The Life and Legacy of Edwin Hubble: Pioneering Astronomer and Discoverer of the Expansion of the Universe
H1929, Edwin Hubble was appointed as the successor to George Ellery Hale, who had served as the director of the Mount Wilson Observatory since its construction. This appointment marked the beginning of what would become one of the most significant careers in the history of astrophysics. Hubble's work fundamentally changed our understanding of the cosmos, leading to the recognition of the universe’s vast scale and the remarkable discovery that it is expanding.
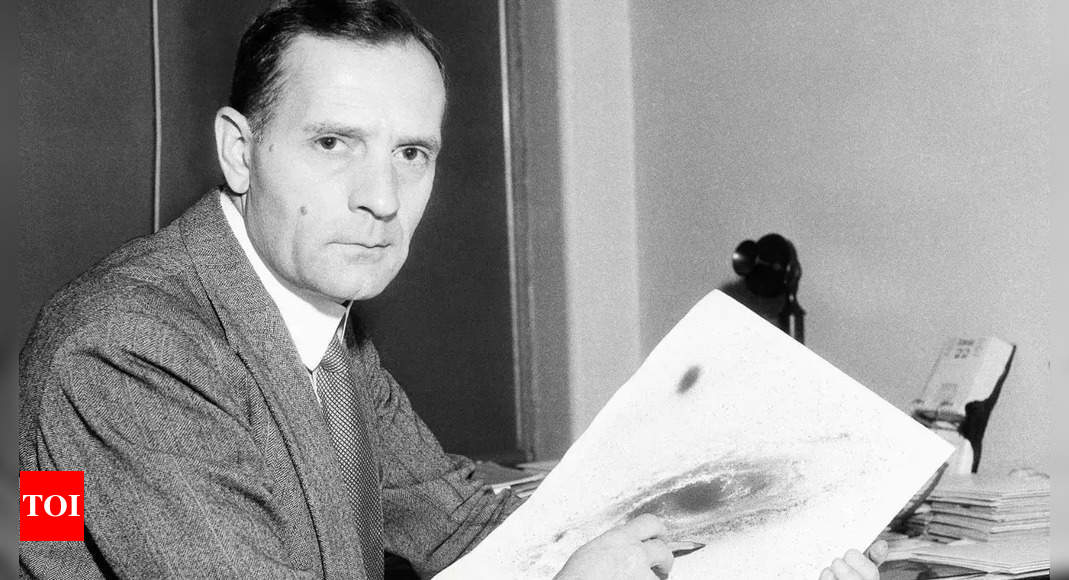
Edwin Powell Hubble (1889-1953) was born in Marshfield, Missouri, into a family steeped in academic tradition. His father was a lawyer, and his mother came from a family of educators. Growing up, Hubble showed an early interest in mathematics and science, particularly in optical physics and astronomy. He attended the University of Chicago, where he earned his Bachelor's degree in Philosophy and Physics, followed by a Master’s degree in Astronomy.
After graduation, Hubble began his career at the Mt. Wilson Observatory in Pasadena, California. The observatory’s powerful 100-inch Hooker telescope allowed him unprecedented views of distant star systems and nebulae, tools essential for his groundbreaking research. It was at this time that Hubble first became interested in the nature of these fuzzy, gas-filled structures that were often referred to as “nebula.” However, it was his meticulous observations and astute scientific methods that would eventually reveal their true nature.
The Nature of Nebulas
Initially, Hubble observed several spiral nebulae and noted their striking similarities to well-known features within our own galaxy, the Milky Way. He began by studying M31, also known as the Andromeda Galaxy, using the Hooker telescope. Through careful analysis of the nebula’s structure, Hubble deduced that these objects were not mere dust clouds within our galaxy as some scientists believed, but entire galactic systems far beyond the Milky Way.
In 1924, Hubble published his findings which provided definitive evidence that M31 was indeed an external galaxy. He supported his argument by analyzing the brightness of variable stars called Cepheid variables within Andromeda. By comparing these brightness levels with analogous stars in the Milky Way, he was able to determine distances accurate enough to establish the scale of Andromeda relative to our own galaxy. His calculations indicated that M31 was more than twice as far away from Earth as the largest estimate of the size of the Milky Way at the time.
