Understanding Blockchain Technology
The digital age has ushered in extraordinary innovations, reshaping countless facets of our world. Among these transformative technologies, blockchain stands out as one of the most revolutionary. While often associated with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, blockchain's potential spans far beyond digital currencies. Its implications are vast, affecting sectors ranging from finance to healthcare, logistics to entertainment. To fully grasp the potential impact of blockchain technology, it is essential to understand its core components, workings, and applications.
What is Blockchain Technology?
At its heart, blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that enables secure and transparent transactions. It is a decentralized database controlled by a network of computers, rather than a single entity. Each transaction is recorded as a "block," which is then linked to the previous one, creating a "chain." This chain of blocks is secured through cryptographic measures, ensuring data integrity and security.
The concept of blockchain was first introduced in 2008 by an anonymous entity known as Satoshi Nakamoto in the whitepaper, "Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System." Initially, blockchain served as the underlying technology for Bitcoin, but its uses have expanded significantly in the years since, promising transformative change across various industries.
How Does Blockchain Work?
To appreciate the inner workings of blockchain technology, consider a ledger or record book that stores entries. In this analogy, each block is like a page in this book, filled with transaction data. Unlike traditional ledgers, blockchain is maintained by a global network of computers, known as nodes. These nodes work together to verify and validate every transaction, ensuring that all entries are legitimate and accurate.
The Core Components of Blockchain
1. **Decentralization* Traditional databases are centralized, controlled by a single entity. In contrast, blockchain is decentralized, relying on a network of nodes to validate transactions. This reduces reliance on a central authority, potentially lowering costs and increasing data security.
2. **Immutability* Once data is entered into the blockchain, it becomes nearly impossible to alter or delete. This feature ensures the integrity and trustworthiness of the information recorded.
3. **Transparency* Each node in the blockchain network has access to the entire database and its complete history. This transparency helps prevent fraud and ensures accountability.
4. **Security* Blockchain incorporates advanced cryptographic techniques to secure data. Each block is encrypted and linked to the previous one, creating a tamper-proof chain.
The Process of Blockchain Transactions
The process of conducting a transaction on a blockchain primarily involves three stages:
1. **Initiation* A transaction is initiated by a participant, who broadcasts it to the network. This transaction can involve sending or receiving assets, such as cryptocurrencies, or executing contracts.
2. **Verification* Network nodes validate the transaction. They check that the initiating party has the necessary assets or permissions and has adhered to the network's rules. Nodes use consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS), to authenticate the transaction.
3. **Recording* Once validated, the transaction is combined with others to form a new block. This block is then added to the existing chain, ensuring the ledger's immutability and transparency.
Applications of Blockchain Technology
The versatility and security of blockchain have led to its exploration and adoption across numerous fields:
Finance
While best known for underpinning cryptocurrencies, blockchain is also redefining traditional finance. It enables faster and cheaper cross-border transactions, enhances the security of financial data, and has given rise to decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, which allow users to borrow, lend, and trade without intermediaries.
Supply Chain Management
Blockchain provides unprecedented transparency within supply chains. By tracking assets in real-time, businesses can improve efficiency, reduce fraud, and ensure product authenticity. It allows consumers to verify the provenance of products, enhancing trust and satisfaction.
Healthcare
In the healthcare sector, blockchain offers secure platforms for sharing patient records, reducing administrative costs, and preventing data breaches. It ensures that patient data is consistent, accurate, and accessible only to authorized individuals.
Entertainment
The entertainment industry is leveraging blockchain to manage intellectual property rights and ensure fair compensation for creators. Blockchain enables new business models, such as tokenization of content, which allows fans to directly support their favorite artists.
Government and Public Services
Governments are exploring blockchain for transparent voting systems, secure identity management, and efficient public service delivery. It promises to reduce fraud, enhance transparency, and improve public trust in government operations.
In conclusion, blockchain technology is a powerful tool that offers transformative potential. Its core attributes of decentralization, transparency, and security allow it to tackle longstanding challenges across various sectors. To truly harness its capabilities, ongoing research, development, and collaboration across industries are essential. As we continue to explore and expand the applications of blockchain, its role in shaping the future of technology and society becomes increasingly evident.
