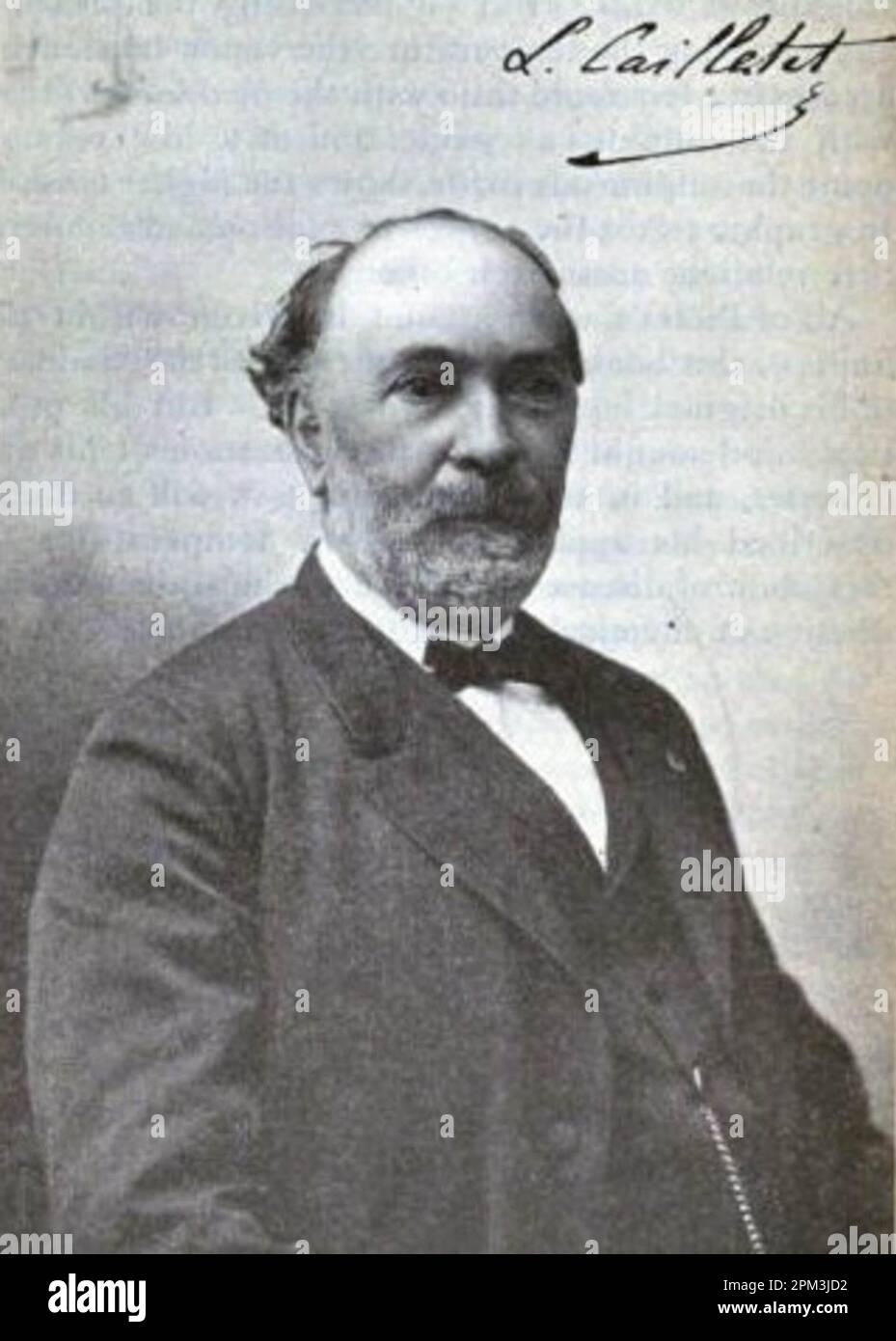
Louis Paul Cailletet: The Pioneering Scientist Who Brought Gases Down to Earth
Introduction
In the annals of scientific history, there are individuals whose pioneering work has profoundly shaped our understanding of the natural world. Among these influential figures is Louis Paul Cailletet, a French physicist and engineer whose groundbreaking experiments with gases significantly advanced the fields of thermodynamics and cryogenics. Cailletet's contributions to science during the 19th century opened the doors to a deeper comprehension of gases and their properties, laying the groundwork for numerous technological advancements that followed.
