John Napier: The Inventor of Logarithms and His Contributions to Mathematics
Introduction to John Napier
Historical Context and Early Life
John Napier, whose full name was John Napier of Merchiston, was a Scottish mathematician and physicist, primarily known for inventing logarithms. Napier was born on April 1, 1550, in Edinburgh, Scotland, amid the tumultuous period of the Scottish Reformation. During his lifetime, Scotland was embroiled in religious and political conflicts, which added to the complexity of his era. Despite the challenging environment, Napier's keen intellect and innovative spirit would propel him to become a significant figure in the history of mathematics.
Background in Education and Family
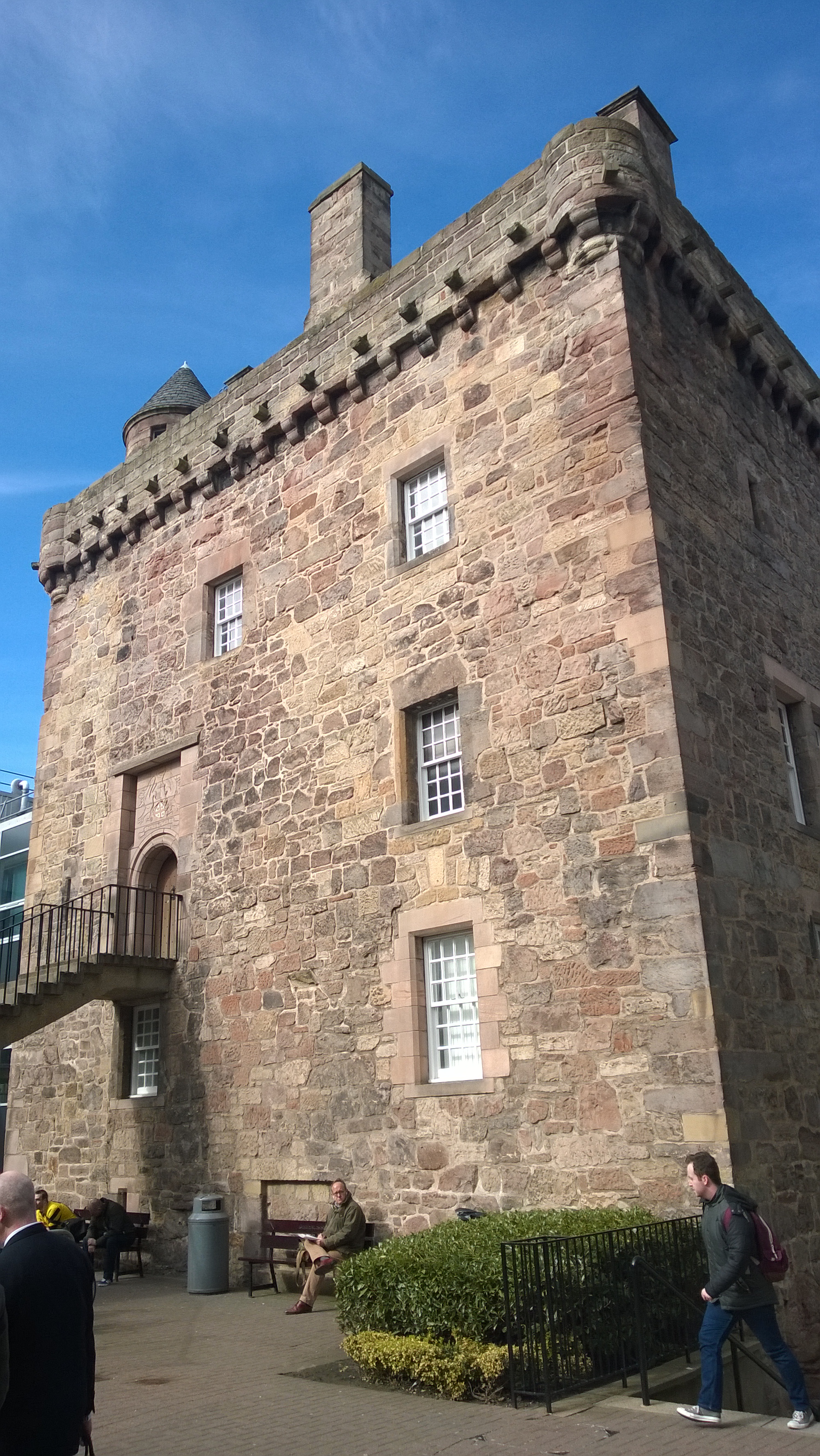
Napier attended the University of St Andrews, where he initially studied theology before eventually shifting his focus to mathematics. After completing his education, Napier returned to his family estate, Merchiston Castle, near Edinburgh, where he would continue his research and writings. The Merchiston estate, owned by the Napiers, provided a conducive environment for Napier to pursue his intellectual pursuits without the immediate pressures of a public education system.