Challenges and Limitations of Blockchain Technology
Despite its remarkable promise and potential, blockchain technology is not without its challenges and limitations. Recognizing these hurdles is crucial for its successful adoption and integration across various sectors. Below are some of the most significant challenges faced by blockchain technology:
Scalability
One of the primary challenges facing blockchain is scalability. As the number of transactions increases, the blockchain can become congested, resulting in slower processing times and higher fees. This issue was famously highlighted with Bitcoin, where network congestion led to delayed transactions and expensive fees, particularly during periods of high demand. Although solutions such as the Lightning Network aim to enhance Bitcoin’s scalability, addressing this challenge remains critical for widespread adoption.
Energy Consumption
Blockchain’s security features, particularly those involving Proof of Work (PoW) consensus algorithms, consume significant amounts of energy. Bitcoin mining, for example, involves solving complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions, requiring substantial computational power and energy. This has raised environmental concerns, pushing developers to explore more sustainable alternatives like Proof of Stake (PoS) or hybrid mechanisms that balance security with energy efficiency.
Regulatory and Legal Concerns
Blockchain operates across decentralized networks often without a central authority, creating regulatory and legal challenges. Governments and regulatory bodies are working to navigate the complex landscape of blockchain to ensure compliance with existing laws while fostering innovation. The lack of a clear regulatory framework can create uncertainties for businesses and investors, potentially slowing the pace of adoption.
Interoperability
For blockchain to reach its full potential, different blockchain networks need to be able to communicate and work seamlessly together. Interoperability remains a significant barrier, as many blockchain platforms operate in silos, limiting the ability to share or transfer data across networks. Efforts are being made to create standards and protocols to enable greater interoperability, but there is still much work to be done to ensure seamless integration across diverse blockchain ecosystems.
Security Risks
While blockchain enhances security by design, it is not immune to vulnerabilities. Smart contracts, which automate processes on blockchains, can have bugs or design flaws that malicious actors might exploit. Additionally, while the core blockchain is secure, peripheral systems and applications like cryptocurrency exchanges can be vulnerable to attacks. Continuous security audits, improved coding practices, and robust security protocols are necessary to mitigate these risks.
Future Trends in Blockchain Technology
Given the ongoing developments in blockchain technology, several trends are expected to shape its future trajectory. These trends highlight the technology’s evolving nature and its potential to continue transforming various industries:
Integration with IoT
The integration of blockchain with Internet of Things (IoT) devices promises to enhance data security and transparency. By using blockchain’s decentralized ledger, IoT networks can ensure the integrity and accuracy of data exchanged between devices, reducing the risk of tampering or unauthorized access. This convergence opens up new possibilities for automated systems in sectors like smart home technology, industrial IoT, and autonomous vehicles.
Emergence of Blockchain in Banking and Finance
Banks and financial institutions are increasingly exploring blockchain to streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance customer experiences. Blockchain can greatly facilitate cross-border transactions, reduce settlement times, and improve compliance. Embracing blockchain can enable traditional financial entities to compete more effectively with emerging fintech companies.
Growth of Decentralized Applications (DApps)
Decentralized applications, or DApps, are expanding beyond finance into areas like gaming, social media, and supply chain management. These applications leverage blockchain's unique properties to offer users increased control, privacy, and profitability. As DApps mature, they may challenge or even disrupt established industries, offering new ways for consumers and businesses to engage with digital services.
Tokenization of Assets
Tokenization refers to converting physical or digital assets into digital tokens on a blockchain. This innovation can revolutionize industries by allowing fractional ownership, increasing liquidity, and enabling new business models. From real estate and art to stocks and commodities, tokenization is expected to open up investments to a broader audience and streamline asset management processes.
Increasing Use of Private Blockchains
While public blockchains receive significant attention, private blockchains are finding use in industry-specific applications where control and privacy are paramount. Businesses often prefer private blockchains for internal processes, supply chain management, and secure data sharing. These blockchains offer the benefits of decentralization while allowing organizations to dictate network visibility and participation.
