Michael Faraday: The Father of Electromagnetism
When we think about the pioneers of science, names such as Albert Einstein and Isaac Newton often come to mind. However, nestled among these giants is Michael Faraday, a self-taught scientist whose groundbreaking discoveries laid the foundations for modern-day electromagnetism and electrochemistry. Faraday’s contributions to science are immeasurable, and his life's work continues to resonate in various fields to this day.
Early Life and Humble Beginnings
Michael Faraday was born on September 22, 1791, in Newington Butts, a small village that is now part of South London. Raised in a working-class family, Faraday’s early life was characterized by modesty and simplicity. His father, James Faraday, was a blacksmith, while his mother, Margaret Hastwell, hailed from a farming family. Despite their economic struggles, they were determined to provide for their four children.
Faraday's formal education was limited, and by the age of 13, he entered the world of work as an errand boy for a local bookseller. It was in this humble setting that Faraday’s unquenchable thirst for knowledge was first sparked. Surrounded by books, he utilized his free time to read voraciously and educate himself about the sciences and the arts. His curiosity led him to experiment and explore concepts beyond his immediate comprehension.
The Turning Point: A Chance Encounter
A pivotal moment in Faraday’s life came in 1812, when he was offered a ticket to attend a series of lectures by the renowned chemist Humphry Davy at the Royal Institution. Enthralled by Davy’s demonstrations, Faraday meticulously took notes, which he later compiled into a bound volume. Fueled by ambition and the desire to delve deeper into the world of science, Faraday sent the notes to Davy with a letter seeking employment or apprenticeship.
Impressed by Faraday's dedication and potential, Davy hired him as an assistant at the Royal Institution. This opportunity proved transformative, providing Faraday with the chance to work alongside and learn from one of the leading scientists of the time. It marked the beginning of Faraday’s illustrious career and set him on the path to make some of the most significant scientific breakthroughs of the 19th century.
Contributions to Chemistry
Faraday’s early work primarily focused on chemistry. One of his first tasks at the Royal Institution was to aid Davy in isolating new elements. Faraday’s meticulous approach to experimentation and his keen analytical skills soon led to discoveries of his own. He discovered the chemical substance benzene in 1825, a significant milestone in organic chemistry. Benzene’s structure and properties have since made it a foundational element in the production of various chemical compounds and everyday products.
Moreover, Faraday’s extensive work in electrochemistry propelled him to unveil the laws of electrolysis, which describe the interactions between electrical currents and chemical reactions in solutions. These laws laid crucial groundwork for future developments in both chemistry and electricity.
The Discovery of Electromagnetic Induction
In 1831, Michael Faraday embarked on an experiment that would alter the course of scientific history: the discovery of electromagnetic induction. Through a series of experiments involving coils of wire and magnets, Faraday realized that a changing magnetic field could induce an electric current in a nearby conductor. This phenomenon, now known as Faraday’s Law of Induction, is the principle behind the operation of transformers, electric generators, and a myriad of other technologies that power our modern world.
Faraday's experiments demonstrated the fundamental relationship between electricity and magnetism, leading to the broader concept of electromagnetism. His work was instrumental in illustrating that electricity could be generated through a magnetic field rather than relying solely on chemical reactions from batteries.
Impact on Modern Science and Technology
The implications of Faraday’s discoveries were far-reaching and profound. The understanding of electromagnetic induction set the stage for the development of electric power generation, which spurred the Industrial Revolution's second wave, fundamentally transforming industries and society. It laid the groundwork for the numerous electrical devices we rely on today, from simple household appliances to complex computer systems.
Moreover, Faraday's innovative approach to scientific investigation influenced future generations of scientists. Albert Einstein famously kept a picture of Faraday in his study, citing him as one of his major inspirations. Faraday’s methodical experimentation and ability to distill complex ideas into simpler concepts served as a model for empirical research. His legacy is a testament to the power of curiosity, perseverance, and the pursuit of knowledge, even in the face of adversity.
In conclusion, Michael Faraday's story is one of triumph over circumstance, relentless inquiry, and pioneering discovery. His life's work continues to resonate, not only in the spheres he directly influenced but across the entire scientific landscape. As we marvel at the myriad technological advancements of our age, we owe a debt of gratitude to this self-taught scholar, whose legacy will forever enlighten future generations.