Contribution to Mathematics
While Napier is renowned for his invention of logarithms, his journey into mathematics was not straightforward. Before logarithms, Napier had already made significant contributions through his works, such as ‘Mirifici logarithmorum canonis descriptio’ (Description of the Wonderful Canon of Logarithms) published in 1614. This work would later influence many areas of science and mathematics profoundly.
The Invention of Logarithms
Challenges in Mathematical Computations
During Napier’s time, calculations involving multiplication, division, and square roots were time-consuming and prone to errors. The use of logarithms was a revolutionary solution to these challenges. Napier recognized the necessity for simplifying calculations and devised logarithms as a practical tool for solving complex mathematical problems.
The Concept of Logarithms
Logarithms are a function that transforms multiplication into addition, making calculation more efficient. The basic idea behind Napier's logarithms was to create a numerical scale that allowed complex multiplications to be reduced to simple additions. Specifically, for any two numbers \(a\) and \(b\) with a base \(r\), the logarithm of \(a\) and \(b\) is defined such that \(a \times b\) corresponds to \(\log_a + \log_b\).
Development of the Logarithmic Tables
Napier's development of logarithms involved a complex process that was initially based on a method called "progressions" or "logarithmic scales." He created a set of logarithmic tables that facilitated the calculation of powers and roots of numbers, significantly reducing the laborious nature of these calculations.
The Impact of John Napier's Work
Mathematical Legacy
The concept of logarithms introduced by Napier revolutionized the field of mathematics. His work provided the foundation for later mathematicians to develop more refined methods of calculation, such as slide rules. The widespread adoption of logarithms in the scientific and mathematical communities allowed for the acceleration of discoveries in astronomy, navigation, and engineering.
Pedagogical Advantages
Napier’s invention simplified the teaching of mathematics. Teachers could now use logarithms to demonstrate the relationships between numbers and facilitate a deeper understanding of algebraic concepts. Napier’s books were instrumental in the educational reform of the time, aiding students and scholars in understanding complex mathematical principles more effectively.
Technological and Scientific Applications
The adoption of logarithms had far-reaching implications beyond pure mathematics. In the realm of science, particularly in astronomy, Napier’s logarithms proved to be a powerful tool. Astronomers could now perform complex calculations with greater accuracy, leading to more precise celestial mappings and the development of new astronomical theories.
Modern Relevance
Although slide rules and manual calculations are now largely obsolete, the principles of logarithms continue to have relevance in modern times. In computer science, logarithms form the basis for the analysis of algorithms, aiding in the understanding of computational complexity. In finance, logarithms are used to analyze growth rates and to calculate compound interest.
Eccentricities and Controversies
Personal Life and Relationships
Despite his revolutionary contributions, Napier’s personal life was marked by controversy and enmity. He had a strained relationship with his brother, Charles, who was a prominent lawyer in Edinburgh. The friction between them led to legal battles that were characteristic of the era, but Napier’s intellectual achievements overshadowed these personal disputes.
Unorthodox Theories
In addition to his work in mathematics, Napier also developed some theoretical proposals that were not widely accepted. In his treatise "A Plaine Discovery of the Whole Revelation of St. John," Napier posited that the Antichrist would rise in the 17th century, which was a subject of much debate and controversy in his time. These unconventional theories did little to enhance his reputation among the academic and religious establishments.
Legacy and Memorials
Napier's legacy is celebrated in various forms, including a statue in St Giles' Cathedral in Edinburgh. The University of Edinburgh awards the "Napiers" medal annually in recognition of outstanding contributions in mathematical sciences. His pioneering work continues to be recognized and studied in educational institutions worldwide.
Conclusion
John Napier's contributions to mathematics were profound and far-reaching. His invention of logarithms not only simplified calculations and made them more accurate but also laid the groundwork for significant advancements in science and technology. While his personal life was marked by some controversy, his mathematical legacy continues to inspire and influence generations of mathematicians and scholars. Through his work, Napier not only advanced the field of mathematics but also demonstrated the transformative power of innovation and intellectual rigor.
