Encryption vs Decryption: Unraveling the Secrets of Cyber Security
Understanding the Basics: What Are Encryption and Decryption?
With the advent of the digital age, cybersecurity has become more crucial than ever before. At the heart of protecting sensitive information is the concept of encryption and decryption. Let's dive into these two fundamental yet critical processes.
Encryption: The Art of Concealment
Encryption is the process of converting plain text or data into a coded form, making it unreadable without a specific key or algorithm. This transformation ensures that even if unauthorized parties intercept the data, they cannot understand its contents. Imagine encrypting your messages like locking them in a secure box that can only be opened with a particular key. This key, often referred to as the decryption key, is necessary to read the encrypted content back into its original form.
There are various types of encryption techniques, including symmetric and asymmetric encryption:
- _symmetric encryption:_
This method uses the same secret key for both encryption and decryption. The most common symmetric encryption algorithms include AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) and DES (Data Encryption Standard). - asymmetric encryption (_public key cryptography):_
In this approach, there are two different keys: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. The RSA algorithm is a widely used example of asymmetric encryption.
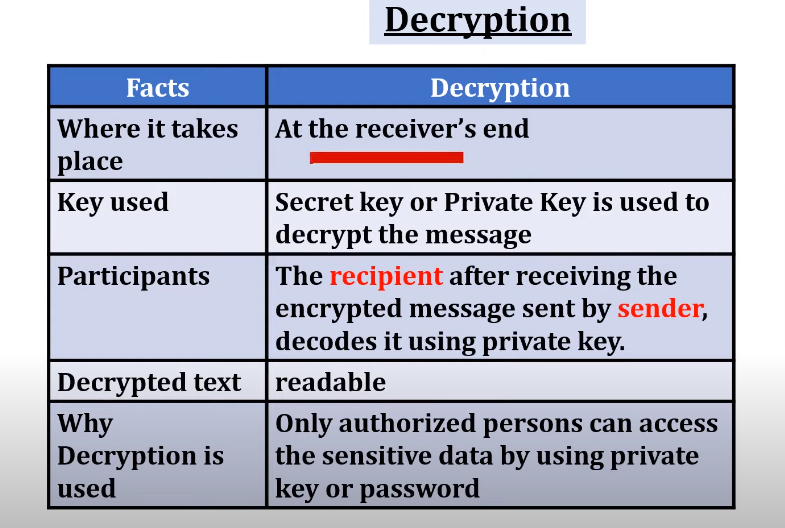
Decryption: Reversing the Lock
Decryption is simply the reverse process of encryption. It involves taking the encrypted data and using a specific decryption key to recover the original message or data. Decryption ensures that only authorized parties who have the correct key can access the information. Think of decryption as being able to unlock the box that was locked earlier using the key that matches the lock.
Decryption is not just the inverse of encryption; it’s an essential component in maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of data throughout its lifecycle. Whether it's storing data securely, transmitting information over the internet, or processing transactions, decryption plays a vital role in ensuring data remains protected.
The Importance of Encryption and Decryption in Today's World
In today's digital landscape, where data breaches and cyber attacks are becoming increasingly common, encryption and decryption are not mere theoretical concepts but practical tools that safeguard sensitive information.
Data Privacy: Encryption helps protect personal and confidential data stored on devices, servers, and during transmission. Banks, healthcare providers, and other industries rely heavily on encryption to ensure that sensitive customer information remains confidential.
Secure Communication: Encryption is at the core of secure communication protocols such as HTTPS, which ensures that any data transmitted between a web browser and a website remains secure from eavesdroppers. Messaging apps also use encryption to protect the privacy of their users' conversations.
Cybersecurity: Encryption is a key element in implementing strong security measures to protect against unauthorized access and cyber threats. By encrypting data, organizations can prevent data leaks and ensure that sensitive information remains in safe hands.
How Encryption and Decryption Work Together in Real-World Scenarios
The interplay between encryption and decryption is fundamental in maintaining the security and privacy of digital information.
Scenario 1: Secure Data Storage
Consider a scenario where a company needs to store sensitive customer data on a server. Before saving any data, the information is processed through an encryption algorithm using a strong key. Once the data is encrypted, even if an attacker gains unauthorized access to the server, they will find nothing more than meaningless ciphertext. The actual data can only be retrieved through the use of the correct decryption key, ensuring that only authorized personnel can access it.
Scenario 2: Secure Email Communication
Email services often employ end-to-end encryption to protect user communications. When a user sends an email containing sensitive information, the message is encrypted on the sender's device using the recipient's public key. Upon reaching the recipient's inbox, the message is automatically decrypted using the recipient's private key. This ensures that the email remains confidential and safe from eavesdroppers, even when passing through various internet service providers and servers.