The Royal Institution: A Hub of Scientific Exploration
During his time at the Royal Institution, Michael Faraday not only cultivated his own scientific pursuits but also significantly contributed to its status as one of the leading scientific institutions in the world. As assistant and later as director of laboratory at the Institution, Faraday played a crucial role in its expansion, orchestrating lectures, experiments, and demonstrations that captivated audiences with the wonders of science.
Faraday believed in the importance of communicating scientific knowledge to the public. He initiated the Christmas Lectures at the Royal Institution in 1825, a tradition that continues to this day. These lectures aimed to present complex scientific concepts in an accessible and engaging manner, sparking interest in science among young and old alike. Faraday’s oratory skills, combined with his ingenious demonstrations, made him one of the most popular science presenters of his time.
Magneto-Optical Effect and Further Innovations
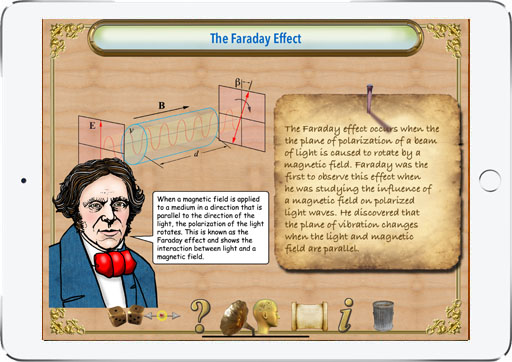
Michael Faraday's pioneering spirit led him to venture into the realm of optics, where he made one of his most intriguing discoveries: the magneto-optical effect, also known as Faraday rotation. In 1845, Faraday demonstrated that a magnetic field could influence polarized light. His experiments revealed that when polarized light passed through a glass placed in a magnetic field, its plane of polarization was rotated. This was the first evidence of a link between light and magnetism, paving the way for the field of quantum electrodynamics and advancing the understanding of the fundamental forces in nature.
Faraday also dabbled in the study of static electricity, leading to the invention of the Faraday cage. This enclosure is designed to block external static and non-static electric fields, ensuring that the interior remains unaffected by external electrical charges. This innovation has become crucial in protecting sensitive equipment from electromagnetic interference and is employed in various scientific and industrial applications today.
Challenges and Triumphs
Despite his towering achievements, Faraday’s journey was not devoid of challenges. Throughout his career, he faced skepticism from some quarters of the scientific community, often due to his lack of formal education and mathematical training. Faraday’s approach to science was highly experimental, and he relied heavily on empirical data rather than mathematical validation. While this sometimes led to criticism, it also underscored the importance of practical experimentation in scientific discovery.
Moreover, Faraday’s health was a recurring concern. In 1839, he suffered a nervous breakdown that incapacitated him for some time. Despite these hurdles, Faraday’s passion for science never waned. He continued his research with tenacity and resolve, ultimately achieving a level of renown that overshadowed early doubts about his qualifications.
Philosophy and Scientific Method
Michael Faraday's view of science was deeply philosophical. He was a devout Christian, and his faith played a significant role in shaping his scientific perspective. Faraday believed that science was a divine pursuit, a means to understand the natural laws created by a higher power. This belief in a cohesive and ordered universe drove him to seek out connections between seemingly disparate phenomena.
Faraday’s scientific method was distinguished by his emphasis on rigorous experimentation and careful observation. He was known for rejecting speculation unsupported by experimental evidence. His insistence on simplicity and clarity in explaining scientific concepts made his work accessible and understandable, both to his contemporaries and to future generations.
A Lasting Legacy
Michael Faraday’s contributions to science extend far beyond his lifetime. His discoveries laid the groundwork for many technological advancements and inspired subsequent generations of scientists. His laws of electromagnetic induction are still taught in physics classes worldwide, and the devices that operate based on these principles are integral to modern society.
Faraday's role in advancing chemistry and physics remains unmatched, and his ethos of scientific exploration continues to inspire researchers today. His legacy is evident in the countless innovations that have emerged from his foundational research, serving as a testament to the enduring power of scientific inquiry.