The Development and Reception of Napier's Logarithms
Initial Publication and Reception
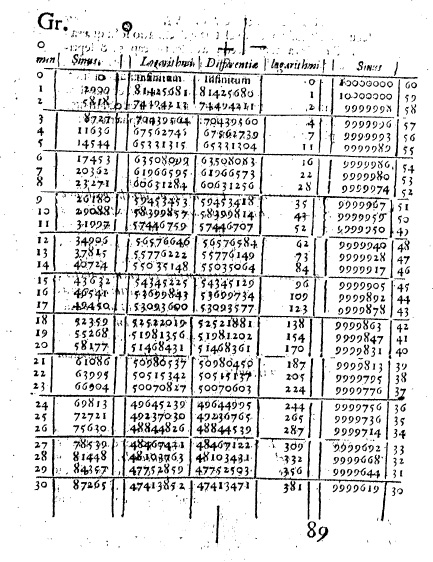
Napier's work, "Mirifici Logarithmorum Canonis Descriptio," was first published in 1614, and it quickly gained widespread attention. The initial reception was mixed; while some mathematicians were intrigued by the simplicity and efficiency of logarithms, others found the concept difficult to grasp. The publication contained 90 pages of text and over 5700 logarithms for sine values, which were computed at every minute interval from 0° to 90°. These tables were meticulously compiled and were designed to aid astronomers and navigators in their calculations.
Collaboration with Briggs
One of the most notable figures who contributed to the popularization of Napier's logarithms was Henry Briggs, an English mathematician. Briggs admired Napier's work immensely and began corresponding with him. Their collaboration was crucial in refining and expanding the concept of logarithms. Briggs proposed a base 10 logarithm system (common logarithms), which Napier initially rejected but later adopted. This change significantly simplified the application of logarithms in everyday calculations.
Evolution of Logarithmic Theory
Over time, Napier continued to refine his theories and methods. In the following years, he published additional works such as "Constructio,\" in which he further detailed the construction of his logarithmic tables. These works were instrumental in solidifying the foundations of logarithmic theory. Napier's contributions were not limited to logarithms alone; he also wrote extensively on spherical trigonometry and geometry, both of which played significant roles in astronomical studies of the era.
Astronomical Applications
Napier's work had a profound impact on astronomy. The calculations required for determining positions on the celestial sphere, computing celestial motions, and predicting eclipses were notoriously complex. Napier's logarithms provided astronomers with a tool to handle these calculations more efficiently. For instance, in his work "Uralem, seu Cosmography, sive Cosmologia,\" Napier described how logarithms could be applied to solve spherical trigonometric equations, making astronomical computations more accurate and less time-consuming.
Impact on Navigation and Cartography
The applications of Napier's logarithms extended beyond astronomy to navigation and cartography. Mariners needed to navigate using complex geographical data, and Napier's methods helped simplify these calculations. The use of logarithms in navigation allowed for more precise determination of latitude and longitude, leading to safer and more reliable sea voyages.
Scientific Instruments and Slide Rules
The invention of logarithms also contributed to the development of practical scientific instruments. One of the most famous was the slide rule, invented independently in Europe. Slide rules utilized Napier's principles and became an indispensable tool for engineers, scientists, and navigators. The simplicity and efficiency of slide rules led to their widespread adoption, even long after paper tables were no longer commonly used.
Napier's Other Contributions to Mathematics and Science
Spherical Trigonometry
Beyond logarithms, Napier made significant contributions to spherical trigonometry. His work "A Plaine Discovery\" not only described logarithms but also included valuable insights into spherical trigonometry, essential for astronomical and navigation calculations. Napier's methods for solving spherical triangles were ahead of his time and continued to be used well into the 17th century.
Geometry and Algebra
Napier was deeply interested in geometry and algebra, although his work in these areas was not as extensive as his contributions to logarithms. Nevertheless, his geometric explorations paved the way for future mathematicians to build upon his ideas. One of his notable geometric contributions was the introduction of the concept of "Napier's Bones,\" a device that used rods to perform multiplication.
Theoretical Proposals
While Napier's mathematical work was lauded, his theological and metaphysical speculations were often criticized during his lifetime. His belief in the Antichrist and his apocalyptic views occasionally overshadowed his mathematical legacy. However, it's important to note that his theoretical proposals, while not strictly related to mathematics, still reflected the intellectual landscape of his time and sparked debates within religious circles.
Legacy in Education
Napier's work profoundly influenced mathematical education. His treatises, particularly "Descriptio,\" became standard texts in universities and schools across Europe. The clarity and depth of his explanations helped students grasp complex mathematical concepts, thereby enhancing the quality of mathematical pedagogy.
Economic and Social Impact
Beyond academia, Napier's logarithms had economic and social implications. The efficiency gains from using logarithms in various fields like commerce and industry helped drive advancements in trade and manufacturing. The ability to perform complex calculations with ease led to increased productivity and innovation.
