Understanding Public Key Infrastructure (PKI): The Foundation of Secure Digital Communication
In today’s digital age, the exchange of information occurs at a pace faster than ever imaginable. From personal emails to financial transactions, every byte of data needs assurance of privacy and authenticity. Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) emerges as the backbone of this secure digital environment, enabling encrypted communications and digital signatures that verify identities. But what exactly is PKI, and why is it indispensable in today’s interconnected world?
What is Public Key Infrastructure?
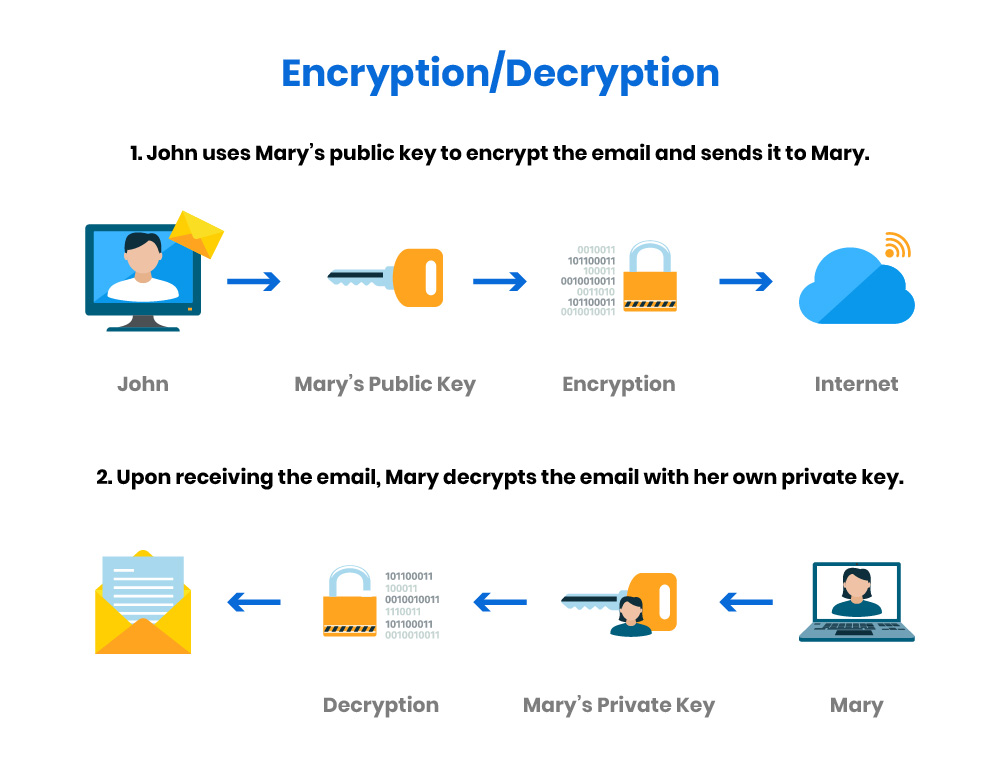
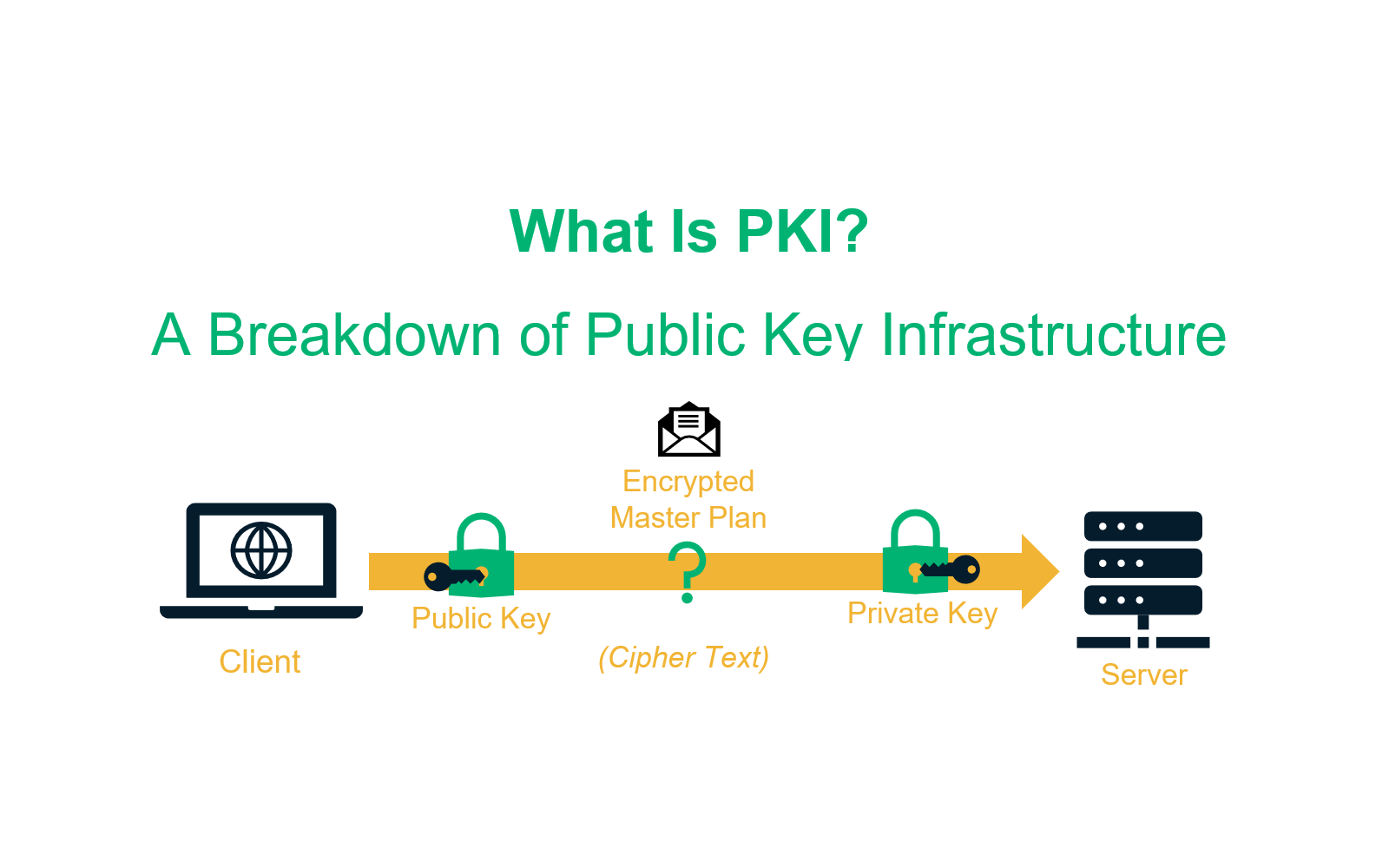
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is a framework of technologies, standards, and practices used to secure communications and authenticate identities across digital networks. At its core, PKI involves the use of cryptographic keys—specifically, a paired set of keys known as the public key and the private key. This pairing allows users to encrypt their data with one key which can only be decrypted with the other key in the pair, thus ensuring secure data exchange.
The infrastructure of PKI is composed of several components, including:
- Certificates: Digital documents that link a public key with an entity's identity, issued by trusted entities known as Certificate Authorities (CAs).
- Certificate Authorities (CAs): Trusted organizations responsible for issuing, revoking, and managing digital certificates.
- Registration Authorities (RAs): Entities that verify the identities of individuals or organizations requesting a digital certificate before it is issued by a CA.
- Certificate Repositories: Secure locations where certificates and their status are stored and made accessible.
- Revocation systems: Mechanisms to invalidate certificates that are no longer trustworthy or required.
The Role of Cryptography in PKI
Cryptography is the science of converting messages into a secure format that can only be understood by intended recipients. PKI makes extensive use of asymmetric cryptography, which employs a pair of mathematically linked keys:
- Public Key: A key that can be freely distributed to anyone who wants to send an encrypted message.
