Saint Jerome: Life, Legacy, and the Vulgate Bible
Introduction to Saint Jerome
Saint Jerome, born Eusebius Sophronius Hieronymus around 347 AD, was a pivotal figure in early Christianity. Renowned as a biblical scholar, theologian, and translator, his most enduring contribution is the Vulgate, the Latin translation of the Bible that remained authoritative for over 1,500 years. Jerome's life, marked by asceticism, intellectual rigor, and occasional controversy, bridges the classical and Christian worlds.
Early Life and Education
Jerome was born in Stridon, a town on the border of modern-day Croatia and Slovenia, to a wealthy Christian family. His early education in Rome immersed him in classical literature, where he developed a deep appreciation for Cicero and other pagan authors. However, a profound spiritual experience led him to embrace monasticism and dedicate his life to Christian scholarship.
Conversion and Asceticism
After his conversion, Jerome sought solitude in the Chalcis desert near Antioch, where he lived as a hermit from 374 to 379 AD. During this period, he studied Hebrew under a Jewish convert, despite his initial aversion to the language. This rigorous ascetic life was marked by intense study, prayer, and the beginning of his lifelong work on scriptural translation.
Priesthood and Role in Rome
Jerome was ordained as a priest in Antioch around 378 AD. His scholarly reputation grew, leading to his appointment as secretary to Pope Damasus I in 382 AD. During his time in Rome, Jerome began the monumental task of translating the Bible into Latin, a project that would later become the Vulgate.
Controversies and Exile
Jerome's tenure in Rome was not without conflict. His sharp critiques of contemporaries and theological opponents earned him enemies. Following the death of Pope Damasus I in 384 AD, Jerome's outspoken nature led to his exile from Rome. This period of adversity, however, allowed him to focus more deeply on his scholarly pursuits.
The Vulgate: Jerome’s Magnum Opus
The Vulgate is Jerome's most significant achievement, a Latin translation of the Bible that he worked on for over 30 years. Unlike earlier Latin versions, Jerome translated directly from Hebrew, Aramaic, and Greek manuscripts, ensuring greater accuracy and clarity. The Vulgate was completed around 405 AD and was later declared the official Latin Bible by the Council of Trent in 1546.
Impact of the Vulgate
The Vulgate had a profound impact on Western Christianity. It standardized the biblical text for liturgical and doctrinal use, influencing theology, art, and culture for centuries. Even today, the Vulgate remains a critical resource for biblical scholars and is still used in 60% of Latin liturgies.
Founding the Bethlehem Monastery
In 386 AD, Jerome founded a double monastery in Bethlehem, which housed both monks and nuns. This monastic community, supported by his close associates Paula and Eustochium, became a center of learning and prayer. Jerome spent his final decades here, continuing his translations, writing commentaries, and engaging in theological debates.
Final Years and Death
Jerome's later years were marked by both productivity and controversy. He engaged in heated debates with figures like Rufinus and the Pelagians, defending orthodox Christian teachings. Jerome died on September 30, 420 AD, leaving behind a legacy that would shape Christian thought for centuries.
Legacy and Patronage
Saint Jerome is celebrated as the patron saint of librarians, scholars, translators, and archivists. His feast day, September 30, honors his contributions to biblical scholarship and monastic life. Jerome's influence extends beyond theology; he is often depicted in art with a lion, symbolizing his tamed temper and intellectual prowess.
Modern Recognition
Today, Jerome is recognized as one of the 37 Doctors of the Church, a title that underscores his enduring importance. His works, including over 120 letters and 100 commentaries, continue to be studied for their theological depth and historical insight. Modern digital projects, such as Vulsearch, are making the Vulgate more accessible than ever.
Conclusion of Part 1
Saint Jerome's life was a blend of intellectual rigor, spiritual devotion, and occasional controversy. His translation of the Bible into Latin, the Vulgate, remains one of the most influential works in Christian history. In the next section, we will delve deeper into Jerome's theological contributions, his controversies, and his enduring impact on modern biblical scholarship.
Theological Contributions and Writings
Beyond the Vulgate, Saint Jerome produced an extensive body of work that shaped early Christian theology. His writings include biblical commentaries, historical chronicles, and theological treatises, many of which remain influential today. Jerome's approach to Scripture was both scholarly and devotional, emphasizing the importance of understanding the Bible in its original languages.
Key Theological Works
Jerome's commentaries on the Old and New Testaments are among his most significant contributions. He wrote detailed exegeses on books like Isaiah, Jeremiah, and the Gospels, blending linguistic precision with spiritual insight. His work De Viris Illustribus (On Illustrious Men), completed in 393 AD, profiles 135 Christian writers, preserving invaluable historical records of early Church figures.
Letters and Correspondence
Jerome's epistles offer a window into his theological debates and personal struggles. He exchanged letters with prominent figures such as Saint Augustine, discussing topics like sin, grace, and biblical interpretation. His correspondence with Paula and Eustochium reveals his role as a spiritual mentor, particularly to women in the early Church.
Controversies and Theological Debates
Jerome's sharp intellect and uncompromising stance on doctrine often led to conflicts. His critiques of Origenism, a theological movement he considered heretical, sparked prolonged debates. Similarly, his disputes with Rufinus over Origen's teachings and his opposition to Pelagianism highlighted his commitment to orthodoxy.
Conflict with Rufinus
One of Jerome's most notable controversies was with Rufinus of Aquileia, a fellow scholar who defended Origen's teachings. Jerome accused Rufinus of distorting Origen's work, leading to a bitter public dispute. Their conflict underscored the broader theological tensions of the time, particularly regarding the interpretation of Scripture and the nature of divine grace.
Opposition to Pelagianism
Jerome was also a vocal opponent of Pelagianism, a movement that denied the doctrine of original sin and emphasized human free will. His writings against Pelagius and his followers reinforced the Church's teaching on the necessity of divine grace for salvation. This debate had lasting implications for Christian theology, particularly in the West.
Cultural and Artistic Influence
Saint Jerome's legacy extends beyond theology into art, literature, and culture. His depiction in Renaissance art often includes symbolic elements like a lion, skull, or cardinal's hat, representing his asceticism, intellectual rigor, and ecclesiastical authority. These images have cemented his place as a cultural icon.
Depictions in Art
Artists such as Albrecht Dürer, Caravaggio, and Leonardo da Vinci have immortalized Jerome in their works. Dürer's engraving Saint Jerome in His Study (1514) captures the scholar in a moment of quiet reflection, surrounded by books and symbols of his erudition. Caravaggio's Saint Jerome Writing (1607) emphasizes his dedication to Scripture, portraying him in a state of deep concentration.
Literary and Media Representations
Jerome's life has inspired numerous literary works and films. The 1951 epic film Quo Vadis features Jerome as a secondary character, reflecting his historical significance. Modern novels and academic studies continue to explore his complex personality, blending piety with a sometimes contentious temperament.
Modern Scholarly and Digital Revivals
In recent years, there has been a resurgence of interest in Jerome's works, particularly the Vulgate. Digital projects like Vulsearch and the Biblia Sacra Vulgata (5th edition) are making his translation more accessible to scholars and laypeople alike. These initiatives leverage modern technology to preserve and disseminate Jerome's legacy.
Digital Projects and AI Analysis
The Vatican Library and several universities have collaborated on digitizing the Vulgate, allowing for advanced textual analysis. AI-assisted tools are now being used to study variations in manuscripts, providing new insights into Jerome's translation methods. These efforts ensure that the Vulgate remains a vital resource for biblical studies in the digital age.
Academic Conferences and Anniversaries
The 1,600th anniversary of Jerome's death in 2020 was marked by international conferences and publications. Scholars gathered to discuss his contributions to theology, linguistics, and monasticism. While no major events are planned for 2025, ongoing research continues to highlight Jerome's relevance in contemporary biblical scholarship.
Jerome’s Enduring Impact on Biblical Scholarship
Jerome's influence on biblical scholarship is immeasurable. The Vulgate served as the foundation for Western Christian theology for over a millennium, shaping doctrines, liturgies, and even vernacular translations like the King James Bible. His emphasis on studying Scripture in its original languages set a precedent for future scholars.
Influence on Later Translations
The Vulgate's precision and clarity influenced later translations, including the Douay-Rheims Bible (16th century), which was based directly on Jerome's work. Even Protestant reformers, despite their critiques of Catholic traditions, relied on the Vulgate for textual comparisons. This cross-denominational impact underscores Jerome's universal significance.
Jerome in Modern Theology
Today, Jerome is cited in 90% of pre-1960s Catholic theological works, a testament to his enduring authority. His writings on exegesis, asceticism, and Church history remain essential reading for seminarians and scholars. The Catechism of the Catholic Church frequently references his teachings, particularly on the interpretation of Scripture.
Conclusion of Part 2
Saint Jerome's life and work exemplify the intersection of faith, scholarship, and controversy. His translation of the Bible, the Vulgate, revolutionized Christian thought and remains a cornerstone of biblical studies. In the final section, we will explore Jerome's lasting legacy, his role as a patron saint, and how his teachings continue to inspire modern believers and scholars alike.
