DeFi: A Revolution in the Financial Sector
Decentralized Finance, or DeFi, is fundamentally reshaping the global financial landscape. By leveraging blockchain technology, DeFi creates an open, permissionless alternative to traditional banking. This innovative system allows users to access financial services directly from each other, bypassing centralized intermediaries like banks and brokers.
What is Decentralized Finance (DeFi)?
DeFi represents a paradigm shift in how financial services are built and delivered. At its core, DeFi is the application of distributed ledger technology to financial services, providing instruments through smart contracts on programmable blockchains. The term itself was formally coined in 2018 by Ethereum developers, marking the beginning of a new financial era built on transparency and accessibility.
Unlike traditional finance (TradFi), which relies on centralized institutions to facilitate transactions, DeFi enables peer-to-peer interactions. This system is mediated by self-executing software programs instead of institutional gatekeepers, creating a more open and inclusive financial ecosystem for users worldwide.
The Fundamental Shift from Centralized Systems
The traditional financial system operates on a centralized model where institutions act as trusted third parties. Banks, credit card companies, and stock exchanges control the flow of money and information. DeFi challenges this model by creating a trustless environment where the code itself enforces the rules.
This shift eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing costs and increasing efficiency. Users maintain direct control over their assets through private keys, fundamentally changing the relationship individuals have with their money and financial services.
How DeFi Works: The Core Mechanics
The entire DeFi ecosystem is powered by a combination of blockchain infrastructure and smart contract technology. These components work together to create a seamless, automated financial system that operates without central control.
The Power of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts form the backbone of all DeFi applications. These are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They automatically facilitate, verify, and enforce the negotiation or performance of a transaction when predetermined conditions are met.
Smart contracts run on open-source software maintained by developer communities, ensuring transparency and collective oversight. This eliminates the need for manual approval processes and human intermediaries, making financial operations faster and more efficient.
Key Operational Principles of DeFi
DeFi operates on several defining principles that distinguish it from traditional finance:
- Automation: Transactions execute automatically through smart contracts without human intervention
- Transparency: All transaction history is publicly visible on the blockchain
- Accessibility: Participation requires only an internet connection and digital wallet
- Speed: Transactions settle in minutes rather than days
- Non-custodial: Users maintain full control of their assets through private keys
Major Financial Services in DeFi
DeFi platforms have democratized access to a comprehensive range of financial services that were previously available only through traditional institutions. The ecosystem now offers sophisticated alternatives to conventional banking products.
Lending and Borrowing Platforms
DeFi lending protocols allow users to lend their digital assets and earn interest, or borrow against their cryptocurrency holdings. These platforms use algorithmic matching rather than credit scores, making lending more accessible. Interest rates are typically determined by supply and demand dynamics rather than set by central authorities.
The process is completely automated through smart contracts, eliminating the need for loan officers or approval committees. Borrowers can access funds almost instantly by providing collateral in cryptocurrency, which is held in smart contracts until the loan is repaid.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs)
Decentralized exchanges enable peer-to-peer trading of digital assets without intermediaries. Unlike traditional exchanges that hold users' funds, DEXs allow traders to maintain control of their private keys throughout the transaction process. This significantly reduces counterparty risk and eliminates the need for custodial services.
DEXs use automated market maker (AMM) models rather than order books, allowing for permissionless trading of any token pair. Liquidity is provided by users who deposit assets into liquidity pools, earning fees from trades executed against their deposited assets.
Yield Farming and Staking
Yield farming involves providing liquidity to DeFi protocols in exchange for rewards, typically in the form of additional tokens. This has become a popular way for investors to generate returns on their cryptocurrency holdings. The returns can be significantly higher than traditional savings accounts, though they come with increased risk.
Staking involves locking up cryptocurrencies to support network operations, such as validating transactions on proof-of-stake blockchains. In return, stakers receive rewards, creating a way to earn passive income while contributing to network security and functionality.
DeFi represents a competitive, contestable ecosystem where multiple protocols compete to offer superior services and user experiences, driving innovation forward.
The Transformative Benefits of DeFi
The adoption of decentralized finance brings numerous advantages that address limitations inherent in traditional financial systems. These benefits extend beyond technical improvements to encompass broader social and economic impacts.
Financial Inclusion and Global Accessibility
DeFi fundamentally democratizes finance by allowing anyone with an internet connection to access sophisticated financial services. This is particularly transformative for the approximately 1.7 billion adults globally who remain unbanked. These individuals can now participate in financial markets without needing approval from traditional institutions.
The pseudonymous nature of DeFi transactions provides privacy while maintaining transparency of the underlying transactions. Users can engage with financial services without submitting extensive personal documentation or meeting minimum balance requirements that often exclude lower-income populations.
Enhanced Transparency and Security
Every transaction on DeFi protocols is recorded on a public blockchain, creating an immutable and transparent audit trail. This level of transparency is unprecedented in traditional finance, where transaction details are typically private. The open-source nature of most DeFi projects allows for community auditing of code, potentially identifying vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
While DeFi has experienced security incidents, the transparent nature of blockchain means that exploits are publicly visible and can be addressed by the community. This contrasts with traditional finance, where security breaches may go undisclosed for extended periods.
Cost Reduction and Efficiency Gains
By eliminating intermediaries, DeFi significantly reduces transaction costs associated with financial services. Traditional cross-border payments that involve multiple banks and currency conversions can incur substantial fees, while DeFi transactions typically cost a fraction of these amounts. The automation of processes through smart contracts also reduces operational costs.
Transaction settlement occurs much faster in DeFi ecosystems compared to traditional banking systems. While international bank transfers can take several days to clear, DeFi transactions typically confirm within minutes, regardless of the geographical location of the participants.
The Technical Architecture Powering DeFi
The sophisticated functionality of Decentralized Finance rests on a robust technical foundation. This architecture enables the complex financial operations that define the DeFi ecosystem while maintaining security and decentralization.
The DeFi Stack: Settlement, Application, and Interface Layers
DeFi systems operate through a layered model often conceptualized as the DeFi Stack Reference (DSR) model. This framework consists of three primary components that work together to deliver financial services. Each layer has distinct responsibilities while interacting seamlessly with the others.
- Settlement Layer: The underlying blockchain infrastructure that records and validates all transactions
- Applications Layer: DeFi protocols that implement specific financial functions like lending or trading
- Interfaces Layer: User-facing applications and wallets that enable interaction with DeFi services
The settlement layer provides the foundational security and consensus mechanism. The applications layer contains the business logic encoded in smart contracts. The interfaces layer translates this functionality into user-friendly experiences accessible to non-technical participants.
Ethereum and the Multi-Chain Ecosystem
Ethereum has emerged as the primary blockchain for DeFi applications, particularly because of its pioneering smart contract functionality. The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) provides a standardized environment for executing decentralized applications. This standardization has fostered tremendous innovation and compatibility across different protocols.
However, the DeFi ecosystem is expanding beyond Ethereum to include multiple blockchain networks. This multi-chain approach addresses scalability challenges and offers users more options. Cross-chain bridges and interoperability protocols are becoming increasingly sophisticated, allowing assets and data to move seamlessly between different blockchain environments.
Key DeFi Protocols and Applications
The DeFi landscape features a diverse array of protocols, each specializing in different financial functions. These applications work together to create a comprehensive alternative to traditional finance.
Leading Lending Protocols
Aave and Compound represent two of the most prominent DeFi lending protocols. These platforms allow users to supply assets to liquidity pools and earn interest, or borrow assets by providing collateral. The interest rates are algorithmically determined based on supply and demand dynamics within each market.
These protocols introduced innovative features like flash loans—uncollateralized loans that must be borrowed and repaid within a single transaction block. Such innovations demonstrate the unique capabilities enabled by blockchain technology that have no direct equivalent in traditional finance.
Automated Market Makers and DEXs
Uniswap pioneered the automated market maker model that revolutionized decentralized trading. Instead of using traditional order books, Uniswap employs constant product market maker algorithms to determine prices. This allows for permissionless trading of any ERC-20 token pair without requiring counterparties.
Other major DEXs like SushiSwap and Curve Finance have built upon this foundation with additional features. These platforms have collectively processed trillions of dollars in trading volume, demonstrating substantial adoption and proving the viability of decentralized exchange models.
