The Life and Legacy of Werner von Siemens: A Pioneer of Modern Technology
Introduction
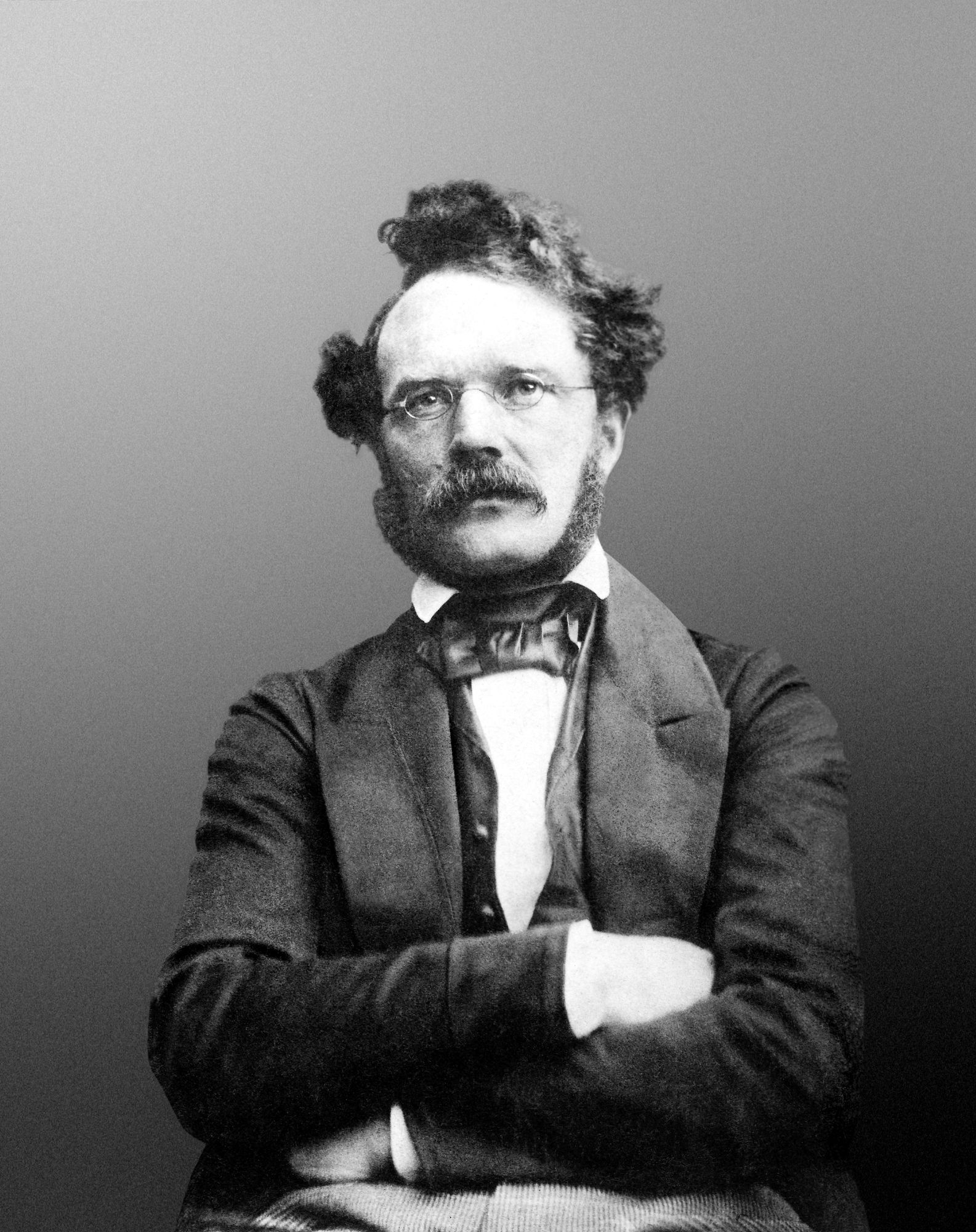
Werner von Siemens was an innovative engineer, inventor, and industrialist whose work laid the foundation for modern electrical engineering and telecommunications. His name is synonymous with the global technology giant Siemens AG, yet his influence extends far beyond the company he founded. Born on December 13, 1816, in Lenthe, near Hanover, Germany, Siemens demonstrated a natural inclination for science and technology from an early age. Throughout his life, he turned his visionary ideas into practical applications that revolutionized industries and improved lives across the globe. In this article, we explore the remarkable achievements and enduring legacy of Werner von Siemens, painting a portrait of a man whose contributions reshaped the technological landscape of the 19th and 20th centuries.