Saint Jerome’s Role as a Patron Saint
Saint Jerome is venerated as the patron saint of librarians, scholars, translators, and archivists, reflecting his lifelong dedication to preserving and interpreting sacred texts. His feast day, celebrated on September 30, honors his contributions to the Church and his enduring influence on Christian intellectual tradition.
Patronage of Librarians and Scholars
Jerome’s meticulous work on the Vulgate and his extensive writings make him a natural patron for those engaged in scholarly pursuits. Libraries and academic institutions often invoke his intercession, seeking wisdom and diligence in research. His emphasis on the importance of original languages in biblical study continues to inspire linguists and theologians.
Influence on Translators and Archivists
As the translator of the Bible into Latin, Jerome is a model for translators worldwide. His commitment to accuracy and clarity set a standard for future generations. Archivists, too, look to Jerome as a symbol of preservation and accessibility, values he embodied through his work in Bethlehem’s monastery, where manuscripts were carefully copied and stored.
Jerome’s Monastic Legacy
Jerome’s founding of the double monastery in Bethlehem was a groundbreaking contribution to monastic life. This community, which included both men and women, became a center of learning, prayer, and scriptural study. His monastic rule emphasized discipline, humility, and devotion to Scripture.
The Bethlehem Monastery’s Structure
The monastery housed approximately 50 monks and nuns by the time of Jerome’s death. Under his guidance, the community followed a rigorous schedule of prayer, study, and manual labor. Jerome’s leadership ensured that the monastery became a hub for biblical scholarship, attracting scholars and pilgrims from across the Christian world.
Impact on Western Monasticism
Jerome’s monastic model influenced later religious communities, particularly in the Benedictine tradition. His emphasis on scriptural study and asceticism shaped the development of Western monasticism, leaving a lasting legacy that extends to modern religious orders.
Jerome’s Teachings on Scripture and Spirituality
Jerome’s most famous dictum, “Ignorance of Scripture is ignorance of Christ”, encapsulates his belief in the centrality of the Bible to Christian life. His teachings on exegesis, prayer, and asceticism remain foundational in Christian spirituality.
The Importance of Scripture
For Jerome, the Bible was not merely a text to be studied but the living word of God. He advocated for a deep, personal engagement with Scripture, urging believers to read and meditate on it daily. His commentaries and letters reflect this conviction, offering practical guidance on how to interpret and apply biblical teachings.
Asceticism and Spiritual Discipline
Jerome’s own life of asceticism—marked by fasting, prayer, and solitude—served as a model for Christian spiritual discipline. He viewed physical mortification as a means to purify the soul and draw closer to God. His writings on asceticism influenced later saints, including Saint Benedict and Saint Bernard of Clairvaux.
Jerome’s Controversial Legacy
While Jerome is celebrated for his scholarly achievements, his contentious personality and theological disputes have also shaped his legacy. His sharp critiques of contemporaries and unyielding stance on doctrine often led to conflict, yet these very traits underscored his commitment to truth.
Debates with Contemporaries
Jerome’s disputes with figures like Rufinus and Pelagius were not merely personal but reflected broader theological tensions. His opposition to Origenism and Pelagianism reinforced orthodox Christian teachings, particularly on the nature of sin and grace. These debates highlighted his role as a defender of the faith.
Modern Reevaluations
Modern scholars have reevaluated Jerome’s legacy, acknowledging both his brilliance and his flaws. His views on women in the Church, for example, were complex—he mentored female scholars like Paula while also expressing misogynistic sentiments in some writings. This duality invites ongoing discussion about his place in Christian history.
Jerome’s Influence on Modern Biblical Studies
The Vulgate remains a cornerstone of biblical studies, even in the modern era. Its precision and historical significance make it an indispensable resource for scholars. Jerome’s methodological approach—translating from original languages and cross-referencing manuscripts—set a precedent for contemporary biblical scholarship.
The Vulgate in Digital Age
Digital projects like Vulsearch and the Biblia Sacra Vulgata have revitalized interest in Jerome’s work. These initiatives provide scholars with unprecedented access to his translation, facilitating new research and interpretations. The Vulgate’s enduring relevance is a testament to Jerome’s scholarly rigor.
Jerome’s Methodology
Jerome’s insistence on studying Scripture in its original Hebrew and Greek languages revolutionized biblical exegesis. His approach influenced later scholars, including Erasmus and Luther, who similarly emphasized the importance of linguistic accuracy in translation. This methodology remains a benchmark in biblical studies.
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Saint Jerome
Saint Jerome’s life and work have left an indelible mark on Christian theology, biblical scholarship, and monastic tradition. His translation of the Bible, the Vulgate, stands as one of the most influential texts in Western Christianity, shaping doctrine and liturgy for over 1,500 years.
Key Takeaways
- Biblical Scholarship: Jerome’s Vulgate remains a foundational text, influencing translations and theological studies.
- Monastic Leadership: His double monastery in Bethlehem set a precedent for Christian communities.
- Theological Debates: Jerome’s defense of orthodoxy shaped early Christian doctrine.
- Cultural Icon: His depictions in art and literature reflect his enduring cultural significance.
Final Thoughts
Saint Jerome’s legacy is a reminder of the power of faith, scholarship, and perseverance. His dedication to Scripture and his unwavering pursuit of truth continue to inspire believers and scholars alike. As we reflect on his contributions, we are reminded of his timeless wisdom: “The Scriptures are the swaddling clothes of the Lord Jesus Christ.” In an age of rapid change, Jerome’s life challenges us to seek deeper understanding and to embrace the transformative power of God’s word.

Understanding the Power of Trial and Error
Have you ever tried something that didn't work out quite right, only to keep trying until you finally hit the mark? If so, congratulations! You've just done trial and error. It's a technique that's been around since the dawn of time, helping us learn from our mistakes and find solutions for problems. Whether you're a student figuring out how to solve a tricky math problem or an entrepreneur trying to figure out what makes your business tick, trial and error plays a crucial role.
In simplest terms, trial and error is a problem-solving approach where you test different methods and ideas to see which one works. Unlike the more conventional methods that focus on planning and theory before taking action, trial and error relies on practical experimentation and real-world feedback. This approach might seem simple on the surface, but it's incredibly powerful in the realm of learning and problem-solving.
The Basics of Trial and Error
Let's dive into some key facts and recent developments related to trial and error. First things first, it's important to understand what exactly we mean by this term. According to various sources, trial and error involves making repeated attempts to solve a problem, each time learning from any failures that you encounter. These failures are not seen as setbacks but rather as valuable data points that help guide you closer to a successful outcome.
Versatile Application Across Fields
One of the remarkable aspects of trial and error is its versatility. It's not confined to any single field—it's used all over the place! Here are a few examples:
- Entrepreneurship: Entrepreneurs often rely heavily on trial and error to test their ideas and strategies without incurring heavy financial costs. By making small investments that pay off if successful and learning from failures, they can refine their products or services and find the right market fit.
- Scientific Experiments: Scientists use trial and error to test hypotheses and theories. They perform experiments, analyze results, and adjust their methods based on what they learn, leading to breakthroughs and discoveries.
- Everyday Problem-Solving: We all have faced situations like trying multiple passwords until we find the right one or figuring out how to assemble a new toy. These are everyday instances of trial and error at work—learning as you go and improving with each attempt.
Historical Importance and Empirical Learning
While trial and error might seem like a relatively recent development, it’s actually one of the oldest and most fundamental learning methods known to both humans and animals. It serves as a cornerstone for how we learn from experience. Unlike purely theoretical methods that rely on logic and deduction, trial and error is rooted in the practical observation and experimentation.
Empirical Approach to Problem-Solving
So, what exactly is an empirical approach? Simply put, it means relying on observation and experiment to gather information and make decisions. In contrast to theories that might work well on paper but fail in practice, trial and error allows us to see what really works through direct experience. By going through the process of attempting something, observing the results, and then adapting our approach based on what happens, we can develop a deeper understanding of the situation.
Learning Through Mistakes
The beauty of trial and error lies in the fact that it teaches us more effectively than purely theoretical learning. When you make a mistake, instead of ignoring it or feeling discouraged, you can use that information to do better next time. This doesn’t just apply to technical skills or academic knowledge—it applies to life in general. Whether you’re learning to cook a new dish, teach a pet a trick, or manage finances, trial and error helps you become more resilient and adaptable.
Critical Thinking and Resilience
Trial and error isn’t just about solving problems; it's also about enhancing critical thinking skills. Each failed attempt is an opportunity to think critically about what went wrong and how you can adjust your approach. This process encourages creativity and innovation by pushing us out of our comfort zones and forcing us to explore new possibilities.
Rather than fearing failure, people who use trial and error embrace it as an essential part of the journey. They understand that every failed attempt brings them closer to success, allowing them to build resilience and a growth mindset. This way of thinking helps them to stay motivated even when the path ahead seems unclear, knowing that persistent effort will eventually lead to positive outcomes.
Incorporating Technology
Modern technology has revolutionized the way we practice trial and error. Tools like computer simulations and artificial intelligence allow us to run numerous experiments quickly and efficiently. These digital platforms provide instant feedback and data analysis, making it easier to identify patterns and refine our methods. As a result, trial and error cycles have become much faster, enabling rapid learning and innovation.