DeFi protocols are designed to be modular and interchangeable, allowing different applications to interact seamlessly—a characteristic known as composability that enables unprecedented innovation.
Derivatives and Synthetic Assets
Synthetix allows users to mint synthetic assets that track the value of real-world assets like commodities, stocks, and fiat currencies. These synthetic assets, or "synths," enable exposure to traditional markets without requiring direct ownership of the underlying assets. This expands investment opportunities for cryptocurrency holders.
Derivative protocols like dYdX offer margin trading, futures, and perpetual contracts in a decentralized format. These platforms provide sophisticated financial instruments previously available only through traditional brokerages, now accessible through non-custodial DeFi interfaces.
The Risks and Challenges in DeFi
Despite its transformative potential, DeFi faces significant challenges that users must carefully consider. Understanding these risks is essential for anyone participating in the decentralized finance ecosystem.
Smart Contract Vulnerabilities and Security Risks
Smart contracts can contain bugs or security flaws that expose user funds to significant risk. Unlike traditional software, deployed smart contracts are typically immutable, meaning flaws cannot be easily patched. This permanence amplifies the consequences of coding errors or vulnerabilities.
The DeFi sector has experienced several high-profile exploits resulting in substantial financial losses. These incidents highlight the importance of thorough security auditing and the limitations of current smart contract development practices. Users must exercise caution and understand that they bear responsibility for their own security.
Market Volatility and Economic Risks
The cryptocurrency assets underlying DeFi protocols experience substantial price volatility. This volatility can create cascading effects throughout the ecosystem. Sharp price declines can trigger automated liquidations in lending protocols, potentially creating market instability.
Additionally, some DeFi protocols employ complex tokenomics that may not be sustainable long-term. Yield farming incentives, liquidity mining rewards, and governance token distributions can create economic models vulnerable to sudden changes in market conditions or user behavior.
Regulatory Uncertainty and Compliance Challenges
The regulatory landscape for DeFi remains ambiguous and varies significantly across jurisdictions. This creates compliance challenges and legal uncertainty for both developers and users. Regulatory agencies worldwide are grappling with how to apply existing financial regulations to decentralized systems.
Key areas of regulatory focus include anti-money laundering (AML) requirements, know-your-customer (KYC) procedures, securities regulations, and tax compliance. The decentralized nature of these protocols creates fundamental challenges for applying traditional regulatory frameworks designed for centralized intermediaries.
- Technical Vulnerabilities: Code exploits and smart contract bugs
- Price Volatility: Rapid cryptocurrency value fluctuations
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Evolving and inconsistent legal frameworks
- User Error: Irreversible mistakes in transaction execution
- Scaling Limitations: Network congestion and high transaction fees
DeFi vs. Traditional Finance: A Comparative Analysis
Understanding the fundamental differences between DeFi and traditional finance clarifies why this technology represents such a disruptive force in the financial sector.
Custody and Control of Assets
In traditional finance, institutions maintain custody of client assets. Banks hold deposits, brokerages hold securities, and payment processors control transaction flows. This creates counterparty risk—the risk that these intermediaries might fail, become insolvent, or restrict access to funds.
DeFi operates on a non-custodial model where users maintain control of their assets through private keys. Funds are held in smart contracts rather than with third parties. This fundamental shift in custody arrangements redistributes responsibility and risk from institutions to individual users.
Accessibility and Inclusion
Traditional financial systems often exclude individuals based on geography, wealth, documentation, or credit history. Banking services require physical infrastructure, minimum balances, and extensive paperwork. These barriers leave billions of people without access to basic financial tools.
DeFi requires only an internet connection and a digital wallet for participation. There are no minimum balance requirements, no geographical restrictions, and no need for credit checks or identification documents. This dramatically lowers barriers to financial participation.
Transparency and Auditability
Traditional financial systems operate with limited transparency. Transaction details are typically private, known only to the parties directly involved and their financial institutions. This opacity can hide inefficiencies, conflicts of interest, or even fraudulent activities.
DeFi transactions are recorded on public blockchains, creating complete transparency. Anyone can audit transaction histories, verify protocol operations, or examine smart contract code. This transparency builds trust through verifiability rather than through institutional reputation.
Operational Hours and Settlement Speed
Traditional financial markets operate within specific hours and close on weekends and holidays. Settlement of transactions, particularly across borders, can take several business days to complete. This delay creates friction and opportunity costs in global finance.
DeFi markets operate 24/7/365 without interruption. Settlement occurs within minutes or even seconds, regardless of the time or day. This continuous operation and rapid settlement significantly improve capital efficiency and market responsiveness.
The Future Evolution of Decentralized Finance
The trajectory of DeFi points toward continued innovation and increasing integration with traditional financial systems. Several emerging trends will likely shape the next phase of development in the decentralized finance sector.
Institutional Adoption and Hybrid Models
Major financial institutions are gradually exploring DeFi integration. This institutional interest could bring significant capital, regulatory clarity, and professional standards to the ecosystem. We are likely to see the emergence of hybrid models that combine elements of both centralized and decentralized finance.
These hybrid approaches might feature permissioned DeFi applications designed for institutional use while maintaining interoperability with public DeFi protocols. Such developments could bridge the gap between traditional finance's regulatory compliance and DeFi's efficiency and transparency.
Enhanced Scalability Solutions
Layer 2 scaling solutions and alternative blockchain architectures are addressing the throughput limitations of earlier DeFi platforms. Technologies like rollups, sidechains, and sharding promise to significantly reduce transaction costs while increasing speed. These improvements are essential for DeFi to support mass adoption.
As these scaling solutions mature, users will experience faster transaction confirmation times and lower fees. This will make DeFi applications more practical for everyday financial activities and micro-transactions, expanding their potential use cases beyond speculative trading and yield farming.
Improved User Experience and Accessibility
The current complexity of DeFi interfaces presents a significant barrier to mainstream adoption. Future developments will focus on simplifying user interactions, abstracting away technical complexity, and creating more intuitive experiences. Better education, onboarding tools, and customer support structures will also emerge.
Wallet technology will evolve to provide both security and simplicity. Social recovery mechanisms, biometric authentication, and insurance products will make self-custody more accessible to non-technical users. These improvements will be crucial for bringing DeFi to the next hundred million users.
The long-term success of DeFi depends on establishing global standards to ensure interoperability among different blockchains and integration with traditional financial systems.
Regulatory Developments and Compliance Frameworks
The evolving regulatory landscape will significantly influence DeFi's development and mainstream adoption. Governments worldwide are developing approaches to balance innovation with consumer protection and financial stability.
Current Regulatory Approaches
Regulatory bodies are taking varied approaches to DeFi oversight. Some jurisdictions are creating innovation-friendly frameworks with regulatory sandboxes, while others are applying existing securities and financial regulations more strictly. The decentralized nature of these protocols challenges traditional regulatory models built around identifiable intermediaries.
Key regulatory focus areas include anti-money laundering compliance, investor protection, taxation, and systemic risk management. Regulators are particularly concerned about potential consumer harm from poorly understood products, fraud, and market manipulation in relatively unregulated environments.
The Path Toward Regulatory Clarity
Industry collaboration with regulators will likely produce more nuanced frameworks that distinguish between different types of DeFi activities. Some protocols may qualify for lighter regulation if they are genuinely decentralized, while others with centralized elements may face stricter oversight similar to traditional financial services.
Compliance tools built directly into DeFi protocols may emerge, enabling automated regulatory adherence without compromising decentralization. These could include transaction monitoring, identity verification layers, and reporting mechanisms that operate transparently on-chain.
DeFi's Impact on Global Financial Systems
Decentralized Finance represents more than just technological innovation—it embodies a philosophical shift toward more open, accessible, and transparent financial systems. Its impact extends beyond cryptocurrency enthusiasts to potentially reshape global economic structures.
Democratization of Financial Services
DeFi lowers barriers to financial participation on an unprecedented scale. Individuals in underserved regions can access sophisticated financial tools without relying on traditional banking infrastructure. This democratization could stimulate economic activity in developing economies and provide new opportunities for wealth creation.