Early Life and Education
Werner von Siemens was the fourth of fourteen children in the Siemens family. His early education was limited due to financial constraints, but this did not hinder his curiosity and passion for learning. Rather than attending a traditional university, Siemens chose the route of military service in the Prussian artillery—a decision that, while seemingly contrary to his interests, afforded him a unique educational opportunity. The military academy in Berlin provided rigorous training in mathematics and physics, crucial subjects for Siemens's later work.
In 1837, Siemens joined the Prussian army, where he would serve for nearly a decade. During this time, he began experimenting with electrical currents and chemical compounds. His early contributions while in the military included inventing an improved method for galvanizing telegraph wire, a device for electric ignition in cannons, and an enhanced brewery press. Despite the limitations of his formal education, Siemens's keen scientific mind and ability to solve practical problems quickly garnered recognition.
The Birth of Siemens & Halske
After leaving military service in 1848, Siemens ventured into business along with Johann Georg Halske, an accomplished mechanic and engineer. Together, they founded the company Siemens & Halske on October 12, 1847, in Berlin. Their first major project was building a telegraph line running from Berlin to Frankfurt, utilizing Siemens's innovative pointer telegraph. Unlike the existing Morse telegraph system, Siemens's design eliminated the need for skillful decoding and instead pointed directly to letters of the alphabet. This invention was a significant improvement, making telegraphy more accessible and understandable, thereby accelerating its adoption across Europe.
The collaboration with Halske proved fruitful, as the company quickly established a reputation for quality and innovation. Siemens’s pointer telegraph was groundbreaking for its simplicity and effectiveness, and it wasn't long before Siemens & Halske was contracted for international projects.
Pioneering Advances in Electrical Engineering
In the following years, Werner von Siemens turned his attention to electrical engineering, a field still in its infancy. One of his most significant early achievements was his invention of the dynamo-electric principle in 1866. By creating a machine that converted mechanical energy into electrical energy without the need for permanent magnets, Siemens revolutionized the production of electricity. This invention made it feasible to generate electricity on a large scale, laying the groundwork for modern power distribution systems.
The dynamo had profound implications, as it enabled direct current electrical networks and powered the first electric street lighting, ushering in a new era of urban illumination. Siemens's relentless pursuit of innovation did not stop there. He continued to explore and develop technologies that expanded the use of electricity, including electric trams and the laying of extensive telegraph lines, playing a pivotal role in shaping the burgeoning infrastructure of industrialized nations.
The Expansion of Siemens’s Influence
Under Werner von Siemens's leadership, Siemens & Halske evolved into a multinational enterprise. By the late 19th century, the company had established offices and manufacturing facilities across Europe, including in the UK and Russian Empire. Siemens took a keen interest in the technical and commercial details of his enterprise, ensuring that the company remained at the cutting edge of innovation.
One of the most ambitious projects orchestrated under his guidance was the Indo-European telegraph line, completed in 1870. Stretching over 11,000 kilometers from London to Calcutta, this engineering marvel enabled rapid communication between Europe and the Indian subcontinent, exemplifying Siemens’s commitment to connecting the world through technology.
While Siemens was a pioneer in technologies that shaped the modern world, his influence transcended the commercial sphere. He was also a staunch advocate of technological education and social responsibility, emphasizing the need for skilled workers to leverage emerging technologies effectively. He supported vocational training initiatives and was instrumental in advancing technical education, believing that the prosperity and progress of industrial societies depended on an informed and skilled populace.
As we explore further into examples of Werner von Siemens's enduring legacy, it becomes increasingly clear why he is celebrated as a visionary of industrial technology.