Furthermore, online resources and communities offer vast libraries of examples and advice for anyone looking to improve their skills. Platforms such as YouTube tutorials, online forums, and educational apps are filled with tips and tricks from experts and enthusiasts alike. Leveraging these resources can significantly enhance our problem-solving abilities by showing us proven techniques and avoiding common pitfalls.
The Future of Trial and Error
So, what does the future hold for trial and error? While it remains a cornerstone of learning and innovation, it's likely to evolve alongside advancements in technology. New AI tools, for instance, could automate much of the trial phase, leaving humans to interpret outcomes and make strategic decisions.
In addition, educators are increasingly recognizing the value of experiential learning methods like trial and error. By providing students with hands-on opportunities to explore and fail, they can develop a stronger grasp of concepts and better prepare for real-world challenges. Schools are incorporating more project-based learning and hands-on activities, fostering an environment where students can confidently embrace their mistakes as stepping stones towards success.
Finding Success Through Iteration
In the end, success in almost any endeavor often comes from a combination of persistence, creativity, and the willingness to accept failure as part of the learning process. Trial and error is a valuable tool that can help us navigate complex and unpredictable situations, teaching us valuable lessons along the way. So, the next time you face a challenge, remember: it’s okay to try something and not succeed at first. Embrace the process, learn from your mistakes, and keep trying until you reach your goal. That’s the true spirit of trial and error!
New Frontiers in Education and Beyond
The application of trial and error extends far beyond entrepreneurship, scientific research, and everyday problem-solving. Its impact is particularly evident in the realm of education, especially in today's rapidly changing world. Educational institutions are increasingly adopting experiential learning methods to foster critical thinking, innovation, and resilience among young learners. These approaches not only enhance academic performance but also prepare students for real-world challenges by equipping them with practical skills and a growth mindset.
Youth-Led Innovation
One striking example of this shift is seen in the growing number of youth-led initiatives and hackathons. Young individuals are using trial and error to come up with innovative solutions to pressing global issues like climate change, social injustice, and technological advancements. Through these events, they collaborate, brainstorm, and test their ideas, learning from feedback and refining their projects. For instance, many students participate in hackathons, building prototypes of technology gadgets or software applications that address specific problems.
These experiences not only provide hands-on learning but also instill confidence and a sense of agency in young learners. By actively participating in the problem-solving process, they develop a deep understanding of the subject matter and gain invaluable skills such as teamwork, creative thinking, and project management. Moreover, such activities often involve mentorship from older professionals and access to resources that would otherwise be out of reach, further enriching the learning experience.
Real-World Application in Curriculum
Incorporating trial and error into the curriculum involves moving away from traditional lecture-based methods and towards more interactive and participatory forms of learning. Teachers are designing lessons that encourage students to engage in real-world problem-solving tasks. For instance, in mathematics classes, students might be given open-ended problems and asked to explore multiple methods to arrive at a solution. Similarly, science classes can involve experimental design projects where students hypothesize, conduct tests, and analyze data, all while receiving guidance and support from instructors.
Another effective strategy is project-based learning, where students work on long-term projects that require them to apply their knowledge and skills in creative and meaningful ways. These projects often involve collaboration with peers and can span multiple subjects, allowing students to see the interconnectedness of different areas of study. For example, a biology project might involve researching local ecosystems, collecting data, and presenting findings to the class, all while developing critical thinking skills.
Digital Tools Facilitating Faster Learning Cycles
The integration of digital tools and simulations has also greatly accelerated the trial and error process. Platforms like CodeLab and Google's Teachable Machine allow students to quickly develop and test code or machine learning models. These tools provide instant feedback, enabling students to iterate on their designs more efficiently. For instance, a user might create a simple game using Scratch and continuously adjust the code to improve gameplay mechanics, all within a few minutes.
Similarly, virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies offer immersive learning environments where students can experiment with complex systems without real-world risks. For example, medical students can practice surgical procedures in VR, or engineers can simulate robotic movements and design improvements. These technologies not only make learning more engaging but also provide a safe space for students to make mistakes and learn from them.
Encouraging Failure and Learning
To fully embrace the power of trial and error, it's crucial to create a culture that values and encourages failure. This means shifting the narrative from seeing mistakes as negative to viewing them as valuable learning opportunities. Educators should emphasize the importance of resilience and persistence, reinforcing the message that it's okay to stumble and that every failure brings us one step closer to success.
Classroom settings should be designed to foster a growth mindset—where students are encouraged to view challenges as opportunities for growth rather than obstacles to avoid. This can be achieved through various strategies, such as regular reflection sessions where students discuss what they learned from their mistakes, or group activities that promote collective problem-solving and peer support. By normalizing failure, students become more comfortable taking risks and pushing their boundaries, ultimately leading to greater overall success.
Combining Methods for Optimal Results
While trial and error is a powerful tool, combining it with other problem-solving strategies can yield even better results. Integrating trial and error with techniques like design thinking, where students follow a structured process of empathy, ideation, prototyping, and testing, can lead to more innovative and sustainable solutions. For example, a design thinking project might involve students conducting user interviews to understand needs, brainstorming solutions collectively, creating prototypes, and then testing and refining these solutions through iterative cycles of trial and error.
Similarly, combining trial and error with the scientific method can result in more robust research and development. By systematically testing hypotheses and analyzing data, students can develop a deeper understanding of the underlying processes and principles. This hybrid approach ensures that both creativity and rigor are maintained throughout the problem-solving process.
Conclusion
In conclusion, trial and error is a versatile and essential problem-solving technique that has stood the test of time. Its applications range from everyday problem-solving to cutting-edge scientific research and entrepreneurial ventures. As technology continues to advance, trial and error becomes faster and more efficient, making it a valuable tool for a wide array of industries and individuals.
The future of this approach lies in its seamless integration with other learning and problem-solving methods. By embracing this method and fostering a culture of resilience and continuous improvement, we can prepare ourselves and future generations to face and overcome whatever challenges may come our way. So remember, every mistake is a step towards success. Embrace trial and error, learn from it, and keep pushing forward!
Fostering a Culture of Learning from Mistakes
Creating a culture of learning from mistakes is crucial for truly harnessing the power of trial and error. In schools and workplaces, leaders play a pivotal role in establishing an environment where failure is not shunned but embraced as a stepping stone to growth. This involves several key practices:
- Open Discourse: Encouraging open discussions about failures and successes can break down the stigma associated with mistakes. By sharing stories of past failures and the lessons learned, individuals feel less alone and more supported. Teachers and managers can facilitate these discussions to highlight how mistakes contributed to eventual success.
- Constructive Feedback: Providing constructive feedback is essential to help those involved understand why a particular approach did not work and how it can be improved next time. This feedback should focus on actionable steps to move forward rather than placing blame.
- Continuous Improvement: Establishing a continuous improvement mindset means constantly seeking ways to refine processes and strategies. By regularly reviewing outcomes and reflecting on what worked and what didn't, organizations and individuals can make incremental adjustments that lead to better overall performance.
Personal Growth Through Trial and Error
Trials and errors do not only benefit professional careers but also contribute to personal growth. Whether tackling a difficult puzzle or trying a new hobby, the process of trial and error cultivates a variety of skills and traits:
- Problem-Solving Skills: Engaging in trial and error helps develop strong problem-solving skills. Individuals learn to break down complex issues into manageable parts, test various hypotheses, and adapt strategies based on feedback.
- Resilience: Repeated experiences of trying something and failing can build resilience. Over time, individuals develop the mental toughness to face challenges head-on and persist even when faced with setbacks.
- Adaptability: The flexibility to pivot and try a new approach when the old one fails fosters adaptability. This skill is crucial in rapidly changing environments where traditional methods may no longer be effective.
- Growth Mindset: Recognizing that intelligence and abilities can grow with effort and practice promotes a growth mindset. This mindset encourages individuals to see failures as temporary setbacks that can be overcome with hard work and determination.
Addressing Criticism and Misconceptions
Some might argue that trial and error can be inefficient or costly. However, the cost of not trying at all is often much higher. Consider the example of an aspiring musician who fears playing an instrument in public due to the risk of failure. While making mistakes publicly can be embarrassing, not taking those risks prevents the musician from improving and potentially achieving great success in the future.
Misconceptions about trial and error often stem from a focus on immediate success rather than the long-term benefits. While it might take several attempts to get something right, each failure provides valuable data and insights that contribute to eventual mastery. In entrepreneurship, for instance, many startups undergo multiple pivot moments before finding a viable business model. These pivots are rarely linear and often involve numerous trials before they hit upon the right direction.
Conclusion
In summary, trial and error is a fundamental tool for learning and innovation that transcends fields and personal endeavors. By embracing this method, we cultivate problem-solving skills, build resilience, and foster a growth mindset. Whether you're a student, entrepreneur, scientist, or just someone facing everyday challenges, adopting a spirit of trial and error can propel you forward toward success.
As we look to the future, let us not only recognize the importance of trial and error but also nurture a community that values and supports it. By doing so, we empower individuals and organizations to innovate, persist, and thrive in an ever-changing world.