Conclusion: The Path Ahead for Blockchain
Blockchain technology presents both immense opportunities and significant challenges. Its potential to revolutionize industries is matched by the hurdles it faces, including scalability, energy consumption, and regulatory uncertainties. As technology evolves, addressing these challenges is vital to unlocking blockchain's full capabilities.
Understanding blockchain's strengths and limitations is crucial for businesses, developers, and policymakers striving to integrate the technology into existing frameworks. As efforts continue to enhance blockchain's efficiency and interoperability, it sits at the forefront of innovation, continually reshaping economic landscapes worldwide.
The future of blockchain is undeniably promising, characterized by rapid development, increased adoption, and significant technological advances. The successful realization of its potential will depend on collaborative efforts to address existing challenges and embrace new trends, ensuring that blockchain continues to pave the way for technological progress and societal transformation.
Blockchain's Global Impact and Case Studies
The global interest in blockchain technology spans multiple industries and governments, each recognizing its potential to transform operations and enhance efficiency. By examining real-world applications, we can better understand blockchain's impact across different sectors and how it addresses specific challenges.
Blockchain in Trade and Logistics
One of the most prominent applications of blockchain is in trade and logistics, where transparency and accuracy in tracking goods are paramount. For instance, IBM and Maersk developed TradeLens, a blockchain-based shipping platform designed to promote efficient global trade by digitizing the supply chain process. TradeLens enables real-time information sharing among participants, reducing paperwork, lowering costs, and minimizing errors.
The use of blockchain in logistics not only streamlines communication but also enhances the trustworthiness of information exchanged between parties. By providing a single, immutable source of truth, blockchain helps businesses combat fraud, verify product origins, and ensure regulatory compliance.
Blockchain in Voting Systems
In democratic systems, the integrity and transparency of voting processes are critical. Blockchain holds the potential to revolutionize voting systems by providing secure, tamper-proof platforms for casting and counting votes. Countries and organizations worldwide are exploring blockchain-based voting mechanisms to ensure election integrity and bolster voter confidence.
For example, Estonia has been a pioneer in electronic voting since 2005, and they've explored blockchain to enhance its reliability further. By utilizing blockchain, votes can be recorded immutably, making it easier to securely audit elections and verify results. This technological advancement promises to increase voter participation, minimize fraud, and improve the overall transparency of electoral systems.
Blockchain for Philanthropy and Aid Distribution
Philanthropic organizations face challenges in transparency and accountability. Blockchain offers solutions by allowing donors to track how funds are allocated and used. This capability fosters trust and encourages more contributions.
Organizations such as the World Food Programme have experimented with blockchain platforms to distribute aid more efficiently. With blockchain, every transaction is recorded and accessible, ensuring that aid reaches intended recipients without intermediaries exploitations. As a result, blockchain can help maximize the impact of charitable donations and aid disbursement across humanitarian initiatives.
Blockchain Education and Skill Development
For blockchain technology to be harnessed effectively, a skilled workforce that understands its intricacies is essential. Education and skill development will play crucial roles in ensuring that businesses, developers, and policymakers can successfully implement and innovate within blockchain landscapes. As the demand for blockchain-related skills grows, educational institutions and organizations are expanding their offerings to prepare individuals for blockchain careers.
Academic and Professional Programs
Universities and colleges are increasingly incorporating blockchain into their curricula, offering specialized courses that cover theoretical and practical aspects of the technology. These programs equip students with the knowledge needed to design, develop, and implement blockchain solutions. Furthermore, professional certifications offered by various organizations provide individuals with the opportunity to gain in-depth expertise and demonstrate competencies in blockchain to potential employers.
Online Learning Platforms
The rapid evolution of blockchain technology demands continuous learning. Online platforms, such as Coursera, Udemy, and edX, offer flexible courses on blockchain development, cryptocurrency, and smart contract programming. These platforms cater to a broad audience, accommodating varying skill levels and schedules. By leveraging these resources, individuals and professionals can stay updated on blockchain advancements and improve their expertise.
The Collaborative Future of Blockchain
The future of blockchain hinges on collaboration between industries, governments, and technology developers. As blockchain technology matures, diverse stakeholders must work together to address existing challenges while exploring innovative applications and use cases.