In honor of his contributions, numerous awards, institutions, and phenomena bear Faraday’s name. The Faraday Medal, awarded by the Institution of Engineering and Technology, and the Faraday Constant in electrochemistry, are just a few examples of his enduring influence. His work is a shining example of the profound impact one individual can have on the world of science and technology.
As we continue to explore new frontiers in science and technology, the principles and methodologies established by Michael Faraday serve as a guiding light. His story reminds us of the power of curiosity, dedication, and the relentless pursuit of knowledge, no matter the obstacles or limitations faced along the way.
Faraday's Influence on Future Innovators
Michael Faraday’s impact extends beyond his discoveries and innovations in electromagnetism and chemistry; he has also served as a beacon of inspiration for countless scientists and engineers who came after him. His approach to scientific inquiry emphasized exploration over formal training, exemplifying that groundbreaking work could stem from intrinsic curiosity and intuitive insight. This philosophy has inspired many notable figures, including Thomas Edison, Nikola Tesla, and James Clerk Maxwell, each of whom made significant contributions to the realms of electricity and magnetism.
James Clerk Maxwell, in particular, drew heavily from Faraday’s experiments. Even though Faraday was not well-versed in advanced mathematics, Maxwell translated Faraday’s qualitative conclusions into a set of formal equations. Maxwell’s equations, which describe the behavior of electromagnetic fields, provided a comprehensive understanding of electromagnetism and are still fundamental to the study of physics today. Through Maxwell’s work, Faraday’s theories found their full mathematical expression, solidifying Faraday’s influence on the scientific landscape.
Recognition and Honors
Throughout his life and posthumously, Faraday received numerous accolades for his extensive contributions to science. He was elected as a fellow of the Royal Society in 1824 and was awarded the Royal Medal in 1835, 1838, and 1846. Despite the honors and offers that came his way, including a proposed knighthood, Faraday remained humble and unassuming, choosing to focus on his scientific work rather than seek personal accolades.
Additionally, Faraday became a foreign member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences and held honorary doctorates and memberships in various scientific societies worldwide. Despite his modest origins, Faraday’s reputation soared beyond the confines of national boundaries, marking him as a scientist of global renown.
A Life of Service and Humility
Faraday’s life extended beyond the realm of scientific achievement; he was a man dedicated to service and community. Despite his scientific pursuits, Faraday was deeply involved in his church, the Sandemanian church, serving as an elder for many years. His personal life was one of simplicity and devotion, and he declined several offers for financial reward and fame, including proposals for lucrative advisory positions.
His wife, Sarah Barnard, whom he married in 1821, was a steadfast companion throughout his journey. Faraday valued the stability and support of his personal life, which complemented the intellectual intensity of his scientific endeavors.
The Final Years and Lasting Legacy
In the latter part of his life, Faraday's health began to decline, although his interest in science remained undiminished. He conducted his last significant study in the late 1850s, exploring the optical properties of gold nanoparticles, a field that would become significant many years later with the development of nanotechnology.
Michael Faraday passed away on August 25, 1867, at the age of 75, leaving behind a legacy of scientific discovery that has continued to empower future generations. He was laid to rest in Highgate Cemetery in London, his modest gravestone bearing testimony to a life driven not by the pursuit of fame but by a passion for uncovering the mysteries of the natural world.
Faraday’s insights and practices burgeoned into the technologies that we take for granted today. From the electric motor and generator to the principles underlying wireless communication and lighting, Faraday’s work set the stage for many of the conveniences that define contemporary living.
His approach to science highlighted the importance of discovery, curiosity, and the relentless search for understanding. The Faraday Society, now known as the Faraday Division of the Royal Society of Chemistry, continues to celebrate his achievements and advance his spirit of inquiry.
In retrospect, Michael Faraday's life and work illuminate the profound impact that one passionate individual can have on the fabric of human knowledge. His example encourages young scientists to ask questions, to embrace failures as stepping stones to success, and to pursue their passions with unwavering dedication. As we look to the future, with emerging fields such as quantum computing and renewable energy systems, Faraday's legacy reminds us of the enduring power of the human intellect to explore and innovate, shaping a brighter future for all.







Comments