The programmability of money through smart contracts enables entirely new financial products and services. These innovations can address specific needs of communities that traditional finance has historically overlooked or underserved.
Redefining Trust in Financial Systems
DeFi shifts trust from centralized institutions to transparent, auditable code and decentralized networks. This represents a fundamental change in how financial trust is established and maintained. The "trustless" nature of blockchain-based systems doesn't eliminate trust but redistributes it to mathematical verification and economic incentives.
This redefinition of trust could reduce systemic risks associated with "too big to fail" financial institutions. By distributing risk across decentralized networks rather than concentrating it in central entities, DeFi could potentially create more resilient financial infrastructure.
Financial Innovation and Composability
The composability of DeFi protocols—their ability to interact and build upon one another—creates unprecedented opportunities for financial innovation. Developers can combine existing building blocks to create new applications quickly, much like assembling Lego pieces. This accelerates innovation cycles far beyond traditional financial product development.
This composability enables complex financial instruments that would be difficult or impossible to create in traditional systems. It also fosters collaboration across projects and reduces duplication of effort, as protocols can specialize in specific functions while interoperating with complementary services.
Practical Considerations for DeFi Participants
For individuals considering participation in DeFi, understanding practical considerations is essential for navigating this emerging landscape safely and effectively.
Security Best Practices
Users must prioritize security when interacting with DeFi protocols. This involves using hardware wallets for significant holdings, implementing multi-signature arrangements where appropriate, and thoroughly researching protocols before investing. Understanding private key management is non-negotiable for DeFi participation.
Additional security measures include using separate wallets for different activities, regularly updating software, and being cautious of phishing attempts. Since transactions are irreversible, preventing unauthorized access is paramount.
- Use hardware wallets for significant asset storage
- Research protocols extensively before committing funds
- Start with small amounts to test understanding
- Verify website URLs and contract addresses carefully
- Keep software updated and use antivirus protection
Risk Management Strategies
Given the volatility and emerging nature of DeFi, appropriate risk management is crucial. This includes diversifying across different protocols and asset types, avoiding over-leverage, and understanding the specific risks of each DeFi activity. Users should only invest amounts they can afford to lose completely.
Staying informed about protocol developments, security audits, and community governance decisions helps participants make educated decisions. Participating in decentralized governance, when available, provides insight into protocol direction and potential risks.
Tax and Record-Keeping Obligations
DeFi transactions often have tax implications that vary by jurisdiction. The programmable nature of DeFi can create complex tax scenarios that may not fit neatly into existing frameworks. Users should maintain detailed records of all transactions, including swaps, yield farming rewards, and gas fees.
Consulting with tax professionals familiar with cryptocurrency regulations is advisable for significant DeFi activity. As regulatory clarity improves, more specialized tools for DeFi tax reporting and compliance will likely become available.
Conclusion: The Transformative Potential of DeFi
Decentralized Finance represents one of the most significant innovations in the financial sector in decades. By leveraging blockchain technology and smart contracts, DeFi creates an alternative financial system that is more open, accessible, and transparent than traditional models. While still in its early stages, its impact is already being felt across global markets.
The journey toward mainstream DeFi adoption will involve addressing current challenges around security, user experience, and regulation. As these challenges are met, DeFi has the potential to complement and eventually transform aspects of traditional finance. The technology enables financial services that are borderless, programmable, and available to anyone with internet access.
DeFi embodies a shift toward financial systems that prioritize transparency, accessibility, and user sovereignty over centralized control. It represents not just technological advancement but a philosophical reimagining of how financial systems should operate in a digital age. As the ecosystem matures, it may help address longstanding issues of financial exclusion and opacity that have characterized traditional finance.
The future of finance will likely feature a blend of centralized and decentralized elements, with each serving different needs and preferences. DeFi's greatest contribution may ultimately be in pushing the entire financial sector toward greater innovation, efficiency, and inclusion. Its continued evolution will be one of the most important financial narratives to watch in the coming decade.
Hedera Hashgraph: Revolutionizing Blockchain Technology
The Emergence of Hedera Hashgraph
The blockchain space has seen its fair share of innovation and competition among various projects vying for market dominance. However, one technology stands out as a disruptor and potential game-changer: Hedera Hashgraph. Originally developed by Swirlds, Hedera Hashgraph is a public distributed ledger that offers unprecedented throughput and latency while maintaining security and decentralization. This decentralized network promises to solve some of the most pressing issues plaguing traditional blockchains, making it a compelling alternative for businesses and individuals seeking efficient and secure transactions.
Understanding Hashgraph
To understand the unique value proposition of Hedera Hashgraph, it's essential to grasp its underlying technology—the Hashgraph consensus algorithm. Unlike other blockchain technologies that rely on proof-of-work (PoW) or proof-of-stake (PoS) to achieve consensus, Hashgraph employs a novel approach that combines both gossip-based and synchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) mechanisms. This hybrid approach allows for significantly faster transaction speeds and more robust security compared to traditional blockchain networks.
A central concept in Hashgraph is the "hashgraph" structure itself. Think of a hashgraph as a tree-like structure where each node represents a transaction or a message that needs to be verified. Each node not only stores information about the transaction itself but also references two parent nodes, which act as a timestamp for the transaction. In this way, the hashgraph provides a clear chronological order, ensuring that all nodes have an accurate view of the transaction history.
Key Features of Hedera Hashgraph
Speedy Transactions: One of the standout features of Hedera Hashgraph is its ability to process thousands of transactions per second (TPS), with some reports citing rates exceeding over 5,000 TPS under optimal conditions. This rapid transaction speed makes it suitable for real-time applications like financial settlements, micropayments, and cross-border transactions, where quick confirmation times are critical.
Decentralization: Like many blockchain technologies, Hedera Hashgraph thrives on decentralization. By distributing the network across multiple nodes, no single point of failure exists, making it resistant to attacks and manipulation. Each participant in the network plays a vital role in validating transactions and reaching consensus, thereby ensuring that the system remains secure and unaffected by any single entity's actions.
Security and Privacy: Security in Hedera Hashgraph is achieved through a combination of cryptographic techniques, such as asymmetric encryption and digital signatures. This ensures that transactions are tamper-proof and that participants can trust the integrity of the network without needing a central authority. Additionally, Hedera Hashgraph offers robust privacy features, allowing users to maintain their anonymity while still ensuring the transparency of the transaction process.
Network Structure and Consensus Mechanism
The Hedera Hashgraph network is made up of a diverse range of nodes, including validators, witnesses, and clients. Validators are responsible for confirming transactions and validating blocks. Witnesses do not directly validate transactions but participate in the hashgraph structure to provide a more robust network. Clients interact with the network to send and receive transactions.
The consensus mechanism used by Hedera Hashgraph is designed to be highly efficient and secure. During a consensus round, validators quickly reach agreement on the order of transactions without requiring extensive computational power or energy consumption. This is achieved through a gossip-based protocol where validators receive and share messages about transactions they have heard about. Eventually, this leads to a global understanding of the correct sequence of events, which is then recorded in the hashgraph structure.
Tokenomics and Governance
Hedera Hashgraph operates without its own native token, unlike many other blockchain platforms. Instead, it utilizes a governance model that involves the Hedera Governing Council and the Hedera Token Service. The Hedera Governing Council, comprised of large corporations and organizations, helps ensure the stability and growth of the network. On the other hand, the Hedera Token Service allows developers to create and deploy custom stablecoins and digital assets on the Hedera platform.
This unique governance structure sets Hedera Hashgraph apart from other chains that rely on tokens for funding and incentive structures. By focusing on enterprise adoption and collaboration, Hedera aims to foster a more inclusive and collaborative ecosystem rather than being driven by the need for token value increases.
Applications and Use Cases
The versatile nature of Hedera Hashgraph makes it well-suited for a wide array of applications and industries. Financial services stand out as a key area where the technology could have a transformative impact. Financial institutions can achieve faster and cheaper cross-border payments, streamline settlement processes, and enhance compliance through immutable records.
Moreover, Hedera Hashgraph can enable innovative business models and services, such as decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, supply chain management, and identity verification systems. Its low-latency performance ensures that these applications can operate seamlessly, providing users with a frictionless experience.