Cross-Industry Collaboration
Collaboration between industries can lead to standardization and interoperability in blockchain platforms, driving widespread adoption. By sharing insights, best practices, and resources, businesses can address common challenges, such as scalability and security, more effectively. Joint ventures and consortia, like the Enterprise Ethereum Alliance and Hyperledger Project, exemplify the collaborative approach to progressing blockchain technology.
Public-Private Partnerships
Governments and the private sector can partner to develop regulatory frameworks that support blockchain innovation while maintaining consumer protection and security. Public-private partnerships can help prioritize cybersecurity efforts, promote research and development, and encourage blockchain adoption across public services and infrastructure.
The Role of Innovation Hubs
Innovation hubs and accelerators can play a vital role in fostering blockchain startups and stimulating technological innovation. By providing resources, mentorship, and networking opportunities, these hubs enable entrepreneurs and developers to experiment with new ideas and refine existing solutions. The nurturing environment they create can yield groundbreaking advancements and encourage further exploration of blockchain's potential.
In conclusion, blockchain technology is at the forefront of a digital revolution with the power to transform industries, drive innovation, and improve transparency and security. Despite facing challenges such as scalability and regulatory concerns, blockchain's potential remains vast and promising. Through education, collaboration, and strategic development, blockchain will continue to shape our technological future, empowering individuals and organizations to achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency and security. As we advance, embracing blockchain's capabilities will undoubtedly pave the way for a more interconnected, transparent, and trustworthy world.





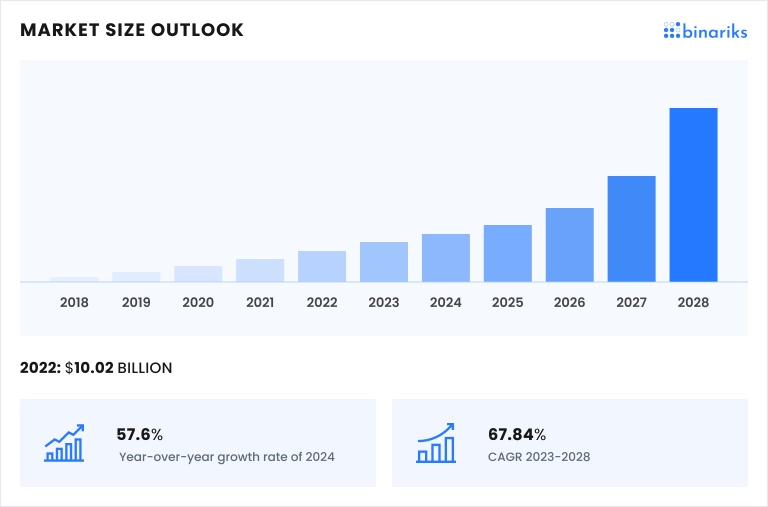

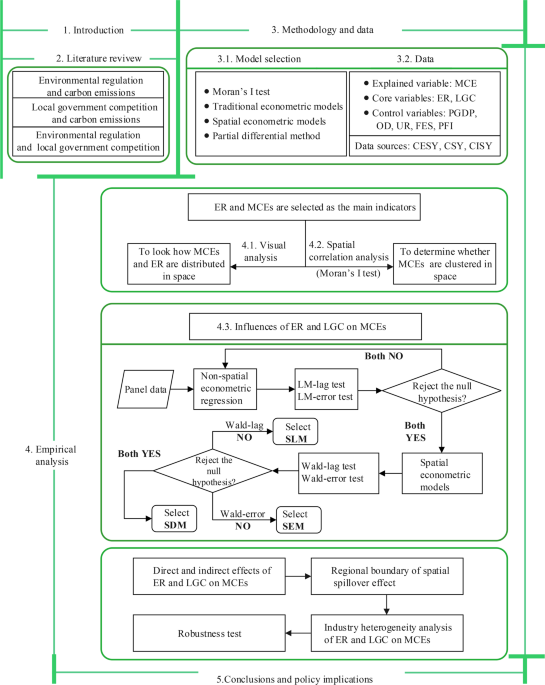


Comments