The Expanding Universe
The discovery of these external galaxies paved the way for Hubble to explore their distribution and motion. In 1929, he made one of the most profound discoveries in astronomy: the expansion of the universe. While working on his doctoral dissertation, Hubble noticed that the light from distant galaxies appeared red-shifted—a phenomenon now known as “redshift.” Redshift occurs when light waves are stretched as the space between us and the source of the light expands, causing the wavelengths to grow longer and appearing red.
In his seminal work, Hubble plotted the recession velocities of galaxies against their distances from Earth. The resulting plot showed a clear linear relationship, which became known as Hubble’s Law. Mathematically, this relationship states \(v = H_0 d\), where \(v\) is the recession velocity of a galaxy, \(d\) is its distance from Earth, and \(H_0\) is the Hubble constant, a measure of the rate at which the universe is expanding.
This finding revolutionized cosmology and had far-reaching implications. It suggested that the universe is not static but is undergoing continuous expansion, a concept that had previously been speculative. Hubble’s law provided a quantitative means to understand how the universe was changing over time.
The Impact of his Discoveries
Edwin Hubble’s contributions to astrophysics extended far beyond his initial discoveries of external galaxies and the expansion of the universe. His work laid the foundation for modern cosmology and led to numerous advancements in astronomical technology and understanding.
One of the most significant impacts of his discoveries was the confirmation of the Big Bang theory. Before Hubble’s observations, the prevailing view was that the universe was eternal and unchanging. By showing that galaxies were moving away from each other and that they were doing so at increasing speeds, Hubble provided compelling evidence that the universe must have originated from a single point in an extreme event—an event now identified as the Big Bang. This discovery opened up entirely new questions and avenues of inquiry for scientists exploring the origin and evolution of the cosmos.
Moreover, Hubble’s work influenced the development of cosmological models. He helped to refine theories about the large-scale structure of the universe and its dynamics. These models would later be tested and revised as more data became available.
The legacy of Hubble is also reflected in the technologies and observational tools he helped pioneer. The Hubble Space Telescope, launched in 1990, bears his namesake and continues to carry out his legacy by providing astronomers with unprecedented insights into distant galaxies, nebulae, and other celestial bodies. The telescope has not only expanded our knowledge but also captured the imagination of millions around the world, inspiring new generations of scientists and enthusiasts.
Hubble’s work also influenced the direction of astronomical research for decades. His emphasis on precision and rigorous scientific methodology set a high standard for all future research. The techniques he used—notably the application of variable star distances to determine galactic distances—became fundamental tools in contemporary astronomy.
Personal Life and Legacy
Despite his groundbreaking contributions, Hubble’s personal life was marked by both triumphs and challenges. He suffered from tuberculosis and struggled with the condition throughout his lifetime, which necessitated frequent hospitalizations. Despite these health issues, Hubble remained committed to his research, demonstrating remarkable resilience and focus.
His professional relationships were also complex. Hubble faced skepticism from the scientific community regarding his initial findings about external galaxies. It wasn’t until other astronomers corroborated his results that they gained widespread acceptance. His collaboration with Vesto Slipher, another prominent astronomer of the time, played a crucial role in validating his conclusions. Their joint efforts significantly contributed to the credibility of the emerging picture of the universe.
On a personal level, Hubble was involved in various aspects of public life. He participated in popular science lectures, engaging with the broader scientific community and the public. His ability to communicate complex ideas in accessible ways contributed to the spread of scientific literacy and interest in astronomy.
Following Hubble’s death in 1953, his legacy continued to grow. He was posthumously awarded numerous honors, including the Royal Astronomical Society’s Gold Medal in 1951, recognizing his exceptional contributions to the field. Memorial observatories and educational institutions often bear his name in recognition of his impact.