Remember, the next time you face a challenge, don't be afraid to give it a try. Every failure brings you closer to success. Embrace trial and error, learn from every step, and continue moving forward with determination and resilience.


Uterine Peristalsis: Mechanisms, Hormonal Control, and Clinical Implications
Introduction to Uterine Peristalsis
Uterine peristalsis refers to the wave-like contractions of the subendometrial myometrium, the inner muscular layer of the uterus. These contractions play a crucial role in reproductive health, particularly during the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle. Controlled primarily by estradiol and influenced by oxytocin, peristalsis facilitates sperm transport and may aid in embryo implantation.
Research, including a foundational 1998 study cited 161 times, highlights the importance of these contractions in fertility and assisted reproductive technologies (ART). Understanding the mechanisms behind uterine peristalsis can improve clinical outcomes in treatments like in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Hormonal Regulation of Uterine Peristalsis
Role of Estradiol in Peristaltic Activity
The dominant follicle releases estradiol, which drives the frequency of uterine contractions. During the follicular phase, estradiol levels rise, peaking just before ovulation. This hormonal surge enhances peristaltic waves, ensuring optimal conditions for gamete transport.
Studies show that exogenous estradiol, such as estradiol valerate, mimics natural peristaltic patterns. However, high doses do not significantly increase contraction frequency due to system refractoriness.
Influence of Oxytocin on Uterine Contractions
Oxytocin acts locally within the endometrial-subendometrial unit, enhancing the effects of estradiol. Unlike systemic oxytocin, which has limited impact, autocrine/paracrine oxytocin plays a key role in modulating peristalsis.
Clinical trials with intravenous oxytocin in the late follicular phase showed minimal additional effects, suggesting that oxytocin's role is supportive rather than primary.
Pharmacological Insights and Clinical Observations
Impact of Clomiphene Citrate on Peristalsis
Clomiphene citrate, a common fertility drug, slightly suppresses peristaltic frequency despite elevating estradiol levels. This paradoxical effect underscores the complexity of hormonal interactions in uterine contractions.
Research indicates that while clomiphene increases estradiol, it does not proportionally enhance peristalsis, likely due to receptor downregulation or other compensatory mechanisms.
Effects of Exogenous Hormones on Uterine Contractions
Administration of human menopausal gonadotropin (hMG) or estradiol valerate closely replicates natural peristaltic patterns. These findings are critical for fertility treatments, where timing and hormonal balance are essential.
Key observations include:
- Natural cycles show a baseline increase in peristalsis, peaking preovulatorily.
- Estradiol valerate/hMG interventions match natural contraction frequencies.
- High estradiol doses do not exceed normal peristaltic peaks, indicating refractoriness.
Physiological Role of Uterine Peristalsis
Directed Peristaltic Waves vs. Luteal-Phase Dysperistalsis
During the follicular phase, peristaltic waves are directed, facilitating rapid transport of sperm and embryos toward the fundus. In contrast, the luteal phase exhibits dysperistalsis—retrograde contractions that may contribute to conditions like endometriosis.
This distinction is vital for diagnosing and treating reproductive disorders, as abnormal peristalsis can impair fertility.
Study Design and Key Findings
Researchers used vaginal sonography to track peristalsis across different phases of the menstrual cycle. The study confirmed that estradiol is the primary driver of contractions, with oxytocin playing a secondary, synergistic role.
Key findings include:
"Peristaltic contractions in the subendometrial myometrium are critical for reproductive success, with estradiol and oxytocin working in tandem to optimize uterine function."
Clinical Relevance and Therapeutic Implications
Applications in Fertility Treatments
Understanding uterine peristalsis is crucial for IVF protocols. Timing embryo transfer with peak peristaltic activity can improve implantation rates. Clinicians must consider hormonal balance to avoid refractoriness in superovulation treatments.
For example:
- IVF timing: Aligning embryo transfer with natural peristaltic peaks enhances success.
- Avoiding high estradiol doses: Prevents system refractoriness and suboptimal contractions.
Research Gaps and Future Directions
While the 1998 study remains foundational, gaps exist in understanding long-term impacts and molecular pathways. Modern imaging techniques and AI-driven analysis could provide real-time insights into peristaltic activity.
Future research should explore:
- Oxytocin receptor dynamics in the endometrial-subendometrial unit.
- Non-invasive monitoring techniques for clinical applications.
- Long-term effects of hormonal interventions on uterine function.
Conclusion of Part 1
This section has introduced the mechanisms, hormonal regulation, and clinical implications of uterine peristalsis. In Part 2, we will delve deeper into diagnostic techniques, therapeutic strategies, and emerging research trends.
Diagnostic Techniques for Assessing Uterine Peristalsis
Vaginal Sonography: The Gold Standard
Vaginal sonography remains the most reliable method for visualizing uterine peristalsis. This non-invasive technique allows clinicians to observe subendometrial contractions in real-time, providing critical insights into reproductive health.
Key advantages of vaginal sonography include:
- High-resolution imaging of the endometrial-subendometrial unit.
- Real-time monitoring of peristaltic waves during different menstrual phases.
- Minimal discomfort for patients, making it ideal for repeated assessments.
Emerging Technologies in Peristalsis Monitoring
Advancements in medical imaging and artificial intelligence (AI) are revolutionizing the study of uterine peristalsis. 3D ultrasound and MRI offer deeper insights into contraction patterns, while AI algorithms can analyze large datasets to predict optimal fertility windows.
Potential future developments include:
- Automated peristalsis tracking via machine learning.
- Portable ultrasound devices for at-home monitoring.
- Integrated hormone-peristalsis mapping for personalized fertility plans.
Therapeutic Strategies for Optimizing Uterine Peristalsis
Hormonal Interventions in Fertility Treatments
Hormonal therapies play a pivotal role in regulating uterine peristalsis, particularly in assisted reproductive technologies (ART). Clinicians often use estradiol supplements to mimic natural cycles, while oxytocin modulators may enhance contraction efficiency.
Common hormonal interventions include:
- Estradiol valerate to simulate follicular phase conditions.
- Human menopausal gonadotropin (hMG) for controlled ovarian stimulation.
- Clomiphene citrate (with caution due to its suppressive effects on peristalsis).
Timing Embryo Transfer with Peristaltic Peaks
In IVF procedures, synchronizing embryo transfer with peak peristaltic activity can significantly improve implantation rates. Studies suggest that transfers performed during the late follicular phase—when contractions are most robust—yield better outcomes.
Key considerations for timing include:
- Monitoring estradiol levels to predict peristaltic peaks.
- Avoiding luteal phase dysperistalsis, which may hinder embryo movement.
- Personalizing protocols based on individual peristaltic patterns.
Uterine Peristalsis and Reproductive Disorders
Link Between Dysperistalsis and Endometriosis
Endometriosis is closely associated with luteal-phase dysperistalsis, where retrograde contractions may contribute to the displacement of endometrial tissue. Research indicates that women with endometriosis exhibit abnormal peristaltic patterns, which could serve as a diagnostic marker.
Clinical observations include:
- Increased retrograde contractions during the luteal phase.
- Reduced directed peristalsis in the follicular phase.
- Correlation with pelvic pain and infertility.
Impact on Unexplained Infertility
In cases of unexplained infertility, abnormal uterine peristalsis may be a contributing factor. Women with suboptimal contraction patterns often struggle with sperm transport and embryo implantation, even when other fertility parameters appear normal.
Potential solutions include:
- Peristalsis-enhancing therapies (e.g., low-dose oxytocin).
- Targeted hormonal adjustments to restore natural contraction rhythms.
- Advanced imaging to identify subtle peristaltic dysfunctions.
Research Gaps and Future Directions
Molecular Pathways and Oxytocin Receptor Dynamics
While the 1998 study established the role of estradiol and oxytocin, molecular mechanisms remain poorly understood. Future research should explore:
- Oxytocin receptor expression in the endometrial-subendometrial unit.
- Signal transduction pathways governing peristaltic contractions.
- Genetic factors influencing individual peristaltic patterns.
Long-Term Effects of Hormonal Interventions
Most studies focus on short-term peristaltic responses to hormonal treatments. However, long-term effects—such as receptor downregulation or uterine fatigue—require further investigation. Clinicians must balance immediate fertility goals with potential long-term risks.
Key questions include:
- Does prolonged estradiol exposure alter peristaltic efficiency?
- Can repeated oxytocin use lead to desensitization?
- Are there cumulative effects of fertility drugs on uterine function?
Conclusion of Part 2
This section has explored diagnostic techniques, therapeutic strategies, and the link between uterine peristalsis and reproductive disorders. In Part 3, we will conclude with a summary of key takeaways, practical recommendations, and the future of peristalsis research.
Key Takeaways and Practical Recommendations
Summarizing the Role of Uterine Peristalsis in Fertility
Uterine peristalsis is a critical yet often overlooked factor in reproductive health. Driven by estradiol and modulated by oxytocin, these contractions facilitate sperm transport and embryo implantation. Understanding their mechanisms can significantly improve fertility treatments and diagnostic approaches.
Key insights include:
- Estradiol dominance in the follicular phase enhances peristaltic frequency.
- Oxytocin’s local action supports but does not override estradiol’s effects.