Early Life and Education
Louis Paul Cailletet was born on September 21, 1832, in Châtillon-sur-Seine, a quaint town nestled in the Burgundy region of France. Raised in a family with an industrial background—his father being a prominent iron master—Cailletet was exposed to the world of metallurgy and engineering from an early age. This environment fostered a natural curiosity and aptitude for scientific inquiry, which he carried with him throughout his life.
His formal education began at the prestigious Lycée Henri-IV in Paris. Following his secondary education, he pursued further studies in engineering, eventually enrolling at the École Centrale des Arts et Manufactures, one of France's leading engineering institutions. It was here that Cailletet honed his skills, learning the intricacies of physics, chemistry, and mechanics, which would serve as the foundation for his future scientific endeavors.
A World of Gases
Cailletet's passion for physics and his technical proficiency led him to focus his research on gases—a relatively underexplored field at the time. The scientific community had long been fascinated by gases, but understanding their behavior, particularly under extreme conditions, remained a considerable challenge. Cailletet aimed to explore these mysteries through experimentation, thus embarking on a journey that would see him overcome many scientific obstacles.
In the late 19th century, the concept of liquefying gases was novel and groundbreaking. Many scientists believed it was impossible to condense permanent gases such as oxygen and nitrogen. However, Cailletet was determined to challenge these assumptions and demonstrate that gases typically perceived as immutable could indeed be transformed into liquids.
The Breakthrough: Liquefaction of Oxygen
One of the most significant moments in Cailletet's career occurred in 1877 when he successfully liquefied oxygen—a feat that had eluded scientists for years. Cailletet's approach involved an innovative method of compressing the gas while simultaneously cooling it to extremely low temperatures. By subjecting oxygen to this combined process within a specially designed apparatus, he achieved an unprecedented scientific breakthrough.
On December 2, 1877, Cailletet reported observing droplets of liquefied oxygen in his laboratory in Paris. This landmark experiment not only validated his theoretical predictions but also shattered long-standing assumptions about the nature of permanent gases. His success was quickly corroborated by other scientists, marking the beginning of a new era in the study of gases.
Cailletet's method laid the groundwork for further advancements in cryogenics—the science of producing and maintaining low temperatures—and provided a crucial underpinning for future research in calorimetry and gas behavior.
Impact on Science and Technology
The implications of Cailletet's work extended far beyond academic circles, influencing a wide range of practical applications. The ability to liquefy gases such as oxygen and nitrogen proved invaluable in various industries, including medicine, where it facilitated the development of modern anesthetics and medical gases.
The burgeoning field of aerodynamics also benefited from Cailletet's contributions, as understanding the behavior of gases under different states became essential in the design and testing of aircraft. Additionally, cryogenics found applications in food preservation and the storage of biological materials, paving the way for techniques that are still in use today.
Recognition and Legacy
In acknowledgment of his accomplishments and pioneering spirit, Louis Paul Cailletet received numerous accolades during his lifetime. Among these were the prestigious Montyon Prize from the French Academy of Sciences and the Légion d'Honneur, reflecting both his scientific achievements and his contributions to French industry.
Cailletet's legacy is enshrined in the ongoing exploration and application of cryogenics, as well as in the continued study of thermodynamics and materials science. By transforming our understanding of gases, he not only expanded the horizons of scientific inquiry but also catalyzed innovation across multiple sectors. His seminal experiments have left an indelible mark on the scientific landscape, underscoring the profound impact that one dedicated individual can have on the world.
Louis Paul Cailletet's story is a testament to the spirit of discovery and the relentless pursuit of knowledge. As we reflect on his contributions, it becomes clear that his work set the stage for future scientific advances, forever altering our perception of the physical universe.
The Scientific Rivalry: Cailletet and Pictet
Amidst the excitement following Cailletet's groundbreaking success with the liquefaction of oxygen, a fascinating episode unfolded in the scientific community, showcasing both the competitive and collaborative spirit inherent in scientific discovery. The same year that Cailletet achieved his breakthrough, another scientist, Raoul Pictet of Switzerland, claimed to have attained similar results using a different method. This simultaneous revelation added a layer of intrigue and rivalry to the narrative of scientific achievement.