Today, the term "Hubble diagram" is used to describe a graph that plots the redshift of galaxies against their distances, encapsulating the essence of Hubble’s discovery. His methods and findings remain cornerstones in astronomical studies, continuing to shape our understanding of the universe.
Beyond the Hubble Constant
Edwin Hubble's discovery of the expanding universe paved the way for a deeper understanding of the cosmos. One of the most significant advancements was the determination of the Hubble constant, \(H_0\), which quantifies the rate of expansion of the universe. The Hubble constant is crucial for estimating the age, size, and expansion rate of the universe. Hubble’s initial value for the constant was around 500 kilometers per second per megaparsec. Over the years, through various observational techniques and improvements in technology, this value has been refined. Current estimates place the Hubble constant at approximately 70 kilometers per second per megaparsec, leading to further insights into the universe’s age, estimated to be around 13.8 billion years old.
Additionally, Hubble’s work on the redshift-distance relationship also revealed that the expansion rate is not constant but could be accelerating. This observation, along with other findings, prompted the development of the Lambda-CDM model, which incorporates dark energy and dark matter to explain the observed behavior of the universe. Dark energy, a mysterious force causing the accelerated expansion, and dark matter, an invisible component influencing the gravitational dynamics of galaxies and the large-scale structure of the universe, both emerged as fundamental aspects of modern cosmology. The Lambda-CDM model is now the standard model of cosmology, providing a comprehensive framework for understanding the universe’s evolution from its early stages to the present day.
Theoretical and Observational Developments
Theoretical developments also progressed significantly due to Hubble’s discoveries. Albert Einstein, whose general theory of relativity was pivotal in understanding how gravity shapes the universe, re-evaluated his theory in light of Hubble’s findings. The original Einstein cosmological model, which assumed the universe to be static, had to make way for a dynamic model that embraced the expanding universe. This shift was not only theoretical but also led to the re-evaluation of the cosmological constant, a term in Einstein’s equation introduced to counteract the effect of expansion. Although Einstein later referred to it as his “biggest blunder,” the cosmological constant has since been reinterpreted and validated by modern observations as a potential explanation for the acceleration of the universe’s expansion.
Observationally, the 1920s and 1930s saw the development of advanced telescopes and spectroscopy techniques. These advancements not only confirmed Hubble’s findings but also provided more precise measurements. Improvements in telescope technology and the use of more accurate distance measurements, such as standard candles like Cepheid variables and Type Ia supernovae, allowed for a more refined understanding of the scale and expansion of the universe. Projects like the Hubble Space Telescope, which was launched in 1990, have significantly advanced our knowledge, allowing for high-resolution images and continuous observations of distant galaxies. Such observations have provided new data on the distribution and movement of galaxies, enhancing the accuracy of cosmological models.
The Challenges and Controversies
Despite his foundational contributions, Hubble faced significant challenges and controversies in his career. One of the most notable was his role in the Great Debate of 1920, where he directly challenged the prevailing view that the Milky Way was the entire universe. The debate pitted Hubble against Harlow Shapley, who believed that the Milky Way was the largest and only galaxy, and Edwin Hubble, who presented strong evidence for the existence of external galaxies. Hubble’s findings were initially met with skepticism, but his detailed observations and analysis eventually swayed the scientific community. This shift not only confirmed the existence of external galaxies but also opened the door to the concept of the vastness of the universe.
Another controversy arose with the interpretation of Hubble’s law. Some scientists argued that the redshift could be attributed to other factors, such as the Doppler effect due to the motion of galaxies. However, Hubble’s meticulous observations using the powerful Hooker telescope provided strong evidence that the redshift was indeed related to the expansion of the universe. This debate highlighted the importance of rigorous experimental methods and precise observations in astronomy.
The Legacy of Hubble's Observations
The legacy of Hubble’s observations extends beyond his own lifetime and continues to influence modern research. The Hubble Space Telescope, named in his honor, has been instrumental in advancing our understanding of the universe. Since its launch, the telescope has provided numerous breakthroughs, including the discovery of black holes, the observation of exoplanets, and the study of the cosmic microwave background, which offers insights into the early stages of the universe. The Hubble Ultra Deep Field, a series of images taken by the telescope, revealed the farthest and oldest galaxies in the universe, offering a window into the universe's youthful stages.