Advancements in Telecommunications and Transportation
Following the remarkable success of his early telegraph projects, Werner von Siemens constantly sought new opportunities to advance the field of telecommunications. In the 1870s, Siemens & Halske embarked on an ambitious project to lay underwater telegraph cables, thereby enabling transcontinental communication. These cables extended under the Atlantic Ocean, connecting far-off lands with remarkable speed and reliability. Siemens's work in this arena set the stage for subsequent innovations in global communication networks and underscored the pivotal role of technology in bridging vast geographic divides.
In addition to telecommunications, Siemens was instrumental in transforming transportation. Recognizing the potential of electric traction, his company developed one of the world's first electric trams, unveiling it in Berlin in 1879. This early success led to widespread adoption of electric trams and further developments in electric locomotion. By the late 19th century, electric trains and trams became prevalent in cities across Europe, thanks to Siemens's trailblazing contributions.
The impact of these innovations did not merely end at technological advancement; they also catalyzed urban development and reshaped how people lived and worked. Commuting over distances became more feasible, urban centers expanded rapidly, and the connectivity brought about by Siemens's electric trams fostered socioeconomic growth. Siemens's legacy in transportation reflects his belief in technology as a driver of societal progress.
Commitment to Education and Industry Standards
Throughout his career, Werner von Siemens staunchly advocated for integration between academia and industry. Recognizing the importance of nurturing future generations with the skills required for technological advancement, he played an active role in advancing technical education. Siemens was involved in establishing numerous educational initiatives, supporting the creation of technical universities, and fostering environments that promoted scientific exploration.
Siemens understood that technological progress relied heavily on standardized systems and processes. To this end, he was involved in creating industry standards, especially in electrical engineering. These standards ensured consistency, interoperability, and safety of electrical systems, facilitating their broader adoption. Siemens's efforts in this arena laid the groundwork for the modern electrical industry, exemplifying his foresight and commitment to the long-term success of technological integration.
His influence extended into developments in the patent system, as he recognized the importance of protecting intellectual property to encourage innovation. Siemens was an advocate for strong patent laws, understanding that inventors needed legal protection to secure their discoveries and drive further advancements. Such advocacy helped create an environment where new ideas could flourish—a critical component for the rapid pace of technological progress during the Industrial Revolution.
Personal Ideals and Ethical Standards
Werner von Siemens was not only a shrewd businessman and brilliant inventor but also a man of principles and ethical standards. He firmly believed in the notion of social responsibility and was known for advocating the welfare of his workers, striving to improve their working conditions and quality of life. At a time when industrial labor conditions were often harsh and exploitative, Siemens's humane approach stood in stark contrast to the era's prevailing attitudes.
He introduced the concept of a profit-sharing scheme for his employees, which was revolutionary for its time. By involving them in the company's success, Siemens aimed to foster a sense of belonging and loyalty among his workforce. This initiative not only improved employee morale but also promoted dedication and innovation within the company.
Moreover, Siemens's environmental consciousness was noteworthy. As industrialization rapidly altered the landscape, he was acutely aware of the potential ecological impacts and actively sought to mitigate them. Although the environmental movement was still in its infancy, Siemens's proactive measures demonstrated an early understanding of sustainable practices.
Enduring Influence and Recognition
Werner von Siemens's legacy is built upon a foundation of innovation, responsibility, and perseverance. His pioneering spirit transformed multiple industries, leaving a lasting imprint on society and technology. He was accorded numerous honors throughout his lifetime, notably receiving the ennoblement, which added "von" to his name in recognition of his services to the Prussian state. Additionally, various scientific accolades commemorated his immense contributions, such as the founding of the Werner von Siemens Ring—an honor bestowed upon those making exceptional contributions to science and technology.
His achievements were not solely technical; he was instrumental in shaping the cultural and industrial landscape of his time, demonstrating how ethical practices and visionary thinking can drive remarkable success. Werner von Siemens passed away on December 6, 1892, in Berlin, yet his ideas and inventions continue to resonate throughout contemporary society.
Today, Siemens AG stands as a testament to Werner von Siemens's vision. It towers as one of the largest industrial manufacturing conglomerates in the world, epitomizing innovation and excellence. The company's enduring commitment to the ideals set forth by its founder—technological advancement, quality, and corporate responsibility—celebrates Siemens's legacy as an enduring force in the industrial world.