Scenario 3: Secure Financial Transactions
In financial transactions, encryption is essential for ensuring that payment information is not intercepted during transmission. The credit card details and other relevant information are encrypted before they are sent via the internet. The transaction is then verified by a secure payment gateway, which decrypts the information, confirming the transaction, and ensuring all data is secure and accurate.
Hence, understanding encryption and decryption is crucial for anyone involved in cybersecurity, from software developers to IT professionals and individuals concerned about online privacy.
Key Mechanisms and Protocols
Key Generation and Exchange
Key Generation involves creating the cryptographic keys necessary for encryption and decryption. These keys should be sufficiently complex to ensure security. A strong key is a sequence of random bits that is unique and unpredictable. There are various methods for generating keys, including using hardware random number generators and software-based algorithms. In symmetric encryption, a single key is used for both encryption and decryption, while in asymmetric encryption, a pair of keys—a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption—is generated.
Key Exchange is another critical aspect. Secure key exchange ensures that the parties involved in a communication can share the necessary keys without compromising their security. Protocols like Diffie-Hellman key exchange allow two parties to establish a shared secret key over an insecure channel, ensuring that the key remains confidential and secure.
Password-Based Encryption
Password-Based Encryption (PBE) is a method where a user's password (a string of characters) is used as the key for encryption and decryption. This ensures that the encryption key is not stored permanently, but is derived from the user's password each time they want to perform an operation. PBE is commonly used in applications like password managers and secure file storage. However, it requires robust handling of the password to prevent unauthorized access. Common algorithms used in PBE include PBKDF2 (Password-Based Key Derivation Function 2) and bcrypt.
One of the main challenges with PBE is ensuring that the password itself is secure. Users must be educated about creating strong passwords and using secure practices, such as not sharing their passwords and avoiding reuse.
Cypher Text and Plain Text
Understanding the difference between ciphertext and plaintext is crucial. Plaintext refers to the original, readable message or data that is to be encrypted. Conversely, ciphertext is the transformed message or data after it has been encrypted. The transformation is performed using a specific algorithm and key. Once the plaintext is encrypted, it becomes ciphertext, which appears as a random string of characters. Only the appropriate decryption process can convert the ciphertext back into the original plaintext.
For example, if a company sends an email containing sensitive information, the plaintext is the original message, while the ciphertext is the encrypted version. Only the intended recipient with the correct decryption key can convert the ciphertext back into the original plaintext. This process ensures that data remains secure during transit and storage.
Security and Vulnerabilities
Security Risks in Encryption
While encryption is an incredibly powerful tool, it is not entirely immune to vulnerabilities. Some common security risks include:
- Weak Keys: Poorly generated or weak keys can make encryption vulnerable to brute force attacks, where an attacker tries to decrypt data by guessing the key through trial and error.
- Improper Encryption Practice: Inconsistent or careless use of encryption can lead to security breaches. For instance, failing to properly store encryption keys or using weak encryption algorithms can compromise security.
- Side-Channel Attacks: These attacks exploit the physical implementation of a cryptographic system to obtain information about the keys or algorithms. For example, timing attacks can measure the time taken to perform cryptographic operations to infer information about the key.
Organizations must implement robust security practices and choose strong encryption algorithms and keys to mitigate these risks. Regular security audits and updates are also crucial to ensure that encryption systems remain secure.
Security Risks in Decryption
Decryption also faces its own set of security challenges:
- Misuse of Decryption Keys: The private key used for decryption must be stored and managed securely. Unauthorized access to the private key can allow an attacker to decrypt all encrypted data. Proper key management practices, such as encryption, access controls, and secure storage, are necessary to protect the private key.
- Exploitation of Weak Protocols: Insecure protocols that support weak or outdated encryption algorithms can be easily decrypted. For example, using outdated algorithms like MD5 for encryption can make the system vulnerable to attacks.
- Security Breaches: Even with strong keys and algorithms, a security breach can still result in the exposure of private keys or plaintext data. Robust cybersecurity measures, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption best practices, are essential to prevent such breaches.
Organizations must stay vigilant and adopt best practices to ensure that the decryption process remains secure and that sensitive data remains protected.
Common Misconceptions
Misconcept 1: Encryption Ensures Absolute Security
One of the most common misconceptions is that encryption provides absolute security. While encryption is a powerful tool for securing data, it is not foolproof. As mentioned earlier, weak keys, poor implementation, and side-channel attacks can compromise the security of encrypted data. Therefore, it is crucial to understand that encryption adds another layer of security but does not eliminate all risks.
For example, if a company uses a weak encryption key or an outdated algorithm, even if the data is encrypted, it can still be vulnerable to attacks. Additionally, improper key management or handling of plaintext data can also compromise security. Therefore, a comprehensive security strategy that includes encryption is necessary to protect against various types of threats.
