Hero of Alexandria: The Ingenious Mathematician and Engineer of Antiquity
Hero of Alexandria, known in Greek as Heron, was an ancient figure whose remarkable contributions to science and engineering are still celebrated today. Active in the first century AD, his works spanned various fields, including mathematics, physics, and mechanics, earning him a place among the most influential minds of antiquity. Hero's inventions and writings not only showcase his innovative spirit but also hint at a deep understanding of fundamental scientific principles that continue to resonate in modern engineering and technology.
Background and Historical Context
Hero lived during a time marked by considerable intellectual activity in the Hellenistic world. Alexandria, where he was based, was a cultural and scientific hub of the ancient world, known for its grand library and academic environment. It attracted scholars from all over, contributing to a rich exchange of ideas and knowledge. This vibrant backdrop undoubtedly influenced Hero, providing him with access to a plethora of knowledge and inspiration from previous luminaries such as Euclid, Archimedes, and Ptolemy.
Despite the lack of extensive biographical details about Hero, his surviving works speak volumes about his intellect and interests. He authored numerous treatises, many of which were later translated into Arabic, Latin, and other languages, ensuring the persistence of his legacy through the ages.
Key Contributions and Works
Hero's influence is particularly notable in his contributions to mathematics and mechanics. One of his most significant mathematical works is "Metrica," a three-volume treatise focusing on geometry and mensuration. In "Metrica," Hero explores calculations related to areas and volumes of various shapes and solids, providing methods and formulas that were ahead of his time. The treatise includes what is now known as "Heron's formula," which calculates the area of a triangle using only the lengths of its sides—a testament to his profound understanding of geometry.
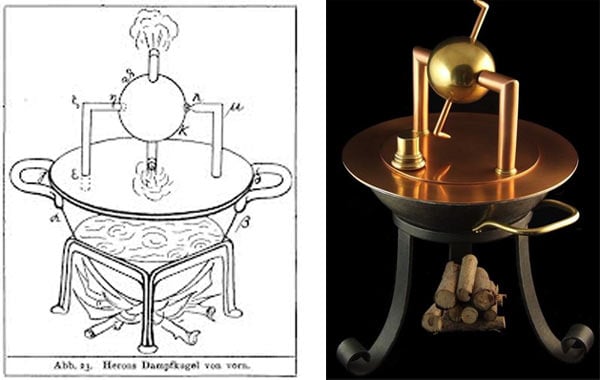
Besides his mathematical endeavors, Hero made significant strides in the field of mechanics. His treatise "Pneumatica" is perhaps the most famous, describing a variety of mechanical devices powered by wind, water, steam, and air pressure. These gadgets, including the aeolipile or Hero's engine, are considered some of the earliest examples of steam-powered technology. The aeolipile, a spherical device that creates rotational motion via steam, is often described as the precursor to the steam engine, highlighting Hero's forward-thinking approach to engineering.
Hero was also adept at designing intriguing automata, often described in his work "Automatopoietic." These automata were mechanical toys and devices that mimicked life-like movements, such as mechanical birds and miniature theaters, showcasing both his creativity and mastery of mechanical principles. These inventions not only delighted audiences of his time but also demonstrated his advanced understanding of automated systems, a field that continues to evolve in modern robotics and AI technology.
Hero's Influence on Mathematics
Hero's contributions to mathematics are particularly significant because they bridge the gap between theoretical and practical applications. His work in geometry and trigonometry laid the groundwork for future mathematical discoveries and provided tools for solving real-world problems. His explorations in optics, particularly in "Catoptrica," delve into the principles of reflection and refraction, concepts that are fundamental to the field of optics today.
The influence of Hero's mathematical insights can be seen in how they were utilized by later scholars across the medieval Islamic world and into the Renaissance. His works were translated and studied extensively, directly impacting the development of mathematical thought in these regions. Hero's methods for solving quadratic equations and his work on geometric constructions were particularly noted for their clarity and practicality, making complex mathematical concepts more accessible to those who followed.
Hero of Alexandria's legacy is marked by his innovative spirit and his ability to merge theoretical knowledge with practical applications. Through his inventions and writings, Hero not only contributed to the scientific progress of his time but also laid foundational stones for the technological advancements that would come centuries later. Whether through his ingenious mechanical creations or his profound mathematical insights, Hero's work continues to inspire and fascinate, highlighting the timeless nature of curiosity and invention. In the next part of this article, we will delve deeper into Hero's experimental techniques and the broader impact of his inventions on subsequent technological developments.
Experimental Techniques and Methodologies
Hero of Alexandria’s approach to science and experimentation was remarkably systematic for his time. He often employed empirical methods, conducting experiments and utilizing practical observations to inform his theories and inventions. This empirical approach is evident in his work "Pneumatica," where Hero meticulously detailed the construction and operation of various mechanical devices, providing clear descriptions and diagrams. These early forms of technical documentation not only communicated complex ideas but also underscored the importance of replicable results—a cornerstone of the scientific method that would be formalized much later.
Hero's work illustrated a deep curiosity about natural phenomena and physical forces such as pressure and gravitation. In "Pneumatica," he explored the properties of air and steam, which he used to create effects such as fountains, musical instruments, and automatic doors. These devices demonstrated not only the marvels of engineering but also the practical applications of scientific principles, making them useful tools for further exploration of physical sciences.
In his treatise "Mechanica," Hero discussed pulleys, levers, and winches, which are fundamental to understanding mechanical advantage. The way he broke down complex mechanical systems into simpler components highlights an early understanding of system thinking, a crucial concept in modern engineering and design processes. By experimenting with these mechanical concepts, Hero contributed to a rudimentary understanding of physics, anticipating some of the principles that would eventually form the backbone of classical mechanics.