As we prepare to delve further into his profound influence on modern industry and reflect upon his continuing impact, it becomes clear that Werner von Siemens was far more than an inventor or industrialist. He was a visionary who saw the transformative power of technology to improve the quality of life and connect humanity, a belief that reverberates through every innovation stemming from his groundwork.
Siemens’s Technological Philosophy and Vision
Understanding Werner von Siemens's impact requires an analysis of his underlying philosophy—a deep-seated belief in the transformative power of technology to improve human life and progress. Siemens envisioned a world where industrial advancements would power not only economic growth but also societal betterment. He sought to harness scientific knowledge to address practical problems, improve efficiency, and increase connectivity, thereby creating a foundation for a more interconnected and prosperous global society.
His ability to foresee the potential of emerging technologies was remarkable. Siemens’s work often preceded the establishment of industries and infrastructures that we now consider indispensable. For instance, through his work in electrification and telecommunication, he laid the groundwork for the modern digital age. By focusing on innovation and sustainability, he not only expanded the boundaries of what was possible in his time but also set a course for future technological exploration.
Expansion into New Frontiers
In the latter years of his career, Werner von Siemens continued to explore and invest in new frontiers that promised to reshape society. This included ventures into the realms of chemical processing and material sciences. Recognizing the untapped potential of synthetic substances, Siemens collaborated with chemists to explore early plastic and compound applications that would eventually revolutionize material science and engineering.
Moreover, Siemens took a profound interest in the transportation sector, seeking to solve the inefficiencies of traditional propulsion systems. His exploration into electric propulsion extended beyond trams to initiatives that hinted at electric automobiles and sea vessels—ideas well ahead of their time that foreshadowed the modern movement towards sustainable transport.
Siemens’s interest in geographical exploration was also pivotal, as he engaged with geodesy and survey technology that helped in mapping regions for developmental purposes. Such endeavors, while tangential, contributed to the broader framework of integrating technology with societal growth, cementing his status as a forward-thinking industrialist.
The Global Legacy of Siemens AG
The company that Werner von Siemens founded, Siemens AG, has grown exponentially since its humble beginnings. Today, it is a multinational corporation with operations in nearly every conceivable sector, including automation, digitalization, energy, and healthcare. The company embodies the values Siemens championed: innovation, quality, and social responsibility. Its continued success stands as living testimony to the enduring principles Werner von Siemens instilled.
Siemens AG has played pivotal roles in numerous technological breakthroughs over the decades, from pioneering advances in clean energy solutions to the development of digitalization strategies that enhance efficiency across industries. The company's emphasis on research and development, alongside strategic partnerships and cutting-edge engineering, reflects the ethos of its founder: always looking beyond present-day challenges to find solutions that pave the way for future prosperity.
Siemens’s long-standing commitment to sustainable initiatives and environmental stewardship aligns closely with the ecological consciousness that Werner von Siemens espoused in his lifetime. Today, the company's endeavors in green technologies and resource-efficient operations highlight a strong adherence to responsible corporate citizenship, mirroring the visionary foresight of its founder.
Conclusion
Werner von Siemens was a trailblazer, whose revolutionary contributions to electrical engineering and telecommunications forever altered the technological landscape of the world. As a relentless innovator, Siemens’s relentless curiosity and ethical demeanor allowed him to surmount the barriers of his era, while establishing a blueprint for modern industry. His belief in technology as a catalyst for societal progress remains deeply ingrained in Siemens AG's corporate philosophy, a company that continues to honor his legacy with every stride in innovation.
Throughout his life, Siemens demonstrated that it is possible to blend visionary thinking with practical application, seamlessly integrating technological advancement with social responsibility. His work, philosophy, and leadership not only catalyzed profound changes in his own time but continue to reverberate in our modern technological society. Werner von Siemens’s far-reaching impact is a testament to the lasting power of innovation when coupled with ambition and humanity.
As we advance into an era defined by rapid technological evolution and digital transformation, reflecting on the life and achievements of Werner von Siemens offers both inspiration and guidance. His enduring legacy illuminates the path forward, reminding us that at its heart, technology remains a tool to connect, uplift, and improve the world for future generations. Siemens's life story is a powerful reminder that visionary innovation, ethical standards, and commitment to human progress form the cornerstone of sustainable success.





















Comments