- Dysperistalsis in the luteal phase may contribute to conditions like endometriosis.
Clinical Recommendations for Fertility Specialists
For clinicians, optimizing uterine peristalsis involves a combination of hormonal balance, timing strategies, and advanced monitoring. Practical steps include:
- Monitoring estradiol levels to predict peak peristaltic activity.
- Avoiding excessive clomiphene citrate, which may suppress contractions.
- Using vaginal sonography to assess peristaltic patterns before IVF.
- Personalizing embryo transfer timing based on individual peristaltic rhythms.
Future Research and Technological Advancements
Potential Breakthroughs in Peristalsis Research
While the 1998 study remains foundational, modern research must address unanswered questions. Future directions include:
- Molecular studies on oxytocin receptor dynamics.
- AI-driven peristalsis tracking for real-time fertility predictions.
- Long-term effects of hormonal interventions on uterine function.
Emerging technologies like 3D ultrasound and machine learning could revolutionize how we diagnose and treat peristaltic dysfunctions.
The Role of AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence is poised to transform fertility research by analyzing vast datasets to identify patterns in uterine contractions. Potential applications include:
- Automated peristalsis analysis from ultrasound scans.
- Predictive modeling for optimal embryo transfer timing.
- Personalized treatment plans based on individual peristaltic profiles.
"The integration of AI into reproductive medicine could unlock new possibilities for diagnosing and treating infertility linked to uterine peristalsis."
Addressing Common Misconceptions
Myth: Higher Estradiol Levels Always Improve Fertility
A common misconception is that maximizing estradiol will always enhance fertility. However, research shows that excessive estradiol can lead to system refractoriness, where the uterus no longer responds optimally to hormonal signals.
Key clarifications:
- Optimal estradiol levels vary by individual.
- High doses may not improve peristalsis beyond natural peaks.
- Balanced hormonal protocols yield better results than aggressive stimulation.
Myth: Oxytocin Is the Primary Driver of Peristalsis
While oxytocin plays a supportive role, it is not the primary regulator of uterine contractions. Estradiol remains the dominant hormone, with oxytocin acting as a modulator rather than a driver.
Important distinctions:
- Oxytocin enhances but does not initiate peristalsis.
- Local oxytocin action (autocrine/paracrine) is more critical than systemic administration.
- Excessive oxytocin does not significantly increase contraction frequency.
Conclusion: The Future of Uterine Peristalsis Research
Uterine peristalsis is a dynamic and essential component of female reproductive health. From its hormonal regulation to its clinical implications, understanding these contractions can lead to better fertility outcomes and more effective treatments for conditions like endometriosis and unexplained infertility.
As research advances, integrating AI, modern imaging, and personalized medicine will further illuminate the complexities of uterine function. Clinicians and researchers must continue collaborating to translate these insights into practical, patient-centered solutions.
"The study of uterine peristalsis is not just about contractions—it’s about unlocking the potential for healthier pregnancies and more successful fertility treatments."
By staying informed and embracing innovation, the medical community can ensure that uterine peristalsis remains a cornerstone of reproductive endocrinology and assisted reproductive technologies.
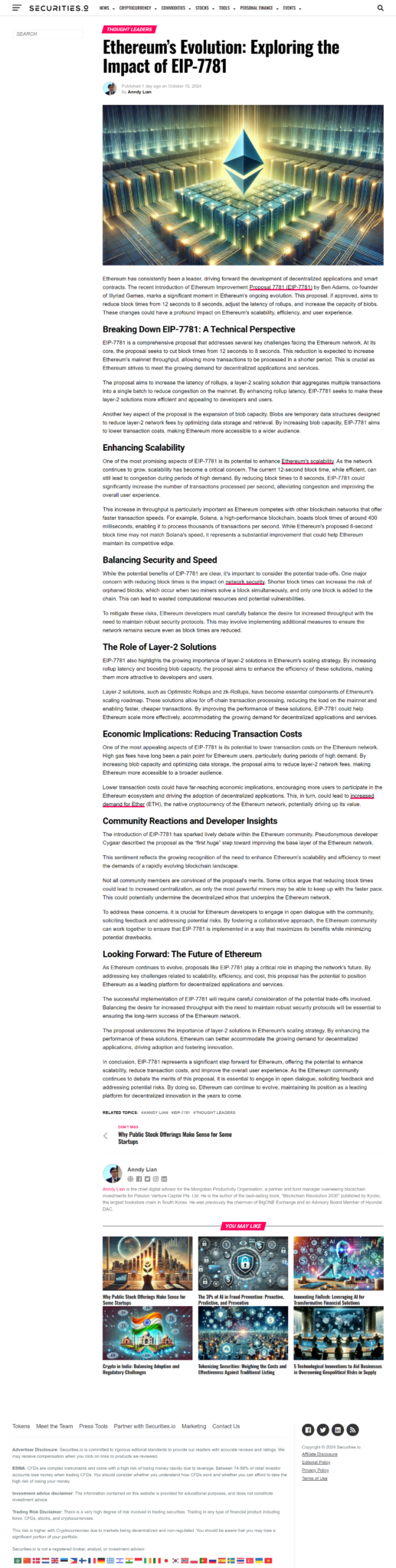
The Evolution and Impact of Ethereum: Revolutionizing the Blockchain Landscape
Ethereum, often described as the second-largest by market capitalization after Bitcoin and one of the most influential projects in the cryptocurrency world, has had a profound impact on the blockchain and decentralized finance (DeFi) landscapes. Since its launch in 2015, Ethereum has continually evolved, serving not just as a platform for digital assets but also as a foundational technology that powers decentralized applications (DApps), digital identity verification systems, and even entire economies.
The Genesis of Ethereum
Ethereum was created by Vitalik Buterin, a Russian-Canadian programmer, and co-founder of Bitcoin Magazine. Originally intended to be a platform for executing code using a smart contract-based system, Ethereum offered a scalable solution for running decentralized applications on a secure network. Unlike Bitcoin, which primarily functions as a store of value and medium of exchange, Ethereum introduced the concept of programmable blockchain, enabling developers to build and deploy custom applications directly on the blockchain.
The initial release of Ethereum came with substantial challenges, including scalability issues and transaction confirmations that sometimes took several minutes. Over time, the Ethereum Foundation, which manages the project, has worked to address these concerns through various updates and upgrades.
The Role of Smart Contracts
A cornerstone of Ethereum's innovative design is the concept of smart contracts—self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code on the blockchain. These contracts operate under predetermined rules stored on the Ethereum network, allowing them to automatically execute when conditions are met without intermediaries. This feature has been a driving force behind the decentralization revolution.
Smart contracts have numerous applications beyond financial transactions. They can facilitate anything from automating insurance claims, voting systems, and supply chain management to managing digital assets such as NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens). NFTs on Ethereum allow creators to grant ownership and provenance to unique items, such as art pieces or collectibles, ensuring authenticity and traceability.
Beyond Initial Coin Offering (ICO) and Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
In the early days, Ethereum gained notoriety for its role in facilitating Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs). ICOs allowed new blockchain projects to raise funds directly from investors by issuing tokens in exchange for ether (the native cryptocurrency of Ethereum). However, while ICOs were initially praised for their potential to democratize financial services, they also faced significant challenges, including regulatory scrutiny and security vulnerabilities that led to notable scams.
Despite these early issues, Ethereum's core strengths in smart contract capability and decentralization paved the way for the emergence of DeFi. DeFi applications built on Ethereum provide financial services such as lending, borrowing, and trading without the need for traditional banks or financial intermediaries.
Key DeFi protocols like Uniswap, Compound, and Aave have redefined the decentralized finance space, offering users direct access to a wide range of financial tools. These platforms utilize Ethereum’s gas fees mechanism to manage transaction costs and security, allowing for near-instantaneous and low-cost operations even during periods of high network activity.
Challenges and Innovations
Ethereum faces several challenges as it continues to scale and adapt to evolving market demands. One primary issue is transaction scalability, as Ethereum’s blockchain struggles to handle a large volume of transactions in a timely manner. To address this, Ethereum has implemented major upgrades such as the Casper protocol to transition to proof-of-stake consensus, reducing energy consumption and improving efficiency. Additionally, initiatives like Optimistic Rollups and Validium promise to enhance transaction throughput while maintaining security and reliability.
User experience remains another critical aspect of Ethereum’s growth. High gas fees remain a significant barrier for some users, especially in periods of network congestion. Efforts such as the development of Layer 2 solutions aim to offload transactions off the main blockchain, thereby reducing fees and increasing throughput.
The security of Ethereum is another focus area, with the ongoing transition to a proof-of-stake consensus mechanism designed to improve both security and sustainability. The move away from energy-intensive proof-of-work is not only beneficial for the environment but also aims to prevent attacks that could compromise the network.
Funding and Funding Sources
Funding for Ethereum development and community activities comes from multiple sources. Notably, Ethereum is open source and relies significantly on community contributions. However, there is also funding derived from institutional investors, venture capitalists, and non-profit organizations dedicated to advancing the blockchain ecosystem.