Furthermore, Hubble’s work has inspired a generation of scientists and continues to inform technological advancements. The development of new telescopes and observation methods, such as the James Webb Space Telescope, builds upon the legacy of the Hubble Space Telescope. These instruments are crucial for expanding our understanding of the universe and continue to refine the models of the cosmos. The insights gained from these observations not only further our scientific knowledge but also challenge us to ask new questions about the nature of the universe and our place within it.
In addition to the Hubble Space Telescope, other observatories and instruments have emerged in the wake of Hubble’s legacy. Large ground-based telescopes like the Large Synoptic Survey Telescope (LSST) are designed to survey the sky in unprecedented detail, aiming to map the distribution of galaxies and detect the effects of dark matter and dark energy on large scales. These instruments are crucial for future studies that will deepen our understanding of the cosmos and the fundamental laws that govern it.
Impact on Public Perception and Education
Hubble’s discoveries also transformed public perception of the cosmos, making the universe seem less like a static entity and more like a dynamic and expansive place. Hubble’s images, which are among the most iconic and recognizable in the history of astronomy, have captured the public imagination. These images, from the vibrant gas clouds of the Horsehead Nebula to the distant spiral arms of NGC 253, have become symbols of the beauty and mystery of the universe. They inspire fascination and curiosity, encouraging people to explore the night sky and learn more about the cosmos.
Moreover, Hubble’s legacy has had a significant impact on education and public science communication. Educational programs and public lectures often feature Hubble’s discoveries, highlighting the importance of scientific inquiry and the use of advanced technology in astronomy. The Hubble Telescope Live Events, where live observations and discoveries are shared with the public, have become a source of excitement and wonder, engaging people from all walks of life in the scientific endeavor.
The educational resources derived from Hubble’s observations also play a vital role in STEM education. Curriculums across the world incorporate Hubble’s discoveries and images, providing students with hands-on learning experiences and fostering a deeper understanding of cosmology. This not only enhances scientific literacy but also fosters a sense of wonder and appreciation for the natural world.
Conclusion
Edwin Hubble’s contributions to astronomy are immeasurable. From his pioneering discovery of external galaxies to his groundbreaking work on the expansion of the universe, Hubble’s legacy continues to shape our understanding of the cosmos. His meticulous observations, innovative methods, and rigorous scientific approach have not only advanced the field of astronomy but have also inspired a generation of scientists and educators. The ongoing work of the Hubble Space Telescope and other advanced observatories ensures that Hubble’s impact will continue to be felt for years to come, as new generations continue to explore the wonders of the universe.
The Future of Cosmic Exploration
The legacy of Edwin Hubble continues to shape the future of cosmic exploration. As technology advances, new telescopes and observatories are being developed to probe the mysteries of the universe further. The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), for example, offers enhanced capabilities over the Hubble Space Telescope. With its larger primary mirror and advanced instruments, the JWST can observe the universe in infrared light, allowing it to peer through the first stars and galaxies that formed after the Big Bang. This will provide crucial insights into the early universe and the formation of the first structures in the cosmos.
Other telescopes like the Square Kilometer Array (SKA) and the European Extremely Large Telescope (E-ELT) are designed to conduct large-scale surveys of the sky, detecting faint radio signals and visible light from distant galaxies. These projects aim to map the distribution of matter in the universe at various scales, offering a comprehensive view of the cosmic web and the dark matter that underpins its structure. The combined efforts of these telescopes will provide a more complete picture of the universe’s history and evolution.
Continued Exploration and Discovery
The search for exoplanets is another area where Hubble’s legacy lives on. The Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) and the upcoming Habitable Exoplanets Observatory (HabEx) are designed to detect Earth-like planets in other star systems. Hubble has already contributed significantly to this field by characterizing the atmospheres of exoplanets and estimating their potential for habitability. These discoveries not only expand our understanding of planetary systems but also bring us closer to the search for extraterrestrial life.