Challenges and Future Prospects
No technology is without its challenges, and Hedera Hashgraph is no exception. One of the primary hurdles is achieving mainstream adoption. Compared to established technologies like Ethereum and Bitcoin, Hedera Hashgraph has limited brand recognition and user base. Addressing this requires extensive outreach and strategic partnerships with major industry players.
Another challenge lies in regulatory clarity. Although the technology offers enhanced privacy and security features, navigating regulatory landscapes around decentralized applications can be complex. Governments and regulatory bodies are still grappling with how to classify and regulate cryptocurrencies and blockchain technologies, which poses a risk to wider adoption.
Looking ahead, Hedera Hashgraph holds promising prospects for overcoming these challenges. As the world becomes increasingly interconnected and data-driven, a fast, secure, and scalable decentralized network like Hedera can play a crucial role in driving innovation. Collaborations with enterprises and continuous improvements to the technology will likely strengthen its position in the market.
Conclusion
Hedera Hashgraph represents a significant leap forward in blockchain technology. With its superior performance and robust security, it addresses many of the shortcomings of existing blockchain solutions. As more businesses recognize the potential benefits of Hedera Hashgraph in their operations, we can expect to see increased adoption and innovation within the ecosystem.
Technology Partnerships and Collaboration
Hedera Hashgraph has made significant strides in forming strategic partnerships to enhance its technological capabilities and expand its user base. These collaborations aim to leverage the unique strengths of Hedera Hashgraph, such as its high throughput and low latency, to address specific industry needs. For instance, in the financial services sector, Hedera has partnered with companies like BNY Mellon, a global leader in asset servicing, and State Street Corporation, a multinational financial services company. These partnerships have led to the development of innovative solutions tailored to the requirements of financial institutions, such as automated settlements and real-time payment processing.
In the realm of DeFi, major players like ChainSafe Systems and ChainSafe Labs have integrated Hedera Hashgraph into their platforms. These integrations have resulted in improved liquidity and scalability, making DeFi more accessible and efficient for users. Additionally, the partnership with ChainSafe has helped in creating secure and compliant DeFi applications, ensuring that users can trust the systems they interact with.
Moreover, Hedera Hashgraph has established a partnership with Polkadot, a multi-chain ecosystem, to explore cross-chain interoperability. This collaboration could potentially revolutionize the way different blockchain networks interact, paving the way for a more interconnected and decentralized digital economy.
Community and Ecosystem
The success of any blockchain network relies heavily on its community and ecosystem. Hedera Hashgraph has been building a strong community of developers, businesses, and enthusiasts from the onset. The Hedera Hashgraph website provides extensive resources and support, making it easier for new members to understand and engage with the platform. The Hedera Hashgraph API and SDKs have been designed to be user-friendly, facilitating the development of various applications and services.
The Hedera Hashgraph community includes a diverse range of participants, from small startups to large enterprises. Companies like ConsenSys, a leading blockchain solutions provider, have been actively working on Hedera-based projects, contributing to the ecosystem’s growth and innovation. These partnerships have not only facilitated the creation of new applications but also enhanced the overall user experience through continuous improvement and updates.
The Hedera Hashgraph GitHub repository is a testament to the community’s enthusiasm and contribution. Developers from around the world regularly contribute code, report bugs, and suggest new features, fostering an open and collaborative environment. This open-source model encourages innovation and ensures that the platform remains flexible and adaptable to the evolving needs of its users.
Security and Compliance
One of the critical factors in the success of any blockchain technology is its security and compliance. Hedera Hashgraph has taken several steps to ensure that it meets stringent security standards. The implementation of robust cryptographic techniques, such as secure hash functions and digital signatures, guarantees the security of transactions and data. These measures help prevent unauthorized access, tampering, and fraudulent activities, thereby maintaining the integrity of the network.
Moreover, Hedera Hashgraph has been actively working towards achieving regulatory compliance. The Hedera Governing Council, with its diverse membership, plays a crucial role in ensuring that the network operates within the legal framework. This includes working with regulatory bodies and industry stakeholders to address any concerns and provide transparent and secure solutions. This approach not only enhances the legitimacy of Hedera Hashgraph but also ensures that businesses can trust the platform for their critical operations.
The Hedera Hashgraph network has also implemented advanced security features such as zero-knowledge proofs and privacy-enhancing technologies. These features allow users to maintain their privacy while still ensuring the transparency of transactions. For example, zero-knowledge proofs can be used to verify the authenticity of transactions without revealing sensitive information, providing a balance between security and privacy.
Scalability and Interoperability
One of the most significant challenges for blockchain technologies is scalability. Hedera Hashgraph addresses this challenge through its innovative architecture. The technology’s ability to handle thousands of transactions per second makes it suitable for high-throughput applications, such as real-time payments and decentralized marketplaces. Hedera Hashgraph’s design allows for smooth scaling, ensuring that the network can accommodate a growing number of users and applications without compromising on performance.
Interoperability is another key aspect that sets Hedera Hashgraph apart. The network’s ability to interact with other blockchains and decentralized networks through bridges and protocols ensures that it can serve as a versatile platform for various use cases. By fostering cross-chain interoperability, Hedera Hashgraph can help in building a more interconnected and seamless digital ecosystem. This interoperability is particularly important for businesses operating in multiple markets, as it enables them to leverage the benefits of different blockchain networks while maintaining a unified approach.
Another aspect of scalability is the network’s ability to handle large volumes of data. Hedera Hashgraph’s efficient data management techniques ensure that transaction data is stored and managed in a way that minimizes overhead and maximizes efficiency. This is crucial for applications that require extensive data processing, such as decentralized finance and supply chain management.
Economic and Environmental Impact
Blockchain technology, particularly cryptocurrencies, has often been criticized for its high energy consumption and carbon footprint. However, Hedera Hashgraph addresses this issue through its innovative consensus mechanism. By eliminating the need for extensive computational power, Hedera Hashgraph significantly reduces energy consumption, making it a more environmentally friendly solution. This is particularly important as governments and organizations globally strive to combat climate change and promote sustainability.
The economic impact of Hedera Hashgraph is also noteworthy. By enabling faster and cheaper transactions, the technology has the potential to reduce costs for businesses and consumers. This is especially beneficial for businesses operating in industries with high transaction volumes, such as financial services and e-commerce. The technology can help businesses reduce their operational costs and improve their competitive edge.
Future Roadmap and Research & Development
To continue driving innovation and maintain its position as a leading blockchain network, Hedera Hashgraph has a well-defined roadmap and a strong commitment to ongoing research and development. The team regularly updates the network to address emerging challenges and incorporate new technologies. For instance, the development of Hedera Health, a dedicated service for medical blockchain applications, showcases Hedera Hashgraph’s commitment to addressing specific industry needs.
The Hedera Hashgraph Research & Development (R&D) team is continuously exploring new innovations and technologies. This includes the development of new consensus algorithms, privacy-enhancing protocols, and advanced security measures. The R&D team’s efforts are aimed at making Hedera Hashgraph even more powerful and versatile, enabling it to meet the evolving demands of its users.
Apart from technological advancements, the Hedera Hashgraph team is also focused on enhancing user experience and accessibility. The team is working on improving the usability of the platform, making it more intuitive and user-friendly. This includes the development of user-friendly tools and interfaces, as well as ongoing support and documentation.
Moreover, the Hedera Hashgraph team is dedicated to fostering a vibrant and collaborative community. The team regularly engages with users, developers, and industry stakeholders to gather feedback and insights. This collaborative approach ensures that the platform evolves in a way that best meets the needs of its diverse user base.
Conclusion
Hedera Hashgraph has established itself as a leading decentralized network with unique features that set it apart from other blockchain technologies. Its high throughput, robust security, and innovative consensus mechanism make it well-suited for a wide range of applications. The network’s strong community, strategic partnerships, and ongoing R&D efforts further reinforce its potential for future growth and success. As more businesses and organizations recognize the benefits of Hedera Hashgraph, we can expect to see continued innovation and adoption in the blockchain space.