The Ethereum Foundation plays a crucial role in managing these funds and facilitating development. Projects like GETH (Go implementation of the Ethereum Virtual Machine) and Parity (Rust implementation) receive support for their continued development, ensuring the longevity and robustness of the Ethereum network.
Additionally, numerous grants programs and crowdfunding initiatives have emerged to support innovative projects on the Ethereum network. These programs encourage a diverse range of ideas and applications, fostering creativity and innovation within the DeFi and broader blockchain communities.
Roadmap and Future Outlook
Ethereum’s roadmap for the future is ambitious, encompassing several major updates and improvements aimed at enhancing performance, expanding functionality, and increasing user adoption. The Ethereum 2.0 upgrade, officially launched in December 2022, marked a significant milestone by transitioning parts of the network to a proof-of-stake model. Additional components of ETH 2.0 include shard chains and increased security features, all designed to boost transaction processing capacity.
Much of the ongoing work revolves around scaling solutions, with Layer 2 protocols like Polygon (formerly Matic Network) playing a vital role in offloading transaction volumes from the mainchain. These Layer 2 networks offer solutions that maintain the decentralized spirit of Ethereum while providing users with faster and cheaper transaction capabilities.
Looking ahead, Ethereum plans to address long-standing issues such as energy efficiency and environmental impact. The continued evolution of proof-of-stake and other innovative consensus mechanisms will play a crucial role in achieving these goals. Moreover, ethical considerations regarding privacy, data protection, and accessibility will increasingly shape future developments on the platform.
The broader outlook for Ethereum is one of continued growth and transformation. As more businesses, governments, and individuals adopt blockchain technology, the role of Ethereum as a leading platform for innovation and development is expected to expand further. With a vibrant community and strong commitment to ongoing improvement, Ethereum stands poised to drive transformative change across multiple industries and sectors.
Decentralized Applications (DApps) and the Future of Web3
The concept of decentralized applications (DApps) has emerged as a cornerstone of Ethereum's potential to transform industries and transform the internet itself. DApps, built on blockchain technology, operate without a central authority and are transparent, secure, and censorship-resistant. By leveraging smart contracts, DApps can automate processes, store data, and execute actions in a secure and reliable manner.
One of the most notable DApps on Ethereum is Augur, a decentralized oracle and prediction market platform. Augur allows users to place bets on the outcome of future events, providing insights into market sentiments and trends. Another prominent DApp, MakerDAO, is a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) that enables users to collateralize assets to mint stablecoins, such as DAI. This system ensures that collateral can back the value of the stablecoin, reducing risk and enhancing trust among users.
The development and use of DApps on Ethereum have sparked a broader discussion about the future of the internet, often referred to as Web3. Web3 refers to a vision where data, value, and control are distributed rather than controlled by a central entity. This concept challenges traditional models of the internet, offering a more equitable and decentralized infrastructure.
Another significant aspect of Web3 is the integration of decentralized identity verification systems. These systems provide a secure and transparent way for individuals to manage their digital identities. Projects like uPort and Civic are working on solutions that use Ethereum to verify and manage user identities without the need for centralized authorities. This not only enhances privacy but also simplifies the process of authentication for applications and services.
Challenges and Regulatory Considerations
While DApps and Web3 offer exciting opportunities, they also face significant challenges, including regulatory scrutiny and legal frameworks. Governments and financial institutions are grappling with the implications of decentralized systems, recognizing both their potential benefits and risks. In many jurisdictions, DApps and related technologies are subject to varying degrees of regulation, which can impact their adoption and usability.
Regulatory challenges are particularly evident in the financial sector, where DApps and DeFi platforms must navigate complex legal landscapes. For instance, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the United States has taken a firm stance on regulating certain DeFi projects as securities, leading to a significant shift in the industry. These regulations, while necessary, can also stifle innovation and limit user access in some regions.
To address these challenges, industry players and regulators are collaborating to develop frameworks that balance innovation and security. Initiatives like self-regulatory organizations (SROs) and industry consortia are emerging to provide guidelines and best practices for developers and users. These collaborative efforts aim to create a more harmonious ecosystem where DApps and DeFi can thrive while adhering to legal and ethical standards.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
The environmental impact of blockchain technology, particularly Ethereum’s proof-of-work consensus mechanism, has become a significant concern. The energy-intensive process of securing the network has led to extensive criticism regarding its carbon footprint. While proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanisms offer a more sustainable approach, the transition from proof-of-work (PoW) to PoS has not been without controversy.
The Ethereum community and developers are exploring various solutions to reduce the environmental impact of the network. One promising approach is the concept of "sharding," which involves dividing the Ethereum blockchain into smaller, interconnected segments called "shards." Each shard can handle a portion of the network's transactions, significantly increasing throughput while reducing the energy consumption required to secure the entire network.
Another solution is the integration of external proof-of-stake validators, which allow validators to securely and efficiently verify transactions without relying on expensive mining hardware. These solutions aim to strike a balance between security, scalability, and environmental sustainability, ensuring that Ethereum can continue to support a wide range of applications while minimizing its ecological footprint.
Impact on Industries and Markets
The impact of Ethereum and DApps extends well beyond the blockchain community, affecting various industries and financial markets. In the real estate sector, smart contracts can facilitate property transactions, automating the process of verifying ownership, registering transfers, and managing contracts. This not only reduces the need for intermediaries but also provides a more transparent and efficient system for stakeholders.
Supply chain management stands to benefit greatly from decentralized technologies. By incorporating smart contracts and blockchain-based systems, supply chain operations can become more transparent and secure. This helps in tracking the movement of goods, ensuring authenticity, and preventing counterfeiting. Companies like Provenance and VeChain are already implementing such solutions, enhancing trust and reducing fraud in the global supply chain.
The impact on financial markets is particularly pronounced. Beyond DeFi, Ethereum supports the issuance and trading of digital assets, including securities, tokens, and futures. This opens up new opportunities for investors to access markets that were previously off-limits due to regulatory barriers. Digital asset exchanges and marketplaces built on Ethereum provide a platform for trading these assets, facilitating liquidity and market participation.
Conclusion
Ethereum has emerged as a pivotal force in the blockchain universe, offering a platform for decentralized innovation and transformative applications. From enabling DApps and DeFi to revolutionizing industries and markets, Ethereum’s potential is vast and ever-evolving. As the platform continues to address challenges and integrate new technologies, it holds the promise of shaping a more decentralized and equitable future.
While regulatory hurdles, environmental concerns, and technological limitations persist, the momentum behind Ethereum and its ecosystem remains strong. With ongoing developments and collaborations, Ethereum is likely to become an integral part of the global digital infrastructure, driving change and creating new opportunities for individuals and organizations alike.
Community and Governance Structures
At the heart of Ethereum's success lies its active and engaged community. The decentralized nature of the project means that governance decisions often involve broad participation from stakeholders, rather than being made by a single entity. This democratic structure is achieved through various mechanisms, including proposals on decentralized platforms such as Augur and MakerDAO.
Ethereum’s governance is currently managed through on-chain and off-chain channels. On-chain proposals refer to the process where users can make changes to the protocol through formal proposals that require sufficient support to pass. These proposals are voted on by token holders via special smart contracts, ensuring transparency and inclusivity in decision-making.
Off-chain governance, on the other hand, involves discussions and debates on forums like Ethereum Stack Exchange and Ethereum Foundation’s GitHub repository. These discussions guide future developments and help shape the direction of the ecosystem. The community plays a crucial role in identifying and prioritizing the needs of the network, contributing to its continuous evolution.
Partnerships and Collaboration
Ethereum has formed numerous partnerships and collaborations to enhance its ecosystem and reach new markets. Working closely with tech giants, startups, and academic institutions, Ethereum has expanded its influence in various sectors. Some notable partnerships include:
- Geth and Parity: Ethereum clients developed by Geth and Parity offer different programming interfaces and optimizations, catering to diverse developer communities.
- Polygon (formerly Matic Network): Polygon acts as a Layer 2 solution, increasing Ethereum’s transaction throughput while maintaining security and decentralized characteristics. This partnership aims to solve scalability issues and reduce transaction fees.
- Microsoft: Microsoft partners with Ethereum to promote blockchain adoption in enterprise environments. This collaboration brings together Microsoft’s cloud services and Ethereum’s decentralized technology to enhance business productivity and security.
- Nasdaq: Nasdaq and Ethereum have collaborated to explore how blockchain can improve financial markets and ensure transparency and efficiency. Their joint efforts have resulted in pilot projects and workshops focused on integrating Ethereum into stock exchanges.
These partnerships reflect Ethereum’s strategy of fostering a robust and interconnected ecosystem that supports a wide range of applications and use cases.
Challenges Ahead: Scaling and Security
As Ethereum continues to grow in popularity and adoption, scaling and security remain critical challenges. The network’s ability to handle large volumes of transactions efficiently and securely is essential for widespread acceptance and integration into mainstream industries.
Scalability concerns have driven the development of various Layer 2 solutions, such as state channels, rollups, and optimistic rollups. These technologies allow for the offloading of transactions and computations to secondary layers, while maintaining the security guarantees of the main Ethereum blockchain. By reducing contention on the mainchain, Layer 2 solutions aim to drastically lower transaction fees and enhance user experience.