Pictet employed a distinct approach to liquefy oxygen, using a combination of carbonic acid release and then sudden decompression to achieve the necessary conditions for liquefaction. His results were announced just days after Cailletet’s, leading to a remarkable convergence in scientific literature. Both methods were remarkable for their ingenuity, and their almost simultaneous success in demonstrating the liquefaction of oxygen highlighted the creative problem-solving and innovation driving the scientific community of the time.
The rivalry between Cailletet and Pictet was largely amicable. It underscored the era's fervent pursuit of knowledge and the spirit of collective advancement. The achievements of both scientists are often regarded as complementary contributions to our understanding of gases, and their concurrent successes led to further interest and investment in cryogenic research.
Beyond Oxygen: Expanding the Study of Gases
Having established the feasibility of liquefying oxygen, Cailletet turned his attention to other gases thought to be "permanent" in their gaseous state. His relentless curiosity and methodical approach led him to explore a range of gases, including nitrogen, hydrogen, and carbon monoxide. By applying his proven methods of extreme pressure and temperature manipulation, Cailletet achieved breakthroughs in these areas too, further confirming his status as a leader in the field of cryogenics.
Through his continued efforts, Cailletet was instrumental in refining the scientific understanding of the laws governing gas behavior. His work helped solidify the principles of thermodynamics and provided empirical evidence supporting theoretical models of gas compression, expansion, and phase transitions. Each step forward attracted the attention of scientists across Europe, spurring research in diverse fields such as astrophysics, meteorology, and chemical engineering.
Innovative Apparatus and Techniques
Central to Cailletet's successes were the innovative tools and technologies he developed to facilitate his experiments. His apparatus for liquefying gases incorporated not only mechanical brilliance but also scientific precision. The devices he engineered allowed for precise control over pressure conditions and temperatures, ensuring the reproducibility and accuracy of his results.
One notable device was the high-pressure chamber he designed, crafted to withstand the immense forces encountered during the compression of gases. Such an invention was crucial for conducting safe and effective experiments, reducing hazards associated with operating under extreme pressures. It set the stage for future advancements in engineering high-pressure equipment, benefiting a variety of industrial and scientific applications.
Cailletet's commitment to improving experimental methodology underscores his role not just as a scientist, but as an innovator adept at bridging theory with practical application. His forward-thinking approaches underscored the potential for lab-based discoveries to translate into real-world solutions and technological progress.
Influence on Future Scientists
The ramifications of Cailletet's work resonated far beyond his own experiments. Future scientific giants—such as Heike Kamerlingh Onnes, who later discovered superconductivity, and James Dewar, who invented the vacuum flask—found inspiration in Cailletet's successes and methods. These scientists built upon his foundational work in cryogenics to further explore the intricate behavior of materials at low temperatures.
The paradigm shift initiated by Cailletet in the understanding of phase transitions and material properties at cryogenic temperatures fostered an environment ripe for breakthroughs in both theoretical and applied physics. His liquefaction of gases directly influenced the work of subsequent generations, enabling scientists to probe deeper into the mysteries of the universe, from subatomic particles to the vastness of cosmic phenomena.
Legacy and Enduring Impact
Louis Paul Cailletet's scientific endeavors transcended the boundaries of 19th-century physics, forging pathways that continue to influence contemporary research and innovation. His name is often celebrated in lectures, textbooks, and scientific discussions, serving as a reminder of the pioneering spirit that defines scientific advancement. The methods and principles he developed continue to inform modern techniques in fields such as quantum mechanics, materials science, and environmental science.
Beyond his immediate scientific contributions, Cailletet's legacy is reflected in the spirit of curiosity and rigorous experimentation he championed. As technology continues to evolve, the foundations laid by Cailletet persist in our ongoing quest to decipher the mysteries of the physical world. His story is a testament to the power of creativity, dedication, and perseverance in advancing human understanding and improving our quality of life.
In summary, Louis Paul Cailletet was far more than an experimenter of physical phenomena; he was a visionary whose work consistently pushed the boundaries of what was considered possible in the scientific explorations of his time. His contributions to the comprehension and manipulation of gases paved the way for numerous technological advancements and scientific inquiries, leaving an indelible mark on both the fields of physics and engineering.
Cailletet's Role in Industrial Advancement
While Louis Paul Cailletet is predominantly celebrated for his scientific contributions, it's essential to recognize how his work influenced industrial advancements. By transforming gases into liquids, he inadvertently catalyzed innovations across multiple sectors. His methods were crucial for industries that required the storage and transport of gases in a form that was more manageable and economical.