Real-World Applications and Case Studies
Several real-world applications and case studies highlight the tangible benefits of using Hedera Hashgraph. For example, the United Nations Global Green Ribbon Award recognized the World Food Programme (WFP) for its adoption of Hedera Hashgraph to improve the transparency and efficiency of food assistance programs. This collaboration has helped in tracking food donations and ensuring that aid reaches the intended beneficiaries in a timely and secure manner. By leveraging Hedera Hashgraph's low-latency, high-throughput capabilities, the WFP can conduct real-time checks and balances, reducing the risk of fraud and mismanagement.
Another notable case study is the partnership between Hedera Hashgraph and VeChain, a leading blockchain platform focused on supply chain traceability. Together, they developed a system that tracks the journey of luxury goods from production to retail. This solution ensures that consumers can verify the authenticity and origin of products, thereby enhancing brand trust and protecting against counterfeiting. The integration of Hedera Hashgraph into VeChain's ecosystem provides a secure and efficient way to manage complex supply chains, addressing the challenges of authenticity and traceability.
Furthermore, the Canadian payment network Bambora leveraged Hedera Hashgraph to create a real-time payment platform. This platform is designed to support merchants in processing transactions instantly, offering a seamless user experience. The platform's ability to handle thousands of transactions per second makes it ideal for e-commerce and other high-volume payment ecosystems. By integrating Hedera Hashgraph, Bambora has been able to reduce transaction times and improve overall payment processing efficiency, ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its many advantages, Hedera Hashgraph faces several challenges that need addressed for it to become even more scalable and user-friendly. One major challenge is the issue of network congestion during peak times. While the technology can handle high transaction volumes, ensuring smooth operation during periods of high demand remains a critical concern. Hedera Hashgraph is continually working on optimizing its consensus algorithms and network architecture to enhance performance, particularly during peak usage periods.
Another challenge is the need for more comprehensive regulatory guidance. While the technology has made significant strides in achieving compliance, the lack of clear regulatory frameworks can be a significant deterrent for businesses looking to adopt blockchain solutions. As a result, Hedera Hashgraph is actively engaged with regulatory bodies and industry stakeholders to advocate for a more supportive regulatory environment. This collaboration aims to promote the responsible and widespread adoption of blockchain technology.
To address these challenges and stay ahead of the curve, Hedera Hashgraph is focusing on several key areas for future development. One area of focus is improving cross-chain interoperability. By enabling seamless communication between different blockchain networks, Hedera Hashgraph can help in building a more integrated and interconnected digital economy. Additionally, the team is exploring the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to enhance the network's security and operational efficiency. These technologies can help in detecting and mitigating potential threats in real-time, ensuring the continued security and reliability of the network.
Furthermore, Hedera Hashgraph is investing in research and development to explore new use cases and applications. The network is particularly interested in exploring the potential of decentralized identity solutions, smart contracts, and decentralized finance (DeFi). Decentralized identity solutions can provide individuals with control over their personal data, ensuring privacy and security. Smart contracts can enable automated and trusted transactions in a wide range of sectors, while decentralized finance can offer new opportunities for decentralized lending, savings, and trading.
Hedera Hashgraph is also emphasizing the importance of community engagement and education. The team believes that fostering a strong and supportive community is essential for the long-term success of the network. To achieve this, Hedera Hashgraph is organizing webinars, workshops, and conferences to provide users with valuable insights and best practices. Additionally, the team is collaborating with educational institutions to develop courses and training programs that can help in building a skilled workforce equipped with the knowledge and skills needed to work with blockchain technology.
Conclusion
Hedera Hashgraph is at the forefront of blockchain innovation, offering a unique set of features that address many of the challenges faced by traditional blockchain networks. From its ability to handle thousands of transactions per second to its robust security and cross-chain interoperability, Hedera Hashgraph is poised to play a significant role in shaping the future of decentralized finance and beyond. As businesses continue to explore and adopt blockchain technology, the real-world applications and case studies demonstrate the transformative potential of Hedera Hashgraph. With ongoing improvements and a strong focus on community engagement, Hedera Hashgraph is well-positioned to become a leading force in the blockchain ecosystem.

Celo: The Blockchain Revolutionizing Payments and Finance
An Introduction to Celo
Celo is a new blockchain project that aims to bring financial services to the masses, particularly in developing countries. Founded in 2020, Celo is built on top of the Ethereum network but offers a faster, more scalable, and user-friendly environment for financial transactions. What sets Celo apart is its focus on making digital money available to every individual through its unique infrastructure and governance model.
The Problem Celo Solves
The world currently faces significant challenges when it comes to financial inclusivity. According to the World Bank, around 1.7 billion adults worldwide either do not have a bank account or do not use one. This lack of access to formal financial services hampers economic growth and exacerbates social inequalities. Traditional banking systems can be costly and inefficient, especially for those residing in remote or low-income areas. This is where Celo steps in to offer a solution.
Key Features of Celo
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Celo has built its foundations on DeFi principles, which means users can transact directly on the platform without relying on traditional intermediaries like banks. This eliminates costly transaction fees and speeds up the transfer of funds, regardless of the geographical distance between sender and recipient.
Digital Currencies
Celo introduces its own digital currencies designed to make transactions more accessible and convenient. The network supports a native cryptocurrency called CEL, as well as stablecoins that peg their value to real-world assets such as the US Dollar. Stablecoins are crucial because they provide pricing stability and reduce the risk associated with volatility in the crypto market.
Broad Network Compatibility
To ensure widespread adoption, Celo supports interchain compatibility through a protocol known as "Sequencer." This integration enables users to seamlessly switch between different blockchain networks, thereby expanding the potential user base.
Celo's Governance Model
A key strength of Celo lies in its governance model, which encourages community participation and ensures transparency. Users can participate in decision-making processes through a token-based voting system. Any member holding Celo tokens can cast votes on proposed upgrades, policy changes, and other critical decisions impacting the network.
Token Economics
The token economy on Celo is designed to incentivize healthy network activity. Users who stake CEL tokens receive a portion of transaction fees as rewards, promoting a virtuous cycle of adoption and security. Additionally, holders can delegate their tokens to validators to earn additional rewards.
The Role of Celo in Financial Inclusion
Celo’s mission is to make global financial services accessible to everyone, regardless of their socioeconomic status. By providing a secure and affordable platform for digital payments, the project aims to bridge the gap between the unbanked and the financially literate. Here are some specific ways through which Celo is making an impact:
Benefits for the Unbanked
- Reduced Costs: Traditional remittance services often charge high fees. Celo offers near-zero transaction costs, making it an attractive alternative.
- Fast Transactions: Unlike slower settlement times associated with conventional cross-border payments, Celo transactions are nearly instantaneous.
- Financial Literacy: Educational materials provided by Celo facilitate understanding of basic finance concepts, empowering users to make better financial decisions.
Use Cases in Developing Countries
Developing economies often struggle with limited access to credit and financial products. Celo is addressing this issue by offering microloans and savings plans within its ecosystem. These services are designed to be easily accessible and affordable, catering to the unique needs of small-scale entrepreneurs and regular users.
Empowering Women and Marginalized Communities
Cryptoassets and decentralized finance can empower marginalized communities, including women, by providing them with tools to manage their finances independently. Through Celo’s robust governance and user-friendly interface, these communities gain greater control over their resources and are better positioned to participate in the global economy.
The Technology Behind Celo
Underpinning Celo’s ambitious goals is cutting-edge technology that enhances security, scalability, and interoperability. Here’s an overview of how these technologies contribute to Celo’s success:
Proof-of-Stake Consensus
Celo operates using the proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, which is inherently more energy-efficient compared to proof-of-work (PoW). Validators who stake tokens are chosen based on their staked amounts and randomness factors, ensuring a fair and secure environment.
Rapid Transaction Speeds
To handle high volumes of transactions efficiently, Celo utilizes a sharding approach. By dividing the network into smaller sub-networks called shards, Celo significantly reduces confirmation times while maintaining data integrity across the network.
Interoperability with Other Blockchains
The Sequencer protocol allows Celo to interact with other major blockchain platforms, facilitating the exchange of value across different ecosystems. This interoperability is crucial for expanding Celo’s reach and integrating with established financial infrastructure.
