is a need to understand better the potential side effects and adverse reactions, particularly in vulnerable groups. The regulatory frameworks governing probiotics are evolving to ensure safety and efficacy, and as the science progresses, so too will the standards and guidelines that govern them.
In conclusion, as we seek to embrace a holistic approach to health, the incorporation of probiotics into our lifestyles symbolizes a shift towards recognizing the integral role of microorganisms in our well-being. The prevailing evidence underscores that probiotics might be one keystone of our health infrastructure, imparting profound effects beyond the gut. As we continue to navigate the complex interplay between these microorganisms and our health, it is imperative to be guided by rigorously conducted research and informed by knowledgeable health practitioners. The journey into the world of probiotics is just beginning, and the future appears ripe with potential for these microscopic allies to help us lead healthier, more vibrant lives.







Comments