- Private Key: A secret key kept by the owner, used to decrypt messages and sign digital documents to ensure their authenticity.
The public key encrypts data that only the corresponding private key can decrypt, providing a secure means of communication. Conversely, data signed with a private key can be verified using the public key, providing integrity and authentication to digital interactions.
Applications of PKI
The versatility of PKI extends across various applications, significantly enhancing security and trustworthiness in digital operations. Some of the essential applications include:
- Secure Communications: Ensures the confidentiality and privacy of messages using encryption protocols like SSL/TLS, widely used in securing websites and emails.
- Digital Signatures: Provide verification of the authenticity and integrity of electronic documents, ensuring that data has not been altered.
- User Authentication: Replaces traditional password-based systems with certificate-based authentication, increasing security in enterprise environments.
- IoT Device Security: Secures the interactions between internet-connected devices, preventing unauthorized access and data breaches.
Benefits of Implementing PKI
Organizations that adopt PKI benefit from a reliable and scalable security framework. Key advantages include:
- Enhanced Security: Robust encryption and authentication mechanisms reduce vulnerabilities and protect sensitive information from cyber threats.
- Scalability: PKI can easily accommodate the growth of users and devices, making it suitable for both small businesses and large corporations.
- Cost-Effectiveness: By streamlining security protocols and reducing the risks of breaches, PKI can lead to reduced operational costs over time.
- Improved Trust: Digital certificates foster trust between parties, ensuring the authenticity of participants in digital communications.
As digital transformation continues to advance, the reliance on PKI as a cornerstone of secure digital communication becomes increasingly crucial. Yet, understanding the mechanics, benefits, and challenges of PKI is essential for organizations and individuals alike.




Comments