Historical Milestones
Since its inception, Celo has achieved several milestones that underscore its commitment to innovation and growth:
Initial Launch
In early 2020, Celo launched its mainnet, marking the beginning of its journey toward revolutionizing financial inclusion. The launch included comprehensive testing phases to ensure the stability and security of the network.
Partnerships and Integrations
Throughout 2021, Celo formed partnerships with notable organizations such as Circle, the company behind the stablecoin USDC. These collaborations helped enhance Celo’s utility and credibility.
User Adoption
By mid-2022, Celo reported over one million registered users and hundreds of thousands of unique monthly active users. The rapid adoption highlights the growing interest in Celo’s innovative solutions.
Challenges Ahead
No project is without its challenges, and Celo is no exception. Addressing these hurdles is essential for its long-term sustainability:
Growing Competition
The blockchain space is highly competitive, with numerous projects vying for attention and usage. Celo must innovate continuously to stay ahead of emerging rivals and maintain user trust and satisfaction.
Regulatory Uncertainty
Lack of uniform regulations across jurisdictions creates challenges for cryptocurrencies and DeFi projects. Celo must navigate this complex landscape while advocating for regulatory clarity and support.
Scalability and Performance
As Celo scales, performance optimization remains crucial. Improvements in throughput and latency will be vital to meet growing demand and ensure a smooth user experience.
In summary, Celo represents a forward-thinking approach to financial inclusion and digital transformation. With a strong foundation in DeFi principles and a robust governance model, the project is well-positioned to reshape the landscape of global finance. As it continues to grow and overcome challenges, Celo has the potential to significantly improve the lives of millions around the world.
Future Prospects and Potential Impact
Looking ahead, Celo aims to continue expanding its ecosystem and increasing its impact on global financial inclusion. Here are some potential areas where Celo could thrive:
Integration with Traditional Banking Systems
One of the most exciting opportunities for Celo is integrating with traditional banking systems. By partnering with traditional financial institutions, Celo could help bridge the digital divide, enabling users to access both traditional and DeFi services. Such integrations could include collaborative ventures to set up hybrid banking services, combining the security and reach of traditional finance with the convenience and accessibility of DeFi.
Expanding to New Markets
Celo’s success largely depends on its ability to attract a diverse user base globally. Expanding to new markets requires addressing unique regional challenges and adapting accordingly. For instance, in Africa, Celo could focus on integrating with local payment systems and collaborating with telecommunications companies to promote mass adoption. Similarly, in Southeast Asia, partnerships with governments and NGOs could help establish Celo as a trusted financial solution for millions of citizens.
Innovative Product Launches
To keep users engaged and drive further adoption, Celo is likely to introduce new products and services. For example, the introduction of CeloGold, a gold-backed stablecoin, could appeal to users concerned about economic instability. Celo could also explore the development of non-fungible tokens (NFTs) for artists and creators in developing countries, providing them with a platform to sell their work.
Economic Implications and Societal Benefits
The economic benefits of adopting Celo extend beyond individuals and communities; they also have broader implications for national and regional economies:
Boost to Small Businesses
Small businesses in underdeveloped regions often face numerous challenges, such as limited access to funding and slow payment processes. By providing them with low-cost, fast, and secure payment methods, Celo can significantly enhance their cash flow and operational efficiency. This can lead to increased productivity and job creation, contributing to overall economic growth.
Promotion of Financial Literacy
Financial literacy is a critical asset for individuals and societies. Celo’s educational programs can empower people with the knowledge necessary to understand and utilize new financial tools effectively. This can lead to better decision-making, reduced poverty levels, and more equitable distribution of wealth. Moreover, financial literacy initiatives can help prevent fraud and misuse of digital assets.
Strengthening Economic Resilience
During economic disruptions or crises, individuals and businesses need reliable and resilient financial systems. Celo’s stable coin ecosystem, combined with its decentralized nature, offers a safer alternative to traditional financial systems that can be volatile during turbulent times. This resilience can help protect people’s savings and livelihoods during crisis periods.
Collaboration and Community Engagement
To achieve its ambitious goals, Celo must foster strong collaborations with various stakeholders, including:
Partnerships with Local Governments
Local governments can play a crucial role in promoting Celo. By working closely with policymakers, Celo can advocate for favorable regulatory environments and develop tailored solutions that address the unique needs of each country or region. Partnerships may involve joint initiatives to educate the public, distribute Celo tokens, and integrate blockchain technology into existing governmental services.
Collaborations with NGOs and Nonprofits
NGOs and nonprofits can be invaluable allies in Celo’s mission to promote financial inclusion. These organizations possess extensive networks and grassroots experience, which can help Celo reach underserved populations more effectively. Collaborative projects could include distributing Celo tokens to refugees and disaster victims, providing them with essential financial tools and resources.
Community Building through Celo Labs
Celo Labs, a subsidiary focused on community building and education, plays a pivotal role in fostering a supportive ecosystem. Through webinars, workshops, and hackathons, Celo Labs encourages community engagement and innovation. These events can bring together developers, entrepreneurs, and users to share ideas and collaborate on new projects, driving the growth and evolution of the Celo network.
Technological Innovations
As Celo continues to evolve, it is imperative to focus on technological advancements that enhance the user experience and improve network capabilities:
Enhanced Security Measures
Ensuring the security of user data and transactions is non-negotiable. Celo must continually improve its security protocols, such as multi-factor authentication, encryption standards, and smart contract auditing. Additionally, the integration of zero-knowledge proofs can increase privacy and confidentiality, giving users peace of mind.
Interoperability Expansion
While Celo already supports interoperability with other blockchains, there remain opportunities for expansion. Collaborating with other emerging blockchain projects, such as Polkadot and Cosmos, can create a larger interconnected network, enabling seamless cross-chain communication and reducing siloed operations.
Advancements in User Experience
To attract and retain users, Celo needs to prioritize improving the user experience. This includes simplifying onboarding processes, enhancing wallet functionality, and making transactions more intuitive. User feedback is crucial in refining these aspects, so Celo should actively engage with users to gather insights and suggestions for improvement.
In conclusion, Celo’s journey towards global financial inclusion is far from over. Continued innovation, strategic partnerships, and community engagement will be key to its success. As the project navigates the challenges and opportunities ahead, Celo has the potential to transform the financial landscape globally, bringing much-needed prosperity and empowerment to millions.
Stay tuned for updates on Celo’s exciting journey and join us in shaping a more inclusive and connected future through blockchain technology.
The Roadmap for Growth and Success
To achieve these milestones, Celo has outlined a comprehensive roadmap that guides its strategic direction and tactical execution. Here are the key components of this roadmap:
Phase 1: Consolidation and Expansion
The first phase focuses on consolidating the current user base and expanding the ecosystem. This involves:
- Scaling Infrastructure: Enhancing the network's capacity to handle higher volumes of transactions and ensuring seamless performance.
- Marketing and Outreach: Launching targeted marketing campaigns to educate potential users and attract a broader audience.
- Partnerships: Strengthening and forming new partnerships with financial institutions, governments, and NGOs to broaden the reach of Celo.
Phase 2: Innovation and Product Development
The second phase is centered on innovation and product development:
- New Product Launches: Introducing innovative financial products such as CeloGold (gold-backed stablecoins), CeloCredit (microloans and credit systems), and CeloPay (advanced payment solutions).
- Technology Advancements: Investing in research and development to improve security, scalability, and user experience.
- Educational Programs: Expanding educational initiatives to promote financial literacy and digital awareness among users.
Phase 3: Global Expansion and Impact
The final phase aims to expand globally and measure the impact of Celo’s initiatives:
- International Rollouts: Launching operations in new markets with tailored solutions to suit local needs and customs.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Implementing sustainable practices within the network to reduce environmental impact.
- Impact Assessment: Conducting rigorous studies to evaluate the socio-economic impact of Celo’s initiatives, ensuring they deliver meaningful benefits to communities.
Engagement with Stakeholders
To build a strong and vibrant community, Celo engages with various stakeholders:
Active Participation in Decentralized Governance
Celo emphasizes the importance of decentralized governance. Through its token-based voting system, users and stakeholders have the power to propose and vote on network changes, ensuring a democratic decision-making process.