The Aeolipile: A Marvel of Ancient Engineering
One of Hero’s most remarkable inventions is certainly the aeolipile, often cited as the first recorded steam engine. The aeolipile consists of a hollow, sealed vessel with one or more projecting nozzles that rotate when steam is expelled from them. Hero’s device made use of steam’s momentum to produce rotational motion, demonstrating the principle of jet propulsion well before its time.
The device was primarily intended for amusement and demonstration purposes rather than practical applications, which speaks to the then-limited understanding of the potential of steam power. Nevertheless, the aeolipile symbolized a significant conceptual leap in utilizing steam to generate mechanical motion. It showcases an early grasp of the transformative power of heat energy—a principle that would not see widespread application until the Industrial Revolution, nearly two millennia later.
Hero’s conceptual understanding, as showcased in the aeolipile, was a profound precursor to the realization of steam engines used in transportation and industry. It illustrates how ancient discoveries, although not immediately exploited, can lay the groundwork for future technological advancements.
The Impact on Subsequent Technological Developments
Hero of Alexandria’s work did not stop with his lifetime. His contributions became the bedrock upon which later scholars and engineers built, particularly during the medieval period. The translation of his works into Arabic by scholars in the Islamic Golden Age played a pivotal role in Caging up Hero’s scientific insights, contributing to advancements in fields such as optics, mechanics, and engineering.
His treatises served as educational resources that informed the works of Islamic inventors and thinkers like Al-Jazari and Al-Khwarizmi. For instance, Hero’s explorations in hydraulics and automata clearly influenced Al-Jazari’s mechanical creations, which included sophisticated water clocks and mechanical automata. In this way, Hero’s legacy was woven into the fabric of an increasingly global body of technical knowledge.
During the Renaissance, the resurgence of interest in Greek and Roman texts brought Hero’s works back into the spotlight in Europe. His influence can be seen in the emerging focus on empirical methods and experimentation that characterized this period. Thinkers such as Leonardo da Vinci studied and were inspired by Hero’s works, drawing parallels between Hero’s innovations and their engineering endeavors.
Hero’s pioneering spirit and scientific methodologies underscore the timelessness of curiosity-led inquiry. By daring to merge theoretical exploration with tangible, mechanical construction, Hero fashioned a legacy that has transcended time—a testament to the enduring power of human ingenuity and the continuous quest to understand and manipulate the world around us. In the next continuation of this article, we will explore the evolution of steam technology from Hero’s aeolipile to the industrial steam engines that reshaped the world, highlighting the transformative nature of innovation across the ages.
The Evolution of Steam Technology
Hero of Alexandria's aeolipile is a fascinating historical landmark in the evolution of steam technology. While it was largely confined to demonstrations during Hero’s era, the basic principles it showcased would eventually ignite a technological revolution. Fast forward several centuries to the 18th century, when the latent potential of steam power was finally realized in the form of practical steam engines.
The Industrial Revolution saw steam engines become a focal point of technological advancement, driving machinery in mills, factories, and locomotives. Innovators like Thomas Newcomen and, later, James Watt expanded upon the basic principles of steam power that Hero had observed. Watt’s improvements, including the separate condenser, significantly increased the efficiency of steam engines, allowing them to power a range of industrial functions and transportation systems, effectively reshaping the global economy and society.
Hero’s vision of employing steam for motion laid the intellectual groundwork for these advancements. While his inventions did not directly lead to the steam engines of the Industrial Revolution, the underlying concepts were undeniably foundational. Hero’s aeolipile exemplifies how ideas can lay dormant, awaiting the right conditions—economic, cultural, and technological—to blossom fully.
The Legacy of Hero’s Innovations
Hero of Alexandria remains an inspiring figure in the annals of scientific and engineering history. His broad approach to the natural world—encompassing mathematical rigor, experimental observation, and creative ingenuity—offers a model for interdisciplinary exploration. Hero’s work exemplifies how the synthesis of different fields can yield innovations that are both imaginative and scientifically robust.
The modern world continues to reflect his legacy. The concepts he explored in mechanics and pneumatics reverberate through numerous modern technologies, from simple machines to complex automated systems. In robotics and automation, for instance, Hero’s pioneering automata serve as historical antecedents to present-day advancements. His explorations of life's mechanics still resonate with engineers and scientists designing intricate and responsive robotic systems.
Hero’s approach also paved the way for a philosophy of learning and discovery that values experimentation as a crucial component of scientific inquiry. His systematic methodologies highlight an early understanding of problem-solving and design thinking, principles that remain vital in today’s technological and scientific endeavors.
Conclusion: Celebrating an Ancient Visionary
In commemorating Hero of Alexandria, we celebrate more than just an ancient inventor; we acknowledge a visionary whose work transcends time and place. Hero’s fusion of theory and application, his relentless curiosity, and his innovative spirit are underscored in each of his creations and writings. These artifacts and ideas have perpetuated through millennia, inspiring countless generations to push the boundaries of what was thought possible.
Hero's story reminds us of the enduring nature of discovery and invention. The pursuit of knowledge, as shown through his life and work, is an ever-evolving journey. It teaches us that the seeds of innovation often require patience, time, and the right environment to grow.
As we develop new technologies that continue to transform our world, Hero's influence is a source of inspiration, reminding us of the power of imagination combined with scientific inquiry. His legacy stands as a bridge from the ancient world to modern times, a testament to the timeless and universal quest to understand and harness the forces of nature for the benefit of humankind. Hero of Alexandria embodies the spirit of innovation that drives humanity to explore the complexities and wonders of the universe, prompting us to ask: What else can we achieve when curiosity leads the way?





















Comments