The liquefaction of gases, enabled by Cailletet's techniques, revolutionized the metal industry by facilitating safer and more efficient processes. Liquid oxygen, for instance, found its use as an oxidizing agent in steel production, improving the efficiency and outcome of metallurgical processes. Similarly, the ability to store gases in a liquid state simplified their transportation and broadened their industrial applications, thereby boosting the capability of chemical industries to produce fertilizers, fuels, and other essential compounds.
Furthermore, industrial cryogenics made significant strides as a result of Cailletet's pioneering efforts, impacting sectors ranging from space exploration to refrigeration. Liquefied gases became vital in space rocket technology, enabling enhanced propulsion systems crucial for sending humans and satellites into space. The evolution of refrigeration and air conditioning technologies owes much to advancements in understanding gas behavior, ensuring food preservation and comfort in varying climates.
Educational and Public Influence
In addition to his technical legacies, Cailletet's work inspired a deeper public appreciation and understanding of science. During his time, scientific achievement was beginning to capture the public's imagination, with societies eager to promote scientific literacy and curiosity among general audiences. Cailletet, through his lectures and demonstrations, played a role in demystifying complex scientific principles and sharing the tangible benefits of scientific inquiry.
He worked tirelessly to communicate his discoveries beyond academia, engaging with scientific societies and the general public through lectures and publications. His efforts not only highlighted the importance of scientific research but also underscored its potential to drive social and industrial progress.
By doing so, Cailletet contributed to the burgeoning movement for popular science education. His ability to distill complex concepts into relatable narratives catalyzed interest in the sciences, encouraging future generations to explore and pursue careers in scientific disciplines. This public engagement laid the groundwork for a society more informed and supportive of scientific research and technological innovation.
Challenges and Resilience in Research
Despite the accolades and recognition, Cailletet's journey was fraught with challenges and setbacks typical of groundbreaking research. The transition from theoretical predictions to practical experimentation often entailed overcoming substantial technical difficulties and unanticipated failures.
Nonetheless, Cailletet’s resilience and unwavering dedication were instrumental in surmounting these obstacles. He exemplified the practice of engaging iteratively with scientific challenges—an approach dictated by the scientific method, where hypotheses are rigorously tested and refined through experimentation. This persistence not only defined his career but also served as a model of scientific rigor and determination for future researchers.
His ability to troubleshoot experimental issues, adapt existing methodologies, and innovate new techniques was a testament to the flexible and responsive mindset needed to pioneer new scientific frontiers. It highlighted the iterative nature of scientific progress, where failures serve as stepping stones to future successes.
Recognition Beyond His Time
While Cailletet received honors during his lifetime, his contributions have continued to gain recognition well beyond his era. Today, his work is often cited in discussions of early cryogenics and the development of methods to manipulate the states of matter. Institutions and scholars frequently revisit his work, acknowledging the foresight and technical skill he brought to the scientific community.
Educational curricula and museums dedicated to the history of science often feature Cailletet’s breakthroughs, ensuring that his legacy endures not only in academic and industrial contexts but also in cultural and educational spheres. This posthumous acknowledgment reflects the ongoing importance of his pioneering work in understanding fundamental physical processes.
The Broader Impact of Cailletet's Legacy
Louis Paul Cailletet's legacy encompasses more than just his scientific achievements; it represents a paradigm shift in our approach to exploring the natural world. His innovative methods and relentless pursuit of knowledge exemplify the boundless possibilities that arise when a curious mind meets scientific rigor.
Cailletet’s work laid the intellectual and technical groundwork necessary for continued exploration into the thermodynamic properties of gases—a field that has expanded to include research into superconductivity, quantum mechanics, and molecular biology. His legacy invites us to consider the transformative power of science, encouraging inquisitiveness and persistence in the pursuit of innovation and understanding.
Ultimately, Cailletet’s story is one of curiosity and courage, a narrative that continues to inspire scientists striving to unlock the mysteries of the universe through determination and innovation. It is a reminder of the value of scientific inquiry in enhancing both technological capabilities and the collective knowledge of humankind. Through Louis Paul Cailletet's journey, we are reminded of the profound impact that individual contributions can have on the wider tapestry of scientific and industrial progress, urging current and future innovators to push the boundaries of possibility in the relentless quest for discovery.























Comments