Security is another key issue, particularly given the increasing value of assets stored and transacted on the Ethereum network. Ensuring the robustness of smart contracts and protecting against vulnerabilities is paramount. Ongoing efforts include rigorous audits, bug bounties, and the establishment of safety mechanisms to mitigate risks.
The emergence of zk-SNARKs (Zero-Knowledge Succinct Non-Absurd Arguments of Knowledge) presents a promising approach to enhancing security and privacy. These cryptographic proofs allow for the verification of transactions without revealing sensitive information, thereby enhancing the confidentiality of interactions on the blockchain.
Future Prospects: Quantum Computing and Beyond
The horizon for Ethereum continues to expand as researchers and developers explore advanced cryptographic techniques and quantum computing. Quantum computing has the potential to break current cryptographic schemes, necessitating the development of post-quantum cryptographic protocols. Ethereum is actively involved in researching and implementing these solutions to ensure the network remains secure in the face of future computational threats.
In addition to cryptography, Ethereum is exploring the integration of machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance its functionality. AI can be leveraged to automate complex processes, improve smart contract performance, and enable more sophisticated applications. For example, AI-driven analytics can provide valuable insights into market trends and user behavior, helping to optimize DApp performance and user engagement.
Conclusion
Ethereum has come a long way since its inception, evolving from a simple platform to a multifaceted ecosystem with a broad range of uses and applications. From decentralized finance and smart contracts to digital identities and supply chain management, Ethereum continues to push the boundaries of what is possible with blockchain technology.
Despite facing challenges such as regulatory hurdles, environmental impacts, and scalability issues, Ethereum shows no signs of slowing down. Its resilient community, ongoing innovations, and strategic partnerships signal a bright future for the platform. As emerging technologies like quantum computing and AI continue to integrate with blockchain, Ethereum is positioned to play a central role in shaping the landscape of decentralized applications and web3.
As the world increasingly seeks more decentralized and transparent systems, Ethereum remains a beacon of innovation, driving the next wave of technological and societal progress.



Hedera Hashgraph: Revolutionizing Blockchain Technology
The Emergence of Hedera Hashgraph
The blockchain space has seen its fair share of innovation and competition among various projects vying for market dominance. However, one technology stands out as a disruptor and potential game-changer: Hedera Hashgraph. Originally developed by Swirlds, Hedera Hashgraph is a public distributed ledger that offers unprecedented throughput and latency while maintaining security and decentralization. This decentralized network promises to solve some of the most pressing issues plaguing traditional blockchains, making it a compelling alternative for businesses and individuals seeking efficient and secure transactions.
Understanding Hashgraph
To understand the unique value proposition of Hedera Hashgraph, it's essential to grasp its underlying technology—the Hashgraph consensus algorithm. Unlike other blockchain technologies that rely on proof-of-work (PoW) or proof-of-stake (PoS) to achieve consensus, Hashgraph employs a novel approach that combines both gossip-based and synchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) mechanisms. This hybrid approach allows for significantly faster transaction speeds and more robust security compared to traditional blockchain networks.
A central concept in Hashgraph is the "hashgraph" structure itself. Think of a hashgraph as a tree-like structure where each node represents a transaction or a message that needs to be verified. Each node not only stores information about the transaction itself but also references two parent nodes, which act as a timestamp for the transaction. In this way, the hashgraph provides a clear chronological order, ensuring that all nodes have an accurate view of the transaction history.
Key Features of Hedera Hashgraph
Speedy Transactions: One of the standout features of Hedera Hashgraph is its ability to process thousands of transactions per second (TPS), with some reports citing rates exceeding over 5,000 TPS under optimal conditions. This rapid transaction speed makes it suitable for real-time applications like financial settlements, micropayments, and cross-border transactions, where quick confirmation times are critical.
Decentralization: Like many blockchain technologies, Hedera Hashgraph thrives on decentralization. By distributing the network across multiple nodes, no single point of failure exists, making it resistant to attacks and manipulation. Each participant in the network plays a vital role in validating transactions and reaching consensus, thereby ensuring that the system remains secure and unaffected by any single entity's actions.
Security and Privacy: Security in Hedera Hashgraph is achieved through a combination of cryptographic techniques, such as asymmetric encryption and digital signatures. This ensures that transactions are tamper-proof and that participants can trust the integrity of the network without needing a central authority. Additionally, Hedera Hashgraph offers robust privacy features, allowing users to maintain their anonymity while still ensuring the transparency of the transaction process.
Network Structure and Consensus Mechanism
The Hedera Hashgraph network is made up of a diverse range of nodes, including validators, witnesses, and clients. Validators are responsible for confirming transactions and validating blocks. Witnesses do not directly validate transactions but participate in the hashgraph structure to provide a more robust network. Clients interact with the network to send and receive transactions.
The consensus mechanism used by Hedera Hashgraph is designed to be highly efficient and secure. During a consensus round, validators quickly reach agreement on the order of transactions without requiring extensive computational power or energy consumption. This is achieved through a gossip-based protocol where validators receive and share messages about transactions they have heard about. Eventually, this leads to a global understanding of the correct sequence of events, which is then recorded in the hashgraph structure.
Tokenomics and Governance
Hedera Hashgraph operates without its own native token, unlike many other blockchain platforms. Instead, it utilizes a governance model that involves the Hedera Governing Council and the Hedera Token Service. The Hedera Governing Council, comprised of large corporations and organizations, helps ensure the stability and growth of the network. On the other hand, the Hedera Token Service allows developers to create and deploy custom stablecoins and digital assets on the Hedera platform.
This unique governance structure sets Hedera Hashgraph apart from other chains that rely on tokens for funding and incentive structures. By focusing on enterprise adoption and collaboration, Hedera aims to foster a more inclusive and collaborative ecosystem rather than being driven by the need for token value increases.
Applications and Use Cases
The versatile nature of Hedera Hashgraph makes it well-suited for a wide array of applications and industries. Financial services stand out as a key area where the technology could have a transformative impact. Financial institutions can achieve faster and cheaper cross-border payments, streamline settlement processes, and enhance compliance through immutable records.
Moreover, Hedera Hashgraph can enable innovative business models and services, such as decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, supply chain management, and identity verification systems. Its low-latency performance ensures that these applications can operate seamlessly, providing users with a frictionless experience.
Challenges and Future Prospects
No technology is without its challenges, and Hedera Hashgraph is no exception. One of the primary hurdles is achieving mainstream adoption. Compared to established technologies like Ethereum and Bitcoin, Hedera Hashgraph has limited brand recognition and user base. Addressing this requires extensive outreach and strategic partnerships with major industry players.
Another challenge lies in regulatory clarity. Although the technology offers enhanced privacy and security features, navigating regulatory landscapes around decentralized applications can be complex. Governments and regulatory bodies are still grappling with how to classify and regulate cryptocurrencies and blockchain technologies, which poses a risk to wider adoption.
Looking ahead, Hedera Hashgraph holds promising prospects for overcoming these challenges. As the world becomes increasingly interconnected and data-driven, a fast, secure, and scalable decentralized network like Hedera can play a crucial role in driving innovation. Collaborations with enterprises and continuous improvements to the technology will likely strengthen its position in the market.
Conclusion
Hedera Hashgraph represents a significant leap forward in blockchain technology. With its superior performance and robust security, it addresses many of the shortcomings of existing blockchain solutions. As more businesses recognize the potential benefits of Hedera Hashgraph in their operations, we can expect to see increased adoption and innovation within the ecosystem.
Technology Partnerships and Collaboration
Hedera Hashgraph has made significant strides in forming strategic partnerships to enhance its technological capabilities and expand its user base. These collaborations aim to leverage the unique strengths of Hedera Hashgraph, such as its high throughput and low latency, to address specific industry needs. For instance, in the financial services sector, Hedera has partnered with companies like BNY Mellon, a global leader in asset servicing, and State Street Corporation, a multinational financial services company. These partnerships have led to the development of innovative solutions tailored to the requirements of financial institutions, such as automated settlements and real-time payment processing.
In the realm of DeFi, major players like ChainSafe Systems and ChainSafe Labs have integrated Hedera Hashgraph into their platforms. These integrations have resulted in improved liquidity and scalability, making DeFi more accessible and efficient for users. Additionally, the partnership with ChainSafe has helped in creating secure and compliant DeFi applications, ensuring that users can trust the systems they interact with.
Moreover, Hedera Hashgraph has established a partnership with Polkadot, a multi-chain ecosystem, to explore cross-chain interoperability. This collaboration could potentially revolutionize the way different blockchain networks interact, paving the way for a more interconnected and decentralized digital economy.
Community and Ecosystem
The success of any blockchain network relies heavily on its community and ecosystem. Hedera Hashgraph has been building a strong community of developers, businesses, and enthusiasts from the onset. The Hedera Hashgraph website provides extensive resources and support, making it easier for new members to understand and engage with the platform. The Hedera Hashgraph API and SDKs have been designed to be user-friendly, facilitating the development of various applications and services.
The Hedera Hashgraph community includes a diverse range of participants, from small startups to large enterprises. Companies like ConsenSys, a leading blockchain solutions provider, have been actively working on Hedera-based projects, contributing to the ecosystem’s growth and innovation. These partnerships have not only facilitated the creation of new applications but also enhanced the overall user experience through continuous improvement and updates.