Furthermore, the study of dark matter and dark energy remains a crucial aspect of modern astrophysics. New observational techniques and simulations are being developed to better understand these mysterious components of the universe. The Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) and the Vera C. Rubin Observatory, with its wide-field imaging capabilities, are poised to make significant strides in this area. By mapping the large-scale structure of the universe and measuring the clustering of galaxies, these instruments aim to refine our understanding of the dark components and their roles in the expansion of the universe.
The Interdisciplinary Impact of Hubble’s Discoveries
The discoveries and methodologies developed by Hubble have had a profound interdisciplinary impact. They have influenced fields such as physics, mathematics, and even philosophy. The concept of a dynamic universe has reshaped our understanding of time and space, challenging traditional concepts and leading to new theories in physics. The study of dark matter and dark energy has spurred developments in theoretical physics, leading to the exploration of alternative theories like modified gravity and extra dimensions. These new frameworks not only push the boundaries of physics but also challenge our fundamental understanding of reality.
In mathematics, the large-scale structure and expansion of the universe have inspired new mathematical models and theorems. The application of complex mathematical techniques to astronomical data has opened up new avenues for research, connecting abstract mathematical concepts with observable phenomena. This interdisciplinary approach has not only advanced the frontiers of scientific research but has also fostered a deeper understanding of the mathematical underpinnings of the cosmos.
Public Engagement and Scientific Literacy
The impact of Hubble’s discoveries extends beyond the scientific community, greatly enhancing public engagement with science. The Hubble Space Telescope’s public outreach initiatives, such as the Hubble Deep Field and its stunning images, have captured the imagination of people worldwide, fostering a greater appreciation for the scientific method and the wonders of the cosmos. These initiatives, combined with educational programs in schools and public lectures, have played a critical role in promoting scientific literacy and inspiring interest in astronomy among the general population.
Additionally, the media and public interest in space exploration have been significantly influenced by Hubble’s discoveries. From documentaries to popular science books, Hubble’s contributions have been widely covered, reaching a broad audience. This widespread interest has also fueled public support for space exploration and astronomy, leading to increased funding and investment in space research. The public’s fascination with space continues to drive innovation and inspire new generations of scientists and engineers.
Literature and the Cultural Impact
The cultural influence of Hubble’s discoveries can be seen in literature, art, and popular culture. Poets, writers, and artists have drawn inspiration from the vast and mysterious cosmos, creating works that reflect the awe and wonder inspired by Hubble’s observations. In literature, books like Carl Sagan’s "Cosmos" have popularized scientific concepts and inspired readers to explore the vastness of the universe. In art, space-themed works by contemporary artists explore themes like the infinite nature of the universe and the search for meaning.
The cultural impact of Hubble’s discoveries also extends to popular media, such as films, television shows, and video games. From movies like "Interstellar" to television series like "The Expanse," Hubble’s discoveries have been woven into these narratives, further enhancing public interest and engagement with the subject matter. This interweaving of science, art, and popular culture not only entertains but also educates, fostering a broader appreciation for the scientific endeavor.
Conclusion
The contributions of Edwin Hubble to our understanding of the universe are unparalleled. His work has not only expanded our scientific knowledge but has also transformed the way we perceive the cosmos. As technology continues to advance and new observatories are built, Hubble’s legacy will continue to guide and inspire the next generation of astronomers and scientists. The ongoing exploration of the universe will build upon his discoveries, leading to a deeper understanding of the nature of the cosmos and our place within it. Hubble’s legacy is a testament to the power of scientific inquiry and the enduring quest to understand the mysteries of the universe.
Through the ongoing work of observatories like the Hubble Space Telescope and the many others that follow in its footsteps, we continue to unravel the secrets of the cosmos, guided by the vision and dedication of Edwin Hubble. As we look to the future, Hubble’s legacy serves not only as a historical reference but as a beacon for future exploration and discovery. The journey of understanding the universe is one that continues, and Hubble’s contributions will remain a cornerstone of this ongoing quest.




















Comments