Misconcept 2: Decryption Always Requires a Private Key
Another common misconception is that decryption always requires a private key. While this is generally true, there are exceptions. For instance, symmetric encryption uses the same key for both encryption and decryption. In such cases, the same key used for encryption is required to decrypt the data. The use of symmetric keys makes it crucial to securely manage and distribute these keys.
On the other hand, asymmetric encryption uses a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. In this scenario, the private key is typically the only key required to decrypt the data. However, the public key can be freely distributed as long as it is used for encryption. Understanding the differences between symmetric and asymmetric encryption is essential to implementing them effectively and securely.
Future Trends in Encryption and Decryption
Quantum Computing and Its Impact
Quantum computing is transforming the field of cryptography. Quantum computers have the potential to perform calculations much faster than classical computers, which could render many traditional cryptographic algorithms obsolete. However, quantum computing also offers new opportunities for encryption, such as quantum key distribution (QKD), which uses quantum properties to ensure secure communication.
QKD relies on the principles of quantum mechanics to create a secure key exchange. Any attempt to intercept the communication would be immediately detected due to the non-local properties of quantum states. This has the potential to revolutionize the way secure communication is handled, making it virtually unbreakable.
Biometric Encryption
Biometric encryption combines encryption with biometric data such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or voice patterns. This approach enhances security by eliminating the need for users to remember complex passwords. Instead, the biometric data is used to generate encryption keys, making the process more convenient and secure.
One challenge with biometric encryption is ensuring that the biometric data is securely collected, stored, and managed. Organizations must implement robust data protection measures to prevent the misuse of biometric data. Additionally, the key generation and management process must be foolproof to avoid compromising the security of the encrypted data.
Conclusion
Encryption and decryption are indispensable tools in the fight against cyber threats. They provide the necessary safeguards to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access and breaches. By understanding the principles, mechanisms, and challenges of encryption and decryption, organizations can implement robust security measures to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their data.
As technology continues to advance, new methods and protocols will emerge, further enhancing the capabilities of encryption and decryption. Staying informed and vigilant about the latest trends and best practices is crucial for maintaining strong cybersecurity measures.
Conclusion (Continued)
Encryption and decryption play a pivotal role in modern cybersecurity. By understanding the fundamental concepts and practices associated with these processes, organizations and individuals can better protect their data from cyber threats. Regular updates, robust security practices, and vigilance are essential to ensure that encryption and decryption continue to provide the necessary safeguards.
As technology advances, new challenges and opportunities will arise. Quantum computing, biometric encryption, and other emerging technologies are transforming the cryptographic landscape. By staying informed and adopting best practices, we can navigate the complex world of encryption and decryption and continue to safeguard our digital assets.
Additional Tips for Strengthening Your Encryption Practices
Here are some additional tips to help you enhance your encryption and decryption practices:
1. Use Strong Encryption Algorithms
Always opt for strong and well-established encryption algorithms such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) with a key length of 256 bits. Avoid using outdated or weak algorithms, such as DES or 3DES, as they are more susceptible to security breaches.
2. Implement Key Management Best Practices
Proper key management is critical for the security of your encrypted data. Use key management systems (KMS) to securely store and manage encryption keys. Implement access controls, regular key rotations, and secure key backups to prevent unauthorized access and ensure key availability.
3. Stay Updated with Security Patches and Updates
Regularly update your encryption software and protocols to address newly discovered security vulnerabilities. This ensures that you have the latest protections against emerging threats. Stay informed about updates and patches from your software vendors to protect your encryption systems effectively.
4. Educate Your Team
Security is a collective responsibility. Educate your team on the importance of encryption and the best practices for secure data handling. Training and awareness programs can help ensure that everyone in your organization follows secure practices, reducing the risk of human error leading to data breaches.
5. Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide not just a password but also another form of verification, such as a fingerprint, a security token, or a one-time code. MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, making it difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access even if they have a user’s login credentials.
6. Monitor and Audit Encryption Processes
Regularly monitor and audit your encryption processes to detect any security issues. This includes monitoring key usage, evaluating the health of encryption keys, and reviewing access logs. Continuous monitoring and auditing help identify potential security risks and ensure that your encryption practices remain effective.
Final Thoughts
Encryption and decryption are powerful tools in the fight against cybercrime and data breaches. By understanding these processes and implementing best practices, we can protect sensitive information and maintain the integrity and confidentiality of our digital assets. Stay informed, stay vigilant, and stay secure.
Remember, encryption and decryption are not just technical processes; they are critical components of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy. By staying up-to-date with the latest trends, best practices, and emerging technologies, we can continue to safeguard our digital world.




















Comments