Community Events and Workshops
Celo hosts regular webinars, workshops, and hackathons to foster collaboration among developers, entrepreneurs, and users. These events not only drive innovation but also build a sense of community and shared purpose.
Partnership with Influential Organizations
Celo collaborates with influential organizations to amplify its impact. For example, partnerships with major banks and fintech companies can help integrate Celo into existing financial systems, making it more accessible to a wider audience.
Overcoming Challenges and Maintaining Momentum
As Celo progresses, it faces a range of challenges. To maintain momentum and overcome these obstacles, the project must:
Address Regulatory Issues
Regulatory uncertainties pose a significant challenge. Effective advocacy and collaboration with regulatory bodies can help navigate these issues. Transparency and clear documentation of Celo’s protocols and compliance with international standards will be crucial.
Ensure Technical Stability and Reliability
Technical stability is essential to build user trust. Regular updates, bug fixes, and continuous monitoring of the network are necessary to maintain reliability and security. Transparent communication about system upgrades and downtime will also help manage user expectations.
Build User Trust and Loyalty
User trust and loyalty are critical for sustained growth. Celo can achieve this by providing a seamless and secure experience, offering robust customer support, and continuously improving user engagement and satisfaction.
The Future Outlook
The future outlook for Celo is bright, with significant potential for impact. Several factors support this optimism:
Increasing Popularity
As more individuals and businesses recognize the benefits of decentralized finance and financial inclusion, Celo’s popularity is likely to grow exponentially. The project’s ability to deliver fast, secure, and cost-effective financial services will only strengthen its position in the market.
Positive User Feedback
The positive user feedback from early adopters indicates that Celo’s vision resonates with many people. Continued innovation and expansion can further bolster user satisfaction and attract new users.
Evolving Market Landscape
The evolving market landscape presents both challenges and opportunities. Emerging trends such as central bank digital currencies (CBDCs), DeFi, and Web3 technologies are all aligned with Celo’s mission. By innovating and staying ahead of these trends, Celo can maintain relevance and stay competitive.
Conclusion
As Celo continues its journey towards global financial inclusion, it remains committed to delivering accessible and innovative financial solutions. With its robust roadmap, strong community engagement, and strategic partnerships, Celo is poised to make a significant impact on the financial landscape. Whether you’re an investor, developer, or simply an interested observer, Celo’s progress and potential offer exciting opportunities for collaboration and innovation.
Join the Celo community today and be part of this transformative movement towards a more inclusive and connected future.
IOTA: The Future of Blockchain and Decentralized Technology
The world of blockchain technology continues to evolve, offering innovative solutions to complex challenges. One such groundbreaking technology is IOTA, a decentralized platform designed specifically for the Internet of Things (IoT). Founded in 2015 by Dominik Schlosser, David Søderqvist, Dr. Serguei Popov, and Dr. Johannes Stelzer, IOTA seeks to disrupt traditional blockchain by eliminating fees and enabling near-zero transaction costs while ensuring scalability and decentralization.
A Revolution in Blockchain
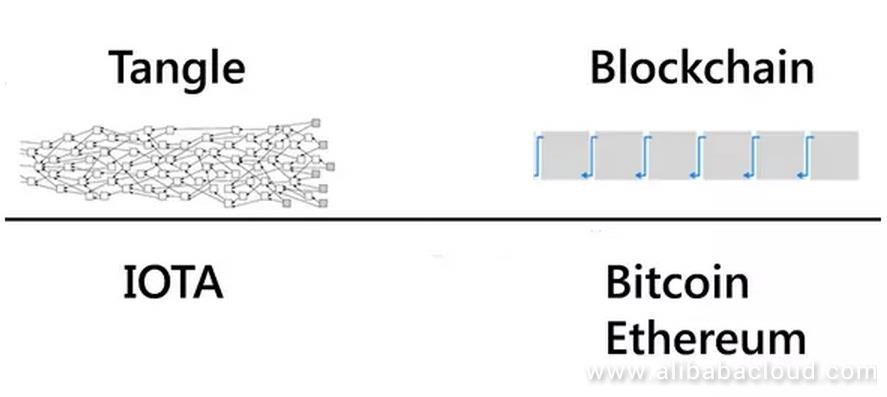
IOTA's unique approach differs greatly from conventional blockchain platforms. Traditional blockchain systems like Bitcoin and Ethereum use proof-of-work (PoW) or proof-of-stake (PoS) protocols to validate transactions. These mechanisms ensure security but come at the cost of significant energy consumption and high transaction fees. Unlike these platforms, IOTA utilizes a revolutionary technology called Tangle, which fundamentally changes how blocks are validated and stored.
The Tangle Technology
The heart of IOTA is its Tangle technology, which operates without miners or transaction fees. Instead of blocks, transactions form a directed acyclic graph (DAG), where each new transaction confirms two previous transactions. This process is known as “double-spending,” and it forms a chain of connected transactions without the need for traditional blockchain structures.
This approach significantly reduces the computational load and eliminates the need for miners, making IOTA highly scalable and capable of processing a vast number of transactions per second. Moreover, the absence of transaction fees can enable micropayments and other cost-sensitive applications within IoT networks.
Advantages of Tangle
One of the primary benefits of Tangle is its ability to achieve true decentralization. Each user acts as both a participant and a validator, creating a self-regulating network immune to centralized attacks. Additionally, IOTA’s lightweight nodes can operate on minimal hardware, making it accessible even to low-power devices pervasive in IoT ecosystems.
IOTA also excels in terms of speed. Transactions confirm almost instantly, bypassing the slow blockchain confirmation times that have been a bottleneck in mainstream cryptocurrencies. Furthermore, the protocol is designed to support smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps), expanding its potential use cases far beyond simple value transfers.
Applications and Industries
The potential applications of IOTA span various industries, from finance and supply chain management to automotive and smart city infrastructure. Here are some key areas where IOTA could make a significant impact:
Financial Services
IOTA can revolutionize the financial services industry by facilitating more secure and efficient cross-border payments. Its zero-fee transactions can enable instant micropayments, reducing costs and enhancing the accessibility of financial services for the unbanked population.
Supply Chain Management
By providing transparent and immutable records, IOTA can enhance traceability and authenticity in supply chains. Companies can use IOTA to track goods through every stage of production, ensuring that products are genuine and ethically sourced. This transparency can help combat counterfeiting and enhance consumer trust.
Smart Cities
With the proliferation of IoT devices, smart cities can harness IOTA’s capabilities to optimize resource utilization and improve citizen services. From traffic management to environmental monitoring, IOTA can enable real-time data exchanges and automated responses, making urban environments more sustainable and efficient.
Automotive Industry
In the automotive sector, IOTA can facilitate vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication and improve safety, congestion management, and overall efficiency. Additionally, it can support autonomous driving technologies by enabling fast, secure, and cost-effective communication between vehicles and infrastructure.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite its promising features, IOTA faces several challenges that must be addressed to achieve widespread adoption. One significant concern is the scalability issue related to the Tangle DAG structure. While IOTA claims it can handle millions of transactions per second, the practical implementation remains to be fully validated.
Another challenge is the need for interoperability with existing blockchain systems. To become a dominant player in the decentralized ecosystem, IOTA must find ways to integrate seamlessly with other blockchain technologies and standards. Cross-chain interoperability solutions may hold the key to unlocking the full potential of IOTA within a broader ecosystem.
Potential Solutions
To overcome these challenges, IOTA developers have initiated several initiatives aimed at improving performance and scalability. The Tangle 2.0 project aims to enhance transaction throughput and reliability by optimizing the underlying DAG structure. Additionally, partnerships with major organizations and research institutions can provide valuable insights and resources to drive innovation.
In conclusion, IOTA represents a fascinating development in the realm of decentralized technology. By addressing key limitations and leveraging its unique features, IOTA has the potential to transform industries ranging from finance to smart cities. As the technology matures and overcomes current hurdles, its impact on global innovation and connectivity is likely to be profound.
Community and Adoption
The success of any blockchain technology hinges not just on its technical merits but also on its community and adoption. IOTA has fostered a vibrant and active developer community that contributes to its growth and improvement. Through initiatives like the IOTA Foundation, the project engages with stakeholders across multiple sectors, promoting education and collaboration.