The Hedera Hashgraph GitHub repository is a testament to the community’s enthusiasm and contribution. Developers from around the world regularly contribute code, report bugs, and suggest new features, fostering an open and collaborative environment. This open-source model encourages innovation and ensures that the platform remains flexible and adaptable to the evolving needs of its users.
Security and Compliance
One of the critical factors in the success of any blockchain technology is its security and compliance. Hedera Hashgraph has taken several steps to ensure that it meets stringent security standards. The implementation of robust cryptographic techniques, such as secure hash functions and digital signatures, guarantees the security of transactions and data. These measures help prevent unauthorized access, tampering, and fraudulent activities, thereby maintaining the integrity of the network.
Moreover, Hedera Hashgraph has been actively working towards achieving regulatory compliance. The Hedera Governing Council, with its diverse membership, plays a crucial role in ensuring that the network operates within the legal framework. This includes working with regulatory bodies and industry stakeholders to address any concerns and provide transparent and secure solutions. This approach not only enhances the legitimacy of Hedera Hashgraph but also ensures that businesses can trust the platform for their critical operations.
The Hedera Hashgraph network has also implemented advanced security features such as zero-knowledge proofs and privacy-enhancing technologies. These features allow users to maintain their privacy while still ensuring the transparency of transactions. For example, zero-knowledge proofs can be used to verify the authenticity of transactions without revealing sensitive information, providing a balance between security and privacy.
Scalability and Interoperability
One of the most significant challenges for blockchain technologies is scalability. Hedera Hashgraph addresses this challenge through its innovative architecture. The technology’s ability to handle thousands of transactions per second makes it suitable for high-throughput applications, such as real-time payments and decentralized marketplaces. Hedera Hashgraph’s design allows for smooth scaling, ensuring that the network can accommodate a growing number of users and applications without compromising on performance.
Interoperability is another key aspect that sets Hedera Hashgraph apart. The network’s ability to interact with other blockchains and decentralized networks through bridges and protocols ensures that it can serve as a versatile platform for various use cases. By fostering cross-chain interoperability, Hedera Hashgraph can help in building a more interconnected and seamless digital ecosystem. This interoperability is particularly important for businesses operating in multiple markets, as it enables them to leverage the benefits of different blockchain networks while maintaining a unified approach.
Another aspect of scalability is the network’s ability to handle large volumes of data. Hedera Hashgraph’s efficient data management techniques ensure that transaction data is stored and managed in a way that minimizes overhead and maximizes efficiency. This is crucial for applications that require extensive data processing, such as decentralized finance and supply chain management.
Economic and Environmental Impact
Blockchain technology, particularly cryptocurrencies, has often been criticized for its high energy consumption and carbon footprint. However, Hedera Hashgraph addresses this issue through its innovative consensus mechanism. By eliminating the need for extensive computational power, Hedera Hashgraph significantly reduces energy consumption, making it a more environmentally friendly solution. This is particularly important as governments and organizations globally strive to combat climate change and promote sustainability.
The economic impact of Hedera Hashgraph is also noteworthy. By enabling faster and cheaper transactions, the technology has the potential to reduce costs for businesses and consumers. This is especially beneficial for businesses operating in industries with high transaction volumes, such as financial services and e-commerce. The technology can help businesses reduce their operational costs and improve their competitive edge.
Future Roadmap and Research & Development
To continue driving innovation and maintain its position as a leading blockchain network, Hedera Hashgraph has a well-defined roadmap and a strong commitment to ongoing research and development. The team regularly updates the network to address emerging challenges and incorporate new technologies. For instance, the development of Hedera Health, a dedicated service for medical blockchain applications, showcases Hedera Hashgraph’s commitment to addressing specific industry needs.
The Hedera Hashgraph Research & Development (R&D) team is continuously exploring new innovations and technologies. This includes the development of new consensus algorithms, privacy-enhancing protocols, and advanced security measures. The R&D team’s efforts are aimed at making Hedera Hashgraph even more powerful and versatile, enabling it to meet the evolving demands of its users.
Apart from technological advancements, the Hedera Hashgraph team is also focused on enhancing user experience and accessibility. The team is working on improving the usability of the platform, making it more intuitive and user-friendly. This includes the development of user-friendly tools and interfaces, as well as ongoing support and documentation.
Moreover, the Hedera Hashgraph team is dedicated to fostering a vibrant and collaborative community. The team regularly engages with users, developers, and industry stakeholders to gather feedback and insights. This collaborative approach ensures that the platform evolves in a way that best meets the needs of its diverse user base.
Conclusion
Hedera Hashgraph has established itself as a leading decentralized network with unique features that set it apart from other blockchain technologies. Its high throughput, robust security, and innovative consensus mechanism make it well-suited for a wide range of applications. The network’s strong community, strategic partnerships, and ongoing R&D efforts further reinforce its potential for future growth and success. As more businesses and organizations recognize the benefits of Hedera Hashgraph, we can expect to see continued innovation and adoption in the blockchain space.
Real-World Applications and Case Studies
Several real-world applications and case studies highlight the tangible benefits of using Hedera Hashgraph. For example, the United Nations Global Green Ribbon Award recognized the World Food Programme (WFP) for its adoption of Hedera Hashgraph to improve the transparency and efficiency of food assistance programs. This collaboration has helped in tracking food donations and ensuring that aid reaches the intended beneficiaries in a timely and secure manner. By leveraging Hedera Hashgraph's low-latency, high-throughput capabilities, the WFP can conduct real-time checks and balances, reducing the risk of fraud and mismanagement.
Another notable case study is the partnership between Hedera Hashgraph and VeChain, a leading blockchain platform focused on supply chain traceability. Together, they developed a system that tracks the journey of luxury goods from production to retail. This solution ensures that consumers can verify the authenticity and origin of products, thereby enhancing brand trust and protecting against counterfeiting. The integration of Hedera Hashgraph into VeChain's ecosystem provides a secure and efficient way to manage complex supply chains, addressing the challenges of authenticity and traceability.
Furthermore, the Canadian payment network Bambora leveraged Hedera Hashgraph to create a real-time payment platform. This platform is designed to support merchants in processing transactions instantly, offering a seamless user experience. The platform's ability to handle thousands of transactions per second makes it ideal for e-commerce and other high-volume payment ecosystems. By integrating Hedera Hashgraph, Bambora has been able to reduce transaction times and improve overall payment processing efficiency, ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its many advantages, Hedera Hashgraph faces several challenges that need addressed for it to become even more scalable and user-friendly. One major challenge is the issue of network congestion during peak times. While the technology can handle high transaction volumes, ensuring smooth operation during periods of high demand remains a critical concern. Hedera Hashgraph is continually working on optimizing its consensus algorithms and network architecture to enhance performance, particularly during peak usage periods.
Another challenge is the need for more comprehensive regulatory guidance. While the technology has made significant strides in achieving compliance, the lack of clear regulatory frameworks can be a significant deterrent for businesses looking to adopt blockchain solutions. As a result, Hedera Hashgraph is actively engaged with regulatory bodies and industry stakeholders to advocate for a more supportive regulatory environment. This collaboration aims to promote the responsible and widespread adoption of blockchain technology.
To address these challenges and stay ahead of the curve, Hedera Hashgraph is focusing on several key areas for future development. One area of focus is improving cross-chain interoperability. By enabling seamless communication between different blockchain networks, Hedera Hashgraph can help in building a more integrated and interconnected digital economy. Additionally, the team is exploring the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to enhance the network's security and operational efficiency. These technologies can help in detecting and mitigating potential threats in real-time, ensuring the continued security and reliability of the network.
Furthermore, Hedera Hashgraph is investing in research and development to explore new use cases and applications. The network is particularly interested in exploring the potential of decentralized identity solutions, smart contracts, and decentralized finance (DeFi). Decentralized identity solutions can provide individuals with control over their personal data, ensuring privacy and security. Smart contracts can enable automated and trusted transactions in a wide range of sectors, while decentralized finance can offer new opportunities for decentralized lending, savings, and trading.
Hedera Hashgraph is also emphasizing the importance of community engagement and education. The team believes that fostering a strong and supportive community is essential for the long-term success of the network. To achieve this, Hedera Hashgraph is organizing webinars, workshops, and conferences to provide users with valuable insights and best practices. Additionally, the team is collaborating with educational institutions to develop courses and training programs that can help in building a skilled workforce equipped with the knowledge and skills needed to work with blockchain technology.
Conclusion
Hedera Hashgraph is at the forefront of blockchain innovation, offering a unique set of features that address many of the challenges faced by traditional blockchain networks. From its ability to handle thousands of transactions per second to its robust security and cross-chain interoperability, Hedera Hashgraph is poised to play a significant role in shaping the future of decentralized finance and beyond. As businesses continue to explore and adopt blockchain technology, the real-world applications and case studies demonstrate the transformative potential of Hedera Hashgraph. With ongoing improvements and a strong focus on community engagement, Hedera Hashgraph is well-positioned to become a leading force in the blockchain ecosystem.