Contemporary Views and Historical Significance
Modern Interpretation
Today, Napier's contributions are widely recognized for their historical significance. His work on logarithms is considered one of the most important developments in the history of mathematics. The principles he introduced laid the groundwork for modern computational techniques and have influenced countless scientific and technological advancements.
Legacy and Commemoration
Napier's legacy has been commemorated through various means. Statues and memorials are erected in his honor, and his achievements are often highlighted in educational curricula. The University of Edinburgh awards the Napiers Medal annually to recognize groundbreaking contributions in mathematical sciences, continuing Napier's tradition of excellence in mathematics.
Influence on Future Mathematicians
Many mathematicians and scientists have cited Napier as a key inspiration. His innovative approach to problem-solving and his willingness to explore new areas of mathematics encouraged subsequent generations to push the boundaries of knowledge. Notable figures such as Isaac Newton and Pierre-Simon Laplace built upon Napier's work, contributing further to the field of mathematics.
Conclusion
John Napier's contributions to mathematics and science cannot be overstated. His invention of logarithms revolutionized calculations and paved the way for numerous technological and scientific advancements. From simplifying astronomer’s tasks to enabling safer sea journeys, Napier's work had a lasting impact on society. Today, his legacy continues to inspire mathematicians and engineers, and his groundbreaking ideas remain integral to our understanding of mathematics and its applications.
John Napier's Personal Life and Contemporaneous Influences
Family and Personal Life
John Napier's personal life was marked by both achievements and personal dramas. Born into a wealthy family, Napier inherited the Merchiston Castle estate from his uncle Robert Stuart, Lord Arthure, in 1566. The castle, with its extensive lands and natural resources, provided Napier with a comfortable life and the means to indulge his intellectual pursuits. Despite his financial stability, Napier's home life was not without its complexities. His relationship with his brother, Charles, was strained, which led to legal disputes that occupied a significant portion of his late years.
Correspondence and Collaboration
Napier maintained a network of correspondents across Europe, including scholars and mathematicians. His extensive correspondence is a valuable record of intellectual exchange during the early 17th century. These letters, preserved in the National Library of Scotland, provide insight into Napier’s thoughts and collaborations. One of his most significant correspondences was with the German mathematician Johannes Kepler, who shared similar interests in mathematics and astronomical studies.
Legacy and Posthumous Recognition
Following Napier's death in 1617, his work on logarithms continued to garner attention. Over the centuries, his contributions to mathematics have been recognized and celebrated. In 1624, a commemorative stone was placed at the entrance of the Merchiston Castle grounds, and the town of Edinburgh has several streets and landmarks named after him. Today, Napier is remembered not just for his mathematical innovations but also for his broader intellectual contributions.
John Napier in Popular Culture and Modern Perception
Popular Receptions
In the modern era, Napier's legacy has been widely acknowledged in popular culture. His contributions to logarithms are frequently referenced in literature, films, and television shows. For instance, in the popular science documentary series "The Story of Science: Big Ideas,” Napier is highlighted as a key figure in the development of modern mathematics.
Historical Literature and Biographies
Numerous biographical works and historical literature have been devoted to Napier. Notable among these are the books by Alexander Karraker's "John Napier, the Life and Works of a Child of the Renaissance\" and the biography by W. Y. Miksad, which provide in-depth analysis of Napier’s life and achievements. These works offer a comprehensive understanding of Napier’s contributions and the context in which he worked.
Scientific and Academic Discourse
In contemporary academic discourse, Napier’s work is often discussed in the context of the scientific revolution. His logarithmic theory is a focal point of discussions on the advancements in mathematics and their implications for scientific progress. Modern scholars continue to explore how Napier’s ideas have shaped modern computational methods and scientific thought.
Conclusion
John Napier stands as a pivotal figure in the history of mathematics. His invention of logarithms not only revolutionized calculation methods but also paved the way for numerous scientific and technological innovations. Beyond his professional achievements, Napier’s personal life and the way he integrated his intellectual contributions into the larger cultural and historical landscape make him a fascinating figure. His legacy continues to inspire and influence mathematicians, scientists, and scholars worldwide, ensuring that his impact endures through the ages.
In summary, John Napier was more than just a mathematician; he was a visionary whose innovations transcended his time. His work on logarithms remains a cornerstone of modern computational techniques, and his life serves as an inspiration for those who strive to make significant contributions to the world of knowledge. Through his pioneering efforts and enduring legacy, Napier's impact on mathematics and science remains a testament to the power of innovation and intellectual curiosity.





















Comments