The foundation plays a crucial role in supporting research, development, and community engagement. It provides grants and sponsorships to projects that align with IOTA’s vision, helping to fund innovations and applications within the IOTA ecosystem. Additionally, the foundation organizes hackathons, meetups, and conferences that bring together developers, enthusiasts, and industry experts to share ideas and best practices.
IOTA’s community-driven approach fosters a spirit of openness and collaboration. This culture has led to the formation of numerous open-source libraries, tools, and dApps that leverage IOTA technology. These contributions not only enhance the functionality of IOTA but also accelerate its adoption by providing tangible examples and solutions for real-world problems.
Partnerships and Collaboration
Strategic partnerships are essential for IOTA’s expansion into new markets and industries. To date, the project has established collaborations with leading companies and institutions, demonstrating its versatility and potential. For instance, IOTA has partnered with car manufacturers like BMW and Volkswagen to develop advanced车联网应用。此外,IOTA还与多家知名公司合作,包括宝马(BMW)和大众(Volkswagen),以开发先进的车联网应用。
In the automotive sector, IOTA is working on integrating its technology into vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communications. This can enhance the safety, efficiency, and connectivity of modern automobiles. By leveraging IOTA’s zero-fee transactions and high-speed confirmations, automakers aim to create more resilient and responsive transportation networks.
Furthermore, IOTA’s partnerships extend to the financial industry. Major banks and financial institutions have been exploring the use of IOTA for cross-border payments, micropayments, and fraud detection. The absence of transaction fees and the ability to process near-instantaneous transactions make IOTA an attractive option for these applications. Collaborations with financial players not only validate IOTA’s technical capabilities but also expand its reach into sectors with stringent regulatory requirements.
Regulatory Environment
The regulatory landscape is critical for any technology that seeks to enter the mainstream market. IOTA has faced scrutiny from governments and regulatory bodies, particularly concerning privacy and security concerns. In response, the IOTA Foundation and its developers have actively engaged with regulators to address these issues and ensure compliance.
The project has implemented robust security measures to protect users’ data and maintain the integrity of its network. Transparent audit processes and regular updates to its whitepapers and documentation provide stakeholders with detailed information about IOTA’s protocols and architecture. As regulatory frameworks evolve, IOTA continues to adapt its technology to meet regulatory standards while preserving its core principles.
Towards a Safer and More Secure Future
The quest for a safer and more secure future is a shared goal among many blockchain projects, including IOTA. The project recognizes that trust is paramount in deploying decentralized technologies on a large scale. To this end, IOTA has made significant strides in enhancing cybersecurity and user protection.
One key aspect of IOTA’s commitment to security is the implementation of advanced cryptographic algorithms. While traditional blockchain systems rely on public-key cryptography for security, IOTA employs more sophisticated techniques to prevent common attacks such as double spending and Sybil attacks. The Tangle’s double-spending mechanism, combined with its DAG structure, provides inherent resistance against adversarial behaviors.
IOTA also emphasizes the importance of node management and security. Users are encouraged to run lightweight nodes, which consume less power and resources compared to full nodes. By distributing the validation burden across numerous participants, the network becomes more resilient to attacks and ensures consistent decentralization.
Conclusion
In summary, IOTA stands at the forefront of blockchain innovation, offering a transformative solution with the potential to reshape various industries. While it faces challenges such as scalability and regulatory acceptance, IOTA’s community-driven approach, strategic partnerships, and focus on security and usability position it well for future success.
As the technology continues to evolve, IOTA is poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of decentralized technology. Whether it’s through advancements in vehicular communications, financial services, or smart city infrastructure, IOTA’s commitment to a decentralized, feeless, and secure future makes it an exciting subject for continued exploration and investment.
Conclusion and Future Outlook
As IOTA continues to evolve, its potential for disruptive change in various sectors remains strong. However, to fully realize its vision, the project must address several ongoing challenges. Scalability, interoperability, community engagement, and regulatory compliance are areas that require continuous attention and innovation.
Scalability: While the Tangle technology offers significant advantages in terms of transaction throughput and cost-efficiency, the real-world performance of the Tangle under heavy loads remains a topic of interest. Ongoing efforts, such as Tangle 2.0, are aimed at addressing these limitations and enhancing the network’s capacity to handle a growing number of transactions seamlessly. The success of these initiatives will determine whether IOTA can truly scale to meet the demands of large-scale applications.
Interoperability: Achieving seamless integration with existing blockchain platforms is crucial for IOTA’s long-term success. As more players enter the decentralized technology space, the ability to interoperate with other protocols (such as Ethereum, Bitcoin, and Stellar) becomes increasingly important. Interoperability efforts not only broaden the applicability of IOTA technology but also enable a more cohesive and interconnected decentralized ecosystem.
Community Engagement: Building a strong and engaged community is vital for the sustained growth of any technology project. IOTA’s foundation and developer communities continue to play a critical role in driving innovation and adoption. Encouraging contributions from developers, fostering open-source collaboration, and promoting educational resources are essential steps in maintaining community momentum. Engaging with emerging technologies and supporting young talents can help ensure that IOTA remains at the cutting edge of decentralized technology advancements.
Regulatory Compliance: Navigating the complex and evolving regulatory landscape is a continuous challenge. As IOTA expands its footprint into regulated industries such as finance and automotive, compliance with local and international regulations becomes increasingly important. Proactively engaging with regulatory bodies, participating in standards-setting processes, and adopting best practices in governance and transparency are key strategies for ensuring sustainable growth and acceptance.
Ethical Considerations and Sustainable Growth
IOTA’s success is not just about technological innovation; it also hinges on ethical considerations and sustainable growth. Ensuring that the technology promotes fairness, inclusiveness, and privacy is fundamental to its long-term viability. Here are a few key considerations:
Fairness and Inclusiveness: One of the hallmark features of decentralized technology is its potential to democratize access to financial and other resources. IOTA should strive to ensure that its technology benefits a wide range of users, including those in underserved populations. Initiatives to promote financial inclusion, especially in developing countries, can help realize this potential.
Privacy and Data Protection: As IOTA integrates more deeply into our digital lives, maintaining user privacy and data protection becomes increasingly important. Implementing strong encryption and anonymization techniques can help safeguard user information. Transparency about data handling practices and user consent policies can also build trust and ensure that users feel secure in their interactions with the network.
Sustainability: The environmental impact of blockchain technologies, particularly those that rely heavily on Proof of Work (PoW), is a growing concern. IOTA’s zero-transaction fee model and energy-efficient Tangle design provide a significant advantage in this regard. Encouraging further research into sustainable and eco-friendly approaches to blockchain technology can help minimize the ecological footprint of decentralized networks.
Call to Action
The journey of IOTA reflects the broader narrative of blockchain technology—a path filled with possibilities and challenges. For those interested in contributing to or participating in this transformative technology, there are several ways to get involved:
Get Involved: Join the IOTA community by attending webinars, meetups, or hackathons. Engage with the developer community on GitHub, participate in forums, and contribute to open-source projects. The more individuals and organizations contribute, the stronger and more resilient the IOTA ecosystem will become.
Explore Applications: Explore the diverse range of applications enabled by IOTA. From financial services and supply chain management to smart cities and automotive innovation, there are countless ways to leverage IOTA’s technology for real-world benefits. Whether you’re a developer, researcher, or entrepreneur, there’s always a place for you in the IOTA ecosystem.
Support Research: Support academic and industrial research into blockchain and decentralized technologies. Engage with research institutions, sponsors, and funding agencies to advance the state-of-the-art in IOTA and blockchain technology.
A Final Word
As we conclude this exploration of IOTA, it is clear that this technology holds immense promise for transforming the world. From streamlining transactions to driving innovation in various industries, IOTA is setting new benchmarks for decentralized technology. With ongoing efforts in scaling, interoperability, and community engagement, IOTA is well-positioned to continue evolving and disrupting the status quo.
Whether you are already involved in the IOTA community or are curious about the future of blockchain technology, there is much to discover and contribute. Together, we can continue to push the boundaries of what is possible and create a more secure, connected, and sustainable future.